Professional Documents
Culture Documents
List of Terms Earth and Space Science
Uploaded by
api-3559476040 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views5 pagesOriginal Title
list of terms earth and space science
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
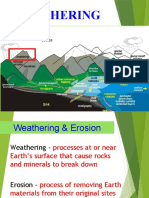
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views5 pagesList of Terms Earth and Space Science
Uploaded by
api-355947604Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Unit 4 – Earth and Space Science
Key Term Definition Link
Precipitation is a vital
component of how
Water
water moves through
cycle/hydrologi
Earth’s water cycle,
c cycle.
connecting the ocean,
Say what it is
land, and atmosphere.
and give a
simple diagram.
(The simple diagram is https://pmm.nasa.gov/education/water-cycle
1 down)
Transpiration is the
process where plants
Transpiration
absorb water through https://biologydictionary.net/transpiration/
2 the roots.
Precipitation is any
liquid or frozen water
that forms in the
atmosphere and falls
precipitation back to the Earth. It
comes in many forms,
like rain, snow. Along
with evaporation and https://www.vocabulary.com/dictionary/precipitation
3 condensation.
Surface runoff is water,
from rain, snowmelt, or
other sources, that
Surface run off flows over the land
surface, and is a major https://www.sciencedaily.com/terms/surface_runoff.ht
component of the m
4 water cycle.
Condensation is the
change in the state of
matter from the gas
Condensation
phase to the liquid https://www.thoughtco.com/definition-of-
phase. It is the reverse condensation-604411
5 of vaporization.
Precipitation is any
liquid or frozen water
that forms in the
atmosphere and falls
precipitation back to the Earth. It
comes in many forms,
like rain, snow. Along
with evaporation and https://www.vocabulary.com/dictionary/precipitation
6 condensation.
to cause (a liquid) to
percolate pass through a porous https://www.dictionary.com/browse/percolate
7 body; filter.
the water beneath the
Ground water surface of the ground, https://www.dictionary.com/browse/groundwater
8 consisting largely of
surface water that has
seeped down.
(the source of water in
springs and wells).
the cycle of rising and
falling of the surface of
Tides bodies of water caused
by the attraction of the https://www.yourdictionary.com/tide
9 moon and the sun.
relatively thin life-
Biosphere supporting stratum of https://www.britannica.com/science/biosphere
10 Earth’s surface.
the solid portion of the
earth (distinguished
Geosphere
from atmosphere, https://www.dictionary.com/browse/geosphere
11 hydrosphere).
Atmosphere refers to
the gases surrounding a https://www.thoughtco.com/definition-of-atmosphere-
Atmosphere
star or planetary body 604801
12 held in place by gravity.
the solid part of a https://www.merriam-
Lithosphere celestial body (such as webster.com/dictionary/lithosphere
13 the earth)
the water on or
surrounding the surface
of the globe, including
hydrosphere
the water of the oceans
and the water in the https://www.dictionary.com/browse/hydrosphere
14 atmosphere.
The cryosphere refers
to the areas of Earth
that are covered by ice
and snow. These are
primarily located near https://www.encyclopedia.com/environment/energy-
the poles and at high government-and-defense-magazines/cryosphere
15 Cryosphere altitudes.
the region below the https://www.dictionary.com/browse/asthenosphere
16 Asthenosphere lithosphere.
a solid made up of a
bunch of different https://www.ducksters.com/science/rocks.php
17 Rock minerals.
is the geological
process in which
earthen materials are
Erosion worn away and
transported by natural https://www.nationalgeographic.org/encyclopedia/ero
forces such as wind or sion/
18 water.
the action of the
weather conditions in https://www.merriam-
altering the color, webster.com/dictionary/weathering
19 Weathering texture, composition, or
form of exposed
objects.
Rocks formed by the
cooling and solidifying
of molten materials.
Igneous rock Igneous rocks can form
beneath the Earth's
surface, or at its https://www.dictionary.com/browse/igneous-rock
20 surface, as lava.
Rock that has formed
through the deposition
and solidification of
Sedimentary sediment, especially
rock sediment transported
by water (rivers, lakes,
and oceans), ice https://www.dictionary.com/browse/sedimentary-rock
21 (glaciers), and wind
any of a class of rocks
that result from the
Metamorphic alteration of preexisting
rock rocks in response to https://www.britannica.com/science/metamorphic-
changing environmental rock
22 conditions.
is the part of the earth https://www.nationalgeographic.org/encyclopedia/ma
Mantle between the core and ntle/
23 the crust.
the molten, liquid rock
that issues from a
Lava
volcano or volcanic https://www.dictionary.com/browse/lava
24 vent.
rock formed at or near
the Earth’s surface by
Sedimentary the accumulation and
lithification of sediment https://www.britannica.com/science/sedimentary-rock
25 (detrital rock)
a continuous process
by which rocks are
created, changed from
Rock cycle
one form to another,
destroyed, and then https://www.dictionary.com/browse/rock-cycle
26 formed again.
A mineral is an element
or chemical compound
that is normally
Mineral
crystalline and that has https://www.sciencelearn.org.nz/resources/1770-what-
been formed as a result are-minerals
27 of geological processes.
any sudden shaking of
the ground caused by
Earthquake the passage of seismic https://www.britannica.com/science/earthquake-
waves through Earth’s geology
28 rocks.
any remains of a living
thing of a former
fossil
geologic age, as a https://www.dictionary.com/browse/fossil
29 skeleton.
molten material
beneath or within the
Magma earth's crust, from
which igneous rock is https://www.dictionary.com/browse/magma
30 formed.
Earth's core is
responsible for the https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/earth-and-
Earth’s core
generation of Earth's planetary-sciences/earth-core
31 magnetic field.
https://www.sciencedaily.com/terms/crust_(geology).h
Earth’s crust a crust is the outermost tm
32 layer of a planet.
a central sun with its
associated planets,
asteroids, meteors,
Solar system
satellites (i.e.,moons),
and comets that are http://www.extremescience.com/solar-system.htm
33 "captured" in its orbit.
1- Mercury
2- Venus
3- Earth
Name the 4- Mars
planets in the 5- Jupiter
solar system 6- Saturn
7- Uranus
8- Neptune http://www.extremescience.com/solar-system.htm
34 9- pluto
List the planets four planets closest to
in the solar the sun — Mercury, https://www.space.com/16080-solar-system-
system starting Venus, Earth and Mars planets.html
35 from the sun —
New Moon
Waxing Crescent
First Quarter
Waxing Gibbous
Full
Phases of the
Waning Gibbous
moon
Third Quarter
Waning
Crescent https://www.ducksters.com/science/phases_of_the_m
Dark Moon oon.php
36
Draw a picture
of all the
phases of the
moon and
name each
37 phase. (Down)
the phenomenon of
Global warming
increasing average air
temperatures near the
surface of Earth over
the past one to two http://www.extremescience.com/solar-system.htm
38 centuries.
Ozone Layer the layer of the upper
atmosphere where
most atmospheric https://www.dictionary.com/browse/ozone-layer
39 ozone is concentrated.
any of various gaseous
compounds (such as
carbon dioxide or
methane) that absorb https://www.merriam-
Greenhouse infrared radiation, trap webster.com/dictionary/greenhouse%20gas
40 Gas heat in the atmosphere.
Water cycle diagram:
Phases of the moon:
You might also like
- List of Terms Earth and Space ScienceDocument5 pagesList of Terms Earth and Space Scienceapi-345837027No ratings yet
- Unit 4Document4 pagesUnit 4api-456760133No ratings yet
- List of Terms Earth and Space ScienceDocument5 pagesList of Terms Earth and Space Scienceapi-355232330No ratings yet
- Unit 4Document2 pagesUnit 4api-357335815No ratings yet
- List of Terms Earth and Space Science 1Document4 pagesList of Terms Earth and Space Science 1api-481066283No ratings yet
- List of Terms Earth and Space ScienceDocument4 pagesList of Terms Earth and Space Scienceapi-350245383No ratings yet
- Order of SuperpositionDocument4 pagesOrder of SuperpositionHadjmil KamensaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.2 Exogenic ProcessesDocument31 pagesChapter 2.2 Exogenic ProcessesLeonessa CortesNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Notes of Soil Mechanics and Foundation EngineeringDocument9 pagesUnit 1 Notes of Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineeringsuchit singhNo ratings yet
- September 22 2020 WeatheringDocument57 pagesSeptember 22 2020 WeatheringDequilla, Hanna Angela P.No ratings yet
- Pre Test 21stDocument4 pagesPre Test 21stHanna cayogyogNo ratings yet
- Geology Chapter FourDocument42 pagesGeology Chapter FourYoni RebumaNo ratings yet
- Geo 04 - Geomorphic Processes - Chapter NotesDocument3 pagesGeo 04 - Geomorphic Processes - Chapter NotesAK RaghavNo ratings yet
- Weathering, Soil and ErosionDocument52 pagesWeathering, Soil and ErosionWinz QuitasolNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 LessonDocument18 pagesWEEK 1 LessonLmaoNo ratings yet
- CE6301 Engineering Geology Part A CombDocument20 pagesCE6301 Engineering Geology Part A CombElakiya RajanNo ratings yet
- Thering and Erosion: WeatheringDocument36 pagesThering and Erosion: WeatheringBRAHMA REDDY AAKUMAIIANo ratings yet
- DumpDocument5 pagesDumpErick John FrontetasNo ratings yet
- Stamford University Bangladesh CEN 203 Lecture on Earth's Layers and Volcanic HazardsDocument23 pagesStamford University Bangladesh CEN 203 Lecture on Earth's Layers and Volcanic HazardsNafin AfnanNo ratings yet
- Chapter I Introduction To Soil MechanicsDocument8 pagesChapter I Introduction To Soil MechanicsBijayan PudasainiNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Reviewer (FINALS)Document7 pagesEarth Science Reviewer (FINALS)athy3456No ratings yet
- Lecture Note Course Code-Bce 303 Geotechnical Engineering-IDocument127 pagesLecture Note Course Code-Bce 303 Geotechnical Engineering-IMahesh RamtekeNo ratings yet
- Review of Final ExamDocument5 pagesReview of Final ExamLira MacoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Soils and Soil DevelopmentDocument5 pagesChapter 12 Soils and Soil DevelopmentCherie YanNo ratings yet
- Hydrovolcanic ProcessesDocument5 pagesHydrovolcanic Processesjunior.geologiaNo ratings yet
- Gte 1Document20 pagesGte 1Samta TayadeNo ratings yet
- Geotech OneDocument47 pagesGeotech Onejulius hot sebeneNo ratings yet
- INTEGRATED WEATHERING PROCESSUSDocument12 pagesINTEGRATED WEATHERING PROCESSUSkomalNo ratings yet
- Petrology ofDocument22 pagesPetrology ofDaljeet SidhuNo ratings yet
- Earth Processes and LandformsDocument3 pagesEarth Processes and LandformsJanina Frances RuideraNo ratings yet
- The effects of weathering and erosion processesDocument5 pagesThe effects of weathering and erosion processesJoshua Neil CarigoNo ratings yet
- Upload 1Document14 pagesUpload 1Rp karanNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Earth ProcessesDocument5 pagesUnit 9 Earth ProcessesJerrol SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Ch-2 Earth MovementDocument7 pagesCh-2 Earth MovementCareer IAS free IAS online CoachingNo ratings yet
- Earth Natural ProcessDocument45 pagesEarth Natural ProcessJosh FuriscalNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Soil MechanicsDocument66 pagesIntroduction to Soil Mechanicspaul machariaNo ratings yet
- Soil MechanicsDocument123 pagesSoil MechanicsAloke Majumder100% (2)
- Seabed: StructureDocument13 pagesSeabed: StructureSebastian GhermanNo ratings yet
- Weathering RevDocument41 pagesWeathering RevJoana Jean SuymanNo ratings yet
- Geological Processes on EarthDocument6 pagesGeological Processes on EarthBrendan Lewis DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Ch3 Earth Structure Rocks and Mineralss 2022 2023Document13 pagesCh3 Earth Structure Rocks and Mineralss 2022 2023Yousif MawloodNo ratings yet
- Weathering and Denudation: A Project by Lakshay Sharma Student of Class 9 Roll No. 51Document13 pagesWeathering and Denudation: A Project by Lakshay Sharma Student of Class 9 Roll No. 51Vallari V100% (1)
- Water ResourcesDocument27 pagesWater Resourcessharon ranjitha paulNo ratings yet
- PDC Topic - Understanding and Designing For A Bioregions Climate and Landscape - Terra PermaDocument18 pagesPDC Topic - Understanding and Designing For A Bioregions Climate and Landscape - Terra Permagns_vcNo ratings yet
- WEATHERINGDocument3 pagesWEATHERINGMarilou Chalanao EstebanNo ratings yet
- Weathering and erosion processesDocument22 pagesWeathering and erosion processesYuvaraj DNo ratings yet
- 12 2nd Quarter Reviewer 1Document40 pages12 2nd Quarter Reviewer 1Kim DahyunNo ratings yet
- Water Cycle 1.1.1 (C-D)Document5 pagesWater Cycle 1.1.1 (C-D)Royal ComedianNo ratings yet
- Group 1 ReportDocument19 pagesGroup 1 ReportKimmy Jane FloresNo ratings yet
- EARTH-SCIENCE_REVIEWERDocument5 pagesEARTH-SCIENCE_REVIEWERiyahxsNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Geotechnical EnggDocument15 pagesUnit 1 - Geotechnical Enggpeople reality by Dharmendra vishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Exogenetic Processes-Ii: StructureDocument19 pagesExogenetic Processes-Ii: StructureSoumyaPandeyNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Quarter 2 Week 1 - Ruby May AquinoDocument11 pagesEarth Science Quarter 2 Week 1 - Ruby May AquinoRuby AquinoNo ratings yet
- Debris Flow..Document11 pagesDebris Flow..Hlbeen MohammedNo ratings yet
- Exogenic Forces ClassificationDocument8 pagesExogenic Forces ClassificationDevraj H SNo ratings yet
- Geomorphology Assignment - Zachary Alfajri Kurniawan - 21040122190048 PDFDocument15 pagesGeomorphology Assignment - Zachary Alfajri Kurniawan - 21040122190048 PDFZachary Alfajri KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Dtw.9.wheathering and DenudationDocument5 pagesDtw.9.wheathering and DenudationniroopswaradNo ratings yet
- Geology Notes 2Document6 pagesGeology Notes 2Lily QuiNo ratings yet
- ELS Q1 Module-2Document10 pagesELS Q1 Module-2Teacher Charlyn VlogNo ratings yet
- Khadeejas PDPDocument6 pagesKhadeejas PDPapi-355947604No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan TampletDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Tampletapi-355947604No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan TampletDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Tampletapi-355947604No ratings yet
- WelcomeDocument5 pagesWelcomeapi-355947604No ratings yet
- CertificateDocument1 pageCertificateapi-355947604No ratings yet
- Action Plan Template Sample 1Document3 pagesAction Plan Template Sample 1api-355947604No ratings yet
- Feedback 2 - Khadeeja Ahmad Ali Shaheen Alhosani h00298810Document3 pagesFeedback 2 - Khadeeja Ahmad Ali Shaheen Alhosani h00298810api-355947604No ratings yet
- Feedback 3 - Khadeeja Ahmad Ali Shaheen Alhosani h00298810Document3 pagesFeedback 3 - Khadeeja Ahmad Ali Shaheen Alhosani h00298810api-355947604No ratings yet
- RwservletDocument9 pagesRwservletapi-355947604No ratings yet
- Feedback 2 - Khadeeja Ahmad Ali Shaheen Alhosani h00298810Document3 pagesFeedback 2 - Khadeeja Ahmad Ali Shaheen Alhosani h00298810api-355947604No ratings yet
- Khadeeja-Formative Report Form - Science SesonsDocument2 pagesKhadeeja-Formative Report Form - Science Sesonsapi-355947604No ratings yet
- MCT-MST Summative Report Form - KhadeejaDocument7 pagesMCT-MST Summative Report Form - Khadeejaapi-355947604No ratings yet
- Khadeeja-Formative Report Form - English Lesson PhonicsDocument2 pagesKhadeeja-Formative Report Form - English Lesson Phonicsapi-355947604No ratings yet
- Feedback 3 - Khadeeja Ahmad Ali Shaheen Alhosani h00298810Document3 pagesFeedback 3 - Khadeeja Ahmad Ali Shaheen Alhosani h00298810api-355947604No ratings yet
- Khadeeja-Formative Report Form - English Lets ReadDocument2 pagesKhadeeja-Formative Report Form - English Lets Readapi-355947604No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan TampletDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Tampletapi-355947604No ratings yet
- PlantDocument4 pagesPlantapi-355947604No ratings yet
- Khadeeja-Formative Report Form - Math Numbers To 120Document2 pagesKhadeeja-Formative Report Form - Math Numbers To 120api-355947604No ratings yet
- Teaching PhilosophyDocument2 pagesTeaching Philosophyapi-355947604No ratings yet
- Khadeeja Ahmed PDP FainalDocument12 pagesKhadeeja Ahmed PDP Fainalapi-355947604No ratings yet
- My CVDocument2 pagesMy CVapi-355947604No ratings yet
- School: NA Alternative Task: H00298810 Khadeeja Ahmad Ali Shaheen AlhosaniDocument9 pagesSchool: NA Alternative Task: H00298810 Khadeeja Ahmad Ali Shaheen Alhosaniapi-355947604No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson Planapi-355947604No ratings yet
- Weekly ReflectionDocument1 pageWeekly Reflectionapi-355947604No ratings yet
- Online LearningDocument7 pagesOnline Learningapi-355947604No ratings yet
- Teaching PhilosophyDocument2 pagesTeaching Philosophyapi-355947604No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson Planapi-355947604No ratings yet
- Part of PlantDocument6 pagesPart of Plantapi-355947604No ratings yet
- Living Things LessonDocument6 pagesLiving Things Lessonapi-355947604No ratings yet
- Time Schedule For Micro Teaching Fall 202010 2Document6 pagesTime Schedule For Micro Teaching Fall 202010 2api-383497107No ratings yet
- MPS Multis Varios 2007 PDBDocument204 pagesMPS Multis Varios 2007 PDBlist16947No ratings yet
- Dfe 29 JGDocument91 pagesDfe 29 JGKale ArbroughNo ratings yet
- Central Air ConditioningDocument8 pagesCentral Air ConditioningZay KumikusNo ratings yet
- Pedestrian Airbag Tech Helps Cushion ImpactsDocument7 pagesPedestrian Airbag Tech Helps Cushion Impactsmaulik_20_8No ratings yet
- Temperature Variation and Its Importance in MeteorologyDocument9 pagesTemperature Variation and Its Importance in Meteorologyahmet gürbüzNo ratings yet
- SpeechDocument2 pagesSpeechFredie Dalay-on UnggayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1, Bangladesh at A GlanceDocument21 pagesLecture 1, Bangladesh at A GlanceTawfeeq HasanNo ratings yet
- Draft Consolidated CIIP As of 28 Jan 2015Document584 pagesDraft Consolidated CIIP As of 28 Jan 2015Rick GarciaNo ratings yet
- S85001-0367 - Rate-Of-rise, Fixed Temperature Heat DetectorsDocument2 pagesS85001-0367 - Rate-Of-rise, Fixed Temperature Heat DetectorsSudiatmoko SupangkatNo ratings yet
- Spontaneous Ignition of Hydrogen: Literature ReviewDocument22 pagesSpontaneous Ignition of Hydrogen: Literature Reviewemraan khanNo ratings yet
- AD3VA Player Book - Beta Draft 05 (Bookmarked)Document225 pagesAD3VA Player Book - Beta Draft 05 (Bookmarked)warlordbcm1100% (1)
- Swimming Pool Calculation: To Calculate Pipe SizingDocument21 pagesSwimming Pool Calculation: To Calculate Pipe SizingElia Mekdad100% (2)
- Albania's Geography in 40 CharactersDocument5 pagesAlbania's Geography in 40 CharactersEmpire100No ratings yet
- Structure Revisi Baru - TrawasDocument76 pagesStructure Revisi Baru - TrawasEdy KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Appearance Adjectives Color Adjectives Condition Adjectives Feelings (Bad) AdjectivesDocument10 pagesAppearance Adjectives Color Adjectives Condition Adjectives Feelings (Bad) AdjectivesEstherEscuderoNo ratings yet
- Table 4.7 Major Natural Extreme Events and Disasters, 2006-2015Document35 pagesTable 4.7 Major Natural Extreme Events and Disasters, 2006-2015Maria Micaela CabarlesNo ratings yet
- Getting Returning Vets Back On Their Feet: Ggoopp EennddggaammeeDocument28 pagesGetting Returning Vets Back On Their Feet: Ggoopp EennddggaammeeSan Mateo Daily JournalNo ratings yet
- Forecasting and Time Series Analysis Using The Sca Statistical System Box JenkinsDocument422 pagesForecasting and Time Series Analysis Using The Sca Statistical System Box JenkinsOscar EduardoNo ratings yet
- LDRRF Schemes in Khulna, Satkhira, Chandpur, Bhola, Pirojpur, BorgunaDocument59 pagesLDRRF Schemes in Khulna, Satkhira, Chandpur, Bhola, Pirojpur, BorgunaCDMP BangladeshNo ratings yet
- 1920 Australianmeteor00taylrichDocument332 pages1920 Australianmeteor00taylrichUlf DunellNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Probability and StatisticsDocument67 pagesAn Introduction To Probability and StatisticsLuis Carlos Aristizábal50% (4)
- Refrigerador LG GR43W11CVFDocument11 pagesRefrigerador LG GR43W11CVFOrlando YaguasNo ratings yet
- Willingness To Pay More For 'Green' HotelsDocument85 pagesWillingness To Pay More For 'Green' HotelsДмитрий Sinkov67% (3)
- EXAMINATION 200 BLDG TECH 2 – WOOD CONSTRUCTION SCORESDocument10 pagesEXAMINATION 200 BLDG TECH 2 – WOOD CONSTRUCTION SCORESJohn Michael BlancaflorNo ratings yet
- It is/there is sentencesDocument1 pageIt is/there is sentencessatharheartNo ratings yet
- Instruments 170506004404Document48 pagesInstruments 170506004404Anonymous fIfG9Z3VDNo ratings yet
- 2206c-E13tag2&3 Tpd1688e4Document20 pages2206c-E13tag2&3 Tpd1688e4Daniel Graterol100% (2)
- Niven, Larry - at The Bottom of A HoleDocument10 pagesNiven, Larry - at The Bottom of A Holehilly8No ratings yet
- Roof Our PrjectDocument33 pagesRoof Our PrjectHundeejireenyaNo ratings yet
- ThermoCond 19 enDocument4 pagesThermoCond 19 enAnonymous 7z6OzoNo ratings yet