Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MCQ in Field Effect Transistor Devices
Uploaded by
Paolo PerezOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MCQ in Field Effect Transistor Devices
Uploaded by
Paolo PerezCopyright:
Available Formats
MCQ in Field Effect Transistor Devices
Monday, January 13, 2020 5:05 PM
Practice Exam Test Questions
1. Which of the following controls the level of ID? VGS
2. Which of the following is (are) not an FET? p-n channel
3. What is the range of an FET's input impedance? 1 MΩ to several hundred MΩ
4. Which of the following transistor(s) has (have) depletion and enhancement types? MOSFET
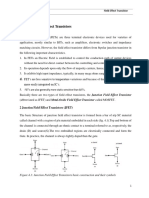
5. A BJT is a current-controlled device. The JFET is a voltage-controlled device.
6. The BJT is a bipolar device. The FET is a unipolar device.
7. Which of the following is (are) the terminal(s) of a field-effect transistor (FET). Drain, Gate,
Source
8. What is the level of IG in an FET? Zero ampere
9. At which of the following is the level of VDS equal to the pinch-off voltage? When ID becomes
equal to IDSS, When VGS is zero volts, IG is zero
10. At which of the following condition(s) is the depletion region uniform? No bias
11. Refer to the following characteristic curve. Calculate the resistance of the FET at VGS = -0.25 V if
ro = 10kΩ. 11.378 kΩ
12. What is the level of drain current ID for gate-to-source voltages VGS less than (more negative than)
the pinch-off level? Zero ampere
13. The three terminals of the JFET are the gate, drain and source.
14. The level of VGS that results in ID = 0 mA is defined by VGS = VP.
15. The region to the left of the pinch-off locus is referred to as the ohmic region.
16. Which of the following represent(s) the cutoff region for an FET? ID = 0 mA, VGS = VP, IG = 0
17. Referring to this transfer curve. Calculate (using Shockley's equation) VGS at ID = 4 mA. -2.54 V
18. Referring to this transfer curve, determine ID at VGS = 2 V. 0.444 mA
Electronics Engineering Corner Page 1
19. What is the ratio of ID / IDSS for VGS = 0.5 VP? 0.25
20. The drain current will always be one-fourth of IDSS as long as the gate-to-source voltage is one-
half the pinch-off value.
21. Which of the following ratings appear(s) in the specification sheet for an FET? Voltages between
specific terminals, current levels, power dissipation
22. Refer to this portion of a specification sheet. Determine the values of reverse-gate-source voltage
and gate current if the FET was forced to accept it. -25 Vdc, 10 mAdc
23. Hand-held instruments are available to measure βdc for the BJT.
24. How many terminals can a MOSFET have? 3 or 4
25. Which of the following applies to MOSFETs? No direct electrical connection between the gate
terminal and the channel, Desirable high input impedance, Uses metal for the gate, drain and
source connections
26. Referring to the following transfer curve, determine the level of VGS when the drain current is 20
mA. 1.66 V
Electronics Engineering Corner Page 2
27. Refer to the following curves. Calculate ID at VGS = 1 V. 4.167 mA
28. It is the insulating layer of SiO2 in the MOSFET construction that accounts for the very desirable
high input impedance of the device.
29. Refer to the following figure. Calculate VGS at ID = 8 mA for k = 0.278 x 10^-2 A/V2. 3.70 V
30. The transfer curve is not defined by Shockley's equation for the enhancement-type MOSFET.
Electronics Engineering Corner Page 3
30. The transfer curve is not defined by Shockley's equation for the enhancement-type MOSFET.
31. Which of the following applies to safe MOSFET handling? Always pick up the transistor by the
casing, power should always be off when network changes are made, always touch ground
before handling the device
32. What is the purpose of adding two Zener diodes to the MOSFET in this figure? To protect the
MOSFET for both polarities
33. Which of the following is (are) the advantage(s) of VMOS over MOSFETs? Reduced channel
resistance, higher current and power ratings, faster switching time
34. Which of the following FETs has the lowest input impedance? JFET
35. Which of the following input impedances is not valid for a JFET? 108 Ω
Fill in the blanks Questions
1. A junction field-effect transistor (JFET) is a voltage-controlled device.
2. The FET is a unipolar device depending solely on either electron (n-channel) or hole (p-channel)
conduction.
3. One of the most important characteristics of the FET is its high-input impedance.
4. The MOSFET transistor has become one of the most important devices used in the design and
construction of integrated circuits for digital computers.
5. In the n-channel transistor, the drain and source are connected to the n-type channel while the gate
is connected to the two layers of the p-type material.
6. In an FET transistor, the depletion region is wider near the top of both p-type materials.
7. The pinch-off voltage continues to drop in a parabolic manner as VGS becomes more and more
negative.
8. The region to the right of the pinch-off locus is commonly referred to as the constant-current /
saturation / linear amplification region.
9. As VGS becomes more negative, the slope of each curve in the characteristics becomes more
horizontal corresponding with an increasing resistance level.
10. The transfer curve can be obtained by using both Shockley's equation and by output
characteristics
11. The active region of an FET is bounded by ohmic region, cutoff region, power line.
12. A(n) curve tracer can be used to check the condition of an FET.
13. In a curve tracer, the per step reveals the distance between the VGS curves for the n-channel
device.
14. In an FET circuit, VGS is normally the parameter to be determined first.
15. The primary difference between the construction of a MOSFET and FET is the construction of the
gate connection.
16. The primary difference between the construction of depletion-type and enhancement-type
MOSFETs is the absence of the channel.
17. The level of VGS that results in the significant increase in drain current in enhancement-type
MOSFETs is called threshold voltage VT.
18. In an n-channel enhancement-type MOSFET with a fixed value of VT, the higher the level of
VGS, the more the saturation for VDS.
19. The enhancement-type MOSFET is in the cutoff region if applied VGS is less than or equal to
Electronics Engineering Corner Page 4
19. The enhancement-type MOSFET is in the cutoff region if applied VGS is less than or equal to
VGS(Th).
20. The specification sheet provides VGS(on), ID(on), VGS(Th) to calculate the value of k for
enhancement-type MOSFETs.
21. CMOS has high input impedance, fast switching speeds, and lower operating power levels.
22. The FET resistance in the ohmic region is largest at VP and smallest at the origin.
23. The silicon dioxide (SiO2) layer used in a MOSFET is an insulator.
24. In an n-channel depletion-type MOSFET, the region of positive gate voltages on the drain or
transfer characteristics is referred to as the enhancement region with the region between cutoff and
the saturation level of ID referred to as the depletion region.
25. VMOS FETs have a positive temperature coefficient that will combat the possibility of thermal
runaway.
Link: https://pinoybix.org/2019/07/mcq-in-field-effect-transistor-devices-boylestad.html
Electronics Engineering Corner Page 5
You might also like
- EEE111+ (Exp+7) +Study+of+Switching+CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesEEE111+ (Exp+7) +Study+of+Switching+CharacteristicsFaria SharifNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument22 pagesElectronicsVARSHITH REDDY JNo ratings yet
- Fet (2014) PDFDocument87 pagesFet (2014) PDFJoanne Mendoza IlaoNo ratings yet
- Electronics Hons C3 FET Field Effect TransistorDocument21 pagesElectronics Hons C3 FET Field Effect TransistorGawrav BaishyaNo ratings yet
- Ece-Research Work 1Document10 pagesEce-Research Work 1Peale ObiedoNo ratings yet
- MOSFET SEMICONDUCTOR FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORDocument38 pagesMOSFET SEMICONDUCTOR FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORVimal KunwarNo ratings yet
- Jfet MosfetDocument25 pagesJfet Mosfethrishabhraj710No ratings yet
- Vlsi Group-B Q&aDocument13 pagesVlsi Group-B Q&aROHAN CHOWDHURYNo ratings yet
- Bel 06 Field Effect TransistorDocument17 pagesBel 06 Field Effect TransistorBharavi K SNo ratings yet
- Unit - Vi Field Effect TransistorDocument16 pagesUnit - Vi Field Effect TransistorBhavaniPrasadNo ratings yet
- 1 To 5 ManualDocument30 pages1 To 5 ManualRoshan DodiyaNo ratings yet
- Electronics Ii: BY Professor Omotosho T. Victor & DR Akinwumi SayoDocument46 pagesElectronics Ii: BY Professor Omotosho T. Victor & DR Akinwumi SayoOmotosho Temidayo VictorNo ratings yet
- Module 4 FET MOSFETDocument23 pagesModule 4 FET MOSFETsenthilnathanNo ratings yet
- On Mosfets (Prepared) 1Document75 pagesOn Mosfets (Prepared) 1Ankit RajNo ratings yet
- FET Charcateristics (CS Configuration)Document6 pagesFET Charcateristics (CS Configuration)Bhanu KodaliNo ratings yet
- Cmos Sessional 1Document5 pagesCmos Sessional 1Ashish KumarNo ratings yet
- FET/MOSFET Characteristics: ObjectiveDocument13 pagesFET/MOSFET Characteristics: ObjectiveZeeshan RafiqNo ratings yet
- 10 Mosfet+CharacteristicsDocument5 pages10 Mosfet+CharacteristicsKarthikKumarNo ratings yet
- BE 4 UnitDocument15 pagesBE 4 Unit08sunnyjaganNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Devices Lecture Notes: JFET and MOSFETDocument25 pagesSemiconductor Devices Lecture Notes: JFET and MOSFETdevashri gaurkedeNo ratings yet
- DCID Experiment MergedDocument94 pagesDCID Experiment MergedSumer SainiNo ratings yet
- Ministry Of Higher Education Northern Technical University Technical College /Mosul Department Of Computer Engineering MOSFET CharacterizationDocument11 pagesMinistry Of Higher Education Northern Technical University Technical College /Mosul Department Of Computer Engineering MOSFET Characterizationالزهور لخدمات الانترنيتNo ratings yet
- EE386 FET - Field Effect TransistorsDocument7 pagesEE386 FET - Field Effect TransistorsKeshara WeerasingheNo ratings yet
- Debre Markos University Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Computer Engineering (PG)Document10 pagesDebre Markos University Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Computer Engineering (PG)enidegNo ratings yet
- AEC Lab ManualDocument75 pagesAEC Lab Manualphalanetra100% (1)
- Analog and Digital Electronics (Subject Code: 17CS32) Lecturer NotesDocument59 pagesAnalog and Digital Electronics (Subject Code: 17CS32) Lecturer NotesKarthik v BhatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Micro Electronics Circuit NotesDocument59 pagesChapter 1 Micro Electronics Circuit NotesswamySLR100% (1)
- Experiment No 3a MOSFET CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesExperiment No 3a MOSFET CharacteristicsManikandan P Engineering EEE100% (1)
- Akhil Bee.Document33 pagesAkhil Bee.yashNo ratings yet
- Controlled Devices FET, BJT, IGBTDocument51 pagesControlled Devices FET, BJT, IGBTHolloGramNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument61 pages1 Introductionfiraol temesgenNo ratings yet
- BEng FETDocument13 pagesBEng FETJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- J-FET (Junction Field Effect Transistor)Document28 pagesJ-FET (Junction Field Effect Transistor)Jobins GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Field Effect Transisters (FET)Document22 pagesField Effect Transisters (FET)Raja PosupoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document16 pagesChapter 4firomsaguteta12No ratings yet
- Field Effect Transistors (FET) : Comparison Between BJT and FETDocument9 pagesField Effect Transistors (FET) : Comparison Between BJT and FETpranavraikar1No ratings yet
- Mos Transistor TheoryDocument144 pagesMos Transistor TheorymailtolokiNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of BJTs and MOSFETs (39Document10 pagesCharacteristics of BJTs and MOSFETs (39Umar AkhtarNo ratings yet
- L-6 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel) 8Document3 pagesL-6 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel) 8GagneNo ratings yet
- Notes Module2 (FET Part) Basic Electronics 22BBEE203Document12 pagesNotes Module2 (FET Part) Basic Electronics 22BBEE203Hani MNo ratings yet
- 3-PPT MosfetDocument28 pages3-PPT MosfetVaibhavNo ratings yet
- Electronic II-1Document10 pagesElectronic II-1Isaac DanielNo ratings yet
- Final MosfetDocument33 pagesFinal MosfetabdallaNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design Important Questions On MOSFET For Exams: VoltageDocument5 pagesVLSI Design Important Questions On MOSFET For Exams: VoltageTarun SinghalNo ratings yet
- VLSI DESIGN: MOS TRANSISTORDocument162 pagesVLSI DESIGN: MOS TRANSISTORBasheer V.PNo ratings yet
- EDC-II Unit-3 Field Effect Transistor & MOSFET TheoryDocument34 pagesEDC-II Unit-3 Field Effect Transistor & MOSFET TheorysamarthNo ratings yet
- Expt 13 - JFET-CharaceristicsDocument8 pagesExpt 13 - JFET-CharaceristicssamarthNo ratings yet
- ECE221 MOSFETs-I SRMAP PDFDocument30 pagesECE221 MOSFETs-I SRMAP PDFRajeshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Fet Devices AnsDocument12 pagesChapter 6 Fet Devices AnsRovina LacunaNo ratings yet
- Chapter ForDocument17 pagesChapter Forbelacheweshetu222No ratings yet
- B.SC Electronics D2 P3 (2021) SolutionsDocument10 pagesB.SC Electronics D2 P3 (2021) SolutionsShubham KeshriNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS (FET) EditDocument58 pagesCHAPTER 5 FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS (FET) Editruhiyahnazihah_15106No ratings yet
- Electronics Chapter 4Document16 pagesElectronics Chapter 4YidnekachewNo ratings yet
- Field Effect Transistor, Ujt, SCR, Triac: Scope of The ChapterDocument8 pagesField Effect Transistor, Ujt, SCR, Triac: Scope of The ChapterAkhilesh PandeNo ratings yet
- Ee 211 Chapter 3Document19 pagesEe 211 Chapter 3RickNo ratings yet
- 01chapter 5-1Document55 pages01chapter 5-1AhmNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesFrom EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- MCQ in Field Effect Transistor DevicesDocument5 pagesMCQ in Field Effect Transistor DevicesPaolo PerezNo ratings yet
- Silicon Controlled RectifiersDocument2 pagesSilicon Controlled RectifiersPaolo PerezNo ratings yet
- Additional Notes On Electronic CircuitsDocument11 pagesAdditional Notes On Electronic CircuitsPaolo PerezNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 - TVM & Equivalence 2.0Document5 pagesExercise 1 - TVM & Equivalence 2.0Bayu PurnamaNo ratings yet
- SOCTEC2 Globalization TechDocument4 pagesSOCTEC2 Globalization TechPaolo PerezNo ratings yet
- STUDENT ENROLLMENT RECORD FOR PAOLO PEREZDocument1 pageSTUDENT ENROLLMENT RECORD FOR PAOLO PEREZPaolo PerezNo ratings yet
- DISMATH HNICEM2019 v2Document6 pagesDISMATH HNICEM2019 v2Paolo PerezNo ratings yet
- Calculate Simple and Compound Interest RatesDocument2 pagesCalculate Simple and Compound Interest RatesPaolo PerezNo ratings yet
- SOCTEC2 Globalization TechDocument4 pagesSOCTEC2 Globalization TechPaolo PerezNo ratings yet
- MCQ in DC Biasing - BJTsDocument6 pagesMCQ in DC Biasing - BJTsPaolo PerezNo ratings yet
- MCQs in Electric CircuitsDocument5 pagesMCQs in Electric CircuitsPaolo PerezNo ratings yet
- Simple CircuitsDocument5 pagesSimple CircuitsPaolo PerezNo ratings yet