Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 11 - Gear - 9
Uploaded by
HEMANTKHERAOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 11 - Gear - 9
Uploaded by
HEMANTKHERACopyright:
Available Formats
Example Problem 11-1: Velocity Ratios and Gear Trains Example Problem 11-1: Velocity Ratios and Gear
Problem 11-1: Velocity Ratios and Gear Trains
(cont’d.)
(11-1)
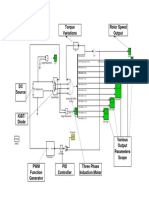
• For the set of four gears shown below, calculate output speed, output
torque, and horsepower for both input and output conditions and overall N2 N4
Vr = •
velocity ratio: N1 N3
60 60 9
Vr = • =
20 20 1
− Output speed:
n1
n4 =
Vr
1
3600 rpm • = 400 rpm
9
− Output torque:
T4 = T1 Vr
9
T4 = 200 in-lb • = 1800 in-lb
1
August 15, 2007 37 August 15, 2007 38
Example Problem 11-1: Velocity Ratios and Gear Trains Example Problem 11-2: Velocity Ratios and Gear Trains
(cont’d.)
• For the gear train shown below, determine the train value, output speed,
− Input horsepower: output direction, output torque, and output power.
(2-6)
Tn
hp =
63,000
200 in-lb 3600 rpm
hp =
63,000
hp = 11.4
− Output horsepower:
1800 in-lb 400 rpm
hp =
63,000
hp = 11.4
August 15, 2007 39 August 15, 2007 40
Example Problem 11-2: Velocity Ratios and Gear Trains Example Problem 11-2: Velocity Ratios and Gear Trains
(cont’d.)
(cont’d.)
− Direction:
– Train value: NB N N
Vr = • D • E (11-1) • If: Gear A – clockwise
NA NC ND
Gear B – counterclockwise
65 60
Vr = • = 9.75 / 1 Gear C – counterclockwise
20 20
Idler cancels out and has no effect on overall train value. Gear D – clockwise
Gear E – counterclockwise
– Output speed:
NA 3000 rpm
nE = = = 307.7 rpm
Vr 9.75 / 1 − Output power:
rev min
P = TnE = 97.5 Nm 307.5
min 60 sec
π
– Output torque:
TE = T A Vr P = 1571 Nm/sec or
J
or W
s
TE = 10 Nm (9.75 / 1) = 97.5 Nm
P = 1.57 kW
August 15, 2007 41 August 15, 2007 42
You might also like
- EE201 Tutorial-7 Transformer 23sep19 PDFDocument61 pagesEE201 Tutorial-7 Transformer 23sep19 PDFSrikarNo ratings yet
- DC Motor DrivesDocument39 pagesDC Motor DrivesAnuar Nuafzan100% (1)
- Carraro Transmission Parts CatalogDocument15 pagesCarraro Transmission Parts CatalogMichael Kubler67% (3)
- Types of BeltsDocument5 pagesTypes of BeltsMichael Huffman50% (2)
- Chapter 1 - GearsDocument51 pagesChapter 1 - GearsVictor CastillonNo ratings yet
- Gear shaping and shaving process overviewDocument22 pagesGear shaping and shaving process overviewSumesh Vijayan0% (1)
- Load Test On D.C. Series MotorDocument5 pagesLoad Test On D.C. Series Motorramniwas123No ratings yet
- Chuong 3 - Dieu Khien Toc Do Dong Co KDBDocument55 pagesChuong 3 - Dieu Khien Toc Do Dong Co KDBThiên HảiNo ratings yet
- Torque Slip CharacteristicsDocument24 pagesTorque Slip Characteristicsavi013No ratings yet
- Brake Test On DC Shunt MachineDocument9 pagesBrake Test On DC Shunt MachineNagendrababu VasaNo ratings yet
- assdDocument12 pagesassdjoe leeNo ratings yet
- EDA (MCT) Lab ManualDocument32 pagesEDA (MCT) Lab ManualThanigaigriezmann GkNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Drives (Compatibility Mode)Document63 pagesDC Motor Drives (Compatibility Mode)Anuar NuafzanNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Drive: - General Concept - Speed Control - SCR Drives - Switched-Mode DC DrivesDocument34 pagesDC Motor Drive: - General Concept - Speed Control - SCR Drives - Switched-Mode DC Drivespipiq10No ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering: MSC Full-Time CourseDocument17 pagesElectrical Engineering: MSC Full-Time CourseFabiano Bezerra BezerraNo ratings yet
- Practice machine (2)Document2 pagesPractice machine (2)azsaad112No ratings yet
- BrushlessDC BasicsDocument1 pageBrushlessDC BasicsJimNo ratings yet
- 18 ECE5041 BrushlessDcMachines 18Document16 pages18 ECE5041 BrushlessDcMachines 18saurabh bansalNo ratings yet
- For Synchronous GeneratorDocument34 pagesFor Synchronous GeneratorNIKESH PATELNo ratings yet
- EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT MODELDocument8 pagesEQUIVALENT CIRCUIT MODELJUANNo ratings yet
- Torque and speed variations of an asynchronous machineDocument1 pageTorque and speed variations of an asynchronous machineJaved Ahmed LaghariNo ratings yet
- IGBT Shovel Inverter ControlDocument11 pagesIGBT Shovel Inverter ControlGumercinda AlvizNo ratings yet
- Measure The Gain Constant of The Output Potentiometer (Volts Per Radian) : Analysis and DiscussionDocument4 pagesMeasure The Gain Constant of The Output Potentiometer (Volts Per Radian) : Analysis and DiscussionNirmal Prasad PantaNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument28 pagesInduction Motorsumithra100% (2)
- Open CC DC Shunt GenDocument4 pagesOpen CC DC Shunt GenEnter your NameNo ratings yet
- Dc.machineDocument6 pagesDc.machinedearlight17No ratings yet
- Gear Train: - Simple - Compound - EpicyclicDocument18 pagesGear Train: - Simple - Compound - EpicyclicGaurav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Testing 3-Phase Induction MotorsDocument12 pagesTesting 3-Phase Induction MotorsAshok PNo ratings yet
- Mp-In001 - En-P Servomoteur ReférenceDocument26 pagesMp-In001 - En-P Servomoteur ReférenceAbdou DENo ratings yet
- Expt No: Date:: Load Test On Kaplan TurbineDocument4 pagesExpt No: Date:: Load Test On Kaplan TurbineAlex ChollackalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document12 pagesLecture 3Assma MohamedNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Part 2Document19 pagesDC Motor Part 2DanielNo ratings yet
- Circuit Diagram For Load Test On DC Shunt Motor: Three Phase Auto Transformer MDocument4 pagesCircuit Diagram For Load Test On DC Shunt Motor: Three Phase Auto Transformer MBalaji SNo ratings yet
- Eee3091F: Energy Conversion Induction Machines II (Chapter 5 - PC Sen)Document29 pagesEee3091F: Energy Conversion Induction Machines II (Chapter 5 - PC Sen)Yousuf IsaacsNo ratings yet
- Basic DC MotorsDocument17 pagesBasic DC MotorsFlavian IliesNo ratings yet
- EE 4PM4 Quiz 1 Solutions - 2016-17Document4 pagesEE 4PM4 Quiz 1 Solutions - 2016-17PreethamNo ratings yet
- Advanced Power Systems: Dr. Kar U of WindsorDocument41 pagesAdvanced Power Systems: Dr. Kar U of WindsorbisqothisyamNo ratings yet
- Sistemas Avanzados de PotenciaDocument41 pagesSistemas Avanzados de PotenciaMario Wenso Morales CoutiñoNo ratings yet
- Gearbox OutletDocument1 pageGearbox OutletAnkit KalariaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Sept16Document41 pagesLecture 1 Sept16Balakrishna S GajangiNo ratings yet
- Feed motors for SINAMICS S110/S120 at line 380-480V 3 ACDocument6 pagesFeed motors for SINAMICS S110/S120 at line 380-480V 3 ACJosé Manuel GonzálezNo ratings yet
- 2018 PI Exam SolutionDocument9 pages2018 PI Exam SolutionAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines II Atif Iqbal PDFDocument52 pagesElectrical Machines II Atif Iqbal PDFSantosh VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Machine Elements SummaryDocument24 pagesMachine Elements SummaryjelmerNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Torque MeasurementDocument8 pagesDynamic Torque MeasurementDanNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual & Observation Book: Clrr10-Applied Electrical and Electronics Engineering LaboratoryDocument9 pagesInstruction Manual & Observation Book: Clrr10-Applied Electrical and Electronics Engineering LaboratoryAditi PatilNo ratings yet
- Synchronous K-NotesDocument11 pagesSynchronous K-Notesomkar budigeNo ratings yet
- Load Test On DC Series MotorDocument3 pagesLoad Test On DC Series Motorramniwas123No ratings yet
- IM Phasor Diagram, NO Load and Blocked Rotor Test and Torque Slip CharacteristicDocument19 pagesIM Phasor Diagram, NO Load and Blocked Rotor Test and Torque Slip CharacteristicDEBADATTANo ratings yet
- Problem Solving On D C Machines PDFDocument16 pagesProblem Solving On D C Machines PDFSelvaraj ParamasivanNo ratings yet
- 00 - Drivetechnology BasicsDocument28 pages00 - Drivetechnology Basicsmikifit1No ratings yet
- Rotating Electrical MachinesDocument75 pagesRotating Electrical MachinesRajan SinghNo ratings yet
- 8 9 EMEC Polyphase Induction Machines Part I&IIDocument52 pages8 9 EMEC Polyphase Induction Machines Part I&IIOruc MusayevNo ratings yet
- PCS - Alternating Current SnajnDocument2 pagesPCS - Alternating Current SnajnMoon KnightNo ratings yet
- EEE373 Electric Motor Drive: Asst. Prof. Dr. Mongkol Konghirun Ee, KmuttDocument16 pagesEEE373 Electric Motor Drive: Asst. Prof. Dr. Mongkol Konghirun Ee, KmuttMohd Mohsin KhanNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Induction MachinesDocument46 pagesThree-Phase Induction MachinesWakgari TadesaNo ratings yet
- Three Phase IMDocument17 pagesThree Phase IMmohamedNo ratings yet
- 6 Lab: Motor Constants: 6.1 PrelabDocument4 pages6 Lab: Motor Constants: 6.1 Prelabkrish3291No ratings yet
- Advanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkFrom EverandAdvanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkNo ratings yet
- Gear 1 PDFDocument1 pageGear 1 PDFHEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of Spur GearDocument1 pageNomenclature of Spur GearHEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Type of Gear - 2Document1 pageType of Gear - 2HEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Fundamental Law and Involute Curve: R / R Constant (Constant Speed Ratio)Document1 pageFundamental Law and Involute Curve: R / R Constant (Constant Speed Ratio)HEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Type of GearDocument1 pageType of GearHEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Gear - 10Document1 pageChapter 11 - Gear - 10HEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Type of Gear - 3Document1 pageType of Gear - 3HEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Gear 2 PDFDocument1 pageGear 2 PDFHEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Gear - 12Document1 pageChapter 11 - Gear - 12HEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Gear - 2Document1 pageChapter 11 - Gear - 2HEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Gear Pitch Diameter, Circular Pitch and Center Distance CalculationDocument1 pageGear Pitch Diameter, Circular Pitch and Center Distance CalculationHEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Gear - 8Document1 pageChapter 11 - Gear - 8HEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Gear - 7Document1 pageChapter 11 - Gear - 7HEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Gear - 6Document1 pageChapter 11 - Gear - 6HEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Gear Pitch Diameter, Circular Pitch and Center Distance CalculationDocument1 pageGear Pitch Diameter, Circular Pitch and Center Distance CalculationHEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Gear - 5Document1 pageChapter 11 - Gear - 5HEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Gear - 3Document1 pageChapter 11 - Gear - 3HEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- SLRCDocument32 pagesSLRCHEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Gears Design Principles and ApplicationsDocument1 pageGears Design Principles and ApplicationsHEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- .QM 23e Ppap Level 1Document26 pages.QM 23e Ppap Level 1Eb Mohamed TahaNo ratings yet
- Rotor Gear Box WPA WPS WPX WPO WPDA WPDSDocument20 pagesRotor Gear Box WPA WPS WPX WPO WPDA WPDSHEMANTKHERA100% (1)
- Moktrans - SRC Helical Gearbox PDFDocument32 pagesMoktrans - SRC Helical Gearbox PDFHEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- High-Speed Gear DrivesDocument12 pagesHigh-Speed Gear DriveswillalizadeNo ratings yet
- Hirork Gearsand Drive ProfileDocument1 pageHirork Gearsand Drive ProfileHEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Characteristics Of: Corrugated Hdpe PipeDocument17 pagesCharacteristics Of: Corrugated Hdpe PipeHEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Moktrans - SRC Helical Gearbox PDFDocument32 pagesMoktrans - SRC Helical Gearbox PDFHEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Extrusion TechnologyDocument12 pagesExtrusion TechnologyHEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- SGN 160 PR: Diesel Genset ModelDocument4 pagesSGN 160 PR: Diesel Genset ModelHEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Lift and Escalator Motor Sizing Methods ExplainedDocument22 pagesLift and Escalator Motor Sizing Methods ExplainedHEMANTKHERA100% (2)
- NOV Gill Services Handling Tools BrochureDocument8 pagesNOV Gill Services Handling Tools BrochureAnonymous VNu3ODGavNo ratings yet
- Sonalica Tractor Catalog PDFDocument75 pagesSonalica Tractor Catalog PDFBishnu AdhikariNo ratings yet
- TH2004R PDFDocument96 pagesTH2004R PDFCarlos PereiraNo ratings yet
- PC Finisher SR4060 (D611) 120412Document61 pagesPC Finisher SR4060 (D611) 120412Mario German100% (1)
- VW 010 087 089 090 PDFDocument4 pagesVW 010 087 089 090 PDFReinaldo De Oliveira SilvaNo ratings yet
- Cat ZFDocument239 pagesCat ZFMarkus Glarner100% (1)
- 35 DS01 ME10 B - JM - MechanicalBench PDFDocument2 pages35 DS01 ME10 B - JM - MechanicalBench PDFluismariogallegoNo ratings yet
- Oil stock card monitoring systemDocument33 pagesOil stock card monitoring systemAndo Wibowo TariganNo ratings yet
- Asian Warner 55-50SN Seminar General DescriptionDocument15 pagesAsian Warner 55-50SN Seminar General DescriptionTawatchai BoonpermNo ratings yet
- D155A-6 Power Train System: Dubai Training and Demonstration CenterDocument15 pagesD155A-6 Power Train System: Dubai Training and Demonstration CenterMichael David100% (1)
- CHEVROLET (DAEWOO) Lacetti (J200) 1.8 16V F18D3: Timing Belt: Removal/installationDocument7 pagesCHEVROLET (DAEWOO) Lacetti (J200) 1.8 16V F18D3: Timing Belt: Removal/installationJuan Jesus FernandesNo ratings yet
- ServiceDocument342 pagesServicenicola mentiNo ratings yet
- Types of GearboxDocument7 pagesTypes of GearboxAndre RichardNo ratings yet
- 800 Series HelicalDocument44 pages800 Series HelicalashkansoheylNo ratings yet
- T.E. (Mechanical Engineering) Semester VDocument5 pagesT.E. (Mechanical Engineering) Semester Vmanil patilNo ratings yet
- Auto Manual Two Wheelers PDFDocument40 pagesAuto Manual Two Wheelers PDFEdwin Ttito100% (1)
- DTS 1.3-1.4 Problems in Design of Flat BeltDocument39 pagesDTS 1.3-1.4 Problems in Design of Flat Beltr nilakandanNo ratings yet
- T2800 Extra Instructions Mounting CassetteDocument2 pagesT2800 Extra Instructions Mounting CassetteValentin BeatoNo ratings yet
- Sheave Pulley 1-08-002-09Document6 pagesSheave Pulley 1-08-002-09nishanth132No ratings yet
- Valvoline Maxlife Multi Vehicle ATFDocument2 pagesValvoline Maxlife Multi Vehicle ATFOcto Adhi W PryhantoNo ratings yet
- Product Recommendation ZF Ecolite Transmissions 6 S 700 TO, 6 S 800 TO, 6 S 1000 TODocument1 pageProduct Recommendation ZF Ecolite Transmissions 6 S 700 TO, 6 S 800 TO, 6 S 1000 TOعندما تحكم القوةNo ratings yet
- History of automatic transmissionsDocument1 pageHistory of automatic transmissionsGary M TrajanoNo ratings yet
- Parts List: P-MK01-E (2005.07)Document81 pagesParts List: P-MK01-E (2005.07)RB STNo ratings yet
- AODE-4R75E VacTest PDFDocument2 pagesAODE-4R75E VacTest PDFAlonso IbarraNo ratings yet
- A On Selection of Gearbox For Epicycle Gear Train: PresentationDocument15 pagesA On Selection of Gearbox For Epicycle Gear Train: PresentationPavs PavaniNo ratings yet
- Dual Clutch TransmissionDocument7 pagesDual Clutch TransmissionVijay Pawar100% (1)