Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson No. 3: Inorganic Chemistry (Sci Ac5)
Lesson No. 3: Inorganic Chemistry (Sci Ac5)
Uploaded by
Franklin BayaniOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson No. 3: Inorganic Chemistry (Sci Ac5)
Lesson No. 3: Inorganic Chemistry (Sci Ac5)
Uploaded by
Franklin BayaniCopyright:
Available Formats
TEACHERS EDUCATION PROGRAM
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY (SCI AC5)
MODULE 2
Lesson No. 3
I. TITLE:
CHEMICAL BONDS AND ITS TYPES
II. EXPECTED LEARNING OUTCOMES:
Differentiate the types of chemical bonds
Attribute the different properties and uses of chemical bonds
III. INTRODUCTION:
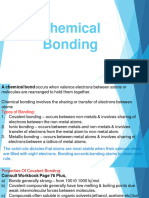
Chemical Bond
A force that holds two or more atoms of same or different elements together called chemical
bond.
Types of Chemical Bond
Ionic bond
Covalent bond
Coordinate covalent bond
Metallic bond
IV. SUBJECT CONTENT:
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Forms of Chemical Bonds
• There are 2 extreme forms of connecting or bonding atoms:
• Ionic—complete transfer of electrons from one atom to another
• Covalent—electrons shared between atoms
***Most bonds are somewhere in between.
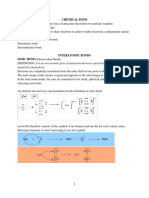
Ionic compounds / IONIC BONDS
A bond formed by the transfer of valence electron of metal atom to the outer most shell of
non-metals atom.
Key: Metal + Nonmetal
- Essentially complete electron transfer from an element of low IE (metal) to an element of high
electron affinity (EA) (nonmetal)
Na(s) + 1/2 Cl2(g) Na+ + Cl- NaCl (s)
- primarily between metals (Grps 1A, 2A and transition metals) and nonmetals (esp O and
halogens)
- NON-DIRECTIONAL bonding
via Coulomb (charge) interaction
Covalent Bonding
A bond formed by the mutual sharing of valence electron between the atoms.
Key: Nonmetal + Nonmetal
Covalent bond is the sharing of the VALENCE ELECTRONS of each atom in a bond.
Recall: Electrons are divided between core and valence electrons.
ATOM core valence
Na 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 [Ne] 3s1
Valence Electrons
- Number of valence electrons is equal to the Group number.
Non Polar Covalent Bond
A bond formed by the mutual sharing of electrons between atoms of same element.
Polar Covalent Bond
A bond formed by the mutual sharing of electrons between the atoms of different
elements.
Coordinate Covalent Bond
A bond formed by the sharing of electrons but shared pair donated by one of the atoms
called donor while other that accept called acceptor.
Metallic Bond
A bond in which metallic cations are held together by sea of delocalized electrons.
Key: Metal + Metal
V. SUMMARY:
Ionic bond is formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another. The bond is an
electrostatic attraction between oppositely charge ions.
Covalent bond is formed when a pair of electrons are shared between two atoms. If both electrons
comes from one atom, the bond is called coordinate covalent bond.
In a polar covalent bond, the electron cloud is shifted more toward one of the atoms; in a
nonpolar covalent bond, the electron cloud is equally distributed.
If there are two pairs of electrons between two atoms, it is called a double bond.
If there are three pairs, it is a triple bond.
VI. SELF ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS:
1. Why it is important to know the different types of bonding? Explain.
2. How can people use the advantage of knowing the different types of bonding?
VII. ACTIVITY:
Create a table of the different types of chemical bonds showing the substances involve and their
given examples that we encounter in our environment.
Prepared by: IRENE M. MORA
Instructor
You might also like
- RIVER MOORE - Gizmo Periodic TrendsDocument9 pagesRIVER MOORE - Gizmo Periodic TrendsRiver MooreNo ratings yet
- Module in Campus Journalism (AC4)Document5 pagesModule in Campus Journalism (AC4)Franklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond TypeDocument8 pagesChemical Bond TypeShabbir TamboliNo ratings yet
- Test 3 Bonding Review Sheet-Final VersionDocument7 pagesTest 3 Bonding Review Sheet-Final VersionJuventie PrimastutiNo ratings yet
- 2023 Grade 11 Learner Support DocumentDocument131 pages2023 Grade 11 Learner Support DocumentanathinothandoNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Chemical Bonding and NomenclatureDocument11 pagesModule 3: Chemical Bonding and NomenclatureJay Mark CapanangNo ratings yet
- PHSC GR 11 REVISION DOCUMENT APRIL 2022 Collated Final Final PDFDocument66 pagesPHSC GR 11 REVISION DOCUMENT APRIL 2022 Collated Final Final PDFPhilNo ratings yet
- S9Q2T2L2 Types of Chemical BondingDocument37 pagesS9Q2T2L2 Types of Chemical BondingMark Kevin Cagande EscletoNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondDocument8 pagesChemical BondRohan lallNo ratings yet
- Class 9th Chemistry Unit#4 Structure of MoleculesDocument8 pagesClass 9th Chemistry Unit#4 Structure of MoleculesIrfanullahNo ratings yet
- 01-Metallic BondingDocument2 pages01-Metallic BondingNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 - Q2-Week 2Document17 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 - Q2-Week 2DebbieNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 6 ReviewDocument3 pagesChemistry Chapter 6 Reviewjuan carlos quispe mamaniNo ratings yet
- Reading-The Different Types of BondsDocument2 pagesReading-The Different Types of BondsSeu WorkNo ratings yet
- Islamic University, Kushtia-7003: Department of PharmacyDocument29 pagesIslamic University, Kushtia-7003: Department of PharmacyRayhanuzzaman ShazibNo ratings yet
- Class 10th Chemistry NotesDocument4 pagesClass 10th Chemistry NotesRehan KhanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Chapter 22 Section 2 Pages 694-702Document14 pagesChemical Bonding: Chapter 22 Section 2 Pages 694-702elisaNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Chemical Bonds101Document22 pagesLec 2 Chemical Bonds101memoryboybooNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 Types of Compounds Based On Their PropertiesDocument9 pagesScience: Quarter 2 Types of Compounds Based On Their PropertiesAriel Lomugdang PatricioNo ratings yet
- Chem BondDocument10 pagesChem BondMIRIAM BATHANNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument9 pagesAssignmentalishbajaved159No ratings yet
- MELC 7 Chemical Bonding 1Document32 pagesMELC 7 Chemical Bonding 1A Dee YoungNo ratings yet
- Bond - HTML: SPM Form 4 Chemistry - Chemical BondsDocument29 pagesBond - HTML: SPM Form 4 Chemistry - Chemical Bondseric sivaneshNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical BondsDocument3 pagesTypes of Chemical BondssalimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6final Chemical Bonding IL 12 2022 TemplateDocument20 pagesLecture 6final Chemical Bonding IL 12 2022 TemplateMohammedNo ratings yet
- Ppt-Periodic TableDocument5 pagesPpt-Periodic TableNeil John Santos ParasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Atomic StructureDocument9 pagesAssignment 1 Atomic StructureAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document9 pagesChapter 5Hina RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument11 pagesOrganic Chemistryzaryabfaraz314No ratings yet
- Structure and BondingDocument12 pagesStructure and BondingNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- Mariano Marcos State University: PCHM 121: Pharmaceutical Inorganic Chemistry With Qualitative AnalysisDocument14 pagesMariano Marcos State University: PCHM 121: Pharmaceutical Inorganic Chemistry With Qualitative AnalysisKaizenNo ratings yet
- Dental Biomaterial Book (61-71)Document146 pagesDental Biomaterial Book (61-71)Abdelruhman SobhyNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument18 pagesChemical BondingJade GumonayNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical BondsDocument6 pagesTypes of Chemical BondsjoeldpenosNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Wlas QTR 2 Week 3 ValidatedDocument10 pagesScience 9 Wlas QTR 2 Week 3 ValidatedMYLENE B. ZABALLERONo ratings yet
- Physical Science Lesson 2 - Intramolecular Forces of AttractionDocument26 pagesPhysical Science Lesson 2 - Intramolecular Forces of Attractionrainjarrenperegrino13298No ratings yet
- Science 9 q2 Mod2Document16 pagesScience 9 q2 Mod2Prince U KennardNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1.3 NotesDocument32 pagesChemistry 1.3 NotescheeheNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Chemistry As A Central ScienceDocument2 pagesMODULE 1 Chemistry As A Central ScienceEmma Cristie BalahadiaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument6 pagesChemical BondingdanielmahsaNo ratings yet
- Bonding - Covalent N Metallic BondDocument22 pagesBonding - Covalent N Metallic Bondwadheea.thaufeeqNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument132 pagesChemical BondingKowser mahmud100% (1)
- Chapter 2Document22 pagesChapter 2mehrunnisaqaisar111No ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument22 pagesChemical BondingJr CarpelaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding MDocument23 pagesChemical Bonding MnewmowneeshNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond TypesDocument5 pagesChemical Bond Typesapi-287081563No ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument9 pagesChemical Bondingangie432meNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure PDFDocument56 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure PDFAbhishek AgrahariNo ratings yet
- VBT MotDocument23 pagesVBT Motskyanan592No ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument69 pagesChemical Bondingirenerielo19No ratings yet
- Biochemistry 2nd SemesterDocument46 pagesBiochemistry 2nd SemesterEmelly Galvez PadillaNo ratings yet
- Definition: What Is A Chemical Bond? Different Types of Chemical Bonds With Examples FaqsDocument33 pagesDefinition: What Is A Chemical Bond? Different Types of Chemical Bonds With Examples FaqsMedakayala Nagasravanthi 20PHD7125No ratings yet
- CHEMICAL BONDING - NotesDocument30 pagesCHEMICAL BONDING - NotesP YNo ratings yet
- Three Types of Chemical BondingDocument97 pagesThree Types of Chemical Bondingriza loveresNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding For B.tech 1st Year byDocument8 pagesChemical Bonding For B.tech 1st Year byJishnuNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument53 pagesChemical Bondingpream.s1323No ratings yet
- Chemical Bond 21Document16 pagesChemical Bond 21Thanks OdoiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding (Engineering Chemistry Lecture)Document13 pagesChemical Bonding (Engineering Chemistry Lecture)kiana Jessica MonroeNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument19 pagesChemistry37 CM3Vijayalaxmi KambleNo ratings yet
- G9 Q2 W2 Ionic or Covalent CompoundsDocument17 pagesG9 Q2 W2 Ionic or Covalent CompoundsCherrilyn Enverzo33% (3)
- Presented By:: Section: A Group No.: 4Document56 pagesPresented By:: Section: A Group No.: 4Bela GhummanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet
- Fifth Grade Lesson Plan - Solid Liquid and GasDocument4 pagesFifth Grade Lesson Plan - Solid Liquid and GasFranklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- The Land Reform Under Marcos: Not Yet The Final One: Make Your Publications VisibleDocument7 pagesThe Land Reform Under Marcos: Not Yet The Final One: Make Your Publications VisibleFranklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- What's The Matter? Solids, Liquids, and Gases!: Learning ObjectivesDocument2 pagesWhat's The Matter? Solids, Liquids, and Gases!: Learning ObjectivesFranklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- Polytechnic College of BotolanDocument3 pagesPolytechnic College of BotolanFranklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- Copy Editing Contest: SAMPLE TEST 2016-2017Document7 pagesCopy Editing Contest: SAMPLE TEST 2016-2017Franklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- Formerly Botolan Community CollegeDocument4 pagesFormerly Botolan Community CollegeFranklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- Soc Sciac1 Module 4Document3 pagesSoc Sciac1 Module 4Franklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- Module 18Document3 pagesModule 18Franklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- Formerly Botolan Community CollegeDocument3 pagesFormerly Botolan Community CollegeFranklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- Polytechnic College of Botolan: P (X, y Q (X, y PQ X X y y P (3, 5) Q (14,55) PQ X X y y X PQ PQ PQ PQ PQ 61Document2 pagesPolytechnic College of Botolan: P (X, y Q (X, y PQ X X y y P (3, 5) Q (14,55) PQ X X y y X PQ PQ PQ PQ PQ 61Franklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- MODULE Soc Sci Ac1.5Document9 pagesMODULE Soc Sci Ac1.5Franklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Soc Sci Ac1Document3 pagesModule 2 Soc Sci Ac1Franklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Is The Variety of Life On Earth and The Essential Interdependence of All Living ThingsDocument2 pagesBiodiversity Is The Variety of Life On Earth and The Essential Interdependence of All Living ThingsFranklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- RUBRIC For Essay Exam Question: CriteriaDocument1 pageRUBRIC For Essay Exam Question: CriteriaFranklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson No.4: Inorganic Chemistry (Sci Ac5)Document5 pagesLesson No.4: Inorganic Chemistry (Sci Ac5)Franklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- Biological Diversity: Derived CharactersDocument4 pagesBiological Diversity: Derived CharactersFranklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- Hierarchy of Classification of Organisms: Biological DiversityDocument3 pagesHierarchy of Classification of Organisms: Biological DiversityFranklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- Teachers Education Program: Inorganic Chemistry (Sci Ac5)Document4 pagesTeachers Education Program: Inorganic Chemistry (Sci Ac5)Franklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- Bio Handouts 20 Diversity of Organisms and ClassificationDocument3 pagesBio Handouts 20 Diversity of Organisms and ClassificationFranklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- Short Stories Angel Look Out Transcript PDFDocument1 pageShort Stories Angel Look Out Transcript PDFFranklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- Diversity of Organisms and ClassificationDocument3 pagesDiversity of Organisms and ClassificationFranklin BayaniNo ratings yet
- Atoms Review TestDocument6 pagesAtoms Review Testapi-290668569No ratings yet
- ''Chapter 1 ChemistryDocument23 pages''Chapter 1 ChemistryAung LayNo ratings yet
- Consumer-Chem Q1 Mod2 Properties-of-Common-Chemicals v3Document16 pagesConsumer-Chem Q1 Mod2 Properties-of-Common-Chemicals v3Shane TabalbaNo ratings yet
- Chem L1 Modelling Compounds WorksheetDocument5 pagesChem L1 Modelling Compounds WorksheetbecsucrecontactNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GeochemistryDocument12 pagesIntroduction To GeochemistrygengkapakNo ratings yet
- Group I Elements Aka The Alkali Metals: K(S) +O2 (G) KO2(s)Document3 pagesGroup I Elements Aka The Alkali Metals: K(S) +O2 (G) KO2(s)nNo ratings yet
- Atoms: Frederick A. Bettelheim William H. Brown Mary K. Campbell Shawn O. FarrellDocument45 pagesAtoms: Frederick A. Bettelheim William H. Brown Mary K. Campbell Shawn O. FarrellShereen Al-ObinayNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 Types of Compounds Based On Their PropertiesDocument9 pagesScience: Quarter 2 Types of Compounds Based On Their PropertiesAriel Lomugdang PatricioNo ratings yet
- Solutions-Manual-For-Essentials-Of-Materials-Science-And-Engineering-Si-Edition-3rd-Edition-By-Askeland CHAPTER2Document10 pagesSolutions-Manual-For-Essentials-Of-Materials-Science-And-Engineering-Si-Edition-3rd-Edition-By-Askeland CHAPTER2Lourdes Marie Rosalejos OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry 5Th Edition Timberlake Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument49 pagesBasic Chemistry 5Th Edition Timberlake Test Bank Full Chapter PDFflorenceronaldoxo0100% (14)
- Mock Test: About Disha PublicationDocument23 pagesMock Test: About Disha PublicationkeerthyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class 12 Exemplar Questions and AnswersDocument39 pagesChemistry Class 12 Exemplar Questions and AnswersBilly Jasneel SinghNo ratings yet
- Electron Configuration in The Periodic TableDocument3 pagesElectron Configuration in The Periodic TableAliyah RemorozaNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem Basic ElectronicsDocument113 pages1st Sem Basic ElectronicsSrinivas RaoNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year Short Questions Complete BookDocument99 pages2nd Year Short Questions Complete BookZain ZuhabNo ratings yet
- BlongDocument11 pagesBlongMeriza SagaNo ratings yet
- Science 8 3rd Grading ExamDocument3 pagesScience 8 3rd Grading ExamJon Mitchel GalangNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Chapter NotesDocument192 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter NotesTarunNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Part 3Document71 pagesINTRODUCTION TO ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Part 3Triphon Gyle BalidiongNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure of MatterDocument21 pagesElectronic Structure of MatterRosé ParkNo ratings yet
- Class 10 CH 8 Important QuestionsDocument31 pagesClass 10 CH 8 Important QuestionsagrimNo ratings yet
- 2 Atomic Structure & BondingDocument15 pages2 Atomic Structure & BondingAl K MicNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Class X Summative Assessment Ii Science: Code No. 086Document5 pagesAnswer Key Class X Summative Assessment Ii Science: Code No. 086ChandaNo ratings yet
- 12 P Block Revision Notes QuizrrDocument70 pages12 P Block Revision Notes QuizrrÃrjït ShûklãNo ratings yet
- (Graduate Texts in Physics) Ulf W. Gedde, Mikael S. Hedenqvist - Fundamental Polymer Science (Graduate Texts in Physics) - Springer (2019)Document501 pages(Graduate Texts in Physics) Ulf W. Gedde, Mikael S. Hedenqvist - Fundamental Polymer Science (Graduate Texts in Physics) - Springer (2019)Faique S.No ratings yet
- Third Form Chemistry Packet #2Document11 pagesThird Form Chemistry Packet #2Lizbeth ChiNo ratings yet
- Classplusapp - NEET CHEM-Ch 3Document16 pagesClassplusapp - NEET CHEM-Ch 3Muhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document53 pagesChapter 11NathanNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument8 pagesChemistryJHALAK SINGHNo ratings yet