100% found this document useful (1 vote)
381 views4 pagesUnderstanding Transverse, Longitudinal, and Surface Waves
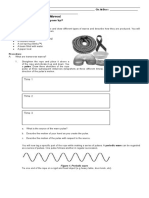
This document describes three types of waves: transverse waves, longitudinal waves, and surface waves. It provides instructions for experiments to observe each type of wave using a rope, coil spring, and water basin. For transverse waves, holding one end of a rope and vibrating it up and down creates a pulse that moves perpendicular to the rope. For longitudinal waves, vibrating one end of a coil spring back and forth parallel to its length creates compressions and rarefactions that propagate along the spring. For surface waves in water, tapping the surface radially creates concentric circular wave fronts, but individual water molecules move in small orbital patterns without being transported from their positions.
Uploaded by
Cindirella GalosCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
381 views4 pagesUnderstanding Transverse, Longitudinal, and Surface Waves
This document describes three types of waves: transverse waves, longitudinal waves, and surface waves. It provides instructions for experiments to observe each type of wave using a rope, coil spring, and water basin. For transverse waves, holding one end of a rope and vibrating it up and down creates a pulse that moves perpendicular to the rope. For longitudinal waves, vibrating one end of a coil spring back and forth parallel to its length creates compressions and rarefactions that propagate along the spring. For surface waves in water, tapping the surface radially creates concentric circular wave fronts, but individual water molecules move in small orbital patterns without being transported from their positions.
Uploaded by
Cindirella GalosCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd