Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PC-I Abe Sahat Water Project (7-8-17)
Uploaded by
FAHAD HASSANOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PC-I Abe Sahat Water Project (7-8-17)
Uploaded by
FAHAD HASSANCopyright:
Available Formats
GOVERNMENT OF THE PUNJAB
HOUSING URBAN DEVELOPMENT AND
PUBLIC HEALTH ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT
PC-I
KHADIM-E- PUNJAB ABE SEHAT PROJECT
INSTALLATION OF WATER FILTRATION PLANTS ON EXISTING
PHED FUNCTIONAL RURAL WATER SUPPLY SCHEMES
ESTIMATED COST RS: 8,865 million
HOUSING , URBAN DEVELOPMENT & PUBLIC
HEALTH ENGINEERING DEPRTMENT
Date of Preparation of PC-1
August-2017
GOVERNMENT OF PAKISTAN
PLANNING COMMISSION
PC-1 FORM
(SOCIAL SECTOR)
1 Name of the Project KHADIM-E- PUNJAB ABE SEHAT PROJECT
(Installation Of Water Filtration Plants On Existing
PHED Functional Rural Water Supply Schemes)
2 Location Total 1,807 Water filtration plants shall be installed
on 1,743 functional rural water supply schemes
already executed by PHED in 21 districts of the
Punjab (Attock, Rawalpindi, Jhelum, Chakwal,
Mianwali, Bhakkar, Khusaab, Sargodha, T.T Singh,
Chiniot, Jhang, Gujrat, Gujranwala, Hafizabad,
Sialkot, Narowal, Mandi Bahudin, Lahore, Pakpattan,
Shiekhupura & Nanakana Sahib). Detail attached as
Annexure-A.
The criteria for site selection will be based on the
following:
I. Selecting rural areas of Northern and Central
Punjab excluding 55 Tehsils of Phase I of
Khadim-e-Punjab Saaf Pani Program which
are presently being covered by Punjab Saaf
Pani Company South & Punjab Saaf Pani
Company North.
II. Those sites will be selected only where
PHED’s Functional Rural Water Schemes
exist.
Project is divided in 8 different contracts keeping in
view the geographical spread of the area.
The detail of contracts is as under:-
Contract I: In this contract, 146 No. filtration plants
will be installed in District Attock.
Contract II: In this contract, 283 No. filtration plants
will be installed in District Rawalpindi.
Contract III: In this contract package, 270 No. plants
will be installed in district Jehlum and Chakwal.
Contract IV: In this Contract package, 172 No.
plants shall be installed in Districts Mianwali and
Bhakkar.
Contract V: In this Contract package, 238 No. plants
will be installed in Khushaab & Sargodha.
Contract VI: In this Contract 243 No. plants shall be
installed in T.T Singh, Chiniot and Jhang.
Contract VII: In this Contract package 307 No.
Plants will be installed in districts Gujrat,
Gujranwala, Hafizabad, Silakot, Narowal, Mandi
Bahudin.
Contract VIII: This package includes 148 No. plants
in districts Lahore, Pakpatan, Shiekhupura and
Nankana Sahib.
3 Authority Responsible
Sponsoring Government of the Punjab, HUD & PHED
Execution PMU, Khadm-e-Punjab Aab-e-Sehat Project
Operation &Maintenance Contractor for first 5 years through PSPC-North will
complete the job of O & M.
Concerned Federal Ministry Nil
4 Plan provision
If the project is included in Nil
medium term / five year plan,
specify actual allocation.
If not included in the current
plan, what warrants its C.M. Directive Punjab.
inclusion and how is it now
proposed to be
accommodated. Nil
If the project is proposed to
be financed out of block
provision Nil
Provision in the current
PSDP/ADP
5 Project objectives and its
Relationship with spectral The development objective of the proposed project is to
objectives provide water purification plants of 1,000/2,000/4,000 &
6,000 liters per hour capacity in 21 districts of Punjab
(Northern and Central) consisting of various stages
including pre-filtration works, filtration, purification and
ultra-violet disinfection.
The following are the main objectives of the project under
which various activities will be carried out every year to
meet the objectives.
Objective 1. Collect available data pertaining to the water
distribution system, identify drinking water supply
problems and select locations in 21 districts of Punjab for
installation of water purification plants at Rural Water
Supply Scheme (RWSS).
Output 1.1: Sites selected for provision of water
purification plants after detailed analysis of water supply
sources.
Activities:
I. Notify the establishment of the Project
Management Unit (PMU).
II. Hold meeting of the steering committee to obtain
input on the desired goals of the project.
III. Identification of the concerned local government
authority! District hospitals where plants are to be
installed.
IV. Notifying Project Management Unit (PMU).
V. Develop a complete project organization.
VI. Preparation of detailed work plan.
VII. The PMU will select sites in line with the finalized
criteria for site selection in consultation with
PHED Govt. of Punjab.
VIII. Work out the current and projected population who
can be benefited at the selected sites.
IX. Estimate the water use at selected places.
X. Prepare water distribution system maps showing
locations of water supplies (i.e., wells), storage
facilities (and volume), and water mains.
XI. Collect pumping water level records from the tube
wells and declining groundwater levels.
XII. Identify any inconsistent water rates of tube well
supplies.
Objective 2: Identification of drinking water quality by
testing the quality of water of wells and the storage
facilities at selected locations and select model mechanism
of treatment required.
Output 2.1: Drinking water quality of selected sources
analyzed.
Activities:
I. Conduct detailed survey at each selected site.
Obtain water samples from selected/ identified
sources
II. Conduct routine phsio-chemical, biological and
bacteriological analyses to assess the water
quality at the laboratories identified by the PMU
or local government institution
III. Obtain concentration of fluoride, iron, nitrate,
nitrite, residual chlorine, chloride, alkalinity,
hardness, sulfate, conductivity, iodine, pH and
total dissolved solid and faecal coliform in water.
IV. Identify areas where the supplied drinking water
is not in compliance with the WHO standards
Output 2.2: Model/mechanism of treatment selected and
technical specifications and design finalized for erecting of
water purification plant.
Activities:
I. Analyze results obtained under activity II and III
of 2.1.
II. Select mode of treatment required as provided
above consisting of 4 stages.
III. Provision of a Nitrate chamber in the assembly if
the source water is high in Nitrates or Nitrites.
IV. Provision of a water softener chamber if the source
water is high in calcium and magnesium.
V. Prepare technical specifications for each of the
units including but not limited to chlorination feed
system, retention tanks, rapid sand filters,
housings, activated carbon filters, chlorine
metering pump, UV sterilizer, nitrate chamber (if
required) and water softener chamber (if required).
VI. These technical specifications should include (but
not limited to) information pertaining to model,
flow rate, rnax. filtered water flow, pressure drop,
maximum and minimum working pressure bar, test
pressure bar, media volume, size of sand filter,
material of filtration chambers, inlet and out let
material, filtration media, working pressure for
filtration shells, material specification for filtration
shell, purification media for activated carbon, UV
Lamp model, UV power consumption, Ultra violet
output, lamps size, design pressure for lamps, UV
dosage etc.
VII. Finalize the design of the plant at each of the
selected sites.
Objective 3: Preparation of tender documents,
advertisement of tenders and finalization of the contractor/
supplier for the provision/ construction of water
purification plants at public places complete in all respects
Output 3.1: Water purification plants operational at
selected sites
Activities:
I. Prepare tender documents for the construction and
provision of water purification plants at selected
sites.
II. Advertise the letter of interest (Lol) in the
newspaper.
III. Shortlist and finalize the company / contractor to
undertake the construction! Provision of water
purification plants at public places.
IV. Award the contract to lowest bidder on turnkey
basis.
V. Supervise and coordinate the construction of water
purification plants along with the representatives
of the PMU Engineers and Sub-Engineers.
VI. Prepare running! Operating instructions manual.
VII. Provide training to operators.
VIII. Commissioning of plants.
IX. Handing over to Village Committees after 5 years
of O&M by the contractor.
X. Provide training to local community for Operation
and Maintenance of plants.
XI. Periodic checking! Analysis of filtered water.
Environment sector has direct relationship with water
quality of drinking and agriculture sources. Water is the
basic necessity of life but it is the dilemma of our society
that a major chunk of country's population is deprived from
clean drinking water and the reports of WHO, National
Council for Water Research and a number of other
research organizations revealed that the water supplied to
the village population of many parts of the Punjab is
contaminated and not fit for human consumption. This
situation has lead to pressure on Government's health
budget and the poor's pockets.
In an effort to improve the taste and quality of their
drinking water, many consumers in Pakistan have turned to
bottled water as a first alternative to drinking unfiltered tap
water. However, those bottled water users are quickly
discovering that all bottled water is not the healthy
drinking water they want, and it is very expensive. In
addition, infrequent testing for contaminants and sporadic
inspection of processing plans must be solved before
bottled water can be assumed to be sanitaryas even regular
tap water.
It is priority of the Provincial Government to provide clean
drinking water to its people. Unfortunately, most of the
water sources are contaminated and there is no proper
mechanism exits whereby poor people could get clean
water (both biologically and chemically treated). The
project will be having a roll on effect once initiated.
Project has relation with health sector. In addition to
many other benefits living standards of inhabitants
will definitely be raised by providing safe and clean
drinking water. People will surely be escaped from
threats like most widely spreading disease hepatitis
and other stomach diseases.
6 Description, justification
& technical parameters
There is no doubt that majority of the population of the
Description of Project province is exposed to the hazard of drinking unsafe and
polluted water. As is evident from the data presented, the
water supplies in all the major cities and rural areasare found
microbiologically unfit for human consumption. It is
therefore no surprise that the inhabitants of these cities
frequently suffer from the incidence of waterborne diseases.
It also gives indications of the very serious extent of the
problem that could be prevalent in much greater proportions
in smaller towns and rural areas of Punjab.
Water may contain inorganic chemicals, such as
bicarbonates, chloride, calcium, fluoride, iron, iodide,
magnesium, nitrate, phosphate, potassium, sodium and
sulfate, and organic compounds like debris of food,
dead plant and animal, faculae, phenolic substances,
pesticides, detergents and pathogens. The description
of parameters commonly used for drinking water is
provided at Annexure of Technical Parameters. They
might come from natural source or artificial source.
Some components are known as essential nutrients.
They are good for health at adequate level but not good
at excess level or absolute Nil. Some are toxic by
themselves. Polluted water is often turbid, with a
particularly unpleasant odor and taste. However, water
may remain colorless while containing a large number
of pathogens. The descript-ion of raw water problems
is provided at Annexure of Technical Parameters.
Previously no consolidated effort was made to monitor
quality of drinking water at the province level. The study
concluded that most of the drinking water samples in the
surveyed cities are found fit for consumption with respect to
physicochemical and aesthetic water quality parameters,
however, the situation of drinking water quality due to
bacterial contamination in the country is generally poor. In
none of the cities all samples were safe from bacterial
contamination. In some cities all the samples were found
contaminated with coliform and E.Coli bacteria.
The results of water quality survey conducted by PHED &
UNICEF is as under:
WATER QUALITY SURVEY RESULT (PHED-UNICEF)
IN PUNJAB PROVINCE
Samples
Sample (%)Overall Fit
Fit (%) Chemically
Fit (%) Microbial
Total
District
Name
Sr.
No.
(Nos.)
1 Attock 878 98.6 73.5 73.5
2 Bhakkar 1,161 94.1 94.3 90.6
3 Chakwal 742 91.9 81.9 77.1
4 Chiniot 528 92.6 88.6 88.3
5 Gujranwala 1,606 30.4 13 3.4
6 Gujrat 2,032 42.6 9.3 5.9
7 Hafizabad 680 53.5 79 43.1
8 Jhang 1,139 76.3 100 76.3
9 Jhelum 988 78.9 91.6 73
10 Khushab 628 43.6 26.3 16.4
11 Lahore 500 49.6 58.6 26.6
12 M.B.Din 641 92.2 50.5 46.5
13 Mianwali 542 84.3 38.7 33.2
Nankana
14 645 92.4 40.3 38.3
Sahib
15 Narowal 2,610 82.3 12 10.8
16 Pakpattan 1,110 79.7 88 71.4
17 Rawalpindi 1,246 95.6 64.5 62.8
18 Sargodha 1,590 71.6 100 71.6
19 Sheikhupura 1,289 90.8 90.8 90.7
20 Sialkot 2,970 61.9 57.1 40.7
21 T.T.Singh 981 68.3 93.4 62.6
74.82 64.35 52.51
Grand Total 24,506
% % %
The water quality data of RWSS is attached as Annex-C.
It is essential that solution should be found to ameliorate
these problem areas by undertaking crash program. The
proposed project intends to provide water purification
system combining many different types of water filters and
ultraviolet light disinfection units into complete turn-key
drinking water system that provide a naturally pure and safe
drinking water solution in different cities and rural areas of
Punjab.
The water purification plants will consist of various stages
including pre-filtration works, filtration, and purification
and ultra-violet disinfection. The detailed description of
each of these stages is given below:
Stage I. Pre-Filtration Works:
The purpose of pre-filtration works stage is to identify the
source of water. The source of water could either be the
overhead tanks or the tube wells installed by the authority.
In case of the overhead tank, the regular supply of water for
the purification plant can be ensured. In this case a request
will have to be made to the Housing, Urban Development &
Public Health Engineering Department to provide necessary
space (12 ft* 14 ft) for the placement of the plant and 2
inches water pipe connection from the overhead tank.
In case the supply source is identified as the tube well,
change in the design of the water purification plant will have
to be made by catering for the provision of raw water tank.
The provision of the retention tank is optional and shall be
made in case the source water is very high in suspended
impurities of larger diameter. The particles having a larger
diameter will settle down in the retention tank. This process
removes heavier suspended solids that may cause rapid
clogging of the filter.
Stage II: Filtration:
The purpose of filtration is to remove suspended impurities
such as sand, silt, rust, dust and scale particles up to 1
micron. The simplest form of water filter is the sand filter.
This filter resembles a small reservoir, whose bottom is a
bed of filter sand that rests on a bed of well-graded
aggregate with the largest size aggregate being at the
bottom.
Rapid sand gravity filter (silica sand) should be provided
and designed in such a way that it should be able to remove
all insoluble suspended particles up to one micron particles.
In order to bring the size of suspended particles to one
micron, two additional no. of housings along with the sand
filter should be provided. At solo stage a pre-filter housing
with 5 micron sediment cartridge and at binary stage a
granular activated carbon cartridge with 1 micron sediment
control should be included. All wetted parts would be
stainless steel ASI 304.
An underdrain system of tile or brick will be provided
beneath the gravel to collect the water from the filter area.
The underdrain system should consist of a header or main
conduit extending across the filter bed. Means should be
provided for regulating the flow of water out of the filter
through this header and also for controlling the rate of flow
onto the filter. The filter is to be operated at controlled rates
that should not exceed 3.0 gals ph per square foot of filter
area. The filter bed should consist of about 12 to 20 inches
of gravel and 20 to 40 inches of sand; the depth of water
over the sand bed should at least 5 feet.
Stage III: Purification:
Activated Carbon (AC) is made of tiny clusters of carbon
atoms stacked upon one another. The raw carbon source is
slowly heated in the absence of air to produce a high carbon
material. Passing oxidizing gases through the material at
extremely high temperatures activates the carbon. The
activation process produces the pores that result in such high
adsorptive properties.
Purification system use Granular Activated Carbon filter to
remove Sulphur, Organic Chemicals (Trihalomathanes,
insecticides, pesticides, herbicides and germicides),
Chlorine, bad tastes and odors. Activated carbon (AC)
filtration is most effective in removing organic contaminants
from water. AC filtration does not remove microbes,
sodium, nitrates, fluoride, and hardness. AC works by
attracting and holding certain chemicals as water passes
through it. AC is a highly porous material; therefore, it has
an extremely high surface area for contaminant adsorption.
Activated Carbon requires only periodic backwashing to
eliminate accumulated suspended matter and to re-grade the
filter bed. To obtain maximum efficiency of the activated
carbon, in the absorption process, it is desirable to have the
greatest possible surface area in the smallest practical
volume. The equivalent surface area of 1 pound of AC
should range from 60 to 150 acres. AC filtration should
meet American water works association standard B 604-74.
Stage IV: Ultra Violet Sterilization:
Ultra Violet Sterilization kills microorganisms, disinfects
bacteria and does not change the taste of water or bum
Calcium, Magnesium and Chlorides. Ultraviolet (UV) lamps
will be used for killing bacteria, viruses, bacterial fungi,
algae and protozoa. A chlorine-metering pump would be
provided before the UV sterilizer.
UV units should contain at least two powerful UV lamps
protected inside a quartz sleeve from the water, which
passes through the chamber. UV light is emitted as a result
of current flow through the mercury vapor between the
electrodes of the lamp. The L MV lamps (low pressure
mercury vapor) should produce the majority of their UV
output at 253.7 nm, a wavelength that is very close to the
260 to 265 nm wavelengths which are most effective
inkilling microbes.
The UV light damages the DNA part of the bacteria and
viruses in such a way that they are unable to replicate. A cell
that cannot reproduce is considered dead since it is unable to
multiply to infectious numbers within a host. This is a
highly effective way of destroying bacteria in water and, in a
correctly designed installation, 99.999% reduction is
achievable.
The proposed intervention would also dramatically impact
the underpinnings of poverty, health, education, gender,
social inclusion and income / consumption.
The detail of served population under this project in 21
districts is as under:
Sr. No. of Functional Served
Districts
No. Tehsils Schemes Population
1 Attock 6 146 750,181
2 Bhakkar 4 2 61,361
3 Chakwal 4 124 456,029
4 Chiniot 3 4 41,903
5 Gujranwala 4 16 177,008
6 Gujrat 3 124 347,900
7 Hafizabad 2 3 44,669
8 Jhang 4 3 26,040
9 Jhelum 4 146 419,051
10 Khushab 3 127 711,327
11 Lahore 1 29 495,044
12 Mandi B.Din 3 24 117,387
13 Mianwali 3 164 881,519
14 Nankana Sahb 3 19 110,206
15 Narowal 3 38 202,342
16 Pakpattan 2 57 337,671
17 Rawalpindi 7 280 848,343
18 Sargodha 6 102 415,359
19 Shiekhupura 5 19 249,159
20 Sialkot 4 82 345,346
21 T.T Singh 4 234 1,038,927
Total 78 1,743 8,076,772
The plant type, capacity and served population detail is as
under:
Plant Capacity wise UF RO Total
Capacity serving Plant Plant Plant
(LPH) Population (No.) (No.) (No.)
1,000 0 - 2400 547 23 570
2,000 2401 - 4800 630 17 647
4,000 4801 - 9600 400 20 420
6,000 9601 - 14,400 161 9 170
Total 1738 69 1,807
The detail of proposed contracts is as under:
Proposed Contracts for Filtration Plants
No. of
Contract District
Plants
I Attock 146
II Rawalpindi 283
III Jhelum & Chakwal 270
IV Mianwali & Bhakkar 172
V Khushab & Sargodha 238
VI T.T Singh, Chiniot, Jhang 243
Gujrat, Gujranwala, Hafizabad, Sialkot,
VII 307
Narowal, Mandi Bahudin
Lahore, Pakpattan, Sheikhupura,
VIII 148
Nankana Sahib
Total 1,807
The water source for filtration plants is existing functional
Indicate source and water rural water supply schemes executed by Public health
availability. engineering department. The detail of PHED RWSS is
attached as Annexure- B.
The water demand taken for design calculation is 5 liter
Indicate technical per capita per day (lpcd).
parameters Operational time of plant is 12 hours.
Detailed description of technical parameters, parameters
on the basis of which decision of RO and UF made and
process flow diagram for water filtration plants is
attached as Annexure- C.
Indicate whether the N.A
proposed project is part of
the master plan. If so,
provide details.
The major components under this project to be constructed
are as follows:
Provide detail of civil
works, equipment’s, 1. Raw water tank
2. Filtration Plant
machinery and other
3. Product water tank
physical facilities. 4. Dispensing area
5. Plant room
Number of plants w.r.t capacity is as under:
Installation of UF Plant @ 1,000 LPH i/c
547
Plant room
Installation of UF Plant @ 2,000 LPH i/c
630
Plant room
Installation of UF Plant @ 4,000 LPH i/c
400
Plant room
Installation of UF Plant @ 6,000 LPH i/c
161
Plant room
Installation of RO Plant @ 1,000 LPH i/c
23
Plant room
Installation of RO Plant @ 2,000 LPH i/c
17
Plant room
Installation of RO Plant @ 4,000 LPH i/c
20
Plant room
Installation of RO Plant @ 6,000 LPH i/c
9
Plant room
7 Capital cost estimate
Indicate date of estimation Rs. 8,865 Million
of project cost Capex of project is 5,365 Million and Opex for 5
years is 3,500 Million.
Cost estimates are based on inquiries from suppliers'
Bases of determining the and manufacturers of such equipment. All costs
capital cost. reflect current market prices. Based on Engineer’s Cost
Estimate.
Detailed Cost Estimate is Attached as Annexure- D.
Provide year wise estimates Detail of Component-Wise, Year Wise Physical
of physical activities by main activities is attached as Annexure- E.
components.
Phasing of capital cost be Detail of Year Wise / Component wise Financial
worked out on the basis of phasing is attached as Annexure-F.
each of work as stated above
and provide information.
8 Annual Operation & After Completion of Scheme, the scheme will be operated
Maintenance cost after and maintained by the contractor through PSPC-North for
Completion of the project. first 5 years and then only by Punjab Saaf Pani Company
(North) for next 15 Years. The detail of annual operation
and maintenance cost is attached in detailed cost estimates.
9 Demand & supply Analysis NA
10 Financial plan & mode of
financing
1) Source of financing
Sponsors own resources
Federal Government Scheme will be financed by Government of the Punjab
Provincial Government through special provision of funds for the social sector
projects.
DFI’s / Banks
General Public
Foreign equity
NGO’s beneficiaries
Others
11 Project benefits & analysis
financial By the execution of this project, 8.1 Million
population of rural areas of Punjab will have access to
safe and clean drinking water.
Water-borne diseases are quite common all across
Pakistan. Infants and children are more susceptible to
such diseases. Although advances in technology mean
more diseases can be controlled by low cost
immunization, no immediate breakthroughs are
foreseen for water borne diseases, implying that
improved health requires improvements in drinking
water facilities.
It will combat the waste water born diseases and improve
general health of the public and in return reduce the hospital
and medicine expenses.
Social benefits with
indicator The project has immense social benefits. But these
highly invaluable social benefits cannot be accurately
quantified to carry out financial and economic analysis
in the form of financial indicators. However the social
benefits of the project far outweigh the costs of the
project. Water is vital to all life and central to all efforts
to eliminate poverty. Clearly, building water
purification plants to produce an adequate supply of
potable water will reduce the hazards of drinking
unsafe and contaminated water.
The main expected results of the project benefits
include:
1,807 water purification plants fully functional at
public places in all districts of Punjab.
It will improve hygienic conditions & will result in
control of water born diseases & other epidemics.
People at large will have sustainable access to safe
drinking water.
Human health will be safeguarded.
Reduction in water borne diseases.
Reduction in mortality rate.
Awareness among the society about the health
hazards associated with the drinking of
contaminated water.
Employment generation Unskilled, semi-skilled and skilled labor up to 9,000 persons
will be employed.
Environment impact
The project has no potentially significant and
irreversible impact. The project includes
provision of standard water purification plants at
selected places, water sample analysis at all
selected places and the cost of civil works for
the construction of plants. In addition provision
has been made for Nitrate Chambers + Water
Softener Chambers in order to cater for the
treatment of those water sources which are high
in Nitrates/ Nitrites/ Calcium and Magnesium.
The provision for raw water tanks have been made for
those water sources where the water directly comes
from the tube wells and no overhead tank
provision exists for storage of water.
A screening process was carried out for the
proposed project. The project already seeks
ways to maximize the societal benefits and
avoid or reduce unacceptable impacts resulting
from the drinking of contaminated water There
are no concerns for which environmental
analysis is unnecessary and the project may
proceed without conducing any lEE or ElA
study. Overall it will improve the environmental
sustainability of the area.
impact of delays on 1) It will increase the cost of the project.
project & viability 2) Price escalation will be involved.
3) Community can suffer.
12 Implementation schedule The project will be implemented through the PMU of
Khadim-E- Punjab Abe Sehat Project who will execute
it through contract to a successful bidder. The
contractor will hire man power from local market as
per their requirements.
The detailed implementation schedules i-e Procurement
plan, HR Management Plan, Risk mitigation plan, M &
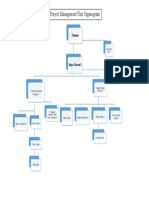
E plan, Organogram and detailed staffing of PMU is
attached as Annexure- G.
Indicate starting and The project will start from 1st July 2017 and will be
completion date of the completed up to 31st March 2018 subject to availability
project of full funds.
Item-wise / year wise
implementation schedule in Detailed Project timeline of the project as attached as
line chart co-related with Annexure-H.
the phasing of physical
activities.
13 Management structure &
Man power requirements
Including specialized skills
During execution and
operational phase
Administrative The following Officer of the PMU will manage the
arrangements for Project.
implementation of the
project. Project Director 1
Deputy Project Director 1
Manager Admin & Finance 1
Manpower requirements Water Quality Expert 1
during execution and Manager Procurement 1
operation of the project Manager Legal & Contracts 1
Manager Community Mobilization 2
Executive secretary 2
Computer Operator 4
General Manger Projects 1
Senior Engineer 4
District Engineer 8
Sub-Engineer 8
a. Notification of the Project Steering Committee
Holding the meeting of Project Steering Committee
b. Identification of the concerned District! local
government authority where plants are to be
installed
c. Preparation of tender documents and awarding
contract on turnkey basis and O&M for five years
d. The PMU Cell will prepare Quarterly Progress
reports indicating the pace of the progress made &
operational constraints, if any, which hinder the
progress of the project.
Role of Provincial Local Government
Departments/ Local Government Institution:
Notification of Project Management Unit
a. Identification! Final selection of proposed sites.
b. Nomination of monitoring officers.
c. Allocation of space (12 ft* 14 ft) for housing the
water treatment plant.
d. Arrangements for water supply connection (at least
2 inches).
e. Arrangements for the provision of electric
connection.
f. Regular administering and supervision of the plant.
g. Nominations of plant operator/s.
h. Responsible for regular operation and maintenance
of the plants. (The project will fund the Operation
and Maintenance cost for a period of five years.
Regular/ Frequent analysis of purified water.
Role of Contractor:
Each plant will be installed on turnkey basis according to the
finalized designs for various places which will include the
following:
a. Provision of water filtration plant as per the design
requirements
b. Provision of Nitrate Chambers + Water Softener
(if required)
c. Provision of special treatment equipment (if
required)
d. Provision of water cooler
e. Fixing of electric connections (internal + external)
f. Fixing of water connection from the main as per
design requirements
g. Fixing of motor pumps
The contractor will be liable for the operation and
maintenance of the plant for a period of five year
through PSPC-North from the date of commissioning
of the plant.
Project management unit has sufficient specialized
manpower as mentioned above to manage and
implement the project. Skilled and semi-skilled
manpower is locally available to handle the execution
of the project.
14 Additional project decisions The project is aimed to provide clean and safe drinking
required to maximized socio water facilities to the 8.1 Million rural population of
economic benefits from the the 78 tehsils of Punjab province.
proposed project. The Domestic & Commercial consumers will be
charged after 5 years for water fetching in order to
Indicate additional projects / meet the annual O & M expenses. For revenue
decisions required to collection an agency or community organization may
optimize the investment be established.
being undertaken on the In case of forcemajure like earthquake and flood etc.
project. may adversely affect the project completion time and
additional cost will be required to rectify the damages
in works for which decision of competent Authority
may be required.
15 Certified that the PC-I has been prepared as per instruction by the planning
commission for the preparation of PC-I for Social Sector projects.
Prepared By: Director (Design)
Office of Chief Engineer (North)
PHED Lahore.
042-99212676
Checked By: Chief Engineer (North)
PHED Lahore.
042-99212674
Forwarded By: Secretary
Govt. of Punjab
HUD & PHED Lahore.
042-99212626
You might also like
- Project DescriptionDocument5 pagesProject DescriptionM ShahidNo ratings yet
- Project DescriptionDocument4 pagesProject DescriptionM ShahidNo ratings yet
- Scheme For Provision of Pumping Machinery For Productivity Enhancement in Khyber PakhtunkhwaDocument53 pagesScheme For Provision of Pumping Machinery For Productivity Enhancement in Khyber Pakhtunkhwahayat aliNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Background: Detail Feasibility of Pandes Lift Irrigation Project, Jayprithvi NP 3, BajhangDocument17 pages1.1 Background: Detail Feasibility of Pandes Lift Irrigation Project, Jayprithvi NP 3, BajhangRoshanNo ratings yet
- DKPL CRZ Compliance ReportDocument7 pagesDKPL CRZ Compliance ReportSamrat DNo ratings yet
- Tor Ladp DasuDocument20 pagesTor Ladp DasufefahimNo ratings yet
- Punjab Govt Scheme Provides Septic Tanks for Weaker HouseholdsDocument6 pagesPunjab Govt Scheme Provides Septic Tanks for Weaker HouseholdsAbhi annaNo ratings yet
- Achievements Details DJBDocument29 pagesAchievements Details DJBNaman MittalNo ratings yet
- Main Report - Sisneghari - FinalDocument54 pagesMain Report - Sisneghari - Finalkiran_karki_8No ratings yet
- Detailed Design and Construction Supervision of Water Supply System, GujratDocument8 pagesDetailed Design and Construction Supervision of Water Supply System, GujratM ShahidNo ratings yet
- Proforma of PC I 6635.00 MillionDocument27 pagesProforma of PC I 6635.00 MillionKhurramNo ratings yet
- Rangpo Drainage Concept PlanDocument20 pagesRangpo Drainage Concept PlanEngineering CivilMantraNo ratings yet
- Water Supply Scheme Project ConceptDocument2 pagesWater Supply Scheme Project ConceptNajeeb uyghurNo ratings yet
- AP NTR Jala Siri Phase II Bore Wells Project Guidelines and Selection Process As Per GO 6 at WWW - Ntrjalasiri.ap - Gov.inDocument8 pagesAP NTR Jala Siri Phase II Bore Wells Project Guidelines and Selection Process As Per GO 6 at WWW - Ntrjalasiri.ap - Gov.inraviamNo ratings yet
- Ide 404Document7 pagesIde 404Yashraj PatidarNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Environmental ACTION PLAN REPORT OF GPCB - VAPI-2010Document95 pagesComprehensive Environmental ACTION PLAN REPORT OF GPCB - VAPI-2010neeraj sharmaNo ratings yet
- Land Acquisition and Resettlement Due DiligenceDocument15 pagesLand Acquisition and Resettlement Due DiligenceChaulapalli Srinivas MurthyNo ratings yet
- Case Studies 3 Hubli DharwadDocument7 pagesCase Studies 3 Hubli DharwadIssac Arul SelvaNo ratings yet
- Waste Water Management: Vishal DasDocument8 pagesWaste Water Management: Vishal Dasvishal dasNo ratings yet
- Project Digest of Kertasari Raw Water Supply - RevDocument5 pagesProject Digest of Kertasari Raw Water Supply - RevM Hardyan PrastyantoNo ratings yet
- PDF_1_20210929100055840Document4 pagesPDF_1_20210929100055840pahuljotNo ratings yet
- Optimising Canal and Groundwater Management ModelsDocument122 pagesOptimising Canal and Groundwater Management ModelsMuhammad Kashif Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Executed WorksDocument3 pagesExecuted WorksDevendra ChandakNo ratings yet
- 00main ReportDocument13 pages00main ReportDeepak YadavNo ratings yet
- Greater Thal CanalDocument113 pagesGreater Thal CanalAvais KhanNo ratings yet
- EOI No 13 18.10.2022Document20 pagesEOI No 13 18.10.2022Chiranjib BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Development of 8-Lane Vadodara - Mumbai ExpresswayDocument16 pagesDevelopment of 8-Lane Vadodara - Mumbai ExpresswayNaman JainNo ratings yet
- Ken Betwa ReportDocument161 pagesKen Betwa ReportNazakat Hussain100% (1)
- Sapgaon Rural Water Supply Scheme Village: Sapgaon, Taluka: Shahapur, District: ThaneDocument19 pagesSapgaon Rural Water Supply Scheme Village: Sapgaon, Taluka: Shahapur, District: ThaneJitendraHatwarNo ratings yet
- Taxali Area Important Landmarks - Key PlanDocument44 pagesTaxali Area Important Landmarks - Key PlanZunaash RasheedNo ratings yet
- DPR Nag River Volume IIIDocument290 pagesDPR Nag River Volume IIIashutosh_shahu1No ratings yet
- Gang Garhi FinalDocument20 pagesGang Garhi FinalSyedShahHasnainNo ratings yet
- Gang Garhi FinalDocument20 pagesGang Garhi FinalSyedShahHasnainNo ratings yet
- Draft TOR - Feasibilty Study & Design of Phase2 at Atiak Sugar - 1st DraftDocument20 pagesDraft TOR - Feasibilty Study & Design of Phase2 at Atiak Sugar - 1st DraftAyella paulNo ratings yet
- PMKSYGuidDocument61 pagesPMKSYGuidbenny mosesNo ratings yet
- Dewatering Method Statement For Waste Water Network SystemDocument13 pagesDewatering Method Statement For Waste Water Network SystemmuhammedpmubarakNo ratings yet
- Integrated MSW Project EIA Report SummaryDocument188 pagesIntegrated MSW Project EIA Report SummaryChan KianNo ratings yet
- Arogyamrutamu Telugu Ayurvedic BookDocument37 pagesArogyamrutamu Telugu Ayurvedic BookgangarajuNo ratings yet
- Interception, Diversion of Drains & Sewage Treatment Works at Farrukhabad-Fatehgarh, Uttar PradeshDocument35 pagesInterception, Diversion of Drains & Sewage Treatment Works at Farrukhabad-Fatehgarh, Uttar PradeshAdditya ChoudhharyNo ratings yet
- Rain Water Harvesting in Ministers Quarter ComplexDocument21 pagesRain Water Harvesting in Ministers Quarter ComplexUmesh Agrawal100% (1)
- Punjab Saaf Pani Project failure due to poor monitoring and evaluationDocument5 pagesPunjab Saaf Pani Project failure due to poor monitoring and evaluationishfi02shahNo ratings yet
- Indrajeet-Water SupplyDocument5 pagesIndrajeet-Water Supplyshivanshvr16No ratings yet
- Cement Quality CheakDocument6 pagesCement Quality CheakJimmyNo ratings yet
- 10705SI001 - Ghangaru Bahuni Khola IPDocument112 pages10705SI001 - Ghangaru Bahuni Khola IPSharad PanditNo ratings yet
- Innovative Institutional Approach Inclusive Sewer System Case Alandur IndiaDocument21 pagesInnovative Institutional Approach Inclusive Sewer System Case Alandur IndiaanjuNo ratings yet
- Strategic Irrigation Project Procurement PlanDocument22 pagesStrategic Irrigation Project Procurement PlanAbib Ansari100% (2)
- India: MFF-Assam Urban Infrastructure Investment ProgramDocument2 pagesIndia: MFF-Assam Urban Infrastructure Investment ProgramNeilootpal KonwarNo ratings yet
- Draft Executive Summary: Manggopoh - Padang Sawah (Link 047.1) Kabupaten AgamDocument91 pagesDraft Executive Summary: Manggopoh - Padang Sawah (Link 047.1) Kabupaten AgamAunur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Small Dams Project (Loan 750-PAK (SF) )Document40 pagesSmall Dams Project (Loan 750-PAK (SF) )Independent Evaluation at Asian Development BankNo ratings yet
- HYDROPONICS - DRAFT BA REPORT (Final) 1Document84 pagesHYDROPONICS - DRAFT BA REPORT (Final) 1gracie koiNo ratings yet
- ToR For Carry Out EIA StudyDocument13 pagesToR For Carry Out EIA StudyvishvamNo ratings yet
- TOR - TRTA 9458-PAK GreaterThal - FR Advertise 180615Document10 pagesTOR - TRTA 9458-PAK GreaterThal - FR Advertise 180615pakshaheenNo ratings yet
- Concept Paper of ISBIG For State ConsultationsDocument37 pagesConcept Paper of ISBIG For State Consultationsrahil1915100% (2)
- Guide Lines RRR-IIIDocument20 pagesGuide Lines RRR-IIISuneel KumarNo ratings yet
- DownloadPfdFile AspxDocument13 pagesDownloadPfdFile Aspxfirozr249No ratings yet
- 10705SI012 - Chyaple Raikare Sana SichaiDocument96 pages10705SI012 - Chyaple Raikare Sana SichaiSharad PanditNo ratings yet
- Vol 2Document559 pagesVol 2erbhaveshparmarNo ratings yet
- Brief Write-Up (Tors) Jalalpur Irrigation ProjectDocument20 pagesBrief Write-Up (Tors) Jalalpur Irrigation ProjectWaqas AhmedNo ratings yet
- MomDocument6 pagesMom995aarveeNo ratings yet
- Planning and Evaluation of Irrigation Projects: Methods and ImplementationFrom EverandPlanning and Evaluation of Irrigation Projects: Methods and ImplementationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Contract 1 Specifications 12.12.2017Document145 pagesContract 1 Specifications 12.12.2017FAHAD HASSANNo ratings yet
- Section 06Document3 pagesSection 06FAHAD HASSANNo ratings yet
- Annexure-C, Description of Technical ParametersDocument8 pagesAnnexure-C, Description of Technical ParametersFAHAD HASSANNo ratings yet
- PC-I Abe Sahat Water Project (7-8-17)Document16 pagesPC-I Abe Sahat Water Project (7-8-17)FAHAD HASSANNo ratings yet
- Khadim-e-Punjab Abe Sehat Project PC-I DetailsDocument1 pageKhadim-e-Punjab Abe Sehat Project PC-I DetailsFAHAD HASSANNo ratings yet
- BOQ KPASP 7-08-2017 (Annex-D)Document38 pagesBOQ KPASP 7-08-2017 (Annex-D)FAHAD HASSANNo ratings yet
- PMU Staff Detail: Designation QtyDocument1 pagePMU Staff Detail: Designation QtyFAHAD HASSANNo ratings yet
- BOQ KPASP 7-08-2017 (Annex-D)Document38 pagesBOQ KPASP 7-08-2017 (Annex-D)FAHAD HASSANNo ratings yet
- PHED Punjab RWSS Data SummaryDocument65 pagesPHED Punjab RWSS Data SummaryFAHAD HASSANNo ratings yet
- Annexure-C, Description of Technical ParametersDocument8 pagesAnnexure-C, Description of Technical ParametersFAHAD HASSANNo ratings yet
- Annexure-G, PMU-Advertisement (Final)Document2 pagesAnnexure-G, PMU-Advertisement (Final)FAHAD HASSANNo ratings yet
- Annexure-G, Staff Job Descriptions-FinalDocument29 pagesAnnexure-G, Staff Job Descriptions-FinalFAHAD HASSANNo ratings yet
- Saaf Pani Program Design Report for Tehsil ChaubaraDocument197 pagesSaaf Pani Program Design Report for Tehsil ChaubaraFAHAD HASSANNo ratings yet
- Annexure-G, Project Implementation Plan FinalDocument19 pagesAnnexure-G, Project Implementation Plan FinalFAHAD HASSAN100% (1)
- Annexure-G, PMU and Consultants OrganogramDocument1 pageAnnexure-G, PMU and Consultants OrganogramFAHAD HASSANNo ratings yet
- Project Management Unit Organogram: ChairmanDocument1 pageProject Management Unit Organogram: ChairmanFAHAD HASSANNo ratings yet
- Project Location: Khadim-e-Punjab Aab-e-Sahat ProgramDocument9 pagesProject Location: Khadim-e-Punjab Aab-e-Sahat ProgramFAHAD HASSANNo ratings yet
- Fuel Tank-Specs-110824Document6 pagesFuel Tank-Specs-110824FAHAD HASSANNo ratings yet
- Khadim-E-Punjab Abe Sehat ProjectDocument1 pageKhadim-E-Punjab Abe Sehat ProjectFAHAD HASSANNo ratings yet
- Fuel Tank-Specs-110824Document6 pagesFuel Tank-Specs-110824FAHAD HASSANNo ratings yet
- Fuel Tank-Specs-110824Document6 pagesFuel Tank-Specs-110824FAHAD HASSANNo ratings yet
- Fuel TankDocument4 pagesFuel TankFAHAD HASSANNo ratings yet
- Student Sex Work Toolkit FINAL December 2020Document11 pagesStudent Sex Work Toolkit FINAL December 2020due ruoteNo ratings yet
- Karen Horney Theorist in Psychoanalysis and Feminine PsychlogyDocument14 pagesKaren Horney Theorist in Psychoanalysis and Feminine PsychlogyaelindahoNo ratings yet
- Graphic Warning LawDocument21 pagesGraphic Warning LawVincentNo ratings yet
- Article 257 261Document9 pagesArticle 257 261Angel EiliseNo ratings yet
- SDS-Dolphin Screen WashDocument10 pagesSDS-Dolphin Screen WashLiz CNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Emotional Intelligence in Employees PerformanceDocument16 pagesThe Effects of Emotional Intelligence in Employees PerformanceMohan SubramanianNo ratings yet
- CPS 2 ToxicologyDocument31 pagesCPS 2 ToxicologyNgọc Hà NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Post Mortem Report FinalDocument3 pagesPost Mortem Report Finalnupur jhodNo ratings yet
- Marginal Ridge Is Severely WeakenedDocument9 pagesMarginal Ridge Is Severely WeakenedChin GeslaniNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Mina Sains ISSN: 2407-9030 Volume 2 Nomor 2, Oktober 2016 71Document9 pagesJurnal Mina Sains ISSN: 2407-9030 Volume 2 Nomor 2, Oktober 2016 71yudhoNo ratings yet
- Understanding Hospital Emergency CodesDocument60 pagesUnderstanding Hospital Emergency CodesRemi0% (1)
- Cot DLP FBS 3RD and 4THDocument11 pagesCot DLP FBS 3RD and 4THMherasul Pasaylo100% (2)
- Balneological Use of Thermal WatersDocument10 pagesBalneological Use of Thermal WatersMary Carmen CarrascoNo ratings yet
- Hearing DisorderDocument64 pagesHearing DisorderЭ.ТөгөлдөрNo ratings yet
- GastrostomiaDocument3 pagesGastrostomiaJuan HernandezNo ratings yet
- YDEW3004-Case Study-316103481Document15 pagesYDEW3004-Case Study-316103481Jenelle Lee ColeNo ratings yet
- Homoeopathy Mother TincturesandUsesDocument34 pagesHomoeopathy Mother TincturesandUsessmithsinghNo ratings yet
- CareHealth Policy 2020-21 Nihit FamilyDocument5 pagesCareHealth Policy 2020-21 Nihit FamilyJacob PruittNo ratings yet
- Rasika DietitianDocument3 pagesRasika DietitianChrill DsilvaNo ratings yet
- 2020 Monitoring Drug TherapyDocument7 pages2020 Monitoring Drug Therapydolemite4No ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Milk v2Document1 pageThe Chemistry of Milk v2Florentina BarbălatăNo ratings yet
- Fentanyl Epidemic Ravaging WisconsinDocument2 pagesFentanyl Epidemic Ravaging WisconsinMike MaybayNo ratings yet
- Love - Bondage or Liberation - A Psychological Exploration of The Meaning, Values and Dangers of Falling in Love PDFDocument209 pagesLove - Bondage or Liberation - A Psychological Exploration of The Meaning, Values and Dangers of Falling in Love PDFPurnendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Early Metabolic Programming - 1 - InfantNutrition - B.Koletzko PDFDocument10 pagesEarly Metabolic Programming - 1 - InfantNutrition - B.Koletzko PDFAnnie RealNo ratings yet
- English Handouts (Pormintilla)Document30 pagesEnglish Handouts (Pormintilla)Rommel BansaleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Risk For InfectionPatrick Renz TibayanNo ratings yet
- Menopause Thesis StatementDocument6 pagesMenopause Thesis Statementallisonweavereugene100% (2)
- Indonesia Healthcare ReportDocument51 pagesIndonesia Healthcare ReportPutri CandraNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 10 Curriculum MapDocument9 pagesMapeh 10 Curriculum MapJoshua LamzonNo ratings yet
- The Teen Brain in Harvard MagazineDocument3 pagesThe Teen Brain in Harvard Magazineapi-247477585No ratings yet