Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Advantages and Disadvantages of Network Topology
Uploaded by
Iffah Husna0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
90 views5 pagesOriginal Title
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF NETWORK TOPOLOGY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
90 views5 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Network Topology
Uploaded by
Iffah HusnaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
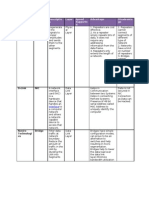
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF NETWORK TOPOLOGY.
NO. TYPES OF TOPOLOGY ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES
1. BUS a) It is easy to setup, a) The cable is limited
manage, and in length. This
deploy is simple. limits the number
b) Small networks are of connectable
ideally adapted for Network Nodes.
this. b) Can only perform
c) c) It costs much well for a limited
less. number of nodes.
The effectiveness
decreases when
the number of
devices connected
to the bus
increases.
c) It is appropriate for
low-traffic
networks. High
traffic raises bus
load, and the
capacity of the
network
decreases.
d) It largely depends
on the central bus.
A fault in the bus
results in network
failure.
e) Isolating faults in
the network nodes
is also not simple.
f) f) Each device on
the network "sees"
all the data being
transmitted,
posing a risk to
safety.
2. RING a) A central server is a) The failure of a
not needed for the single node in the
management of network will cause
this topology. failure of the entire
b) The traffic is network.
unidirectional, and b) The movement or
high-speed data modifications
transmission. made to the
c) A ring is better at network nodes
handling load as affect the
opposed to a bus. performance of the
d) Adding or whole network.
removing network c) Data sent from one
nodes is easy, as node to another
only two has to pass
connections need through all the
to be changed in intermediate
the process. nodes. This makes
e) Its design allows the transmission
the detection of slower in
faults in network comparison to that
nodes. in a star topology.
f) Each node has the
opportunity to
convey data in this
topology. So it is a
very structured
topology of the
network.
g) It is less expensive
than a stars
topology.
3. STAR a) It also enables in- a) Network operation
network isolation is reliant on central
of each devices. hub functioning.
b) It's easy to add or Hence ,central hub
delete network failure leads to
nodes, and can be network-wide
done without failure.
affecting the b) Additionally , the
whole network. number of nodes
c) Because of the that can be added
centralized design, depends on the
faults in the central hub
network devices capacity.
are easy to detect. c) The setup costs are
d) This topology fairly high.
poses less security
risk, as traffic
analysis is simple.
e) As in the case of a
ring network , data
packets do not
have to pass
through several
nodes. Thus, traffic
load can be
handled at
relatively
reasonable speeds
with the use of a
high-capacity
central hub.
4. MESH a) The configuration a) Most connections
of the network do not serve any
nodes is such that significant function
data can be in the system
simultaneously wherein each
transmitted from network node is
one node to connected to some
several other other network
nodes. node. This leads to
b) A single node other network links
failure does not being redundant.
cause the entire b) It requires lots of
network to fail, as cabling. So, the
there are alternate setup and
data transmission maintenance costs
paths. are high.
c) It can handle
heavy traffic, as
any two network
nodes have
dedicated paths
between them.
d) Point-to - point
connection
between every
pair of nodes
enables the
detection of faults.
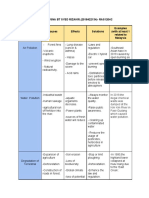
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN PHYSICAL CONNECTIONS OF MEDIA
NO. TYPES DIFFERENCE
1. TWISTED PAIRED CABLE Consists of one or more bundled twisted-
pair wires. Each twisted-pair wire consists
of two separate copper isolated wires,
which are twisted together.
For noise reduction, the wires are twisted
together.
Majorly used in telephone networks, data
networks and cable shielding.
More cheaper
Incapable carrying a signal in over long
distance.
2. COAXIAL CABLE It consists of a single copper wire rounded
by at least three layers: (1) the insulating
material, (2) the woven or braided metal,
and (3) the outer plastic coating .
Majorly used in network cable television
(CATV) , computer network connection
and digital audio.
It can be cabled over longer distances than
twisted-pair cable and fiber optic.
Affordable.
Prone to produce noise during
transmission.
3. FIBER OPTIC Consists of dozens or hundreds of thin
glass or plastic strands which use light to
convey signals. Each strand is as thin as a
human hair, called an optical fibre. Inside
the fiber optic cable, each optical fiber is
surrounded by a latent glass cladding and
a protective coating.
The ability to carry much more signals than
wire cables
Faster data transfer
Less susceptible to noise from other
devices, such as a copy machine
Better security during transmission since
they are less prone to noise
Smaller and thinner in size.
More expensive than cables.
You might also like
- Data Communication Assignment No 1 PDFDocument3 pagesData Communication Assignment No 1 PDFaman khanNo ratings yet
- HW 3Document5 pagesHW 3Mark StephensNo ratings yet
- Networking Assignment 1Document9 pagesNetworking Assignment 1M.Bilal JattNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Network Topologies PDFDocument2 pagesComparison Between Network Topologies PDFNikhil Gobhil100% (1)
- Networks & Network Topologies - Print - QuizizzDocument6 pagesNetworks & Network Topologies - Print - QuizizzBunny starboyNo ratings yet
- NetworkDocument42 pagesNetworkSunitikumar GhoshNo ratings yet
- TopologyDocument1 pageTopologyAlia NadzirahNo ratings yet
- Ignou Mca - MCS-042Document42 pagesIgnou Mca - MCS-042PradeepKumar NeelakantamNo ratings yet
- CN Assignment 1Document13 pagesCN Assignment 1SHUBHAM SHAHNo ratings yet
- Quality of Services Provides Proactive Routing Protocol in ManetDocument4 pagesQuality of Services Provides Proactive Routing Protocol in ManeterpublicationNo ratings yet
- Network Topologies Explained: Mesh, Star, Bus, Ring & Hybrid ModelsDocument20 pagesNetwork Topologies Explained: Mesh, Star, Bus, Ring & Hybrid ModelsMd IshteyaqueNo ratings yet
- EC8552 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE AND ORGANIZATION - RemovedDocument67 pagesEC8552 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE AND ORGANIZATION - Removed30. Suraj IngaleNo ratings yet
- EC8702 Ad hoc and Wireless Sensor Networks MCQDocument14 pagesEC8702 Ad hoc and Wireless Sensor Networks MCQDHANESH R 18EC026100% (1)
- (MCQ) Computer Communication Networks - LMT2Document14 pages(MCQ) Computer Communication Networks - LMT2raghad mejeedNo ratings yet
- Ethernet hub guide: physical layer device for connecting devicesDocument1 pageEthernet hub guide: physical layer device for connecting devicesshinsmart92No ratings yet
- CCNA 3 - Chapter - 1 - Quiz-MinozaDocument4 pagesCCNA 3 - Chapter - 1 - Quiz-MinozaKurt John MiñozaNo ratings yet
- (PDF) Multiple Choice Questions On Wireless CommunicationDocument78 pages(PDF) Multiple Choice Questions On Wireless Communicationayyanar7No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (Topologies, Medium)Document13 pagesAssignment 1 (Topologies, Medium)mian saadNo ratings yet
- Network Topologies: LAN Topologies Physical Bus Topology Advantages of Bus TopologyDocument8 pagesNetwork Topologies: LAN Topologies Physical Bus Topology Advantages of Bus TopologyMary Ann SalvatierraNo ratings yet
- Network Concepts and MediaDocument63 pagesNetwork Concepts and MediaikonNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Architecture and Network TopologyDocument9 pagesComputer Network Architecture and Network TopologyMary Niña VivasNo ratings yet
- Comparing the advantages and disadvantages of repeaters, NICs, and bridgesDocument1 pageComparing the advantages and disadvantages of repeaters, NICs, and bridgesRohan KamatNo ratings yet
- ComputerDocument2 pagesComputercopykitav.inNo ratings yet
- TaskDocument4 pagesTaskhamodashalape26No ratings yet
- Quick Revision NetworkingDocument7 pagesQuick Revision Networkingzahir khanNo ratings yet
- Design and Performance Evaluation of Meghadoot - A Hybrid Wireless Network ArchitectureDocument6 pagesDesign and Performance Evaluation of Meghadoot - A Hybrid Wireless Network ArchitecturegynxNo ratings yet
- Sana’a University Final Term Exam Communication NetworksDocument6 pagesSana’a University Final Term Exam Communication NetworksHamdi M. SaifNo ratings yet
- 3DDocument4 pages3DVibhu GautamNo ratings yet
- Distributed Topology Construction of Bluetooth Wireless Personal Area NetworksDocument11 pagesDistributed Topology Construction of Bluetooth Wireless Personal Area NetworksSasikanth MareeduNo ratings yet
- Student Details:: General (Semester) CSE1004 Network and Communication Embedded Lab VL2021220502957 L5+L6Document14 pagesStudent Details:: General (Semester) CSE1004 Network and Communication Embedded Lab VL2021220502957 L5+L6AKSHATT KAIN 20BCE2167No ratings yet
- Q.No. CO LO(s) Marks R U ADocument4 pagesQ.No. CO LO(s) Marks R U AMahesh DahiwalNo ratings yet
- Interference Map For 802.11 NetworksDocument12 pagesInterference Map For 802.11 Networksmmxy_1No ratings yet
- Computer Networks 1Document18 pagesComputer Networks 1Edwin NfehNo ratings yet
- Networking and Internetworking Devices: 21.1 Review QuestionsDocument3 pagesNetworking and Internetworking Devices: 21.1 Review QuestionsOso PolNo ratings yet
- Ec8552 Computer Architecture and OrganizationDocument67 pagesEc8552 Computer Architecture and OrganizationShamia SathishNo ratings yet
- Computer ScienceDocument5 pagesComputer Sciencemaharjanaarya21No ratings yet
- Receivea: AssociatedDocument3 pagesReceivea: AssociatedShivani MarkandanNo ratings yet
- PuzzlesDocument4 pagesPuzzlessumasivaraviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Network Topologies& DevicesDocument61 pagesChapter 4 Network Topologies& DevicesManofwarriorNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Introduction To Networking Concept: StructureDocument32 pagesUnit 3 Introduction To Networking Concept: StructureAakash GautamNo ratings yet
- A Study and Analysis of Computer Network TopologiesDocument4 pagesA Study and Analysis of Computer Network TopologiesFilip KesteliNo ratings yet
- Elmossallamy 2020Document13 pagesElmossallamy 2020Trần Văn VũNo ratings yet
- Module 1 IoT (7)Document15 pagesModule 1 IoT (7)rakshithvittla1234No ratings yet
- Comprehensive Study of Routing Management in Wireless Sensor Networks-Part-1Document8 pagesComprehensive Study of Routing Management in Wireless Sensor Networks-Part-1tamfinNo ratings yet
- Network Topologies PDFDocument7 pagesNetwork Topologies PDFsyedpandt0% (2)
- INTEGRATION, The VLSI Journal: A. Chariete, M. Bakhouya, J. Gaber, M. WackDocument15 pagesINTEGRATION, The VLSI Journal: A. Chariete, M. Bakhouya, J. Gaber, M. WackRemberto SandovalNo ratings yet
- Network Design & Administration - Q & ADocument10 pagesNetwork Design & Administration - Q & ATapela Ziyela100% (1)
- Local Area Networks - FundamentalsDocument36 pagesLocal Area Networks - FundamentalsMuhammad ArfanNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 Module 1 Study GuideDocument6 pagesCCNA 1 Module 1 Study GuidekimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Networking BY MAYOWADocument14 pagesIntroduction To Computer Networking BY MAYOWAWakaye AbbaNo ratings yet
- 1 Year-Semester One Computer Skills: Dr. Huda Mubarak MohamedDocument23 pages1 Year-Semester One Computer Skills: Dr. Huda Mubarak MohamedですモッケNo ratings yet
- Network Topologies, Protocols and StandardsDocument37 pagesNetwork Topologies, Protocols and Standardsnarasimharao P.V.No ratings yet
- Introduction to Basics of NetworkingDocument23 pagesIntroduction to Basics of NetworkingBhargav SahNo ratings yet
- H-Name: A Hidden-Node Avoidance Mechanism For Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument10 pagesH-Name: A Hidden-Node Avoidance Mechanism For Wireless Sensor NetworksMahesh MiriyalaNo ratings yet
- Data Link Layer: Paolo Costa Costa@cs - Vu.nlDocument14 pagesData Link Layer: Paolo Costa Costa@cs - Vu.nlindrajeet04bsNo ratings yet
- ADHOC QbankDocument3 pagesADHOC Qbankkarthiksvr26No ratings yet
- Wireless Facility Scheduling for Data CentersDocument12 pagesWireless Facility Scheduling for Data CentersUdupiSri groupNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 CN notes(continued)Document13 pagesUnit-3 CN notes(continued)Ketan SharmaNo ratings yet
- IOTDocument4 pagesIOTIffah HusnaNo ratings yet
- "Life in Uitm": Lab Assignment 4 Nur Shafiqah BT Jusli RAT1102ADocument10 pages"Life in Uitm": Lab Assignment 4 Nur Shafiqah BT Jusli RAT1102AIffah HusnaNo ratings yet
- Global Oils and Fats Production Over 40 YearsDocument4 pagesGlobal Oils and Fats Production Over 40 YearsIffah HusnaNo ratings yet
- CH5-System SoftwareDocument47 pagesCH5-System SoftwareIffah HusnaNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 1 Topic 2Document3 pagesQUIZ 1 Topic 2Iffah HusnaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 3-STADocument2 pagesTutorial Chapter 3-STAIffah HusnaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 - Mac-Jul2020Document8 pagesTutorial 2 - Mac-Jul2020Nur SyahiraNo ratings yet
- Sharifah Nuriffah Husna BT Syed Rizakri. (2018422134) - Ras1204C Examples (With at Least 1 Related To MalaysiaDocument2 pagesSharifah Nuriffah Husna BT Syed Rizakri. (2018422134) - Ras1204C Examples (With at Least 1 Related To MalaysiaIffah HusnaNo ratings yet
- Sharifah Nuriffah Husna BT Syed Rizakri. (2018422134) - Ras1204C Examples (With at Least 1 Related To MalaysiaDocument2 pagesSharifah Nuriffah Husna BT Syed Rizakri. (2018422134) - Ras1204C Examples (With at Least 1 Related To MalaysiaIffah HusnaNo ratings yet
- EXTA4Document39 pagesEXTA4Regis RomaryNo ratings yet
- Hardware Modeling Using Verilog - Unit 2 - Week 1 AssignmentDocument3 pagesHardware Modeling Using Verilog - Unit 2 - Week 1 AssignmentgudduNo ratings yet
- Pro Charge Ultra Instruction ManualDocument40 pagesPro Charge Ultra Instruction ManualMónica SantamaríaNo ratings yet
- Specifications: Tx6A Shielded Copper Cabling System TX7000 Shielded Copper Cable - S/FTPDocument2 pagesSpecifications: Tx6A Shielded Copper Cabling System TX7000 Shielded Copper Cable - S/FTPΔΗΜΗΤΡΗΣ ΧΑΡΙΤΑΚΗΣNo ratings yet
- Modern Power System Matlab Simulation, Pspice, SVC-HVDC Transmission, STATCOM, Location of Facts, Power System ME, M.tech, B.Tech, BE Final Year IEEE Projects 2011 - 2012Document3 pagesModern Power System Matlab Simulation, Pspice, SVC-HVDC Transmission, STATCOM, Location of Facts, Power System ME, M.tech, B.Tech, BE Final Year IEEE Projects 2011 - 2012srini_792002No ratings yet
- Electronics (H) QPDocument25 pagesElectronics (H) QPChloe CadoretNo ratings yet
- Lenovo Z370 Z470 Z570 Hardware Maintenance Manual V1.0Document120 pagesLenovo Z370 Z470 Z570 Hardware Maintenance Manual V1.0KSnakeWNo ratings yet
- Powerflex 700S High Performance Ac Drive: Technical Data - Phase I ControlDocument76 pagesPowerflex 700S High Performance Ac Drive: Technical Data - Phase I Controlsofiyan hadyNo ratings yet
- Onkio HTP430 PDFDocument12 pagesOnkio HTP430 PDFerju10No ratings yet
- Electrical System PDFDocument117 pagesElectrical System PDFoz23100% (1)
- Sensor Node Failure Detection Using Round Trip Delay in Wireless Sensor NetworkDocument9 pagesSensor Node Failure Detection Using Round Trip Delay in Wireless Sensor Networksurendar147No ratings yet
- BS BS 1:2002: and Alarm Systems For BuildingsDocument27 pagesBS BS 1:2002: and Alarm Systems For BuildingsMHEP_DANIEL100% (1)
- ControlLogix System User ManualDocument232 pagesControlLogix System User ManualMusad AlQadi Bani Hammad100% (1)
- 8000 Series Information Sheet2Document2 pages8000 Series Information Sheet2Ian RowleyNo ratings yet
- GMT-312 - Multimeter User's ManualDocument26 pagesGMT-312 - Multimeter User's Manualhutz5000No ratings yet
- HW2 SolutionsDocument8 pagesHW2 SolutionsPamela HulseNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7Document2 pagesAssignment 7Lihle Ayabonga NcambacaNo ratings yet
- WeeklyReport JobpacksDocument91 pagesWeeklyReport JobpacksQC CIVIL ENGINEER KAZCOMSERVICENo ratings yet
- Manual - ET Roller 5Document16 pagesManual - ET Roller 5Forum PompieriiNo ratings yet
- Jadual Wim - Penjajaran Coptpa Cu, Wa, PPMPP, PPMPB Dan JPWDocument10 pagesJadual Wim - Penjajaran Coptpa Cu, Wa, PPMPP, PPMPB Dan JPWBakal JenazahNo ratings yet
- COA Lecture 20Document26 pagesCOA Lecture 20Chhaveesh AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Query - R 2.0 4G Perfomance - PCI RETUNE - HourlyDocument215 pagesQuery - R 2.0 4G Perfomance - PCI RETUNE - HourlyShashank PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- 48 50HG-1T PDFDocument52 pages48 50HG-1T PDFAhmad HamoudaNo ratings yet
- Irlb8314Pbf: Application V 30 V R Max 2.4 M 3.2 QG 40 NC I 171 A I 130ADocument8 pagesIrlb8314Pbf: Application V 30 V R Max 2.4 M 3.2 QG 40 NC I 171 A I 130AJosè Miguel López RodriguezNo ratings yet
- TLS-450PLUS Automatic Tank GaugeDocument5 pagesTLS-450PLUS Automatic Tank GaugeJamesNo ratings yet
- 93.0.940 PTD-Fire-Alarm-Panel-R1.23Document47 pages93.0.940 PTD-Fire-Alarm-Panel-R1.23Ralph FranzoiNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi PM710Document73 pagesSpesifikasi PM710Phan'iphan'No ratings yet
- BaylorDocument140 pagesBaylorjairoleonx542691% (11)
- Automatic Field Irrigation SystemDocument7 pagesAutomatic Field Irrigation SystemIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet