Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Group Ii B - Volatile Metals
Uploaded by
Jana Blue0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views4 pagesThis document provides information on various metals including zinc, cadmium, mercury, titanium, chromium, molybdenum, and uranium. It discusses their properties, common compounds, and uses. For example, it notes that zinc is an essential trace element used to release insulin and in galvanization, while mercury is highly toxic and can cause Minamata disease through methylmercury contamination of water supplies. Cadmium is a cumulative poison associated with Itai-itai disease from contaminated drinking water.
Original Description:
GROUP 2B-8B
Original Title
GROUP II B
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information on various metals including zinc, cadmium, mercury, titanium, chromium, molybdenum, and uranium. It discusses their properties, common compounds, and uses. For example, it notes that zinc is an essential trace element used to release insulin and in galvanization, while mercury is highly toxic and can cause Minamata disease through methylmercury contamination of water supplies. Cadmium is a cumulative poison associated with Itai-itai disease from contaminated drinking water.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views4 pagesGroup Ii B - Volatile Metals
Uploaded by
Jana BlueThis document provides information on various metals including zinc, cadmium, mercury, titanium, chromium, molybdenum, and uranium. It discusses their properties, common compounds, and uses. For example, it notes that zinc is an essential trace element used to release insulin and in galvanization, while mercury is highly toxic and can cause Minamata disease through methylmercury contamination of water supplies. Cadmium is a cumulative poison associated with Itai-itai disease from contaminated drinking water.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
GROUP II B – VOLATILE METALS Astringent and antiseptic action
Dentin desensitizer (Topical to the
- Zinc, Cadmium, Mercury
teeth as a 10% solution)
- Metals have relatively low melting points
- Zinc and cadmium are soft metals; Zinc – Eugenol Cement
mercury exists as liquid at room
temperature - Used by dentists for their effect on
- In compounds, elements exist as pulpal pain particularly when restoring
divalent ions but Hg in addition has a teeth with deep lesions
unique property of having a monovalent Zinc Oxide
ion, Hg 2 2+¿
- The oxides and hydroxides of these - Synonym: Zinc White, Flowers of Zinc,
metals are weak bases, with base Pompholyx, Nihil Album, Lana
strength increasing going down the Philosophica, Philospher’s wool
group - Protective, mild astringent and weak
antimicrobial compound
ZINC - Uses:
- Amphoteric Dusting powder
- Does not occur free in nature Physical sunblock
- Ores: Component of Lassar’s paste
Cadmia (zinc ores) The primary ingredient of Calamine
Sphaelerite, Zinc blende (ZnFe)S USP
Smithsonite (ZnCO3) Zinc Stearate
- Used in the manufacture of galvanized
iron - Protective
- Container for batteries and dry cells - Dusting powder
- Essential trace element Zinc Sulfate
- w/ insulin (release from the pancreas)
- deficiency is associated with - Synonym: white Vitriol
parakeratosis and impaired immunity - Astringent, weak antiseptic, emetic
- toxicity: Metal Fume Fever (before)
- antidote for soluble Zn compounds: - Ophthalmic astringent in 0.25% solution
NaHCO3 (only FDA-approved OTC ophthalmic
astringent)
Calamine - Necessity for White Lotion preparation
- synonym: Lapis calaminaria, Prepared White Lotion
calamine, Artificial calamine
- zinc oxide with a small proportion of - Synonyms: Lotio Alba, Lotio Sulfurata,
ferric oxide White sulfide
- a protective with a good drying effect - Zinc sulfate + sulfurated potash
and a mild astringent action - Acting ingredient in White Lotion: ZnS
- Use: parasiticide, topical protectant,
Zinc Chloride antiseptic
- synonyms: Butter of zinc, Burnett’s Zinc Undecylenate
disinfection fluid
- Lucas reagent - Mildly antiseptic and astringent
- Cross and Bevan’s reagent - Dusting powder
- Use:
Zinc Pyrithione Epidemic birth defects and neurologic disease
in Japanese village of Minamata
- Antidandruff shampoo formulation
b. ___ - behavioral pattern characterized by
CADMIUM
changes in mood from shyness, withdrawal,
- Astringent (water-soluble compounds) depression, along with explosive anger
- Found in cigarette smoke
c. ___ - pink palms, pink soles, painful
- Used in the manufacture of stink bombs
erythema of the extremities
- Cumulative poison
- Itai-itai disease Sodium Formaldehyde Sulfoxylate
Chronic cadmium poisoning Dimercaprol (BAL) and Penicillamine
A local Japanese disease caused by (Cuprimine R)
drinking water contaminated by Dimercaptosuccinic acid/ Succimer
cadmium Organic Hg:
The symptoms include sever bone Inorganic Hg salts:
pain, waddling gait, aminoaciduria, Elemental Hg:
glycosuria, severe osteomalacia
Ammoniated Mercury
(bone softening)
- Synonym: White Precipitate, Mercuric
Cadmium Sulfide
amidochloride
- Capsebon R - Use: topical antiseptic
- Shampoo
Mercuric Chloride
For the treatment of dandruff but
causes photosensitization - Synonym: ___, mercury bichloride
- Yellow sulfide - Extremely poisonous (fatal hemorrhagic
gastroenteritis)
Cadmium Sulfate
- Uses: (before)
- Ophthalmic antiseptic For syphilis
Disinfectant (1:1000) for utensils and
MERCURY
surgical instruments
- Synonyms: ___, Asoge, Liquid Silver,
Mercurous Chloride
Messenger of gods (Hermes)
- Can be obtained from Cinnabar/ HgS - Synonyms: ___, mild mercury chloride
- Has diuretic, antiseptic, an - Saline cathartic (before)
- Uses: - Component of Black Lotion (with lime
Thermometers, Barometers, Gas water)
pressure regulators For syphilitic sores
Amalgams
Yellow Mercuric Oxide
Tisyphilitic, and cathartic action
Cumulative poison - Synonym: yellow precipitate
- Ophthalmic anti-infective
Chronic toxicity:
Mercurous Iodide
a. (Minamata disease) – caused by
methylmercury formed in ocean water by - Treatment of syphilis
metabolic action of aquatic organisms on
Mercuric Iodide
elemental Hg discharged from factory.
- Irritant poison
- Alkaloidal reagent Vanadium
Chlormerodrin, Hg 197 Injection; - “Erythronium”
Chlormerodrin Hg 203 Injection - Principal commercial source: Minas
Ragra
Uses: scintillation of scanning of the
- Essential trace element
kidneys or the brain
Tantalum
- To be left in the human body to
GROUP III B – SCANDIUM FAMILY strengthen a broken bone
- Scandium, Yttrium, Lanthanum, GROUP VI B – CHROMIUM FAMILY
Actinium
- Scandium – eka – Boron - Chromium (Cr), Molybdenum (Mo),
- Rare earths: Tungsten (W)
Lanthanides – 14 members
Chromium
(atomic no. 58-71)
Actinides – 14 members (atomic - Glucose Tolerance Factor
no. 90-103) - Essential trace element
- Most stable oxidation state is 3+
GROUP IV B – TITANIUM FAMILY
- 2+ oxidation state are good reducing
- Titanium, Zirconium, Hafnium agents
- Compounds such as dichromates
Titanium Dioxide (Cr2O72-) having 6+ oxidation number
- Uses: are readily reduced to the 3+ state are
Solar ray protective (High refractive thus good oxidizing agents
index) Molybdenum
Sun creams and sun screen
products - Essential trace element
Used as a white pigment in cosmetic - Cofactor for enzymes associated with
paints since it has good covering flavin-dependent enzymes
power and is quite inert - Human Molybdenum Cofactor
Deficiency
Zirconium
Uranium
- Similar to Aluminum
- Antiperspirant, deodorant - Discovered by Becquerel
- Causes skin granuloma - Radioactive element used for the
manufacture of atomic bombs
Zirconium Oxide/ Zirconium Carbonate - No pharmaceutical use
- Former official compounds GROUP VII B – MANGANESE FAMILY
- Antiperspirant
- Treatment of athlete’s foot - Manganese (Mn), Technetium (Tc),
Potassium Permanganate
GROUP V B – VANADIUM FAMILY - Synonym: mineral chameleon
- Strong oxidizing agent
- Vanadium (V), Niobium (Nb), Tantalum - Antiseptic
(Ta)
Technetium Transferrin (siderophilin) – the major
iron transport protein of blood
- Derived from the decay of 99 Mo
plasma
- First element produced artificially
- Most commonly used Toxicity: Hermochromatosis; Hemorrhagic
radiopharmaceutical gastroenteritis
Technetium 99m – Phytate: Liver
- Antidote: deferoxamine
Imaging
- When iron supplements are prescribed,
Technetium 99m – Hepatogluconate:
the oral route is the method of choice
Kidney imaging, renal function
Ferrous form
Technetium 99m – HIDA:
Vitamin C
Hepatobiliary studies
- Parental iron preparations are indicated
Technetium 99m – Etidronate: bone
only in those conditions where either
imaging
iron absorption is defective or the iron
TRIADS salt may be irritating
- Use: Hematinic
- All of the Group VII elements are
- Three officially approved iron salts
grayish-white metals with high melting
available for the oral administration of
and boiling points
iron
- “noble metals”
Ferrous sulfate (most widely used)
GROUP VIII B – IRON TRIAD Ferrous fumarate
Ferrous gluconate
- Iron (Fe), Cobalt (Co), Nickel (Ni)
- Intravenous route:
Iron Iron dextran injection – is a sterile,
colloidal solution of ferric hydroxide
- The chief source of iron in industry is
in complex with partially hydrolyzed
hematite (Fe2O3)
of low MW, in Water for Injection
- The sulfide, iron pyrite (FeS2) looks
Iron Sorbitex Injection – is a sterile
similar to gold and is often called “fool’s
solution of complex iron sorbitol and
gold”
citric acid that is stabilized with the
- Most of the iron found in the body is
aid of dextrin and excess sorbitol
associated with two types of protein:
Hemoproteins and Iron Basham’s Mixture
storage/transport proteins
- Iron + ammonium acetate
Hemoproteins - Styptic
- Astringent
Cytochrome c – a respiratory
enzyme in which iron is complexed Cobalt
in a porphyrin ring system
- Central metal in Vitamin B12
Hemoglobin and myoglobin – stores
- Important in erythropoiesis
and/or transports oxygen
- Used in the manufacture of beers
Iron storage and/or transport proteins
Nickel
Ferritin and hemosiderin – iron
- Old Nick’s copper” or Kupfernickel
storage proteins found in the liver,
- Moderately lustrous silvery metal; used
spleen, and bone marrow
extensively in alloy
Ferritin – water
Raney nickel: Ni and Al alloy
Hemosiderin – water insoluble
You might also like
- Comprehensive Pharmacy Review (Summary)Document8 pagesComprehensive Pharmacy Review (Summary)davenNo ratings yet
- Scientific & Family Name Pinus PalustrisDocument43 pagesScientific & Family Name Pinus PalustrisLyka MarceloNo ratings yet
- Household Cleaning ProductsDocument4 pagesHousehold Cleaning ProductsCIANO, Dellaney Joy A.No ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Aids and NecessitiesDocument4 pagesPharmaceutical Aids and NecessitiesJana BlueNo ratings yet
- Eries: 6.0 TO 8.0 TONDocument12 pagesEries: 6.0 TO 8.0 TONNos GoteNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Stage 7 Sample Paper 1Document14 pagesMathematics Stage 7 Sample Paper 1Gideon Eka Dirgantara50% (2)
- Scientific & Family Name Pinus PalustrisDocument43 pagesScientific & Family Name Pinus PalustrisLyka MarceloNo ratings yet
- Sp3510 User ManualDocument48 pagesSp3510 User Manualchristos1157No ratings yet
- Functional Biology NOTESDocument113 pagesFunctional Biology NOTESRebecca Amy JennerNo ratings yet
- Smart AntennasDocument40 pagesSmart AntennasMeeraNo ratings yet
- Inorgchem - ReviewerDocument6 pagesInorgchem - Reviewerejeraalaysa54No ratings yet
- Common Compounds of Group 2a-6aDocument4 pagesCommon Compounds of Group 2a-6aDakota SimbsNo ratings yet
- PH 113 Lec NotesDocument18 pagesPH 113 Lec NotesJenny Arabela ApiagNo ratings yet
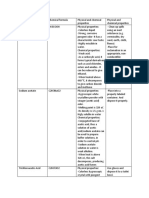
- Name Other Names Physiochemical Properties Pharmacologic Application Source Range of Toxicity Signs and Symptoms Management Qualitative TestDocument2 pagesName Other Names Physiochemical Properties Pharmacologic Application Source Range of Toxicity Signs and Symptoms Management Qualitative TestAlexa Joy C. InguilloNo ratings yet
- Powder - : DF Uses Ing and UsesDocument3 pagesPowder - : DF Uses Ing and UsesAJNo ratings yet
- INORGANIC CHEMISTRY SUPPLEMENTS FinalDocument13 pagesINORGANIC CHEMISTRY SUPPLEMENTS FinalSantielle SablayanNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Inorganic ChemicalsDocument8 pagesMiscellaneous Inorganic ChemicalsMaRiz BalitaanNo ratings yet
- Name Other Names Physiochemical Properties Pharmacologic Application Source Range of Toxicity Signs and Symptoms Management Qualitative TestDocument2 pagesName Other Names Physiochemical Properties Pharmacologic Application Source Range of Toxicity Signs and Symptoms Management Qualitative TestAlexa Joy C. InguilloNo ratings yet
- Inguillo TabulationDocument2 pagesInguillo TabulationAlexa Joy InguilloNo ratings yet
- Post TestsDocument37 pagesPost TestsRobby ZablanNo ratings yet
- Inorgchem Lec Prelim Reviewer 2Document5 pagesInorgchem Lec Prelim Reviewer 2Raven Janica DeangNo ratings yet
- Name Other Names Physiochemical Properties Pharmacologic Application Source Range of Toxicity Signs and Symptoms Management Qualitative TestDocument2 pagesName Other Names Physiochemical Properties Pharmacologic Application Source Range of Toxicity Signs and Symptoms Management Qualitative TestAlexa Joy C. InguilloNo ratings yet
- UNIT-IV AstringentsDocument6 pagesUNIT-IV AstringentsimleenusNo ratings yet
- Santiago, Judea C. 11 Abm-Silang PM March 9, 2021 Worksheet: Directions: Complete The Table BelowDocument3 pagesSantiago, Judea C. 11 Abm-Silang PM March 9, 2021 Worksheet: Directions: Complete The Table BelowJudea SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Bse NseDocument34 pagesBse NseVivek SoniNo ratings yet
- 36-Corrosive Poisons modified-SKP 19Document38 pages36-Corrosive Poisons modified-SKP 19sumedh tulkaneNo ratings yet
- Metallic PoisonDocument12 pagesMetallic Poisonfully hiddenNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 01 May 2022Document25 pagesAdobe Scan 01 May 2022rishabhmi123456No ratings yet
- Phchem NotesDocument17 pagesPhchem NotesJayrine MonteroNo ratings yet
- ENT Case SummeryDocument9 pagesENT Case SummeryMahir AminNo ratings yet
- General Types of AntidotesDocument2 pagesGeneral Types of AntidotesSelena MoonNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Alkali Metal LTDDocument35 pagesPresentation On Alkali Metal LTDSubhash SoniNo ratings yet
- Cinnamon Water: Preparation Category Synonyms Description of Final Product Use/s IngredientsDocument6 pagesCinnamon Water: Preparation Category Synonyms Description of Final Product Use/s IngredientsMaan EspirituNo ratings yet
- Group IBDocument2 pagesGroup IByunelsa enton lopezNo ratings yet
- Pars LD 2Document82 pagesPars LD 2sachin mishraNo ratings yet
- Alkali Metals LimitedDocument26 pagesAlkali Metals Limitedhbkabhi_raiNo ratings yet
- Toxicology Chapter 6Document5 pagesToxicology Chapter 6bLoOdy MasSaCrENo ratings yet
- UsesDocument11 pagesUsesRDXNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Aids and NecessitiesDocument14 pagesPharmaceutical Aids and NecessitiesJake HarryNo ratings yet
- Contact Dermatitis Boards Fodder Summer 2015Document5 pagesContact Dermatitis Boards Fodder Summer 2015JamesNo ratings yet
- Chemical Uses in Daily LifeDocument3 pagesChemical Uses in Daily LifeDaniel RasheediNo ratings yet
- Chemical Storage Colors LandscapeDocument1 pageChemical Storage Colors Landscapekongpop26894ktzNo ratings yet
- Product Offer de CON enDocument14 pagesProduct Offer de CON enForeverNo ratings yet
- 8-Media CatalogDocument6 pages8-Media CatalogWilson JustinoNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Compounds: Group I-A: Alkali MetalsDocument7 pagesInorganic Compounds: Group I-A: Alkali MetalsJessica GutierrezNo ratings yet
- General Guide List For Selecting The Proper Disinfectant That Meets Your Particular RequirementsDocument4 pagesGeneral Guide List For Selecting The Proper Disinfectant That Meets Your Particular RequirementsRaşit AcaroğluNo ratings yet
- Annex Module 6Document6 pagesAnnex Module 6angelo aquinoNo ratings yet
- Clinical ToxicologyDocument17 pagesClinical ToxicologyPauline GamlangaNo ratings yet
- Toxicology SummaryDocument9 pagesToxicology SummaryPatricia JaneNo ratings yet
- Group Iv Anions: - Distinguish by The Insolubility of Their Silver Salts in Acid SolutionDocument24 pagesGroup Iv Anions: - Distinguish by The Insolubility of Their Silver Salts in Acid SolutionSherwin OrdinariaNo ratings yet
- Inorg Chem NotesDocument15 pagesInorg Chem Notesanise santosNo ratings yet
- Inorg Med.1.1-1Document38 pagesInorg Med.1.1-1Kathleen Joy ArutaNo ratings yet
- F B 1Document16 pagesF B 1maoNo ratings yet
- F B 2Document16 pagesF B 2maoNo ratings yet
- Forensic Assignment Muhammad Asghar Roll No. 2357Document5 pagesForensic Assignment Muhammad Asghar Roll No. 2357Faisal AwanNo ratings yet
- Group Ammoniated Mercury: Ravalo, Marc Requine, Hanna Beatriz Reyes, Aline Josh YDocument12 pagesGroup Ammoniated Mercury: Ravalo, Marc Requine, Hanna Beatriz Reyes, Aline Josh YjapzeedeeeNo ratings yet
- BleachingDocument69 pagesBleachingdisha agarwalNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry Final Period 1Document59 pagesInorganic Chemistry Final Period 1Angela JavierNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument3 pagesDocumentKyllene Leonor BigsotNo ratings yet
- Poison and AntidoteDocument5 pagesPoison and Antidoterelaxedits2No ratings yet
- OintmentDocument20 pagesOintmentsn4s7nyxcbNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Common Acids and AlkalisDocument3 pages9.1 Common Acids and AlkalisKitty CheungNo ratings yet
- Chapter Vi, Vii, Viii, IxDocument12 pagesChapter Vi, Vii, Viii, IxKC CallejaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chesmistry 1A 3ADocument9 pagesInorganic Chesmistry 1A 3AJessica GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Project Work On Chemistry: Change of PH During Formation of Curd From MilkDocument16 pagesProject Work On Chemistry: Change of PH During Formation of Curd From MilkYoezer Pelden100% (1)
- 02 - Catalogue - ENDocument27 pages02 - Catalogue - ENAlejandro SiavisnomNo ratings yet
- Engglis Isma E. N (18010107023) Tadris IpaDocument6 pagesEngglis Isma E. N (18010107023) Tadris IpaLita Dwi HasjayaNo ratings yet
- Honey Python TestingDocument2 pagesHoney Python Testinger.honeyraj2016No ratings yet
- 2-Dimensional CCD Is Built In. A New Type of Displacement Sensor Utilizing The Best and Most Up-To-Date Image Processing TechnologiesDocument13 pages2-Dimensional CCD Is Built In. A New Type of Displacement Sensor Utilizing The Best and Most Up-To-Date Image Processing TechnologiesNguyễn Đức LợiNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Energy Flow in An EcosystemDocument13 pages2.1 Energy Flow in An EcosystemJoanne OngNo ratings yet
- Booklet Course 8 Chapter 5Document18 pagesBooklet Course 8 Chapter 5PaolaNo ratings yet
- AtlasPoCu CCC 20190805Document33 pagesAtlasPoCu CCC 20190805David GoteraNo ratings yet
- CTR201Document2 pagesCTR201Vicente RezabalaNo ratings yet
- Responsibility Assignment MatrixDocument2 pagesResponsibility Assignment MatrixXiaomi MIX 3No ratings yet
- Transistor - Transistor Logic (TTL) : I LowDocument17 pagesTransistor - Transistor Logic (TTL) : I LowwisamNo ratings yet
- Industry X.0: Realizing Digital Value in Industrial SectorsDocument15 pagesIndustry X.0: Realizing Digital Value in Industrial SectorsJamey DAVIDSONNo ratings yet
- Learning Guide-34: Participate in Rehabilitationand Restoration of Degraded AreasDocument50 pagesLearning Guide-34: Participate in Rehabilitationand Restoration of Degraded AreasRafez JoneNo ratings yet
- Gec-Tcw Prelims GlobalizationDocument4 pagesGec-Tcw Prelims GlobalizationClarynce MojadoNo ratings yet
- High-Precision Chilled Mirror HygrometerDocument4 pagesHigh-Precision Chilled Mirror HygrometerAldrin HernandezNo ratings yet
- Dine Catalogue Eng 20 21Document318 pagesDine Catalogue Eng 20 21l4k9xxxNo ratings yet
- ECE-Class TT 21-22 EVEN-28.01.22Document13 pagesECE-Class TT 21-22 EVEN-28.01.22Sivakumar PothirajNo ratings yet
- LATsol SMAN 57Document10 pagesLATsol SMAN 57NAYLA NURRIZKYNo ratings yet
- T-506 Cable Fault Pinpointer: FeaturesDocument2 pagesT-506 Cable Fault Pinpointer: FeaturesmohamedmosallamNo ratings yet
- Attachment - Statement HP 2023 January Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and BlackDocument2 pagesAttachment - Statement HP 2023 January Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and BlackWayan PartaNo ratings yet
- Alcon 2020 Corporate Responsibility ReportDocument69 pagesAlcon 2020 Corporate Responsibility ReportRogérioNo ratings yet
- F.2 I.S. Vocabulary List (Unit 7-11)Document14 pagesF.2 I.S. Vocabulary List (Unit 7-11)2E (9) HON MARITA JANENo ratings yet
- Assignment On: Course Title: Course Code: Section Submitted byDocument11 pagesAssignment On: Course Title: Course Code: Section Submitted byAl MozahidNo ratings yet
- Manual PelucheraDocument7 pagesManual Pelucheralvplus0% (1)
- Power Link Module For LD 800PDocument4 pagesPower Link Module For LD 800PSarah FrazierNo ratings yet