Professional Documents
Culture Documents
All Climatology Seminar - 7
Uploaded by
Rohit ShresthaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
All Climatology Seminar - 7
Uploaded by
Rohit ShresthaCopyright:
Available Formats
4.
Literature review
4.1. Study of climatic factors.
There are many climatic factors and should be study for passive building design.
Climatic factors can be classified in two groups’ viz. primary factors and secondary factors.
4.1.1. Primary factors
There are six primary factors.
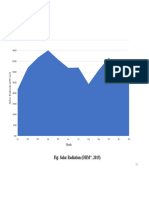
1. Solar radiation (Light and heat)
The spectrum of solar radiation extends from ultra violet through visible light, to infrared
radiation. The latter is the main medium of energy, in the form of heat. The solar energy from
the sun is always constant. How much heat is received at a given point on earth depends on the
angle of incidence atmospheric conditions the length of the day
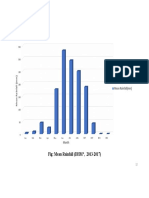
2. Precipitation (rain and snowfall)
A major factor in climatic characteristics is water. It occurs as rain, hail, snow, clouds and
vapour. Not only the quantity, but also the types and seasonal distribution of precipitation are
manifold. For example, in monsoon areas rainfall is concentrated over a certain period of the
year and can be extremely intense and long-lasting. In warm-humid regions it can occur over
the whole year with short downpours almost every day.
3. Wind
The reasons for the development of winds are manifold and vastly complex. The main reason,
however, is the uneven distribution of solar radiation over the globe. It results in differing
surface heating and temperatures. This causes differences in air pressure and, as a consequence,
the development of winds.
4. Humidity
Vapour is water in the form of gas, absorbed by air. Depending on the temperature, the
absorption capacity of the air varies. Relative humidity is defined as humidity at saturation
point (g/m³). 100 / effective humidity (g/m³) = ... %
Air temperature fluctuates considerably during the day and night, and with it the saturation
point. Because the absolute humidity remains constant, the relative humidity changes. If,
however, the absolute humidity exceeds the saturation point, the surplus water condenses and
occurs in the form of fog, clouds, dew or precipitation. The same can be observed when air
rises and thus cools down. Strong thermic upwind result in cumulus clouds; winds crossing
mountains create clouds and precipitation.
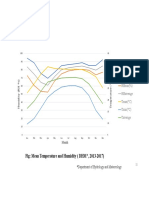
5. Temperature
Temperature is one of the essential and changeable environmental factors. It penetrates
into every region of the biosphere and profoundly influences all forms of life by increasing or
decreasing some of the vital activities of the organism. It is frequently a limiting factor for the
growth or distribution of animals and plants. Normal life activities go on smoothly at a specific
temperature or at a specific range of temperatures. This is called the optimum temperature or
the optimum range of temperature and it ranges from 5o C - 35o C.
You might also like
- Year 11 Geography Preliminary NotesDocument23 pagesYear 11 Geography Preliminary NotesBlakeTamb100% (2)
- BFP-Oplan PaghalasaDocument7 pagesBFP-Oplan PaghalasaMaricar Mangaoang100% (1)
- Introduction To ClimatologyDocument36 pagesIntroduction To ClimatologyMehak SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Weather and Climate - Elements of ClimateDocument28 pagesWeather and Climate - Elements of ClimateSonal Singh100% (1)
- India Political MapDocument1 pageIndia Political MapMediaWatch News100% (2)
- Climatic Concepts, Elements and FactorDocument40 pagesClimatic Concepts, Elements and FactorCrisostomo Andiong Baltazar67% (3)
- Pice HymnDocument2 pagesPice HymnGabb Riel PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Unit I: Climate and Human ComfortDocument66 pagesUnit I: Climate and Human ComfortAtshayaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Climate and Built EnvironmentDocument23 pagesUnit 1 Climate and Built EnvironmentSrilakshmi PriyaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - Science (CLIMATE)Document62 pagesGrade 9 - Science (CLIMATE)Mae Calara100% (1)
- Weather Elements (Clouds, Precipitation, Temperature and More): 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Earth Sciences Books EditionFrom EverandWeather Elements (Clouds, Precipitation, Temperature and More): 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Earth Sciences Books EditionNo ratings yet
- Weather vs Climate in 40 CharactersDocument26 pagesWeather vs Climate in 40 CharactersA.JONAH ELISA SHINYNo ratings yet
- Weather and Climate-Climatic Elements and ControlsDocument31 pagesWeather and Climate-Climatic Elements and ControlsAllen Salvador SaulongNo ratings yet
- Climate and WeatherDocument10 pagesClimate and WeatherLKP GhNo ratings yet
- Group3 WriteUpDocument14 pagesGroup3 WriteUpWhinona FernandezNo ratings yet
- Weather & ClimateDocument22 pagesWeather & Climatemichelle fetalveroNo ratings yet
- ClimateDocument31 pagesClimatePRINCEkyuuNo ratings yet
- Concept of ClimatologyDocument17 pagesConcept of ClimatologyMoin IslamNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 MeteorologyDocument12 pagesLec 2 MeteorologyAsadullah Khan GhalibNo ratings yet
- Architectural Principles & Elements of Architectural DesignDocument13 pagesArchitectural Principles & Elements of Architectural Designkanad kumbharNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 Weather and ClimateDocument7 pagesActivity 3 Weather and ClimateJR ParkNo ratings yet
- Climate: Climatology Is The Study of The Long-TermDocument16 pagesClimate: Climatology Is The Study of The Long-Termenshas4No ratings yet
- Climate Factors of Ethiopia and the HornDocument8 pagesClimate Factors of Ethiopia and the HornBedilu MesfinNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Introduction To Built EnvironmentDocument14 pagesUnit 1: Introduction To Built EnvironmentHasini KadaruNo ratings yet
- Menschen For Menschen FoundationDocument82 pagesMenschen For Menschen FoundationjemsNo ratings yet
- Module 3 (2 of 5)Document3 pagesModule 3 (2 of 5)प्रियांशु मिश्राNo ratings yet
- Environment ManagementDocument11 pagesEnvironment ManagementbillatonyNo ratings yet
- Rainfall and Relative Humidity Occurrence Patterns in Uyo Metropolis, Akwa Ibom State, South-South NigeriaDocument5 pagesRainfall and Relative Humidity Occurrence Patterns in Uyo Metropolis, Akwa Ibom State, South-South NigeriaIOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalNo ratings yet
- Weather and Climate PDFDocument9 pagesWeather and Climate PDFKashvi GoelNo ratings yet
- 800, Climate, As 21Document4 pages800, Climate, As 21asad aliNo ratings yet
- 13 Climate Change ReportDocument17 pages13 Climate Change ReportNorwellah MacmodNo ratings yet
- Science9 ClimateDocument95 pagesScience9 ClimateicebeargoodbearandgrizzyesNo ratings yet
- Agricultural MeteorologyDocument25 pagesAgricultural MeteorologyAman IndwarNo ratings yet
- Weather and Climate - General Science and Ability NotesDocument14 pagesWeather and Climate - General Science and Ability NotesAasma IsmailNo ratings yet
- Cec 102 Lectures NoteDocument38 pagesCec 102 Lectures NoteMohammed AbdulazeezNo ratings yet
- ClimateDocument11 pagesClimateLoeren CaronanNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Weather VariablesDocument3 pagesAtmospheric Weather VariablesSachin Srivastava100% (1)
- Elements of Climate and WeatherDocument20 pagesElements of Climate and WeatherFarheen BanoNo ratings yet
- Green BuildingsDocument27 pagesGreen Buildingsravi1214No ratings yet
- Group 6 ClimateDocument21 pagesGroup 6 ClimateYunaika WardaniNo ratings yet
- Id ClimatologyDocument71 pagesId ClimatologyPrakarti LullaNo ratings yet
- Name: Rachel DuhaylungsodDocument5 pagesName: Rachel DuhaylungsodRachel DuhaylungsodNo ratings yet
- Climate ScienceDocument4 pagesClimate ScienceRamesh ChandraNo ratings yet
- 4 Types of Climate in The PhilippinesDocument3 pages4 Types of Climate in The PhilippinesDA CVRCNo ratings yet
- 1.1.introduction To MeteorologyDocument52 pages1.1.introduction To Meteorologycrissa penaflorNo ratings yet
- Climatology Part 1Document18 pagesClimatology Part 1amanamu436No ratings yet
- Science TestDocument2 pagesScience TestAlberto Suarez DominguezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Earth in Focus NewDocument31 pagesChapter 1 The Earth in Focus NewMarinette MedranoNo ratings yet
- Climate Change (Reviewer)Document12 pagesClimate Change (Reviewer)Keziah PepitoNo ratings yet
- Hydro Meteorological Hazards ObjectivesDocument4 pagesHydro Meteorological Hazards ObjectivesMary Love JuanicoNo ratings yet
- Climate & WeatherDocument53 pagesClimate & WeatherAnn NecdoteNo ratings yet
- The Atmosphere and Atmospheric ChemistryDocument45 pagesThe Atmosphere and Atmospheric ChemistryjaneNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Factors Affecting The Climate of An Area PDF 2023Document7 pagesLesson 6 Factors Affecting The Climate of An Area PDF 2023Fritzgerald CarlinNo ratings yet
- Element of ClimateDocument5 pagesElement of ClimatePEkar Kus-kusNo ratings yet
- What Is Climate? What Is Climate Change?: What's The Difference Between Weather and Climate?Document4 pagesWhat Is Climate? What Is Climate Change?: What's The Difference Between Weather and Climate?Mohammad MohsinNo ratings yet
- Climatology and World WeatherDocument30 pagesClimatology and World Weathermahadi972002No ratings yet
- Global Warming PDFDocument29 pagesGlobal Warming PDFUday GowdaNo ratings yet
- For Module Chapter 3 PDF 1Document15 pagesFor Module Chapter 3 PDF 1secretzNo ratings yet
- For Module Chapter 5 Final PDFDocument25 pagesFor Module Chapter 5 Final PDFJanjesrey GallanoNo ratings yet
- G8 Q2 Melc14Document12 pagesG8 Q2 Melc14Ashly Nicole MoreteNo ratings yet
- Weather Vs ClimateDocument13 pagesWeather Vs ClimateKimpeeNo ratings yet
- The Climate of Ethiopia and the HornDocument30 pagesThe Climate of Ethiopia and the HornTofik Mohammed100% (1)
- Weather and ClimateDocument1 pageWeather and ClimateInmNmNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 45Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 45Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 55Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 55Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 51Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 51Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 67Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 67Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 43Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 43Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 42Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 42Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 52Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 52Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 47Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 47Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 56Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 56Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Bioclimatic Charts Olgyay GivoniDocument1 pageLiterature Review Bioclimatic Charts Olgyay GivoniRohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 54Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 54Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 49Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 49Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 36Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 36Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 50Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 50Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 46Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 46Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 53Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 53Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
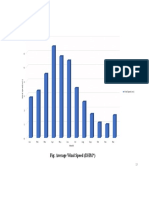
- Fig: Bioclimatic Chart of BiratnagarDocument1 pageFig: Bioclimatic Chart of BiratnagarRohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 37Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 37Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 38Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 38Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 29Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 29Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
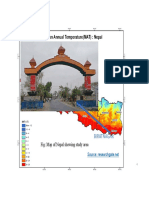
- Biratnagar: Fig: Map of Nepal Showing Study AreaDocument1 pageBiratnagar: Fig: Map of Nepal Showing Study AreaRohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 30Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 30Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 40Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 40Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 25Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 25Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 34Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 34Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 33Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 33Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 26Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 26Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 31Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 31Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 27Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 27Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 32Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 32Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Growing Welwitschia mirabilis from SeedDocument1 pageGrowing Welwitschia mirabilis from SeedS_GyaltsenNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Natural DisasterDocument15 pagesPresentation On Natural Disasterrohillavikas100% (1)
- Module 3 Volcanoes and Volcanic Hazards - MMVillegas 2021Document98 pagesModule 3 Volcanoes and Volcanic Hazards - MMVillegas 2021JHON PATRICK MALINAWANNo ratings yet
- Assessment Report of The Damages Caused by Tropical Storm WashiDocument38 pagesAssessment Report of The Damages Caused by Tropical Storm WashiJohn RamirezNo ratings yet
- WWW Timeanddate Com Weather Oman Muscat ExtDocument4 pagesWWW Timeanddate Com Weather Oman Muscat ExtAsif RiazNo ratings yet
- DRRR Guided PracticeDocument3 pagesDRRR Guided PracticeNur-Aiza AlamhaliNo ratings yet
- Two Seed StoryDocument16 pagesTwo Seed StoryGauri AroraNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 7 (Module 4th Quarter) 2021-2022)Document26 pagesSCIENCE 7 (Module 4th Quarter) 2021-2022)armand bayoran100% (1)
- What Is The Difference Between Currents, Waves & Tides - EHowDocument1 pageWhat Is The Difference Between Currents, Waves & Tides - EHowicemage1991No ratings yet
- 10 English First Flight A Letter To GodDocument5 pages10 English First Flight A Letter To GodRaghavendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Teachers' Handbook - Total Geography - 10Document52 pagesTeachers' Handbook - Total Geography - 10naitiksrivastava60No ratings yet
- Els Week 1Document13 pagesEls Week 1Paolin Pearl Ortiola RapisuraNo ratings yet
- B777 Circling ApproachDocument1 pageB777 Circling ApproachMark Yousry TNo ratings yet
- Runoff CalculationsDocument16 pagesRunoff CalculationsDave Khyl Josol BosqueNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension PracticeDocument6 pagesReading Comprehension PracticeAngelica 01No ratings yet
- AMF+ATS Control PanelDocument4 pagesAMF+ATS Control PanelPablo Gaspar D'Agostini Amengual0% (1)
- Lahan PadiDocument23 pagesLahan PadiSimon32 TooNo ratings yet
- Lab #4Document3 pagesLab #4Michael Namorato IINo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School, Greater Noida Revision Worksheet (Mid-Term) SESSION: 2022-23 Class: Vii Subject: GeographyDocument6 pagesDelhi Public School, Greater Noida Revision Worksheet (Mid-Term) SESSION: 2022-23 Class: Vii Subject: GeographyMohammad AmirNo ratings yet
- Atmos Modbus Protocol 20131212Document8 pagesAtmos Modbus Protocol 20131212Eric Hall100% (1)
- APCE-Oce551 Unit 1Document36 pagesAPCE-Oce551 Unit 1Bhuvanapriyan S100% (1)
- Platypus, Komodo Dragon, and Tornadoes Described in Three ReportsDocument3 pagesPlatypus, Komodo Dragon, and Tornadoes Described in Three ReportsRagil Ardi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Aviation Meteorology IntroductionDocument15 pagesAviation Meteorology IntroductionViplav Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Objectives:: 20/05/2022 Delphine Yvart - Eduardo Pereira - Helena Ferreira - Maria Pinto - Sara Alves - Tomás Miranda 1Document6 pagesObjectives:: 20/05/2022 Delphine Yvart - Eduardo Pereira - Helena Ferreira - Maria Pinto - Sara Alves - Tomás Miranda 1Helena Nadine Mendes FerreiraNo ratings yet
- PipelineprotectionDocument4 pagesPipelineprotectionMino FarmaniNo ratings yet
- Catalogue SUN-NOVA 2023Document13 pagesCatalogue SUN-NOVA 2023euromas.racunovodstvoNo ratings yet