Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elements and Principles Vocab
Uploaded by
Linda DuncanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Elements and Principles Vocab
Uploaded by
Linda DuncanCopyright:
Available Formats
Art Vocabulary
ELEMENTS O F A RT/DESIGN T he v isual “ tools” a
rtists u
se t o c
reate a
rt. T
he e
lements
(categories) i nclude c
olor, v
alue, l ine, f orm, t exture a
nd s pace.
Color (also called “Hue”) in or related to the color spectrum (red, redorange, orange,
yelloworange, yellow, etc.)
Value The lightness or darkness of a surface. Value can be expressed in tints (made by adding
white), tones (made by adding grey) and shades (made by adding black or a
complimentary color).
Line A mark with length and direction, created by a point which moves across the surface; line
can be 2dimensional (pencil on paper) or 3dimensional (wire).
Form Any 3dimensional (3D) object. A form can be measured from top to bottom (height),
side to side (width), and front to back (depth). Form is also a general term that means
the structure or design of the work.
Shape A flat figure created when actual or implied lines meet to surround a space. A change in
color or shading can define a shape. Shapes can be divided into geometric (square, circle,
triangle) and organic (irregular in outline).
Texture The way a surface feels (actual or tactile texture) or appears to feel (implied or visual
texture). Texture can be sensed by touch and sight. Textures are described by words
such as rough, silky, pebbly, etc.
Space The empty or open area between, around, above, below, or within objects. Positive space
is filled by a shape or form. Negative space is empty area surrounding a shape or form.
Space can also be described as creating depth with a foreground, mid ground and
background.
PRINCIPLES O F A
RT/DESIGN G uidelines t hat h
elp a
rtists c
reate d
esigns a
nd c
ontrol h
ow
viewers a re l ikely t o r eact t o i mages. T
hese p rinciples i nclude b alance, c
ontrast, p roportion,
pattern, r hythm, e mphasis, u nity, a
nd v
ariety.
Pattern A choice of lines, colors or shapes repeated over and over in a planned way. Pattern is
also a model or guide for making something.
Unity A feeling that all parts of design are working together as a team.
Balance The arrangement of parts of an artwork seem stable.
Contrast A large difference between two things (rough/smooth, yellow/purple, light/shadow).
Contrast adds excitement, drama and interest to artwork.
Emphasis Area in a work of art that catches and holds the viewer's attention. This area usually has
contrasting sizes, shapes, colors or other distinctive features.
Rhythm A type of visual or actual movement in an artwork. It is created by repeating visual
elements. Rhythms are oven described as regular, alternating, flowing or progressive.
Movement A way of combining visual elements to produce a sense of action. This combination of
elements helps the viewer’s eye to sweep over the work in a definite manner.
You might also like
- Call of Cthulhu - Red Eye of AzathothDocument108 pagesCall of Cthulhu - Red Eye of AzathothAlexander Collings100% (7)
- FLOWER ARRANGEMENT - Perez & PernitoDocument53 pagesFLOWER ARRANGEMENT - Perez & PernitoAlessandra Marigold Aguilar Perez100% (1)
- Solutions of Exercises of Introduction To Differential Geometry of Space Curves and Surfaces (PDFDrive)Document343 pagesSolutions of Exercises of Introduction To Differential Geometry of Space Curves and Surfaces (PDFDrive)shahzeb khan100% (1)
- Purify AuraDocument26 pagesPurify AuraThe Akashic Records home100% (3)
- Collection of Windows 10 Hidden Secret Registry TweaksDocument9 pagesCollection of Windows 10 Hidden Secret Registry TweaksLiyoNo ratings yet
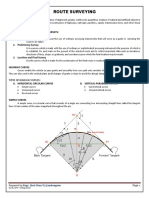
- ABE On Line SURVEYING Class PDFDocument67 pagesABE On Line SURVEYING Class PDFRoan Joy CapalunganNo ratings yet
- CM Level 4Document12 pagesCM Level 4Dawn CalvoNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit Process and ActivitiesDocument20 pagesInternal Audit Process and ActivitiesFreddy ReyesNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Simple CurvesDocument6 pagesTopic 1 - Simple CurvesNicholas Bonn SingNo ratings yet
- PARTLIST-Benelli-Leoncino-500-Leoncino 500-Key69-D2021-12-06-02-06-23pmDocument74 pagesPARTLIST-Benelli-Leoncino-500-Leoncino 500-Key69-D2021-12-06-02-06-23pmCalidad AutomotrizNo ratings yet
- Aerohive Certified Wireless Administrator (Acwa) : Aerohive's Instructor-Led TrainingDocument552 pagesAerohive Certified Wireless Administrator (Acwa) : Aerohive's Instructor-Led TraininggicochavezNo ratings yet
- Two - Point Perspective WorksheetsDocument8 pagesTwo - Point Perspective WorksheetsLinda DuncanNo ratings yet
- Slidedocus Diagnostic Natural Science 4 Primary Byme PlantsDocument2 pagesSlidedocus Diagnostic Natural Science 4 Primary Byme PlantsbegoNo ratings yet
- Taha Sochi - Solutions of Exercises of Introduction To Differential Geometry of Space Curves and Surfaces (2019, CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform)Document271 pagesTaha Sochi - Solutions of Exercises of Introduction To Differential Geometry of Space Curves and Surfaces (2019, CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform)reviset100% (2)
- DLP Integrating ElementsDocument7 pagesDLP Integrating ElementsMerlanie MaganaNo ratings yet
- LPT As Per Asme & IsoDocument2 pagesLPT As Per Asme & IsosbmmlaNo ratings yet
- Creating Instructional Materials: Learning TaskDocument13 pagesCreating Instructional Materials: Learning TaskMike jeron martinez50% (2)
- M01 Mathematics (B1+B2) Rev.00 Pages 2Document10 pagesM01 Mathematics (B1+B2) Rev.00 Pages 2Muhammed MudassirNo ratings yet
- Tong, Xinyue (Dennis), 2011 Edited by Jason Utas and Max Dieckmann, 2013Document5 pagesTong, Xinyue (Dennis), 2011 Edited by Jason Utas and Max Dieckmann, 2013luisgeologoNo ratings yet
- Activity Using Paint: LessonDocument15 pagesActivity Using Paint: LessonJOVITA SARAOSNo ratings yet
- T-Coloringon Certain GraphsDocument3 pagesT-Coloringon Certain GraphsiirNo ratings yet
- M01-Mathematics (B1+B2) Rev.00-Pages-6Document10 pagesM01-Mathematics (B1+B2) Rev.00-Pages-6Muhammed MudassirNo ratings yet
- Map PresentationDocument11 pagesMap Presentationapi-532850293No ratings yet
- M01 Mathematics (B1+B2) Rev.00 Pages 8Document10 pagesM01 Mathematics (B1+B2) Rev.00 Pages 8Muhammed MudassirNo ratings yet
- M01 Mathematics (B1+B2) Rev.00 Pages 14Document9 pagesM01 Mathematics (B1+B2) Rev.00 Pages 14Muhammed MudassirNo ratings yet
- Lec14-Cross Product, Torque, and Angular MomentumDocument13 pagesLec14-Cross Product, Torque, and Angular MomentumpvriiscNo ratings yet
- Research Mid 2Document44 pagesResearch Mid 2Clarisse Angela PostreNo ratings yet
- Physics Lesson Objectives For NSCDocument6 pagesPhysics Lesson Objectives For NSCsheroneilNo ratings yet
- Musical Theatre - Module I - Lesson 01Document12 pagesMusical Theatre - Module I - Lesson 01ayeshastudies888No ratings yet
- Petit, 1987Document12 pagesPetit, 1987Jonathan Esteban Fuentealba Diaz0% (1)
- TEXT (SA2) - Spillway-Appendix 2Document35 pagesTEXT (SA2) - Spillway-Appendix 2tiarNo ratings yet
- M01 Mathematics (B1+B2) Rev.00 Pages 13Document10 pagesM01 Mathematics (B1+B2) Rev.00 Pages 13Muhammed MudassirNo ratings yet
- Track IrregularitiDocument123 pagesTrack Irregularitipalacsan dezideriuNo ratings yet
- Article 31Document39 pagesArticle 31crkdexxNo ratings yet
- M01 Mathematics (B1+B2) Rev.00 Pages 4Document10 pagesM01 Mathematics (B1+B2) Rev.00 Pages 4Muhammed MudassirNo ratings yet
- Static Analysis of Laminated Composite Circular and Annular Plates IJERTV2IS50756Document8 pagesStatic Analysis of Laminated Composite Circular and Annular Plates IJERTV2IS50756yasameenNo ratings yet
- 03 Some Aspects of Three-Dimensional Tonnetze (Gollin 1998)Document13 pages03 Some Aspects of Three-Dimensional Tonnetze (Gollin 1998)RobporeliNo ratings yet
- Data Mining: Exploring Data Data Mining: Exploring Data: Lecture Notes For Chapter 3 Lecture Notes For Chapter 3Document34 pagesData Mining: Exploring Data Data Mining: Exploring Data: Lecture Notes For Chapter 3 Lecture Notes For Chapter 3ibrahim mereeNo ratings yet
- GreekandGothicProgressandDecayintheThreeArtsofArchitectureSculptureandPainting 10082315Document399 pagesGreekandGothicProgressandDecayintheThreeArtsofArchitectureSculptureandPainting 10082315Yiğit KılıçNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Field Theory I (EFT I) /: Dr.-Ing. René MarkleinDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Field Theory I (EFT I) /: Dr.-Ing. René Markleinbhuvana_eeeNo ratings yet
- Extreme PR Oduct Manageme NT: To Buy in An Agile Development EnvironmentDocument9 pagesExtreme PR Oduct Manageme NT: To Buy in An Agile Development EnvironmentNathan BrandNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Curriculum ChecklistDocument2 pagesMath 9 Curriculum Checklistapi-506766912No ratings yet
- Serene Closed Terrarium AdDocument1 pageSerene Closed Terrarium AdPraseetha PrashanthNo ratings yet
- Isagani Cruz Critique On 21st C PDFDocument3 pagesIsagani Cruz Critique On 21st C PDFKian Real CornelioNo ratings yet
- 4elementsofdesign 140422015503 Phpapp01Document46 pages4elementsofdesign 140422015503 Phpapp01Sunil TalekarNo ratings yet
- POLICE PHOTOGRAPHY ReviewerDocument22 pagesPOLICE PHOTOGRAPHY ReviewerRey Mark GedaroNo ratings yet
- Slavicek E InnenDocument79 pagesSlavicek E InnenAlexandru Marius MarinNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 3 Third Periodic TestDocument6 pagesMapeh 3 Third Periodic TestMarianNo ratings yet
- Ce6512 Survey CamyDocument10 pagesCe6512 Survey CamyKalai VananNo ratings yet
- Construction of Radio Receiving Apparatus - Everyday-Mechanics-1916-09Document9 pagesConstruction of Radio Receiving Apparatus - Everyday-Mechanics-1916-09hds0405No ratings yet
- Driver Education Final Exam Review PDFDocument5 pagesDriver Education Final Exam Review PDFLOLZITZMENo ratings yet
- 7 Archeasi December 2018Document4 pages7 Archeasi December 2018silvinus clissonNo ratings yet
- Exercise1 - Situating and MappingDocument38 pagesExercise1 - Situating and Mappinganupama chinni krishnanNo ratings yet
- Docu Menti NG MLA Style: Ngua Ge As Socia TionDocument14 pagesDocu Menti NG MLA Style: Ngua Ge As Socia Tionligie23No ratings yet
- M01 Mathematics (B1+B2) Rev.00 Pages 10Document10 pagesM01 Mathematics (B1+B2) Rev.00 Pages 10Muhammed MudassirNo ratings yet
- Ejemplo Diapo 4Document29 pagesEjemplo Diapo 4anghelo_murillooNo ratings yet
- Area of A Circle and Area of A Right Triangle Inside The Circle (Repaired)Document12 pagesArea of A Circle and Area of A Right Triangle Inside The Circle (Repaired)Joy Alpha NitramNo ratings yet
- I Edc-Cet: FEB 29-MAR 1 2020Document2 pagesI Edc-Cet: FEB 29-MAR 1 2020ananthuNo ratings yet
- Approximate Method For Plug Nozzle DesignDocument2 pagesApproximate Method For Plug Nozzle DesignRou MàissàNo ratings yet
- Pe Lab Manual Class XiiDocument174 pagesPe Lab Manual Class XiiSachith ShankarNo ratings yet
- Annexure I Format To Be Submitted by Listed Entity On Quarterly Basis - Stel Holdings Limited - 30-Jun-2021 I. Composition of Board of DirectorDocument5 pagesAnnexure I Format To Be Submitted by Listed Entity On Quarterly Basis - Stel Holdings Limited - 30-Jun-2021 I. Composition of Board of DirectorRoshan DhongadeNo ratings yet
- Shade Matching: Division of Operative Dentistry Department of Restorative SciencesDocument34 pagesShade Matching: Division of Operative Dentistry Department of Restorative SciencesDaniel WangNo ratings yet
- KWL HernandezDocument1 pageKWL HernandezJohn Anderson HernandezNo ratings yet
- KWL HernandezDocument1 pageKWL HernandezJohn Anderson HernandezNo ratings yet
- Further Concepts For Analysis: I. Additional SystemsDocument5 pagesFurther Concepts For Analysis: I. Additional Systemspaco desantisNo ratings yet
- Contingency Tables Crosstabs Chi Square TestDocument48 pagesContingency Tables Crosstabs Chi Square TestAbii ShivuNo ratings yet
- I P: D C M: Totals NameDocument2 pagesI P: D C M: Totals NameLinda DuncanNo ratings yet
- Design Matrix AssignmentDocument12 pagesDesign Matrix AssignmentLinda DuncanNo ratings yet
- Educator Guide Story Theme: The Puppet Show Subject: Sandow Birk Discipline: Visual Art (Painting and Film)Document9 pagesEducator Guide Story Theme: The Puppet Show Subject: Sandow Birk Discipline: Visual Art (Painting and Film)Linda DuncanNo ratings yet
- Design Principles: CRAP: Linda Duncan, Media ArtsDocument20 pagesDesign Principles: CRAP: Linda Duncan, Media ArtsLinda DuncanNo ratings yet
- How To Photograph Your Work For Art ClassesDocument7 pagesHow To Photograph Your Work For Art ClassesLinda DuncanNo ratings yet
- OP Art Project Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesOP Art Project Lesson PlanLinda DuncanNo ratings yet
- Op-Art Project RubricDocument1 pageOp-Art Project RubricLinda DuncanNo ratings yet
- The Art of Illusion Optical Means:: AnamorphosisDocument2 pagesThe Art of Illusion Optical Means:: AnamorphosisLinda DuncanNo ratings yet
- Optical Art: AnamorphosisDocument6 pagesOptical Art: AnamorphosisLinda DuncanNo ratings yet
- Colored Pencil RemediationDocument1 pageColored Pencil RemediationLinda DuncanNo ratings yet
- And Personal: Up CloseDocument5 pagesAnd Personal: Up CloseLinda DuncanNo ratings yet
- Popcorn ImageryDocument2 pagesPopcorn ImageryLinda DuncanNo ratings yet
- Vincent Van Gogh: "I Am Not An Adventurer by Choice But by Fate."Document11 pagesVincent Van Gogh: "I Am Not An Adventurer by Choice But by Fate."Linda DuncanNo ratings yet
- Art I SyllabusDocument2 pagesArt I SyllabusLinda DuncanNo ratings yet
- SKETCHBOOK ASSIGNMENT: Drawing Without Contour LinesDocument2 pagesSKETCHBOOK ASSIGNMENT: Drawing Without Contour LinesLinda DuncanNo ratings yet
- Guidance Pass Guidance Pass: (Please Print) (Please Print)Document1 pageGuidance Pass Guidance Pass: (Please Print) (Please Print)Linda DuncanNo ratings yet
- Chap 7 D SCM PIMS CoyleDocument15 pagesChap 7 D SCM PIMS CoyleZeeshan QaraNo ratings yet
- TNP Portal Using Web Development and Machine LearningDocument9 pagesTNP Portal Using Web Development and Machine LearningIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Liam Devaney: ProfileDocument2 pagesLiam Devaney: Profileapi-25949163No ratings yet
- Asrat Simru AppDocument36 pagesAsrat Simru Apptadiso birkuNo ratings yet
- Sequencing Offshore Oil and Gas Fields Under UncertaintyDocument11 pagesSequencing Offshore Oil and Gas Fields Under UncertaintyAlbeiro Sierra PachecoNo ratings yet
- Arabic Holiday HomeworkDocument4 pagesArabic Holiday Homeworkapi-320846565No ratings yet
- Lecture 7 DP 0-1 KnapsackDocument53 pagesLecture 7 DP 0-1 KnapsackMostafizur RahamanNo ratings yet
- Syringe Robot ArmDocument12 pagesSyringe Robot ArmAnjali YadavNo ratings yet
- August - Funding CompendiumDocument10 pagesAugust - Funding CompendiumqkjedNo ratings yet
- AI IN AGRICULTURE - EditedDocument6 pagesAI IN AGRICULTURE - EditedMonisha ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- LAPORAN BARANG IMPORT (Setrika, Rice Com, Kompor, Tin Plate, Cat Powder, Plat Besi)Document15 pagesLAPORAN BARANG IMPORT (Setrika, Rice Com, Kompor, Tin Plate, Cat Powder, Plat Besi)Ady YudaNo ratings yet
- Ref - No. 2302875-11218095-5: Sakib AkhtarDocument5 pagesRef - No. 2302875-11218095-5: Sakib AkhtarMONISH NAYARNo ratings yet
- Dow Corning 795 PDFDocument3 pagesDow Corning 795 PDFRyan De Vera PagalNo ratings yet
- Gerph - Module 2 Assignment 1 - ApostolDocument1 pageGerph - Module 2 Assignment 1 - ApostolverlyneNo ratings yet
- Citrix Virtual Apps & Desktops Vs VMware Horizon - BattlecardDocument4 pagesCitrix Virtual Apps & Desktops Vs VMware Horizon - BattlecardVicente MaytaNo ratings yet
- Astra J Sports Tourer - Replacing The Rear LightsDocument2 pagesAstra J Sports Tourer - Replacing The Rear LightsciphardNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIIDocument4 pagesChapter IIIAdrian RanitNo ratings yet
- 35th Annual Dive Show: - Convention Center, San Diego, CaliforniaDocument2 pages35th Annual Dive Show: - Convention Center, San Diego, CaliforniaHà ViNo ratings yet
- Innovi Best Practices 2022 07 07Document30 pagesInnovi Best Practices 2022 07 07sly_boss49No ratings yet
- Automatizando Consolidated SoDocument23 pagesAutomatizando Consolidated SoCHRISTIAN STEVEN HUANATICO CHOMBONo ratings yet
- 300 Ma, High PSRR, Low Quiescent Current LDO: Features DescriptionDocument24 pages300 Ma, High PSRR, Low Quiescent Current LDO: Features Descriptionjustinvil1103No ratings yet
- KIPWindows Driver GuideDocument36 pagesKIPWindows Driver GuidePBTS CORPNo ratings yet
- METHODOLOG1Document3 pagesMETHODOLOG1Essa M RoshanNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument3 pagesPDF DocumentBrodie TeaklesNo ratings yet