Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tut 2,3 - Inverters
Uploaded by
Mahmoud A. Aboulhasan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views5 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views5 pagesTut 2,3 - Inverters
Uploaded by
Mahmoud A. AboulhasanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
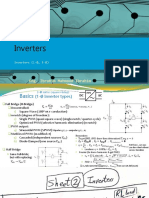
Inverters
Inverters (1-∅, 3-∅)
Eng. Ibrahim Mahmoud Ibrahim
3-∅ same (square=6step)
Basics (1-∅ Inverter types)
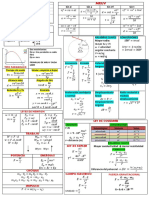
Full Bridge (H-Bridge) 4𝑉𝑑𝑐 4𝑉𝑑𝑐
Uncontrolled: 𝑉𝑛 = 𝑉𝑛 = (cos 𝑛𝛼1 + cos 𝑛𝛼2 +. . )
𝑛𝜋 𝑛𝜋
1) Square Wave (180° OR 𝜋 conduction)
n-notch (degree of freedom) :
2) Single PWM (quasi-square wave) (single-notch / quarter-cycle)
3) Optimized PWM (selective harmonic elimination) (n-notch)
PWM output:
4) Sinusoidal PWM (SPWM): Bipolar (±𝑉𝑑𝑐 ) – unipolar (±𝑉𝑑𝑐 , 0)
Mutli-level PWM: (modified ct)
Remember:
5) Cascaded (independent sources 𝑉𝑑𝑐 ) To get RMS, AVG: draw then determined T, eq, 𝑎 → 𝑏
6) Diode-Clamped (one source 𝑉𝑑𝑐 ) 𝑃𝑅 = 𝑰𝟐𝒓𝒎𝒔 𝑹 , 𝑃𝐸 = 𝑰𝒂𝒗𝒈 𝑬 , 𝑃𝐿(𝑖𝑛𝑑𝑢𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟) = 𝟎
𝑃𝑜
𝜂= , 𝑃𝑖𝑛 = 𝑃𝑜 + 𝑃𝐿𝑜𝑠𝑠 𝑡𝑜𝑡 = 𝑉𝑑𝑐 𝐼𝑠𝑎𝑣𝑔 Not from 𝑖𝑠 curve as
𝑃𝑖𝑛 (𝐷,𝑡𝑟) 𝑟𝑒𝑎𝑙 you draw ideal without
Half Bridge Lossless: 𝜂 = 100% ∴ 𝑃𝑖𝑛 = 𝑃𝑜 care sw transition
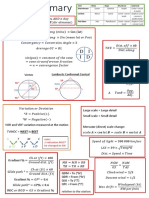
Fourier (to know harmonic & get THD)
Same Full-Bride;
𝑣𝑜 = σ 𝑉𝑛 sin 𝑛𝜃 , 𝑍𝑛 = 𝑅 2 + 𝑛𝜔𝐿 2 , 𝐼𝑛 = 𝑉𝑛 /𝑍𝑛
but with replacing: 2
σ∞ 2
𝑛=2 𝑋𝑛𝑟𝑚𝑠 𝑋𝑟𝑚𝑠 𝑡𝑜𝑡
−𝑋12𝑟𝑚𝑠
𝑉𝑑𝑐 → 𝑉𝑑𝑐 /2 𝑇𝐻𝐷 = =
𝑋1𝑟𝑚𝑠 𝑋1𝑟𝑚𝑠
σ 𝑋𝑛: take some term (approx.) , 𝑋𝑟𝑚𝑠 : from curve & def (exact)
Scanned by CamScanner
Scanned by CamScanner
Scanned by CamScanner
You might also like
- Formulario FisicaDocument1 pageFormulario Fisicanayely merchanNo ratings yet
- Lesson - 7 AC CircuitsDocument15 pagesLesson - 7 AC CircuitsMohamed Munseeth NMNo ratings yet
- All FormulasDocument32 pagesAll Formulasuzairazizsuria1No ratings yet
- AnalysisDocument11 pagesAnalysisNISHANK KANSARANo ratings yet
- Tangents and Curvature of Parametric CurvesDocument7 pagesTangents and Curvature of Parametric CurvesAleksandar MicicNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document8 pagesUnit 1Dr.Sakthivel SNo ratings yet
- Lecture 29-Revision of Unit5 and MCQ PracticeDocument28 pagesLecture 29-Revision of Unit5 and MCQ PracticeAerra ManirajNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 WavesDocument7 pagesLecture 2 WavesMessiah GamingNo ratings yet
- Elec1111 - T08 - S2 2018Document57 pagesElec1111 - T08 - S2 2018Conqueror VictoryNo ratings yet
- Tut 8 DriveDocument10 pagesTut 8 Drivemennaabdelrazik848No ratings yet
- Chapter 7-Ac Steady State AnalyisDocument55 pagesChapter 7-Ac Steady State AnalyisPoni HenryNo ratings yet
- Progress Report - Maria IndiraDocument12 pagesProgress Report - Maria Indirasafira andrianiNo ratings yet
- Formulae, Tables and Guidance Notes For Examination PDFDocument31 pagesFormulae, Tables and Guidance Notes For Examination PDF123No ratings yet
- 09 Handout 1Document6 pages09 Handout 1marjorie ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Antenna-lect5Document14 pagesAntenna-lect5fadwaalhadereeNo ratings yet
- XkjijjnnDocument11 pagesXkjijjnnmohit bhardwajNo ratings yet
- Learn about alternating current and its measurementDocument23 pagesLearn about alternating current and its measurementIndraneil SenguptaNo ratings yet
- EDC Unit-I RectifiersDocument12 pagesEDC Unit-I Rectifiersneha yarrapothuNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument2 pagesFormula SheetdaveasquithNo ratings yet
- Vibration Eng'g - Class NotesDocument14 pagesVibration Eng'g - Class NotesROSE DIANE PILARESNo ratings yet
- 1 L2 Basic Interference (Step by Step) v.2Document7 pages1 L2 Basic Interference (Step by Step) v.2Vincent TionoNo ratings yet
- 4) AC CircuitsDocument40 pages4) AC CircuitsS x DNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS OF HALF-WAVE SYMMETRICAL WAVEFORMSDocument31 pagesANALYSIS OF HALF-WAVE SYMMETRICAL WAVEFORMSLoku VelNo ratings yet
- Analog - Module - 2 - Rectifiers - ECE 1001Document11 pagesAnalog - Module - 2 - Rectifiers - ECE 1001sanjit0907_982377739No ratings yet
- Orbital Mechanics Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesOrbital Mechanics Cheat SheetRodolfo SotoNo ratings yet
- Reynolds Transport TheoremDocument2 pagesReynolds Transport TheoremNati FernandezNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFinal Exam Formula Sheetjanaka100% (1)
- Chapter8s 1-UnlockedDocument19 pagesChapter8s 1-Unlockedjohn wallaceNo ratings yet
- RC Series Circuit AC CircuitsDocument4 pagesRC Series Circuit AC CircuitsTiffany Fate AnoosNo ratings yet
- EEE2044S 2021 Exam Formula SheetDocument2 pagesEEE2044S 2021 Exam Formula SheetChristine PiusNo ratings yet
- SINGLE PHASE HALF WAVE CONTROLLED RECTIFIERDocument7 pagesSINGLE PHASE HALF WAVE CONTROLLED RECTIFIERkhyati patelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document4 pagesChapter 3ourdreamsandfuture2004No ratings yet
- Power Electronics Average and RMS ValuesDocument25 pagesPower Electronics Average and RMS ValuesAhmad Ash SharkawiNo ratings yet
- DC To DC Choppers SummaryDocument21 pagesDC To DC Choppers SummaryjeyyelramosNo ratings yet
- Asset-V1 BuX+EEE321+2021 Summer+Type@Asset+Block@Fault Current Transient On Transmission LineDocument16 pagesAsset-V1 BuX+EEE321+2021 Summer+Type@Asset+Block@Fault Current Transient On Transmission LineAbrar ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-AC STEADY STATE ANALYSIS. Cruicial TopicDocument55 pagesChapter 7-AC STEADY STATE ANALYSIS. Cruicial TopicDouglas OngomNo ratings yet
- The DSB-SCDocument21 pagesThe DSB-SCmhww9jqqpjNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Plane: Short NotesDocument26 pagesMotion in A Plane: Short NotesRiya BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Trigo PupDocument8 pagesTrigo PupShane IsorenaNo ratings yet
- PRE-CALCULUS REVIEWERDocument4 pagesPRE-CALCULUS REVIEWERtravisagpasa123No ratings yet
- AERODYN2 Part 5 Fundamentals of Flight Mechanics For Steady FlightDocument25 pagesAERODYN2 Part 5 Fundamentals of Flight Mechanics For Steady FlightSecretNo ratings yet
- Ch_3-3_Half-wave RectifiersDocument18 pagesCh_3-3_Half-wave RectifiersEmad El shabrwayNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus 15 16 20Document6 pagesIntegral Calculus 15 16 20Sharmaine FajutaganaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 - 9th Edition 4.1. GivenDocument21 pagesCHAPTER 4 - 9th Edition 4.1. Given이재하No ratings yet
- 4-Differential Amplifier Double Ended and Common ModeDocument10 pages4-Differential Amplifier Double Ended and Common ModePrince KratosNo ratings yet
- Advance Mathematical Physics in Cylindrical CoordinatesDocument6 pagesAdvance Mathematical Physics in Cylindrical CoordinatesRaufAhmedNo ratings yet
- Digital - SAT Math Formula SheetDocument2 pagesDigital - SAT Math Formula Sheetnilakrmi420% (1)
- PE Lecture - 5 - NDocument21 pagesPE Lecture - 5 - Nahmed el-sayedNo ratings yet
- Hagen Poisuille EquationDocument4 pagesHagen Poisuille EquationRochakNo ratings yet
- Av M2fa4 AcmachDocument2 pagesAv M2fa4 AcmachAceriel VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Exp6,7,8 2K20CO153Document28 pagesExp6,7,8 2K20CO153divye guptaNo ratings yet
- Single Frequency Transient AnalysisDocument14 pagesSingle Frequency Transient AnalysischristopherNo ratings yet
- Formulario PruebaDocument1 pageFormulario PruebaKarla Berenice Neira ParraNo ratings yet
- GATE AEROSPACE Engineering Aircraft StructuresDocument12 pagesGATE AEROSPACE Engineering Aircraft StructuresVickyNo ratings yet
- Internal Convertion 3Document37 pagesInternal Convertion 3MANISH DASNo ratings yet
- Tut 9 Drive (1)Document23 pagesTut 9 Drive (1)mennaabdelrazik848No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Formula SheetA4Document3 pagesElectromagnetic Formula SheetA4Abdullatif AlbattatNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- C2 - Sec. 4 - B.N. 9 - Mahmoud Ahmed MohamedDocument2 pagesC2 - Sec. 4 - B.N. 9 - Mahmoud Ahmed MohamedMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- C2 - Sec. 4 - B.N. 10 - Mahmoud Khaled MohamedDocument3 pagesC2 - Sec. 4 - B.N. 10 - Mahmoud Khaled MohamedMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- C2 - Sec. 4 - B.N. 11 - Mahmoud Khalil AtiaDocument2 pagesC2 - Sec. 4 - B.N. 11 - Mahmoud Khalil AtiaMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- C2 - Sec. 4 - B.N. 9 - Mahmoud Ahmed MohamedDocument2 pagesC2 - Sec. 4 - B.N. 9 - Mahmoud Ahmed MohamedMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- C2 - Sec. 4 - B.N. 7 - Mahmoud Ahmed AboulhasanDocument2 pagesC2 - Sec. 4 - B.N. 7 - Mahmoud Ahmed AboulhasanMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- G2 - Residential Lighting LaboratoryDocument13 pagesG2 - Residential Lighting LaboratoryMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- C2 - Sec. 4 - B.N. 11 - Mahmoud Khalil AtiaDocument2 pagesC2 - Sec. 4 - B.N. 11 - Mahmoud Khalil AtiaMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- C2 - Sec. 4 - B.N. 8 - Mahmoud Ahmed AbdelghanyDocument1 pageC2 - Sec. 4 - B.N. 8 - Mahmoud Ahmed AbdelghanyMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- Symmetrical Components: ObjectivesDocument3 pagesSymmetrical Components: ObjectivesMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- C2 - Sec. 4 - B.N. 10 - Mahmoud Khaled MohamedDocument3 pagesC2 - Sec. 4 - B.N. 10 - Mahmoud Khaled MohamedMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- Corona DischargeDocument29 pagesCorona DischargeMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- Protection Mid ExamsDocument17 pagesProtection Mid ExamsMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- Digital Control of Servo Motor Simulation & Real-Time ImplementationDocument6 pagesDigital Control of Servo Motor Simulation & Real-Time ImplementationMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- C2 - Sec. 4 - B.N. 8 - Mahmoud Ahmed AbdelghanyDocument1 pageC2 - Sec. 4 - B.N. 8 - Mahmoud Ahmed AbdelghanyMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- C2 - Sec. 4 - B.N. 7 - Mahmoud Ahmed AboulhasanDocument2 pagesC2 - Sec. 4 - B.N. 7 - Mahmoud Ahmed AboulhasanMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- Digital Control of Servo Motor Simulation & Real-Time ImplementationDocument6 pagesDigital Control of Servo Motor Simulation & Real-Time ImplementationMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- UtilizationDocument8 pagesUtilizationMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- Protection 1Document12 pagesProtection 1Mahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- Sec 2Document4 pagesSec 2Mahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- Classical Control TutorialsDocument12 pagesClassical Control TutorialsMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- Inverter SheetDocument1 pageInverter SheetMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- New Doc 2019-03-24 21.19.34Document11 pagesNew Doc 2019-03-24 21.19.34Mahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- Problem 6Document1 pageProblem 6Mahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- Sheet State SpaceDocument7 pagesSheet State SpaceMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- Sheet 3 DR TarekDocument1 pageSheet 3 DR TarekMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- DC DC ConverterDocument2 pagesDC DC ConverterMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- Inverters: Eng. Ibrahim Mahmoud IbrahimDocument9 pagesInverters: Eng. Ibrahim Mahmoud IbrahimMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- Tut 2,3 - InvertersDocument5 pagesTut 2,3 - InvertersMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- 1-Switching Losses SheetDocument1 page1-Switching Losses SheetMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- VrbookbigDocument428 pagesVrbookbigphanthanhhungNo ratings yet
- Brosur Yuema Motor Yu & SaDocument30 pagesBrosur Yuema Motor Yu & SaRizqi SofiajiNo ratings yet
- Esybox - Guía RápidaDocument2 pagesEsybox - Guía RápidaFernando Pérez RuizNo ratings yet
- Practical Econometrics Data Collection Analysis and Application 1st Edition Hilmer Solutions ManualDocument24 pagesPractical Econometrics Data Collection Analysis and Application 1st Edition Hilmer Solutions ManualChadReillynopa100% (39)
- Determinants of Household Carbon Footprints: Alice T. Valerio, Renz S. MascardoDocument26 pagesDeterminants of Household Carbon Footprints: Alice T. Valerio, Renz S. MascardoBillyNo ratings yet
- Integrated Voice Evacuation System VM-3000 Series: Operating InstructionsDocument144 pagesIntegrated Voice Evacuation System VM-3000 Series: Operating InstructionsAbraham GamaNo ratings yet
- Noise Control Sound Absorption GuideDocument32 pagesNoise Control Sound Absorption GuideRukminiPriyankaNo ratings yet
- Jeffrey Epstein39s Little Black Book Unredacted PDFDocument95 pagesJeffrey Epstein39s Little Black Book Unredacted PDFasdasdasd75% (4)
- Gaslands Refuelled QuickRefCardDocument3 pagesGaslands Refuelled QuickRefCardFlávio NetoNo ratings yet
- Instalacion y Operacion Tablero Mando VariadorDocument95 pagesInstalacion y Operacion Tablero Mando VariadorGustavo HuertasNo ratings yet
- Rain Alarm Project by Samar SirohiDocument19 pagesRain Alarm Project by Samar SirohisamNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint Template 18Document20 pagesPowerPoint Template 18Phuong TruongNo ratings yet
- Blockchain:: A Revolutionary Change or Not?Document6 pagesBlockchain:: A Revolutionary Change or Not?sgjatharNo ratings yet
- Iso 13485 Medical Devices 2016 PDFDocument12 pagesIso 13485 Medical Devices 2016 PDFDito PriyambodoNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Flange DesignDocument3 pagesRectangular Flange Designshazan100% (5)
- Dynamic System Analysis Installation and User's Guide: IBM SystemsDocument62 pagesDynamic System Analysis Installation and User's Guide: IBM SystemsKamalkant YadavNo ratings yet
- ConectadosDocument136 pagesConectadosAnonymous 5J2qhNEeNo ratings yet
- Qt Competency Center Agenda OverviewDocument21 pagesQt Competency Center Agenda OverviewDharani Kumar K BNo ratings yet
- PCA preamp data sheetDocument3 pagesPCA preamp data sheetMauricio TerrazasNo ratings yet
- Abb KatalogeditDocument60 pagesAbb KatalogeditSherinSyafarinaSuryanaNo ratings yet
- Safe Operation of Forklifts and Powered Industrial Trucks GuideDocument13 pagesSafe Operation of Forklifts and Powered Industrial Trucks GuidecibewizardNo ratings yet
- Intro to Data Comms & Computer NetworksDocument52 pagesIntro to Data Comms & Computer NetworksFerlyn Maye Angeles BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Functional Test Checklist Air Handling Unit (Ahu)Document5 pagesFunctional Test Checklist Air Handling Unit (Ahu)long minn2No ratings yet
- CSE322 Formal Languages and Automation Theory 17442::arun Malik 3.0 0.0 0.0 3.0 Courses With Numerical and Conceptual FocusDocument11 pagesCSE322 Formal Languages and Automation Theory 17442::arun Malik 3.0 0.0 0.0 3.0 Courses With Numerical and Conceptual FocusSunnyAroraNo ratings yet
- EOI Biometric ApplicationDocument3 pagesEOI Biometric ApplicationFrancis EkemuNo ratings yet
- B. B. ALE Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument36 pagesB. B. ALE Department of Mechanical EngineeringRam Krishna SinghNo ratings yet
- Web App SuccessDocument369 pagesWeb App Successdoghead101No ratings yet
- Analysis of Fatigue Life in Two Weld Class Systems: Master Thesis in Solid MechanicsDocument296 pagesAnalysis of Fatigue Life in Two Weld Class Systems: Master Thesis in Solid Mechanicsgoedel1000No ratings yet
- 002 Prime-G+ Commercial PerformanceDocument18 pages002 Prime-G+ Commercial Performancesameerjp50% (2)
- Accounting For Oracle ReceivablesDocument13 pagesAccounting For Oracle ReceivablesAshokNo ratings yet