Professional Documents
Culture Documents
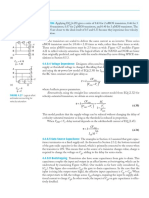
Silicon Lattice and Dopant Atoms: Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si
Uploaded by
Carlos SaavedraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Silicon Lattice and Dopant Atoms: Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si
Uploaded by
Carlos SaavedraCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
3 MOS Transistors 7
Si Si Si Si Si - Si Si Si Si
+
+ -
Si Si Si Si As Si Si B Si
Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si
(a) (b) (c)
FIGURE 1.7 Silicon lattice and dopant atoms
semiconductor because the free carriers are negatively charged electrons. Similarly, a
Group III dopant, such as boron, has three valence electrons, as shown in Figure 1.7(c).
The dopant atom can borrow an electron from a neighboring silicon atom, which in turn
becomes short by one electron. That atom in turn can borrow an electron, and so forth, so
the missing electron, or hole, can propagate about the lattice. The hole acts as a positive
carrier so we call this a p-type semiconductor.
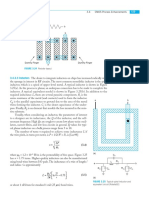
A junction between p-type and n-type silicon is called a diode, as shown in Figure 1.8.
When the voltage on the p-type semiconductor, called the anode, is raised above the n- p-type n-type
type cathode, the diode is forward biased and current flows. When the anode voltage is less
than or equal to the cathode voltage, the diode is reverse biased and very little current flows. Anode Cathode
A Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (MOS) structure is created by superimposing several
layers of conducting and insulating materials to form a sandwich-like structure. These
structures are manufactured using a series of chemical processing steps involving oxidation FIGURE 1.8
of the silicon, selective introduction of dopants, and deposition and etching of metal wires p-n junction diode
structure and symbol
and contacts. Transistors are built on nearly flawless single crystals of silicon, which are
available as thin flat circular wafers of 15–30 cm in diameter. CMOS technology provides
two types of transistors (also called devices): an n-type transistor (nMOS) and a p-type
transistor (pMOS). Transistor operation is controlled by electric fields so the devices are
also called Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors (MOSFETs) or simply
FETs. Cross-sections and symbols of these transistors are shown in Figure 1.9. The n+
and p+ regions indicate heavily doped n- or p-type silicon.
Source Gate Drain Source Gate Drain
Polysilicon
SiO2
n+ n+ p+ p+
p bulk Si n bulk Si
(a) (b)
FIGURE 1.9 nMOS transistor (a) and pMOS transistor (b)
You might also like
- MANUAL CATERPILLAR GAS ENGINE 3516b PDFDocument44 pagesMANUAL CATERPILLAR GAS ENGINE 3516b PDFmath6221079% (14)
- Lab Report VLSIDocument24 pagesLab Report VLSIK Eerti Vyas0% (2)
- 1.1 Mos Transistors: Design and Analysis of D Flip Flop Based Shift RegisterDocument49 pages1.1 Mos Transistors: Design and Analysis of D Flip Flop Based Shift RegistermaniroopNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document40 pagesModule 1Sushanth M100% (1)
- 3.4.1.4 Higher Mobility: High-K Gate Stack TEM (© IEEE 2007.)Document1 page3.4.1.4 Higher Mobility: High-K Gate Stack TEM (© IEEE 2007.)Carlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Module 4 CMOS LogicDocument18 pagesModule 4 CMOS LogicJessie Tess TolentinoNo ratings yet
- FUNDAMENTALS of CMOS VLSI 5th SEM ECE PDFDocument190 pagesFUNDAMENTALS of CMOS VLSI 5th SEM ECE PDFVarunKaradesaiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Basic MOS Technology: Figure 1. Moore's LawDocument18 pagesUnit 1 Basic MOS Technology: Figure 1. Moore's LawSushruth SastryNo ratings yet
- Nehru Arts and Science College (Autonomous) PG and Research Department of Electronics VLSI Design and VHDL Programming Unit-I MOS TransistorDocument12 pagesNehru Arts and Science College (Autonomous) PG and Research Department of Electronics VLSI Design and VHDL Programming Unit-I MOS TransistorkannanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To VLSI: by Bhushan PatilDocument47 pagesIntroduction To VLSI: by Bhushan PatilInderJeet GehlotNo ratings yet
- VLSI UNIT 1 Part - III PDFDocument35 pagesVLSI UNIT 1 Part - III PDFKARTHIKAYEN ANo ratings yet
- Lecture-13: Metal Oxide Semiconductor FET (MOSFET)Document8 pagesLecture-13: Metal Oxide Semiconductor FET (MOSFET)AKSHATHAVENKATESHNo ratings yet
- VLSI Unit 2 Technology - SDocument52 pagesVLSI Unit 2 Technology - SIndrajeet GautamNo ratings yet
- 01 EE6306 - MOS Transistor TheoryDocument74 pages01 EE6306 - MOS Transistor TheoryononahjNo ratings yet
- Mosfet: Surface-Mount D2Pak Volts Amperes Watts MatchstickDocument7 pagesMosfet: Surface-Mount D2Pak Volts Amperes Watts MatchstickJudel AnovaNo ratings yet
- RF CMOS Background: July 2011Document17 pagesRF CMOS Background: July 2011Srijeet TripathyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - CMOS and FabDocument49 pagesLecture 2 - CMOS and FabSai SadiqNo ratings yet
- EC8095 NOTES STANN - by WWW - Easyengineering.net 1aDocument166 pagesEC8095 NOTES STANN - by WWW - Easyengineering.net 1asubhastudies.25No ratings yet
- Part 2i State of The ArtDocument15 pagesPart 2i State of The ArtVarun KumarNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument11 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentbambernitinNo ratings yet
- Eletrónica de Potência: Driving Questions #1Document7 pagesEletrónica de Potência: Driving Questions #1alexandre CaluluNo ratings yet
- Complementary MetalDocument5 pagesComplementary MetalesaidanNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design Module 1 NewDocument30 pagesVLSI Design Module 1 NewpavithraNo ratings yet
- Mosfet: Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect TransistorsDocument47 pagesMosfet: Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistorschandanayadav8490No ratings yet
- MOSFETDocument18 pagesMOSFETAditya PriyadarshiNo ratings yet
- Cmos Vlsi Design Chapter 1Document16 pagesCmos Vlsi Design Chapter 1sarin.gaganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Cmos Circuits - A Brief IntroductionDocument10 pagesChapter 1: Cmos Circuits - A Brief IntroductionjethustadNo ratings yet
- Ec8095-Vlsi Design-607796847-Ec 8095 NotesDocument163 pagesEc8095-Vlsi Design-607796847-Ec 8095 Noteshmpudur1968No ratings yet
- Bec010 Vlsi - NotesDocument109 pagesBec010 Vlsi - NotesFarukh ZafarNo ratings yet
- Microelectronic CircuitDocument696 pagesMicroelectronic CircuitImtiaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- MosfetDocument2 pagesMosfetShaina ArifNo ratings yet
- 1.VLSI IntroductionDocument41 pages1.VLSI Introductionductaingo0123No ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Cmos Circuits - A Brief IntroductionDocument3 pagesChapter 1: Cmos Circuits - A Brief IntroductionbhannuNo ratings yet
- Process Integration - I: Various LayersDocument17 pagesProcess Integration - I: Various LayersBiswaranjan SwainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Metal Oxide Semiconductor FET (MOSFET)Document47 pagesChapter 4 Metal Oxide Semiconductor FET (MOSFET)redhataNo ratings yet
- Lec 7,8 Modern CMOS TechnologyDocument43 pagesLec 7,8 Modern CMOS TechnologyVikram MeenaNo ratings yet
- Transistor Types: Cmos Vlsi Design Oct 2010Document46 pagesTransistor Types: Cmos Vlsi Design Oct 2010sharmila.mNo ratings yet
- Mid TestDocument2 pagesMid TestdremaanNo ratings yet
- MOSFETDocument12 pagesMOSFETVijay ShankarNo ratings yet
- 2 Introduction To MOS (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) Devices and LogicDocument2 pages2 Introduction To MOS (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) Devices and LogicvenkatNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - CMOS Logic, Fabrication and LayoutDocument34 pagesUnit 2 - CMOS Logic, Fabrication and LayoutphillipNo ratings yet
- Mosfet: MOS-FET, or MOS FET) Is A Transistor Used For Amplifying orDocument22 pagesMosfet: MOS-FET, or MOS FET) Is A Transistor Used For Amplifying ordadadabababaNo ratings yet
- Mosfet: Navigation SearchDocument24 pagesMosfet: Navigation SearchAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Design 17EC63: Chetan S, Dept of ECE, SJMIT, ChtradurgaDocument226 pagesVlsi Design 17EC63: Chetan S, Dept of ECE, SJMIT, ChtradurgaShivaprasad B KNo ratings yet
- VLSI Module-1Document119 pagesVLSI Module-1Phanindra Reddy100% (2)
- Mosfet - NptelDocument17 pagesMosfet - NptelAnshuman MitraNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between NMOSDocument5 pagesThe Difference Between NMOSRey TiburonNo ratings yet
- CMOS Transistor Layout KungFu Preliminary ReleaseDocument35 pagesCMOS Transistor Layout KungFu Preliminary ReleaseBabu ChintapalliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CMOS VLSI DesignDocument30 pagesIntroduction To CMOS VLSI DesignAbdelrehim SirajNo ratings yet
- Chapter III. MOS Transistor: .................. ..Slides 2-62Document79 pagesChapter III. MOS Transistor: .................. ..Slides 2-62Jorge RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Hawkins CH 3Document35 pagesHawkins CH 3Rinat EzerNo ratings yet
- VLSI Lec 01Document66 pagesVLSI Lec 01Maheen GulNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document65 pagesModule 2sasindhur r100% (2)
- Unit I Cmos Technology An MOS (Metal-Oxide-Silicon) Structure Is Created by Superimposing Several Layers of ConductingDocument2 pagesUnit I Cmos Technology An MOS (Metal-Oxide-Silicon) Structure Is Created by Superimposing Several Layers of ConductingIshita AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Sic Mos Trench SJ J.spmi.2018.10.016Document14 pagesSic Mos Trench SJ J.spmi.2018.10.016terry chenNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of MosfetDocument19 pagesFabrication of Mosfetnarayana89% (9)
- Microsoft Powerpoint - Vlsi Design AspectDocument89 pagesMicrosoft Powerpoint - Vlsi Design AspectAKASHDIP DUTTANo ratings yet
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesFrom EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Advanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionFrom EverandAdvanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionNo ratings yet
- MOS Integrated Circuit DesignFrom EverandMOS Integrated Circuit DesignE. WolfendaleNo ratings yet
- Logical Effort of Paths: A and C Begin To Rise (Figure 4.28 (C) ) - at First, Both Nodes See ApproximatelyDocument1 pageLogical Effort of Paths: A and C Begin To Rise (Figure 4.28 (C) ) - at First, Both Nodes See ApproximatelyCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Layer Density Rules: Chapter 3 CMOS Processing TechnologyDocument1 pageLayer Density Rules: Chapter 3 CMOS Processing TechnologyCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- CMOS VLSI Design 191Document1 pageCMOS VLSI Design 191Carlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Cmos Vlsi Design 198Document1 pageCmos Vlsi Design 198Carlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- CMOS VLSI Design 192Document1 pageCMOS VLSI Design 192Carlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- 4.4.6.4 Voltage Dependence: Chapter 4 DelayDocument1 page4.4.6.4 Voltage Dependence: Chapter 4 DelayCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Issues: Antenna RulesDocument1 pageManufacturing Issues: Antenna RulesCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Cmos Vlsi Design 162Document1 pageCmos Vlsi Design 162Carlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Circuit Extraction: CONNECT Layer1 Layer2Document1 pageCircuit Extraction: CONNECT Layer1 Layer2Carlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Pitfalls and Fallacies: Targeting A Bleeding-Edge ProcessDocument1 pagePitfalls and Fallacies: Targeting A Bleeding-Edge ProcessCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Circuit Elements: 3.4.3.1 CapacitorsDocument1 pageCircuit Elements: 3.4.3.1 CapacitorsCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- MOSIS Scalable CMOS Design RulesDocument1 pageMOSIS Scalable CMOS Design RulesCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- 3.4 CMOS Process Enhancements: 3.4.3.3 InductorsDocument1 page3.4 CMOS Process Enhancements: 3.4.3.3 InductorsCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 CMOS Processing Technology: 3.4.3.4 Transmission LinesDocument1 pageChapter 3 CMOS Processing Technology: 3.4.3.4 Transmission LinesCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Cmos Vlsi Design 149Document1 pageCmos Vlsi Design 149Carlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- 3.4.3.7 Non-Volatile Memory: P+ Diode N+ Well Contact Collector Base EmitterDocument1 page3.4.3.7 Non-Volatile Memory: P+ Diode N+ Well Contact Collector Base EmitterCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- 3.4.1.2 Silicon On Insulator: Chapter 3 CMOS Processing TechnologyDocument1 page3.4.1.2 Silicon On Insulator: Chapter 3 CMOS Processing TechnologyCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- 3.4.1.5 Plastic Transistors: InterconnectDocument1 page3.4.1.5 Plastic Transistors: InterconnectCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Mask Summary: The Only Mask Involved With Contacts To Active or PolyDocument1 pageMask Summary: The Only Mask Involved With Contacts To Active or PolyCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Micron Design Rules: Chapter 3 CMOS Processing TechnologyDocument1 pageMicron Design Rules: Chapter 3 CMOS Processing TechnologyCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- CMOS Process Enhancements: Layer Rule Description 65 NM Rule (M) TABLE 3.1Document1 pageCMOS Process Enhancements: Layer Rule Description 65 NM Rule (M) TABLE 3.1Carlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Mask Summary: The Masks Encountered For Well Specification May Include N-WellDocument1 pageMask Summary: The Masks Encountered For Well Specification May Include N-WellCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- CMOS VLSI Design 140Document1 pageCMOS VLSI Design 140Carlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- CMOS VLSI Design 138Document1 pageCMOS VLSI Design 138Carlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 CMOS Processing Technology: PassivationDocument1 pageChapter 3 CMOS Processing Technology: PassivationCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Isolation: Chapter 3 CMOS Processing TechnologyDocument1 pageIsolation: Chapter 3 CMOS Processing TechnologyCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Silicon Dioxide (Sio) : Well-Edge Proximity EffectDocument1 pageSilicon Dioxide (Sio) : Well-Edge Proximity EffectCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Gate Oxide: 3.2 CMOS TechnologiesDocument1 pageGate Oxide: 3.2 CMOS TechnologiesCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Gate and Source/Drain Formations: Chapter 3 CMOS Processing TechnologyDocument1 pageGate and Source/Drain Formations: Chapter 3 CMOS Processing TechnologyCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: JK Series 720 Ampere Medium Voltage ControllersDocument46 pagesInstruction Manual: JK Series 720 Ampere Medium Voltage ControllersThe MatrixNo ratings yet
- Royu Wires Devices Price List March 2016Document6 pagesRoyu Wires Devices Price List March 2016AlrwinNo ratings yet
- 16th Edition IEE Regulations PDFDocument488 pages16th Edition IEE Regulations PDFRamal Alirzayev100% (1)
- Control Products CatalogDocument50 pagesControl Products Catalogmk saravananNo ratings yet
- NTPC Interview Sample QuestionsDocument8 pagesNTPC Interview Sample QuestionsNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Toyota AlternatorsDocument3 pagesToyota Alternatorsdohar sNo ratings yet
- A 14Nm Logic Technology Featuring 2 - Generation Finfet, Air-Gapped Interconnects, Self-Aligned Double Patterning and A 0.0588 M Sram Cell SizeDocument3 pagesA 14Nm Logic Technology Featuring 2 - Generation Finfet, Air-Gapped Interconnects, Self-Aligned Double Patterning and A 0.0588 M Sram Cell SizePiyush AmbulgekarNo ratings yet
- Silicon N Channel MOS FET High Speed Power Switching: FeaturesDocument10 pagesSilicon N Channel MOS FET High Speed Power Switching: FeaturesMoez MizouNo ratings yet
- 40MV Transformer TS 2791 FINALDocument12 pages40MV Transformer TS 2791 FINALRanchak KumarNo ratings yet
- Indian Standard: Specification For Power TransformersDocument30 pagesIndian Standard: Specification For Power TransformerspaulsumantaNo ratings yet
- List of IEC Standards - WikipediaDocument26 pagesList of IEC Standards - WikipediaEngr saqibNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic IIDocument33 pagesPhotovoltaic IIcharbel jabbourNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project Common Base TransistorDocument13 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Common Base TransistorKishore BhaskarNo ratings yet
- An 1118Document2 pagesAn 1118John AllenNo ratings yet
- DC SimulationDocument4 pagesDC SimulationJosé Miguel Alayo BerriosNo ratings yet
- SAFTRONICSDF8PLUS AA1152 ManualDocument20 pagesSAFTRONICSDF8PLUS AA1152 ManualMarcelo CabriNo ratings yet
- 110 Electrical Skills StoryBoardDocument11 pages110 Electrical Skills StoryBoardshyamNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet 3KL8431-3UA00: ModelDocument2 pagesData Sheet 3KL8431-3UA00: Modeliotaathi tNo ratings yet
- IV Semester ElectricalDocument30 pagesIV Semester ElectricalSpectre ZeroNo ratings yet
- Delay - DL4 Stomp Box Modelers PDFDocument54 pagesDelay - DL4 Stomp Box Modelers PDFmiguel.oliveirNo ratings yet
- WEG CWM Contactors 50070163 enDocument52 pagesWEG CWM Contactors 50070163 enBelo traderNo ratings yet
- Appendix 1 93M-0501-B13-NC000-DGM-00003 NCC Mainline Power Sectioning Diagram (FDR)Document15 pagesAppendix 1 93M-0501-B13-NC000-DGM-00003 NCC Mainline Power Sectioning Diagram (FDR)AHMED ATIFNo ratings yet
- CH-0037-19 - NOKIA Chile RevCDocument13 pagesCH-0037-19 - NOKIA Chile RevCjmccardenasNo ratings yet
- Rishikesh Suresh TambulkarDocument3 pagesRishikesh Suresh TambulkarHariharan SNo ratings yet
- 3A Ultra Low Dropout Linear Regulator: General DescriptionDocument12 pages3A Ultra Low Dropout Linear Regulator: General DescriptionLoengrin MontillaNo ratings yet
- SI 3010KM DatasheetDocument9 pagesSI 3010KM DatasheetAndres GuioNo ratings yet
- Instruction Sheet C622 Instructions For Spacer Replacement in Contact Blocks Used On 40/70/125 Amp OT III and OTPC Transfer Switches (Kit 541-0766)Document3 pagesInstruction Sheet C622 Instructions For Spacer Replacement in Contact Blocks Used On 40/70/125 Amp OT III and OTPC Transfer Switches (Kit 541-0766)Quang Pham100% (1)
- Metro Vendor ListDocument1 pageMetro Vendor ListHaasini DentalcareNo ratings yet
- BD9882F, FVDocument5 pagesBD9882F, FVbahti1284No ratings yet