Professional Documents
Culture Documents
07.06.21 - SR - Sankalp & ALL - WTM-5 Q.paper With Key & Sol's
Uploaded by
Nishith Reddy 316Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
07.06.21 - SR - Sankalp & ALL - WTM-5 Q.paper With Key & Sol's
Uploaded by
Nishith Reddy 316Copyright:
Available Formats
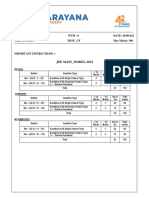
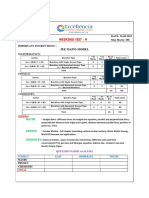
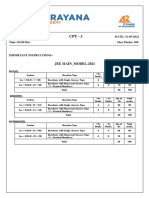
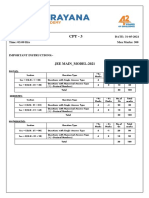
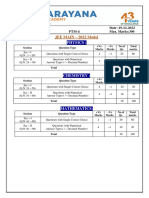
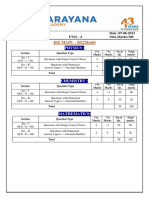
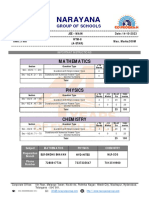
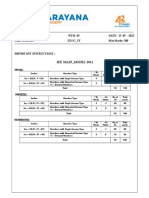
Sec: SR SANKALP & ALL DATE: 07-06-2021
Time: 03:00 Hrs. WTM-5 Max Marks: 300
IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: -
JEE MAINS MODEL
MATHEMATICS:
+Ve - Ve
Section Question Type No.of Total marks
Marks Marks
Sec – I(Q.N : 1 – 20) Questions with
wi Single Answer Type 4 -1 20 80
Questions with Numerical Answer Type
Sec – II(Q.N : 21 – 25) 4 0 5 20
(+/ - Decimal Numbers)
Total 25 100
PHYSICS:
+Ve
- Ve
Section Question Type Mark No.o Total marks
Marks
Sec – I(Q.N : 26 – 45) Questions with Single
Singl Answer Type 4 -1 20 80
Questions with Numerical Answer Type
Sec – II(Q.N : 46 – 50) 4 0 5 20
(+/ - Decimal Numbers)
Total 25 100
CHEMISTRY:
+Ve - Ve
Section Question Type Mark Mark No.of Total marks
Sec – I(Q.N : 51 – 70) Questions with Single Answer Type 4 -1 20 80
Questions with Numerical Answer Type
Sec – II(Q.N : 71 – 75) 4 0 5 20
(+/ - Decimal Numbers)
Total 25 100
Syllabus:
MATHS: Definite integrals + Area
PHYSICS: Complete Electrostatics
CHEMISTRY: Types of conductors Electrolysis Faradays
Faradays laws Conductance and specific
conductance equivalent and molar conductance + solid state
MATHS Max Marks: 100
SECTION – I
(SINGLE CORRECT ANSWER TYPE)
This section contains 20 multiple choice questions. Each question has 4 options (1), (2), (3) and (4) for its
answer, out of which ONLY ONE option can be correct.
Marking scheme: +4 for correct answer, 0 if not attempted and -1 if not correct.
n +1
1
1. ∫
n
f ( x ) dx = n 2 + n then ∫ f ( x ) dx =
−1
A) 0 B) -2 C) 0 D) 4
4 4 2
2. ∫ f ( x ) dx = 4 and ∫ ( 3 − f ( x ) ) dx = 7 Then ∫ f ( x ) dx =
−1 2 −1
A) -2 B) 3 C) 5 D)8
10 10 1
3. If ∫ f ( x ) dx = 5 Then ∑ ∫ f ( k − 1 + x )dx =
0 K =1 0
A) 50 B) 10 C) 5 D) 0
1 x2
log
λ
f ( f ( x ) + f ( − x ))
3
4. ∫
log λ g ( 3x2 ) ( g ( x ) − g ( − x ) )
dx = [where λ > 1]
1
A) 0 B) 1 C) λ D)
λ
3π π
∫ f ( cos x ) dx and I = ∫ f ( cos x )dx then
2 2
5. If I1 = 2
0 0
A) I1 = I 2 B) I1 = 2 I 2 C) I1 = 5I 2 D) I1 = 3I 2
π
2
sin 2 x
6. ∫0 sin x + cos xdx =
1 1
A) 2 log ( 2 +1 ) B)
2
log ( )
2 + 1 C) log ( )
2 +1 D)
2
log ( 2 −1)
π
cos 2 x
7. The value of ∫ x
dx equal to [where a > 0 ] is
−π
1 + a
π π
A) 2π B) C) D) aπ
a 2
4
d esin x 3 sin x3
8. Let
dx
f ( x) =
x
, x > 0 If ∫1 x e dx = F ( K ) − F (1) Then one of the possible
value of K is
A) 16 B) 63 C) 64 D) 15
Sr.Sankalp & All _WTM-5 Page 2
π
2 x (1 + sin x )
9.
−
∫π 1 + cos 2 x
dx =
π2 π
A) B) π2 C) 0 D)
4 2
1 b −t
et dt e dt
10. If ∫ = a then ∫b−1 t − b − 1 is equal to
0
t +1
A) ae − b B) − ae − b C) −be − a D) aeb
5π
4
sin 2 xdx
11. ∫
π cos
4
x + sin 4 c
=
5π π π
A) B) C) π D)
4 2 4
π
π 2
cos x sin 2 x
12. If A=∫ 2
dx then ∫0 x + 1 dx is equal to
0 ( x + 2)
1 1 1 1 1 1
A) A− − B) + −A C) −A D) 1 + −A
2 π +2 2 π +2 π +2 π +2
3π
4
x
13. The value of integral ∫π 1 + sin xdx is
4
π
A) π 2 B) π ( 2 −1 ) C)
2
( 2 +1 ) D) 2π ( 2 −1)
1 1 1
I1 = ∫ e cos xdx, I 2 = ∫ e − x2
cos xdx, I 3 = ∫ e − x dx then
3
−x 2 2
14. If
0 0 0
A) I 2 > I 3 > I1 B) I 2 > I1 > I 3 C) I 3 > I 2 > I1 D) I 3 > I1 > I 2
π
3
tan θ dθ 1
15. If ∫
0 2 K secθ
= 1−
2
( K > 0 ) then the value of K is
1
A) 2 B) 1 C) 4 D)
2
2
sin 2 x dx
16. The value of the integral ∫ (where [ x ] denotes the greatest integer less
−2
x 1
π + 2
than or equal to x) is
A) 0 B) 4 C) 4 − sin 4 D) sin 4
Sr.Sankalp & All _WTM-5 Page 3
π
4
dx
17. The integral ∫π sin 2 x (Tan5 x + cot 5 x ) equals
6
π 1 1
A) Tan −1 B)
40 20 9 3
1 π −1 1 1π −1 1
C) − Tan D) − Tan
10 4 9 3 5 4 3 3
18. Let f and g be continuous Functions on [ 0, a ] such that f ( x ) = f ( a − x ) and
a
g ( x ) + g ( a − x ) = 4 then ∫ f ( x ) g ( x ) dx =
0
a a a a
A) 4 ∫ f ( x ) dx B) −3∫ f ( x ) dx C) ∫ f ( x ) dx D) 2 ∫ f ( x ) dx
0 0 0 0
x 2 x e x
e
The integral ∫ − × log e dx is equal to
x
19.
1 e x
1 1 1 3 1 1 1 3 1 1
A) − + − 2
B) − e − 2
C) − e − 2 D) − −
2 e 2e 2 2e 2 e 2 e 2e2
π /3
π + 4 x3 4π 1
20. If ∫ dx = Tan −1 then ( K1 + K 2 ) =
−π /3 2 − cos x +
π K 1 K 2
3
A) 3 B) 10 C) 5 D) 7
SECTION-II
(Numerical Value Answer Type)
This section contains 5 questions. The answer to each question is a Numerical values comprising of positive or
negative decimal numbers (place value ranging from Thousands Place to Hundredths Place).
Eg: 1234.56, 123.45, -123.45, -1234.56, -0.12, 0.12 etc.
Marking scheme: +4 for correct answer, 0 in all other cases.
21. The area bounded by the curve y = 2 x − x 2 and the straight line y = − x given by P then
[ P ] is equal to [where [.] is G.I.F ]
22. The area bounded by the curves y = cos x, y = sin x between the ordinates x = 0 and
3π
x= is K 2 −l then K +l =
2
23. The area bounded by y = cos x, y = x + 1, y = 0 is K then 2K =
2
24. The area (in sq. units) of the region bounded by the curves 2 x = y − 1 and x = 0 is K
then 3K =
The area contained between the curves xy = a the vertical line x = a, x = 4a ( a > 0 )
2
25.
and x − axis is la 2 log K then l+k =
Sr.Sankalp & All _WTM-5 Page 4
PHYSICS Max Marks: 100
SECTION – I
(SINGLE CORRECT ANSWER TYPE)
This section contains 20 multiple choice questions. Each question has 4 options (1), (2), (3) and (4) for its
answer, out of which ONLY ONE option can be correct.
Marking scheme: +4 for correct answer, 0 if not attempted and -1 if not correct.
26. Units of electric flux are
N- m 2 N
A) B) C) volt-m D) volt/ m 3
C2 C - m2
2
27. A neutral pendulum oscillates in a uniform electric field as shown in figure. If a positive
charge is given to the pendulum, then its time period
A) will increase B) will decrease
C) will remain constant D) will first increase then decrease
28. Three identical charges are placed at corners of an equilateral triangle of side l . If fore
between any two charges if F, the work required to double the dimensions of triangle is
A) −3Fl B) 3Fl C) ( −3 / 2 ) Fl D) ( 3 / 2 ) Fl
29. Charges 2q and − q are placed at ( a,0 ) and ( − a,0 ) as shown in the figure. The
coordinates of the point at which electric field intensity is zero will be ( x,0 ) , where
A) −a < x < a B) x < −a C) x > −a D) 0< x<a
30. Two concentric conduction spheres of radii R and 2R are carrying charges Q and -2Q,
respectively. If the charge on inner sphere is doubled, the potential difference between the
two spheres will
Sr.Sankalp & All _WTM-5 Page 5
A) become two times B) become four times C) be halved D) remain same
31. An infinite line of charge λ per unit length is placed along the y − axis. The work done in
moving a charge q from A ( a,0 ) and B ( 2a,0 ) is
qλ qλ 1 qλ qλ
A) In 2 B) In C) In 2 D) In 2
2πε 0 2πε 0 2 4πε 0 4πε 0
32. An electric dipole is placed perpendicular to an infinite line of charge at some distance as
shown in figure. Identify the correct statement
A) The dipole is attracted towards the line charge
B) The dipole is repelled away from the line charge
C) The dipole does not experience a force
D) The dipole experiences a force as well as a torque
33. If the potential at the centre of a uniformly charged hollow sphere of radius R is V, the\n
electric field at a distance r from the centre of sphere will be (r > R)
VR VR VR VR
A) B) C) D)
r2 R2 r R2 + r 2
Sr.Sankalp & All _WTM-5 Page 6
34. Two thin wire rings each having radius R are placed at a distance d a part with their
coinciding. The charges on the two rings are +Q and –Q. The potential difference between
the centres of the two rings is
Q 1 1
A) zero B) −
4πε 0 R R2 + d 2
Q Q 1 1
C) D) −
4πε 0 d 2 2πε 0 R R2 + d 2
35. Charge Q is given a displacement r = aiˆ + bjˆ in an electric field E = E1iˆ + E2 ˆj. The
work done is
2 2
A) Q ( E1a + E2b ) B) Q ( E1a ) + ( E2 b )
C) q ( E1 + E2 ) a 2 + b2 D) Q E12 + E22 a 2 + b2
36. In the diagram shown, the charge +Q is fixed. Another charge +2q and mass M is projected
from a distance R from the fixed charge. Minimum separation between the two charges if the
1
velocity becomes times of the projected velocity, at this moment is (Assume gravity to
3
be absent)
3 1 1
A) R B) R C) R D) none of these
2 3 2
37. A uniform electric field of strength E exists in a region. An electron enters a point A with
velocity v as shown. It moves through the electric field and reaches at point B. Velocity of
particle at B is 2v at 30° with x − axis. Then,
Sr.Sankalp & All _WTM-5 Page 7
3mv 2 ˆ
A) electric field E = − i
2ea
3mv3
B) rate of doing work done by electric field at B is
2ea
C) Both ( a ) and ( b ) are correct D) Both ( a ) and ( b ) are wrong
38. Two point charges a and b whose magnitude are same,. Positioned at a certain distance along
the positive x− axis from each other. a is at origin. Graph is drawn between electric field
strength and distance x from a.E is taken positive if it is along the line joining from
a to b. From the graph it can be decided that
A) a is positive, b is negative B) a and b both are positive
C) a and b both are negative D) a is negative, b is positive
39. Six charges are placed at the vertices of a rectangular hexagon as shown in the figure. The
electric field on the line passing through point O and perpendicular to the plane of the figure
as a function of distance x from point O is ( x >> a )
Qa 2Qa 3Qa
A) 0 B) C) D)
πε 0 x3 πε 0 x3 πε 0 x 3
40. If the electric potential of the inner shell is 10V and that of the outer shell is 5 V, then the
potential at the centre will be
A) 10 V B) 5 V C) 15 V D) zero
Sr.Sankalp & All _WTM-5 Page 8
41. A solid conducting sphere of radius a having a charge q is surrounded by a concentric
conducting spherical shell of inner radius 2a outer radius 3a as shown in figure. Find the
1
amount of heat produced when switch is closed VA − VC k =
4π e0
kq 2 kq 2 kq 2 kq 2
A) B) C) D)
2a 3a 4a 6a
42. There are four concentric shells A,B,C and D of radii a , 2 a ,3a and 4a respectively. Shells
B and D are given charge + q and − q respectively. Shell C is now earthed. The potential
1
difference VA − VC is k =
4π e0
kq kq kq kq
A) B) C) D)
2a 3a 4a 6a
43. Potential difference between centre and surface of the sphere of radius R and uniform volume
charge density ρ within it will be
ρ R2 ρ R2 ρ R2 ρ R2
A) B) C) D)
6ε 0 4ε 0 3ε 0 2ε 0
44. A uniform electric field of 400 V/m is directed at 45° above the x − axis as shown in the
figure. The potential difference VA − VB is given by
A) 0 B) 4 V C) 6.4 V D) 2.8 V
Sr.Sankalp & All _WTM-5 Page 9
45. Initially the spheres A and B are at potentials VA and VB respectively. Now, sphere B is
earthed by closing the switch. The potential of A will now become
A) 0 B) VA C) VA − VB D) VB
SECTION-II
(Numerical Value Answer Type)
This section contains 5 questions. The answer to each question is a Numerical values comprising of positive or
negative decimal numbers (place value ranging from Thousands Place to Hundredths Place).
Eg: 1234.56, 123.45, -123.45, -1234.56, -0.12, 0.12 etc.
Marking scheme: +4 for correct answer, 0 in all other cases.
46. Two identical coaxial rings each of radius R are separated by a distance of 3R. They are
uniformly charged with charges +Q and −Q respectively. The minimum kinetic energy
with which a charged particle (charged +q) should be projected from the centre of the
negatively charged ring along the axis of the rings such that it reached the centre of the
Qq
positively charged ring is n where n=
8πε 0 R
47. Two identical charges are placed at the two corners of an equilateral triangle. The potential
energy of the system is U. the work done in bringing an identical charge from infinity to the
third vertex is nU where n =
48. A charged particle q is shot from a large distance towards another charged particle Q which
is fixed, with a speed v. If approaches Q up to a closet distance r and then returns. If q were
r
given a speed 2v , the distance of approach would be where n=
n
49. In a uniform electric field, the potential is 10 V at the origin of coordinates and 8 V at each of
( )( ) ( )
the points 1,0,0 , 0,1,0 and 0,0,1 . The potential at the point 1,1,1 will be (In( )
volts)
50. The electric potential at a point ( x, y ) in the x − y plane is given by V = − kxy . The field
intensity at a distance r in this plane, from the origin is proportional to r n where n =
Sr.Sankalp & All _WTM-5 Page 10
CHEMISTRY Max Marks: 100
SECTION – I
(SINGLE CORRECT ANSWER TYPE)
This section contains 20 multiple choice questions. Each question has 4 options (1), (2), (3) and (4) for its answer, out of
which ONLY ONE option can be correct.
Marking scheme: +4 for correct answer, 0 if not attempted and -1 if not correct.
51. Molten CuCl2 is electrolysed using platinum electrodes the reaction occurring at anode is
A) B)
C) D)
52. An edge atom of a cube provides how many atoms in the unit cell
A) 1/2 B) ¼ C) 1/8 D) 1
53. For orthorhombic system, axial ratios are a ≠ b ≠ c and the axial angles are
A) α = β = γ ≠ 90o B) α = β = γ = 90 o
C) α = γ = 90o , β ≠ 90o D) α ≠ β ≠ γ = 90o
o
+ –
54. The ionic radii of Rb and I are 1.46 and 2.16 A respectively. The most probable type of
structure exhibited by it is.
A) CsCl type B) NaCl type C) ZnS type D) CaF2 type
55. The addition of arsenic to germanium makes the latter a
A) metallic conductor B) intrinsic semiconductor
C) mixed conductor D) extrinsic semiconductor
o
56. CsCl has bcc structure with Cs + at the centre and Cl− ion at each corner. If rCs+ = 1.69 A
o
and rCs− = 1.81A, what is the edge length a of the cube?
o o o o
A) 3.50 A B) 3.80 A C) 4.04 A D) 4.50 A
57. Which of the following describes hexagonal closed packed arrangement of spheres?
A) ABCABA………….. B) ABCABC………………
C) ABABA……………. D) ABBABB………………
Sr.Sankalp & All _WTM-5 Page 11
58. The number of atoms present in a unit cell of a monatomic substance (element) of a simple
cubic lattice, body–centred cubic and face centred cubic respectively are
A) 8, 9 and 14 B) 1, 2 and 4 C) 4, 5 and 6 D) 2, 3 and 5
59. Schottky defect causes
A) increase in the density of solid B) decrease in the density of solid
C) no change in the density of solid D) decrease in the connectivity of solids
60. When a cation leaves its normal position in the crystal and moves to some interstitial space,
the defect in the crystal is known as
A) Schottky defect B) F-centre
C) Frenkel defect D) Non-stiochiometric defect
61. Anti–ferromagnetic substances possess
A) low magnetic moment B) large magnetic moment
C) zero magnetic moment D) Any value of magnetic moment
62. Lithium selenide can be described as close-packed array of selenide ions with lithium ions in
all of the tetrahedral holes. Formula of lithium selenide is
A) Li 2Se B)LiSe C) LiSe 2 D) Li3Se
63. An alloy Cu, Au and Ag is found to have Cu constituting the ccp lattice. If Ag atoms occupy
edge centres and Au is present at body centres, the alloy has formula
A) Cu 4 Ag 2 Au B) Cu 4 Ag 4 Au C) Cu 4 Ag 3 Au D) CuAgAu
64. The quantity of current required to produce hydrogen gas from acidulated water at the rate of
per second at STP
A) 8.61 A B) 86.1 A C) 861 A D) 861 A
65. The quantity of electricity required to deposit 10.8 gm of silver from aqueous AgCl solution
when passed for the hour.
A) 2.68 A B) 26.8 A C) 268 A D) 2680 A
66. The time required to deposit all the copper from 250 cm3 of 0.1M CuSO 4 solution with
9.65 A of electricity
A) 5000 Sec B) 500 Sec C) 50 Sec D) 5 Sec
67. The charge in coulombs of one gm-ion of N −3 is
Sr.Sankalp & All _WTM-5 Page 12
A) 2.89 x 105 C B) 4.8 x 10−19 C C) 4.8 x 1019 C D) 3 x 1023 C
68. What mass of silver could be plated on a spoon from electrolysis of AgNO 3 at 1 A current
for 96.5 s.
A) 108 gm B) 10.8 gm C) 1.08 gm D) 0.108 gm
69. A current of 9.65 A is passed through the electrolytic cell for 10 minutes. If the process is
80% efficient the magnesium metal produced is
A) 0.72 gm B) 0.576 gm C) 1.42 gm D) 12 gm
70. The number of electrons involved in the reaction when a faraday of electricity is passed
through an electrolyte in solution is
A)12 x 1046 B) 96500 C) 8 x 1016 D) 6 x 1023
SECTION-II
(Numerical Value Answer Type)
This section contains 5 questions. The answer to each question is a Numerical values comprising of positive or
negative decimal numbers (place value ranging from Thousands Place to Hundredths Place).
Eg: 1234.56, 123.45, -123.45, -1234.56, -0.12, 0.12 etc.
Marking scheme: +4 for correct answer, 0 in all other cases.
71. What is the coordination number of sodium in Na 2 O
72. Cost of electricity for the production of X Litre H 2 at STP at cathode is at rate of Rs.1.Then
the cost of electricity for the production of X Litre of O 2 gas at anode will be (Assume one
mole of electron as one unit electricity).
73. In the electrolysis of a metallic chloride MCl x 3.283 gm of metal (atomic mass 197
assuming) was deposited on the cathode by the passage of 4825C of electronic charge.
Calculate the number of chloride ions per molecule. (Write near integer)
74. What current is to be passed for 0.25 sec. for deposition of certain weight of metal which is
equal to its electrochemical equivalent?
75. The electrolysis of a metal salt was carried out by passing a current of 4 amp for 45 minutes.
It resulted in the deposition of 2.977g metal. If atomic mass of the metal is 106.4g mol –1.
Calculate the charge on metal caution. (Write near integer)
Sr.Sankalp & All _WTM-5 Page 13
SR SANKALP & ALL WTM-5 KEY SHEET
DATE: 07-06-2021
MATHS KEY:
1) A 2) C 3) C 4) A 5) D 6) B 7) C 8) C 9) B 10) B
11) D 12) B 13) B 14) C 15) A 16) A 17) C 18) D 19) B 20) C
21) 4 22) 6 23) 3 24) 2 25) 4
PHYSICS KEY:
26) C 27) A 28) C 29) B 30) A 31) B 32) A 33) A 34) D 35) A
36) A 37) A 38) A 39) B 40) A 41) C 42) D 43) A 44) D 45) C
46) 2 47) 2 48) 4 49) 8 50) 1
CHEMISTRY KEY:
51) A 52) B 53) B 54) B 55) D 56) C 57) C 58) B 59) B 60) C
61) C 62) A 63) C 64) A 65) A 66) B 67) A 68) D 69) B 70) D
71) 4 72) 2 73) 3 74) 4 75) 4
Sr.Sankalp & All _WTM-5 Page 14
SOLUTIONS
MATHEMATICS
1.
2.
3.
4. The given function is odd function
5.
6.
7.
8.
Sr.Sankalp & All _WTM-5 Page 15
9.
10.
11.
12.
Sr.Sankalp & All _WTM-5 Page 16
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
Sr.Sankalp & All _WTM-5 Page 17
18.
19.
20.
Sr.Sankalp & All _WTM-5 Page 18
PHYSICS
Sr.Sankalp & All _WTM-5 Page 19
Sr.Sankalp & All _WTM-5 Page 20
Sr.Sankalp & All _WTM-5 Page 21
Sr.Sankalp & All _WTM-5 Page 22
Sr.Sankalp & All _WTM-5 Page 23
You might also like
- 02.05.21 - SR - MPC ALL - WTM-1 Q.paper With Key & Sol'sDocument18 pages02.05.21 - SR - MPC ALL - WTM-1 Q.paper With Key & Sol'sNishith Reddy 316No ratings yet
- JR MPC WTM-21 - 25-11-2023 - QPDocument19 pagesJR MPC WTM-21 - 25-11-2023 - QPUddesh NaiduNo ratings yet
- 03.01.21 - JR - MPC All - Wtm-26 - Q.paper With KeyDocument14 pages03.01.21 - JR - MPC All - Wtm-26 - Q.paper With KeyNishith Reddy 316No ratings yet
- JR MPC All WTM-18 - 10-11-2023-QPDocument21 pagesJR MPC All WTM-18 - 10-11-2023-QPUddesh NaiduNo ratings yet
- Paper-Ii: Grand Test-5Document33 pagesPaper-Ii: Grand Test-5Vedant TodiNo ratings yet
- Physics: Class: SZ1-A Jee-Main Model Date: 07-08-2021 Time: 3hrs WTM-05 Max. Marks: 300Document20 pagesPhysics: Class: SZ1-A Jee-Main Model Date: 07-08-2021 Time: 3hrs WTM-05 Max. Marks: 300jjgNo ratings yet
- FTM-01, Q.P.22.04Document20 pagesFTM-01, Q.P.22.04nawec98190No ratings yet
- WTM - 7 - Xii-Ic - CF - 13.6.22 - Q.P.Document11 pagesWTM - 7 - Xii-Ic - CF - 13.6.22 - Q.P.Mahesh DodkeNo ratings yet
- @bohring - Bot - 15 - 10 - 23 - SR - IIT - STAR - CO - SCMODEL - @HeyitsyashXDDocument23 pages@bohring - Bot - 15 - 10 - 23 - SR - IIT - STAR - CO - SCMODEL - @HeyitsyashXDDinesh BabuNo ratings yet
- SR Out Going Pte 02 Eamcet 20 04 2023 Qp&keyDocument21 pagesSR Out Going Pte 02 Eamcet 20 04 2023 Qp&keyP SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Mis - SR MPC Jee Mains GT 2 Ex DT 03-07-2020 QP & KeyDocument22 pagesMis - SR MPC Jee Mains GT 2 Ex DT 03-07-2020 QP & KeyUppu EshwarNo ratings yet
- JEE MAIN - 2022 Model: PhysicsDocument7 pagesJEE MAIN - 2022 Model: PhysicsDhruv SharmaNo ratings yet
- 16-04-2022 Xi Iit WTM - QPDocument13 pages16-04-2022 Xi Iit WTM - QPDinesh BabuNo ratings yet
- 25.04.24 - Osr - Star Co-Sc - Jee-Adv - 2023 - P1 - Gta-8 (P2) - QP @Document18 pages25.04.24 - Osr - Star Co-Sc - Jee-Adv - 2023 - P1 - Gta-8 (P2) - QP @sknoushad126No ratings yet
- Isr - Iit - Star Co-Sc (Model-A) - Jee Adv - 2019-P1 - Wat-40 - QP FinalDocument14 pagesIsr - Iit - Star Co-Sc (Model-A) - Jee Adv - 2019-P1 - Wat-40 - QP Finalnobihav525No ratings yet
- WTM Xii-Ic CF 18.4.22 Q.P.Document12 pagesWTM Xii-Ic CF 18.4.22 Q.P.Kripanshu KaushikNo ratings yet
- WTM - 8 - Xii-Ic - CF - 20.6.22 - Q.P.Document11 pagesWTM - 8 - Xii-Ic - CF - 20.6.22 - Q.P.Mahesh DodkeNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-08-29 at 6.12.25 AMDocument24 pagesScreenshot 2023-08-29 at 6.12.25 AMpapupeepuNo ratings yet
- Sri Chaitanya IIT Academy, India: Grand Test-5Document31 pagesSri Chaitanya IIT Academy, India: Grand Test-5ashrithNo ratings yet
- 21.04.24 - Osr - Star Co-Sc - Jee-Adv - 2023 - P1 - Gta-7 (P2) - QPDocument16 pages21.04.24 - Osr - Star Co-Sc - Jee-Adv - 2023 - P1 - Gta-7 (P2) - QPvenkateswararao.yNo ratings yet
- 02-01-21 - JR - IIT CO SUPER CHAINA & SUPER CHAINA N120 JEE MAINS QP PDFDocument16 pages02-01-21 - JR - IIT CO SUPER CHAINA & SUPER CHAINA N120 JEE MAINS QP PDFYugandher BadanaNo ratings yet
- 24-09-23 - JR - Iit - Star Co-Sc (Model-A) - Jee Adv - Nm-I (P-I) - Wat-21 - QPDocument18 pages24-09-23 - JR - Iit - Star Co-Sc (Model-A) - Jee Adv - Nm-I (P-I) - Wat-21 - QPnamratagolechhaNo ratings yet
- CPT - 3 - Xii Ic CF - Mains Paper - 31-05-2021 - q.p.-1Document12 pagesCPT - 3 - Xii Ic CF - Mains Paper - 31-05-2021 - q.p.-1ARYAN PANDEYNo ratings yet
- CPT - 3 - Xii Ic 31-05-2021 (Solved)Document13 pagesCPT - 3 - Xii Ic 31-05-2021 (Solved)ARYAN PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Xi Iit WTM QP 05-06-2021Document7 pagesXi Iit WTM QP 05-06-2021Dinesh BabuNo ratings yet
- CPT 3Document9 pagesCPT 3ARYAN PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Xi - Iit - Ic & Ir - CFTM-1 - 11-09-2023 - QPDocument17 pagesXi - Iit - Ic & Ir - CFTM-1 - 11-09-2023 - QPiitb.akkharcheNo ratings yet
- Xi Jee Ir - FTM-1 - 26-06-23 QPDocument12 pagesXi Jee Ir - FTM-1 - 26-06-23 QPiitb.akkharcheNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-04-12 at 3.19.10 AMDocument25 pagesScreenshot 2022-04-12 at 3.19.10 AMSakshi DadlaniNo ratings yet
- Xi - Iit - Ic & Ir - CFTM-7 - 22-01-2024 - QPDocument16 pagesXi - Iit - Ic & Ir - CFTM-7 - 22-01-2024 - QPaduraj30112007No ratings yet
- 21.04.24 - Osr - Star Co-Sc - Jee-Adv - 2023 - P1 - Gta-7 (P1) - QPDocument24 pages21.04.24 - Osr - Star Co-Sc - Jee-Adv - 2023 - P1 - Gta-7 (P1) - QPvenkateswararao.yNo ratings yet
- SR Scmodel A 2023 P1 Gta 07 P1 Qp&keyDocument35 pagesSR Scmodel A 2023 P1 Gta 07 P1 Qp&keyvenkateswararao.yNo ratings yet
- @bohring Bot × @JEE Tests XII PASS IIT IC GTM 2 EX DT 27 03 2024Document17 pages@bohring Bot × @JEE Tests XII PASS IIT IC GTM 2 EX DT 27 03 2024NikhilGuptaNo ratings yet
- Xii - STD - Iit - B1 - QP (19-12-2022) - 221221 - 102558Document13 pagesXii - STD - Iit - B1 - QP (19-12-2022) - 221221 - 102558Stephen SatwikNo ratings yet
- Xi Iit Ir FTM-4 07-08-2023 QPDocument13 pagesXi Iit Ir FTM-4 07-08-2023 QPiitb.akkharcheNo ratings yet
- 06-04-17 - SR - IPLCO - Jee Adv - Ph-III - GTA-1 - New Model-1 (P1) - Q'PaperDocument30 pages06-04-17 - SR - IPLCO - Jee Adv - Ph-III - GTA-1 - New Model-1 (P1) - Q'PaperUppu EshwarNo ratings yet
- SR Star-30 QP 22-04-2023Document34 pagesSR Star-30 QP 22-04-2023PranayNo ratings yet
- @bohring - Bot - 10co - Iit - A Star Paper - Jee Main @heyitsyashxdDocument20 pages@bohring - Bot - 10co - Iit - A Star Paper - Jee Main @heyitsyashxdDinesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Jun 07, 2022Document19 pagesAdd Maths Jun 07, 2022Amarah MohammedNo ratings yet
- 26-08-2021 Otg SR Iit N Super Chaina Adv (2018 - P2) Question PaperDocument20 pages26-08-2021 Otg SR Iit N Super Chaina Adv (2018 - P2) Question PaperkrishNo ratings yet
- WTM-05 XII IC CF 23-05-22 QueDocument15 pagesWTM-05 XII IC CF 23-05-22 QueKripanshu KaushikNo ratings yet
- 01-08-2021 SR - Super60 (In Coming) Jee-Adv 2017 P2 WTA-38 Question PaperDocument16 pages01-08-2021 SR - Super60 (In Coming) Jee-Adv 2017 P2 WTA-38 Question Paperdasari srinidhiNo ratings yet
- Xi Iit Ir FTM-03 24.07.2023 QPDocument14 pagesXi Iit Ir FTM-03 24.07.2023 QPiitb.akkharcheNo ratings yet
- Xii Stu Ir Iit B-2 CPT-16 12-12-2022 QP 221212 225253Document14 pagesXii Stu Ir Iit B-2 CPT-16 12-12-2022 QP 221212 225253Stephen SatwikNo ratings yet
- Xi - Iit - Ic & Ir - CFTM-04 - 6 - 11 - 2023 - QPDocument18 pagesXi - Iit - Ic & Ir - CFTM-04 - 6 - 11 - 2023 - QPiitb.akkharcheNo ratings yet
- Class Test - 1 (All Subjects) 14-3-2024Document17 pagesClass Test - 1 (All Subjects) 14-3-2024sinisterdhruvNo ratings yet
- 30-10-23 - SR - Iit - Star Co-Sc (Model-A&b) - Jee Adv - Pta-12 - SyllabusDocument28 pages30-10-23 - SR - Iit - Star Co-Sc (Model-A&b) - Jee Adv - Pta-12 - Syllabusadityaatloye999xNo ratings yet
- 12-07-19 SR - Super60 Jee-Adv 2017 P2 WTA-30 QPDocument16 pages12-07-19 SR - Super60 Jee-Adv 2017 P2 WTA-30 QPRohan k s0% (1)
- Sri Chaitanya IIT Academy, India: Paper-IiDocument33 pagesSri Chaitanya IIT Academy, India: Paper-IiashrithNo ratings yet
- 24.03.24 - Osr - Star Co-Sc - Jee-Adv - 2019 - P1 - Gta-2 (P1) - QPDocument19 pages24.03.24 - Osr - Star Co-Sc - Jee-Adv - 2019 - P1 - Gta-2 (P1) - QPAyush GhatakNo ratings yet
- TF: Textile Engineering and Fibre Science: S/121 Food/06-TF - 1ADocument16 pagesTF: Textile Engineering and Fibre Science: S/121 Food/06-TF - 1AChandra Deep MishraNo ratings yet
- 14 04 2024 SR Super60 Elite, Target & LIIT BTs Jee Adv2023 P2OnDocument17 pages14 04 2024 SR Super60 Elite, Target & LIIT BTs Jee Adv2023 P2OnOmkar VanjariNo ratings yet
- 29.05.22 - SR - STAR CO-SC - Jee - Adv - 2016 - P1 - GTA-1 - QPDocument17 pages29.05.22 - SR - STAR CO-SC - Jee - Adv - 2016 - P1 - GTA-1 - QPPhani PadmasriNo ratings yet
- SZ2-A - JEE-ADV (2019-P1) - WTA-03 - QP - EXAM DT - 14-08-2021Document16 pagesSZ2-A - JEE-ADV (2019-P1) - WTA-03 - QP - EXAM DT - 14-08-2021Aswatham SrimedhaNo ratings yet
- FTM - 3 - Xi-Ic - Iit - 10 - 07 - 2023 - QPDocument13 pagesFTM - 3 - Xi-Ic - Iit - 10 - 07 - 2023 - QPprayushwankawalaNo ratings yet
- 01.11.20-Pta 10Document30 pages01.11.20-Pta 10Tejas MagguNo ratings yet
- (@bohring - Bot) 12 11 2023 - JR STAR CO SC (MODEL (@HeyitsyashXD)Document21 pages(@bohring - Bot) 12 11 2023 - JR STAR CO SC (MODEL (@HeyitsyashXD)parthmac22No ratings yet
- 11-06-22 - Inc - Sr.iit - Star Co-Sc (Model-B) - Jee Adv - 2018 (P-I) - Wat-49 - QPDocument16 pages11-06-22 - Inc - Sr.iit - Star Co-Sc (Model-B) - Jee Adv - 2018 (P-I) - Wat-49 - QPJEE LEAKSNo ratings yet
- 11 07 21 SR Iit Star Co Scmodel A&b Jee Adv 2017P2 Wat 50 QPDocument17 pages11 07 21 SR Iit Star Co Scmodel A&b Jee Adv 2017P2 Wat 50 QPNaveen Raj VNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Iec TR 62343-6-8-2011Document14 pagesIec TR 62343-6-8-2011Amer AmeryNo ratings yet
- L15 - Parallel Magnetic CircuitsDocument6 pagesL15 - Parallel Magnetic CircuitsParikshit MishraNo ratings yet
- Igorot Village: Get To Know..Document11 pagesIgorot Village: Get To Know..Elain RagosNo ratings yet
- 500 Word LIST Synonim of TOEFLDocument22 pages500 Word LIST Synonim of TOEFLNurul JulinarNo ratings yet
- Text 5Document7 pagesText 5santoshkumarray490No ratings yet
- Orona Fault CodesDocument19 pagesOrona Fault CodesDanushka Bandara100% (1)
- 31. (NÂNG CAO) Đề soạn theo cấu trúc minh họa 2021 - Tiếng Anh - Đề 31 - DươngDocument15 pages31. (NÂNG CAO) Đề soạn theo cấu trúc minh họa 2021 - Tiếng Anh - Đề 31 - DươngNguyễn Quế Anh100% (1)
- Vanilla Farming: The Way Forward: July 2019Document6 pagesVanilla Farming: The Way Forward: July 2019mituNo ratings yet
- Ficha-Tecnica-Tuberia MechDocument2 pagesFicha-Tecnica-Tuberia MechCarlos salazarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Deflection of Beams - Conjugate Beam MethodDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Deflection of Beams - Conjugate Beam MethodMbali MagagulaNo ratings yet
- TotSK 3.0Document22 pagesTotSK 3.0PedroNo ratings yet
- 19 Free Amigurumi Crochet Patterns: MaterialsDocument4 pages19 Free Amigurumi Crochet Patterns: MaterialsLucica Diaconu100% (1)
- Air Cooler With Checking DoorDocument2 pagesAir Cooler With Checking DoorSuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Aluminum Alloy 6351 T6 Sheet SuppliersDocument10 pagesAluminum Alloy 6351 T6 Sheet Supplierssanghvi overseas incNo ratings yet
- (Rect-15) Experimental Study On Partial Replacement of Cement With Coconut Shell Ash in ConcreteDocument3 pages(Rect-15) Experimental Study On Partial Replacement of Cement With Coconut Shell Ash in Concretefrancis dimakilingNo ratings yet
- Responsible Living: Mantri DevelopersDocument15 pagesResponsible Living: Mantri Developersnadaf8No ratings yet
- (Nano and Energy) Gavin Buxton - Alternative Energy Technologies - An Introduction With Computer Simulations-CRC Press (2014) PDFDocument302 pages(Nano and Energy) Gavin Buxton - Alternative Energy Technologies - An Introduction With Computer Simulations-CRC Press (2014) PDFmarcosNo ratings yet
- KRC1 Start-Up PDFDocument29 pagesKRC1 Start-Up PDFRafael50% (2)
- Sunday Afternoon, October 27, 2013: TechnologyDocument283 pagesSunday Afternoon, October 27, 2013: TechnologyNatasha MyersNo ratings yet
- Modeling The Dynamic and Static Behavior of Chemical ProcessesDocument4 pagesModeling The Dynamic and Static Behavior of Chemical ProcessesFatma CahyaniNo ratings yet
- Research Argumentative EssayDocument6 pagesResearch Argumentative EssayHoney LabajoNo ratings yet
- Xu 2020Document11 pagesXu 2020Marco A. R. JimenesNo ratings yet
- Stratigraphy MCQs With AnswerDocument10 pagesStratigraphy MCQs With Answerkumar Harsh67% (3)
- SW Chapter 21 KeyDocument9 pagesSW Chapter 21 KeykylevNo ratings yet
- RadarDocument65 pagesRadarAsifa LiaqatNo ratings yet
- Ddrive Transmission ReportDocument43 pagesDdrive Transmission Reportelah150% (2)
- Service Manual: RP-6000 MK6 LTD RP-6000 MK6 BDocument44 pagesService Manual: RP-6000 MK6 LTD RP-6000 MK6 BFivor EdwardsNo ratings yet
- DattadasDocument4 pagesDattadasJéssica NatáliaNo ratings yet
- Management Science - Lecture 2Document9 pagesManagement Science - Lecture 2Nicole SallanNo ratings yet
- History of DiamondsDocument21 pagesHistory of Diamondssilvernitrate1953No ratings yet