Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bài 2. Những Phần Tử Sinh Học Chủ Yếu Main Biological Molecules
Uploaded by
Rose DN0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views6 pagesOriginal Title
lesson 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views6 pagesBài 2. Những Phần Tử Sinh Học Chủ Yếu Main Biological Molecules
Uploaded by
Rose DNCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Bài 2.
NHỮNG PHẦN TỬ SINH HỌC CHỦ YẾU
MAIN BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES
1. Đọc hiểu (Reading Comprehension)
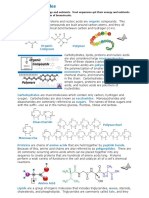
1.1. Inorganic compounds
Inorganic compounds are usually small, ionically bonded molecules.
Water, and many common acids, bases, and salts are examples of inorganic
compounds
Water
Water is the most abundant substance in cells.
Because water is a polar molecule of the decomposition reactions of digestion.
Water is an excellent temperature buffer.
Acids, bases, and salts
An acid dissociates into H+ ions and anions
A base dissociates into OH- ions and cations
A salt dissociates negative and positive ions, neither of which is H+ or OH-
Acid-base balance
The term pH refers to the concentration of H+ in a solution
A solution with a pH of 7 is neutral; a pH below 7 indicates acidity; a pH above
7 Indicates alkalinity.
A pH buffer, which stabilizes the pH inside a cell, can be used in culture media.
1.2. Organic compounds
Organic compounds always contain carbon and hydrogen.
Carbon atoms form up to four bonds with other atoms.
Organic compounds are mostly or entirety covalently bonded, and many of
them are large molecules.
Functional groups
A chain of carbon atoms forms a carbon skeleton.
The letter R may be used to denote a particular functional group of atoms are
responsible for most of the properties of organic molecules.
Frequently encountered classes of molecules are R-OH (alcohol), R-COOH
(organic acids), H2N-R-COOH (amino acids)
Macromolecules
Small organic molecules may combine into very large molecules called
macromolecules.
Monomers usually bond together by dehydration synthesis or condensation
reactions that form water and a polymer.
1.3. Carbonhydrates
Carbohydrates are compounds consisting of atoms of carbon, hydrogen, and
oxygen, with hydrogen and oxygen in a ratio of 2:1.
Carbohydrates include sugars and starches.
Carbohydrates can be divided into three types, monosaccharides,
disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides contain from three to seven carbon atoms.
Monosaccharides may form disaccharides and polysaccharides by dehydration
synthesis.
Polysaccharides and disaccharides may be broken down by hydrolysis, a
reaction involving the splitting of water molecules.
Isomers are two molecules with the same chemical formula but different structures
and properties - for example, glucose (C8H1208) and fructose (C6H1206).
1.4. Lipids
Lipids are a diverse group of compounds distinguished by their insolubility in
water.
Simple lipids (fats) consist of a molecule of glycerol and three molecules of
fatty acids.
A saturated fat has no double bonds between carbon atoms in the fatty acids; an
unsaturated fat has one or more double bonds.
Phospholipids are complex lipids consisting of glycerol, two fatty acids, and
phosphate.
Steroids have carbon ring systems with functional hydroxyl and carbonyl groups.
1.5. Proteins
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins.
Amino acids consist of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and some time sulfur.
Twenty amino acids, peptide bonds (formed by dehydration synthesis) allow the
formation of polypeptide chains.
Protein have four levels of structure - primary (sequence of amino acids),
secondary (regular coils or pleats), tertiary (overall three-dimensional structure of a
polypeptide), and quaternary (two or more polypeptide chains).
Conjugated proteins consist of amino acids combined with other organic or
inorganic compounds.
1.6. Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids - DNA and RNA - are macromolecules consisting of repeating
nucleotides.
A nucleotide is composed of a pentose, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous
base.
A DNA nucleotide consists of deoxyribose (a pentose) and one of these
nitrogenous bases: thymine or cytosine (pyrimidines) or adenine or guanine (purines).
DNA consists of two strands of nucleotides wound in a double helix. The
strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between purine and pyrimidine nucleotides:
A-T and G-C.
An RNA nucleotide consists of ribose (a pentose) and one of these nitrogenous
bases: cytosine, guanine, adenine, or uracil.
1.7. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
ATP stores chemical energy for various cellular activities.
When the bond to ATP's terminal phosphate group is broken, energy is
released.
The energy from decomposition reactions is used to regenerate ATP from
ADP and phosphate.
2. Đọc và dịch sang tiếng Việt các từ vựng mới (Read and Translate into Vietnamese
all new words)
3. Ngữ pháp (Grammars)
3.1. Cách đọc phân số
Thường đọc phân số bằng đọc số đếm cho tử số và số thừ tự cho số ờ mẫu số.
Ví dụ: 1/3: one-third; 1/5: one-fifth; 1/14: one-fourteenth
Thường đọc: 1/2: one-half; 1/4: one-quarter (fourth)
Nếu như tử số lớn hơn 1 thi đọc số đếm, gạch ngang với số thừ.tự kèm theo
3/5: three-fifths; 5/2 five-halves
Với các số lớn hơn hàng trăm thi sẽ đọc từ số + over + sổ đếm ở mẫu số.
147/293: one hundred and forty-seven over two hundred and ninety-three
3.2. Mức độ so sánh
* Mức độ nhỏ hơn của tính từ dài
Volatile: bay hơi
less volatile: khó bay hơi hơn
the least volatile: khó bay hơi nhất
(thêm vào trước tính từ less và the least để chỉ hai mức độ so sánh)
* The... the...
The lighter the percentage of silica, the harder the glass. (Phần trăm oxit silic
càng thấp thì thuỳ tinh càng cứng )
4. Bài tập (Exercises)
4.1. Trả lời câu hỏi (Answer questions)
1. What are organic compounds?
2. What are functional groups?
3. What are carbohydrates?
4. Can you give the definition of lipids and proteins?
5. What is DNA, ATP?
4.2. Dịch sang tiếng Anh (Translate into English)
1. Nước, nhiều loại axit, bazơ, muối là những ví dụ về các hợp chất vô cơ.
2. Từ pH dùng để chỉ nồng độ ion H" trong dung dịch.
3. Dùng dung dịch đệm để ổn định pH trong tế bào và điều chỉnh môt trường
nuôi cáy vi sinh vật.
4. Các polysacarit và disacarit có thề bị cắt mạch bằng axit hoặc enzim.
4.3. Dịch sang tiếng Việt (Translate into Vietmamese)
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology For Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsFrom EverandAnatomy and Physiology For Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Molecules of LifeDocument20 pagesBiochemistry: Molecules of Lifeapi-464344582No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3-Review SentDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 3-Review Senteliza makNo ratings yet
- AP Review Organic CompoundsDocument72 pagesAP Review Organic Compounds둡챙브로No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document9 pagesChapter 9Yash Singh 11th BNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Carbon Compounds: Unit 3: BiochemistryDocument21 pages3.1 Carbon Compounds: Unit 3: Biochemistryapi-520057338No ratings yet
- Organic MoleculesDocument5 pagesOrganic MoleculesHyung BaeNo ratings yet
- Introduction 12Document4 pagesIntroduction 12Abdulrahman AhmadNo ratings yet
- Botnay Notes Class 11Document138 pagesBotnay Notes Class 11Suresh chand100% (1)
- Chapter 02 Winter 2020Document53 pagesChapter 02 Winter 2020LESLI RODRIGUEZ BENDEZUNo ratings yet
- Topic2 Biomolecule PPDocument28 pagesTopic2 Biomolecule PPismail aeryNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Reading Sample Part 1-Edited For NotesDocument2 pagesBiomolecules Reading Sample Part 1-Edited For Notesapi-327757745No ratings yet
- Topic I: Introduction To AnatomyDocument3 pagesTopic I: Introduction To AnatomyCristenNo ratings yet
- Biology ChecklistDocument29 pagesBiology ChecklistgsapkaiteNo ratings yet
- 2 6 Bilogical MoleculesDocument36 pages2 6 Bilogical Moleculesıamnıkolaı 4No ratings yet
- Lec 2Document24 pagesLec 2Abdulrhman MothanaNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULES Note (1st Class)Document10 pagesBIOMOLECULES Note (1st Class)Soumyadeep ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Molecules of LifeDocument5 pagesMolecules of LifeGabriela UnoNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Organic MoleculesDocument7 pagesThe Chemistry of Organic MoleculesPangkat DalawaNo ratings yet
- Ethiopia Institute of Biotechnology: Table: A Comparison of Elements Present in Non-Living and Living MatterDocument25 pagesEthiopia Institute of Biotechnology: Table: A Comparison of Elements Present in Non-Living and Living Mattergebremeskel hagosNo ratings yet
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Document12 pagesStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!M. Amebari NongsiejNo ratings yet
- Submitted To: Meenakshi Ma'am Submitted By: Kunal Singh Shekhawat, Kuldeep Singh RathoreDocument67 pagesSubmitted To: Meenakshi Ma'am Submitted By: Kunal Singh Shekhawat, Kuldeep Singh RathoreKunal Singh Shekhawat100% (1)
- Atoms and MoleculesDocument5 pagesAtoms and MoleculesRelaisa CimafrancaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Chemistry of Life!Document40 pagesBiochemistry: Chemistry of Life!Akhil DonapatiNo ratings yet
- Notes On Lipids and Nucleic Acids-Df 19-1Document21 pagesNotes On Lipids and Nucleic Acids-Df 19-1Albert MweembaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Past Paper QuestionDocument20 pagesBiochemistry Past Paper QuestionAchraf RabadiNo ratings yet
- List of Headings: CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesList of Headings: Carbohydratessneh1509No ratings yet
- Body ChemistryDocument19 pagesBody ChemistryMaisan AbdullghanyNo ratings yet
- Prelim, Chem.b.life. PPT 2Document27 pagesPrelim, Chem.b.life. PPT 2Lindley PareñoNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Level of OrganizationDocument50 pagesThe Chemical Level of OrganizationAizat FarhanNo ratings yet
- Classes of BiomoleculesDocument5 pagesClasses of BiomoleculesChristian BaleNo ratings yet
- Parikh Sneh 100478966 List of HeadingsDocument5 pagesParikh Sneh 100478966 List of Headingssneh1509No ratings yet
- Bio3 SazDocument17 pagesBio3 SazVicente SazilNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument58 pagesBiomoleculesLili MagossNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: The Molecules of LifeDocument8 pagesChapter 3: The Molecules of LifeCourtney FazioNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Notebook PDFDocument105 pagesAP Biology Notebook PDFعمر gamerNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument11 pagesBio Moleculesdemonzslayer809No ratings yet
- Biomolecules Chemistry AssignmentDocument28 pagesBiomolecules Chemistry AssignmentAnurag Singh Thakur67% (3)
- Module 4-Biomolecules: Chemical Composition of Living FormsDocument6 pagesModule 4-Biomolecules: Chemical Composition of Living Formsmpstme placementNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged PDFDocument12 pagesIlovepdf Merged PDFharshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Biological MoleculesDocument28 pagesChapter 4 - Biological MoleculesshammmssNo ratings yet
- Organic CompoundsDocument16 pagesOrganic Compoundsjezzaniexyane28No ratings yet
- Compounds Containing OxygenDocument3 pagesCompounds Containing OxygenLouisse Francheska MercadoNo ratings yet
- HAPP New Module Trans 2Document16 pagesHAPP New Module Trans 2Jared .xNo ratings yet
- CBI4 Structure and Function of BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesCBI4 Structure and Function of BiomoleculesRianna NNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Handout Week5-6Document19 pagesPhysical Science Handout Week5-6Jhay Lorraine Sadian PalacpacNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Chemistry AssignmentDocument23 pagesBiomolecules Chemistry AssignmentArchita PanchalNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Exam 1 - BSC1005 ONLINE - DRDocument9 pagesStudy Guide For Exam 1 - BSC1005 ONLINE - DRJade Melissa MullingsNo ratings yet
- Biology Fall Final ReviewDocument5 pagesBiology Fall Final ReviewtaemintNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and PeptideDocument7 pagesAmino Acids and PeptideHƯNG LIÊU MẠNHNo ratings yet
- Chapt02 - lectureMOD 1Document27 pagesChapt02 - lectureMOD 1Kristin ElderNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Study Guide: NSC 1110 - BiologyDocument14 pagesTutorial Study Guide: NSC 1110 - BiologyKalinda MondeNo ratings yet
- Walang MakakaseethisDocument3 pagesWalang MakakaseethisAlissa YangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Inorganic Compound Inorganic Compound: Acid Base BalanceDocument12 pagesChapter 5: Inorganic Compound Inorganic Compound: Acid Base BalanceSeth SiegfriedNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Life (Biomolecules)Document24 pagesThe Chemistry of Life (Biomolecules)Mam Jay MeeNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate: CarbonDocument6 pagesCarbohydrate: CarbonTrexie JaymeNo ratings yet
- MolBiol HL (2.1, 2.2,2.3.2.4,7.3) BookletDocument37 pagesMolBiol HL (2.1, 2.2,2.3.2.4,7.3) BookletSeo Young YOONNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Chemistry of LifeDocument9 pagesUnit 1 Chemistry of Liferaghad mohammedNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULES NOTE 11aaDocument9 pagesBIOMOLECULES NOTE 11aaGyaniNo ratings yet
- Bio 101 - Integrated Principles of Zoology 18th Edition (Summary of Chapter 2)Document10 pagesBio 101 - Integrated Principles of Zoology 18th Edition (Summary of Chapter 2)Kaeya's asscheeksNo ratings yet
- Harald H. H. W. Schmidt - Franz B. Hofmann - Johannes-Peter Stasch CGMP Generators - Effectors and Therapeutic Implications 2008Document578 pagesHarald H. H. W. Schmidt - Franz B. Hofmann - Johannes-Peter Stasch CGMP Generators - Effectors and Therapeutic Implications 2008Rose DNNo ratings yet
- Tiếng Anh Chuyên Ngành: Bài GiảngDocument21 pagesTiếng Anh Chuyên Ngành: Bài GiảngRose DNNo ratings yet
- Bài 5. Giới Thiệu Về Sản Xuất Bánh Bích Quy Introduction To Biscuit - MakingDocument14 pagesBài 5. Giới Thiệu Về Sản Xuất Bánh Bích Quy Introduction To Biscuit - MakingRose DNNo ratings yet
- Bài 4. Quá Trình Chế Biến Tiếp Theo - Các Loại Thực Phẩm Từ Ngũ Cốc - Secondary Processing - Cereal Based FoodDocument7 pagesBài 4. Quá Trình Chế Biến Tiếp Theo - Các Loại Thực Phẩm Từ Ngũ Cốc - Secondary Processing - Cereal Based FoodRose DNNo ratings yet
- Bernard Mourrain_ Scott Schaefer_ Guoliang Xu Advances in Geometric Modeling and Processing 6th International Conference_ GMP 2010_ Castro Urdiales_ Spain_ June 16-18_ 2010_ Proceedings LectureDocument324 pagesBernard Mourrain_ Scott Schaefer_ Guoliang Xu Advances in Geometric Modeling and Processing 6th International Conference_ GMP 2010_ Castro Urdiales_ Spain_ June 16-18_ 2010_ Proceedings LectureRose DNNo ratings yet
- Bài 2. Những Phần Tử Sinh Học Chủ Yếu Main Biological MoleculesDocument6 pagesBài 2. Những Phần Tử Sinh Học Chủ Yếu Main Biological MoleculesRose DNNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Food Safety and QualityDocument7 pages1.1. Food Safety and QualityRose DNNo ratings yet
- PNW 355 PicklingvegetablesDocument20 pagesPNW 355 PicklingvegetablesLívia Magalhaes CarneiroNo ratings yet
- 5 AcidifiedfoodsDocument2 pages5 AcidifiedfoodsRose DNNo ratings yet
- Aspergillus Flavus: Genomics: Gateway To Human and Animal Health, Food Safety, and Crop Resistance To DiseasesDocument9 pagesAspergillus Flavus: Genomics: Gateway To Human and Animal Health, Food Safety, and Crop Resistance To DiseasesRose DNNo ratings yet
- HACCP Infomation All 1102Document98 pagesHACCP Infomation All 1102Rose DNNo ratings yet
- Aflatoxin B1: Toxicity, Characteristics and Analysis: Mini ReviewDocument8 pagesAflatoxin B1: Toxicity, Characteristics and Analysis: Mini ReviewRose DNNo ratings yet
- Production and Enzyme Activity of An ExtracellularDocument9 pagesProduction and Enzyme Activity of An ExtracellularRose DNNo ratings yet
- Aflatoxin B1: Toxicity, Characteristics and Analysis: Mini ReviewDocument8 pagesAflatoxin B1: Toxicity, Characteristics and Analysis: Mini ReviewRose DNNo ratings yet
- Saberian Hamidi AbbasiDocument10 pagesSaberian Hamidi AbbasiRose DNNo ratings yet
- BAI GIANG 75T English For TourismDocument35 pagesBAI GIANG 75T English For TourismRose DNNo ratings yet
- Phy Sci Test 1 CMHDocument8 pagesPhy Sci Test 1 CMHDaniel Scott RayNo ratings yet
- Review On The Recent Developments in The Solvent Extraction of ZincDocument31 pagesReview On The Recent Developments in The Solvent Extraction of ZincCarlos Mardones LunaNo ratings yet
- On Some Imperative IEEE Standards For Usage of Natural Ester Liquids in TransformersDocument12 pagesOn Some Imperative IEEE Standards For Usage of Natural Ester Liquids in TransformersDante FilhoNo ratings yet
- Hastelloys B3 WeldingrodsDocument3 pagesHastelloys B3 WeldingrodsOZAIRTRADELINKNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesChemistry Cheat SheetgaarryNo ratings yet
- Markscheme: May 2016 Chemistry Higher Level Paper 3Document33 pagesMarkscheme: May 2016 Chemistry Higher Level Paper 3Aleksander ZiolkowskiNo ratings yet
- Ans and Sol Jee Main 2022 Phase 1 25 06 2022 e Chemistry FinalDocument7 pagesAns and Sol Jee Main 2022 Phase 1 25 06 2022 e Chemistry FinalvishNo ratings yet
- Caustic Soda PDFDocument2 pagesCaustic Soda PDFEmad JamshidiNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases Phet: Solution Equation PH Most Abundant MoleculeDocument2 pagesAcids and Bases Phet: Solution Equation PH Most Abundant MoleculeZachary NeuNo ratings yet
- 0620 w19 QP 42 PDFDocument12 pages0620 w19 QP 42 PDFrosganNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ReportDocument109 pagesChemistry ReportMARY JOY PIOSCANo ratings yet
- KV 2Document3 pagesKV 2Branko FerenčakNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Folio Chapter 9 Form 4Document27 pagesChemistry Folio Chapter 9 Form 4Suhaila MohamedNo ratings yet
- A Survey Report On PreservativesDocument46 pagesA Survey Report On Preservatives0921pyNo ratings yet
- Biodegradability Under Marine Conditions of Bio-Based and Petroleum-Based PolymersDocument10 pagesBiodegradability Under Marine Conditions of Bio-Based and Petroleum-Based Polymersbradley wilsonNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 Chemical Reactions and Balancing Chemical Equations IDocument6 pagesActivity 5 Chemical Reactions and Balancing Chemical Equations INivla Genesis100% (2)
- Rhubarb Individual Scientific InvestigationDocument12 pagesRhubarb Individual Scientific InvestigationWika PrayogiNo ratings yet
- 4216-4217 Papaverine HydrochlorideDocument2 pages4216-4217 Papaverine HydrochloridePutri AmandaNo ratings yet
- Chem ProjectDocument14 pagesChem ProjectSudhasathvik ReddyNo ratings yet
- Alkene Reaction GuideDocument41 pagesAlkene Reaction GuideAbhishek Isaac MathewNo ratings yet
- I04IA019EN-A Micropore Size Analysis of Porous CarbonsDocument4 pagesI04IA019EN-A Micropore Size Analysis of Porous CarbonsDwi Sandi Argo ArnowoNo ratings yet
- Aci 221R-96Document3 pagesAci 221R-96farhadamNo ratings yet
- Magic Extraction - Title - Magic Liqueur - The Ultimate Trip - UpdateDocument7 pagesMagic Extraction - Title - Magic Liqueur - The Ultimate Trip - Updatejeej00No ratings yet
- EPA Method 1657 AccuStandardDocument39 pagesEPA Method 1657 AccuStandardduygu9merve100% (1)
- 922 Water ActivityDocument8 pages922 Water ActivityRajib Kumar BaishnabNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Organic Functional Group Transformations IIDocument1,209 pagesComprehensive Organic Functional Group Transformations IIHello World100% (1)
- Technical Report of Formic Acid PlantDocument6 pagesTechnical Report of Formic Acid PlantMuzzamilNo ratings yet
- ICES 2019 Book of Abstracts 1 PDFDocument237 pagesICES 2019 Book of Abstracts 1 PDFilmiNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Root Growth, Antioxidant Enzyme Activity and Mineral Absorability of Carnation Grown in Two SystemsDocument11 pagesEvaluation of Root Growth, Antioxidant Enzyme Activity and Mineral Absorability of Carnation Grown in Two SystemsAhmad Hassan ChNo ratings yet
- Point Defects in SolidsDocument37 pagesPoint Defects in SolidsSachi SinghNo ratings yet
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Meltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalFrom EverandMeltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableFrom EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsFrom EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNo ratings yet
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeFrom EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookFrom EverandBioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Phase Equilibria in Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandPhase Equilibria in Chemical EngineeringRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeFrom EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireFrom EverandA Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (129)
- Transformer: The Deep Chemistry of Life and DeathFrom EverandTransformer: The Deep Chemistry of Life and DeathRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)