Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aiims Covid Doc 1.6.1-1
Aiims Covid Doc 1.6.1-1
Uploaded by
Ankit Rathi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageAiims Covid Doc 1.6.1-1
Aiims Covid Doc 1.6.1-1
Uploaded by
Ankit RathiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
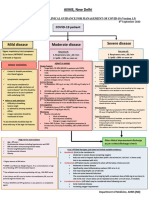
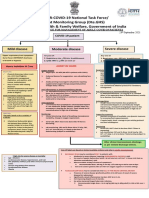
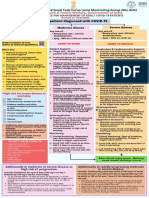
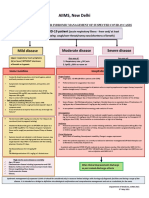
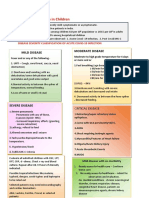
AIIMS, New Delhi
INTERIM CLINICAL GUIDANCE FOR MANAGEMENT OF COVID-19 (Version 1.6)
7th April 2021
COVID-19 patient
Mild disease Moderate disease Severe disease
Upper respiratory tract symptoms Any one of: Any one of:
(&/or fever) WITHOUT shortness 1. Respiratory rate > 24 /min 1. Respiratory rate > 30 /min
of breath or hypoxia 2. SpO2 < 94% on room air 2. SpO2 < 90% on room air
ADMIT IN WARD ADMIT IN ICU
Home Isolation Oxygen Support: Respiratory support
➢ Target SpO2: 92-96% (88-92% in patients with COPD) • Consider use of HFNC in patients with increasing oxygen
➢ Preferred devices for oxygenation: non-rebreathing face requirement, if work of breathing is LOW
✓ Contact & droplet precautions; • A cautious trial of NIV with helmet interface (if available
mask
strict hand hygiene otherwise face mask interface)/CPAP with oro-nasal mask may
➢ Awake proning may be used in those with persistent
also be considered
hypoxia despite use of high flow oxygen (sequential
✓ Symptomatic management • Intubation should be prioritized in patients with high work of
position changes every 1-2 hours)
breathing /if NIV is not tolerated ^^
• Conventional ARDSnet protocol for ventilatory management
✓ Stay in contact with treating Antiviral therapy
Antiviral therapy
physician ➢ Inj Remdesivir 200 mg IV on day 1 f/b 100 mg IV daily for 5
• Antivirals may be considered if duration of illness < 10-14 days
days (can be extended upto 10 days in case of progressive
disease) Anti-inflammatory or immunomodulatory therapy
• Seek immediate medical attention if: ➢ Convalescent plasma (CP) may be considered in carefully • Inj Methylprednisolone 1 to 2mg/kg in 2 divided doses for 5 to
o Difficulty in breathing selected patients 10 days (or equivalent dose of dexamethasone)
o High-grade fever/ severe cough • Tocilizumab may be considered on a case-to-case basis
o A low threshold should be kept Anti-inflammatory or immunomodulatory therapy preferably within 24 to 48 hours of progression to severe
for patients with high-risk factor* ➢ Inj Methylprednisolone 0.5 to 1 mg/kg (or equivalent dose disease
of dexamethasone) IV in two divided doses for 5 to 10 days
❖ Peripheral oxygen saturation (by
Anticoagulation
applying a SpO2 probe to fingers) Anticoagulation • Intermediate dose prophylactic UFH or LMWH (e.g., Enoxaparin
should be monitored at home ➢ Low dose prophylactic UFH or LMWH## (weight based e.g., 0.5mg/kg/dose BD SC) ##
enoxaparin 0.5mg/kg per day SC)
Supportive measures
❖ Tab Ivermectin (200 mcg/kg once Monitoring • Maintain euvolemia
➢ Clinical Monitoring: Work of breathing, Hemodynamic • If sepsis/septic shock: manage as per existing protocol and local
a day for 3 to 5 days) may be antibiogram
considered in patients with high- instability, Change in oxygen requirement
➢ Serial CXR, HRCT Chest (if worsening) Monitoring
risk features* ➢ Serial CXR, HRCT Chest (if worsening)
➢ Lab monitoring: CRP, D-dimer & Ferritin 48-72 hrly; CBC,
❖ Steroids should NOT be used in ➢ Lab monitoring: CRP, D-dimer & Ferritin 24-48 hrly; CBC, LFT,
LFT, KFT 24-48 hrly; IL-6 levels to be done if deteriorating
KFT daily; IL-6 levels to be done if deteriorating (subject to
patients with only mild disease (subject to availability) availability)
*High-risk for severe disease or mortality After clinical Improvement discharge
✓ Advanced age particularly > 60 years
✓ Cardiovascular disease including hypertension and CAD as per revised discharge criteria
✓ DM (Diabetes mellitus) and other immunocompromised
EUA/Off label (use based on limited available evidence):
states
✓ Chronic lung/kidney/liver disease ➢ Remdesivir (EUA) to be considered in
✓ Cerebrovascular disease o Moderate to severe disease (NOT to be used in those with only mild disease)
✓ Obesity o No renal or hepatic dysfunction (eGFR <30 ml/min/m2; AST/ALT >5 times ULN) (Not an absolute contraindication)
➢ Tocilizumab (Off-label) may be considered when all of the below criteria are met
o Severe disease
o Significantly raised inflammatory markers (CRP &/or IL-6)
o Not improving despite use of steroids
^^Higher chances of NIV failure o No active bacterial/ fungal infections
The recommended dose is 4 to 8mg/kg (with a maximum dose of 800 mg at one time) in 100 ml NS over 1 hour (dose can be repeated
## once after 12 to 24 hours depending on clinical response)
LMWH: Low Molecular Weight Heparin: if no contraindication
or high risk of bleeding; UFH: Unfractionated heparin ➢ Convalescent plasma may be considered when following criteria are met
[Type here] o
o
Early moderate disease (preferably within 7 days of disease onset and if seronegative)
Availability of high-titre plasma
➢ Department of Medicine, AIIMS (ND)
You might also like
- AIIMS COVID Algorithm 1.5-1 PDFDocument1 pageAIIMS COVID Algorithm 1.5-1 PDFAnutosh BhaskarNo ratings yet
- COVID19 Management Algorithm 22042021 v1Document1 pageCOVID19 Management Algorithm 22042021 v1shivani shindeNo ratings yet
- AIIMS/ ICMR-COVID-19 National Task Force/ Joint Monitoring Group (Dte - GHS) Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of IndiaDocument1 pageAIIMS/ ICMR-COVID-19 National Task Force/ Joint Monitoring Group (Dte - GHS) Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of IndiaSomnath Das GuptaNo ratings yet
- COVID Management 17th January 2022 DR Suvrankar Datta AIIMSDocument1 pageCOVID Management 17th January 2022 DR Suvrankar Datta AIIMSWhiteNo ratings yet
- COVID Clinical Management 14012022Document1 pageCOVID Clinical Management 14012022Naina DesaiNo ratings yet
- Adult Patient Diagnosed With COVID-19: Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of IndiaDocument1 pageAdult Patient Diagnosed With COVID-19: Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of Indiapramodbankhele3845No ratings yet
- Treatment Protocol Covid-19Document4 pagesTreatment Protocol Covid-19Shiv singhNo ratings yet
- WB Covid Protocol Book 25.09 .20 (1)Document49 pagesWB Covid Protocol Book 25.09 .20 (1)El MirageNo ratings yet
- Treatment Guidance For COVID-19 - 6 December 2020Document1 pageTreatment Guidance For COVID-19 - 6 December 2020meiraimNo ratings yet
- COVID MX BsmmuDocument2 pagesCOVID MX BsmmuNuhiat NahreenNo ratings yet
- AIIMS Issues New Guidelines For Treatment of CovidDocument7 pagesAIIMS Issues New Guidelines For Treatment of Covidsenthil kumarNo ratings yet
- AIIMS Issues New Guidelines For Treatment of Covid-19 Cases: (Enter Post Title Here)Document7 pagesAIIMS Issues New Guidelines For Treatment of Covid-19 Cases: (Enter Post Title Here)senthil kumarNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Confirmed Covid 19 Patient: Department of Health & Family Welfare, Govt of West BengalDocument2 pagesLaboratory Confirmed Covid 19 Patient: Department of Health & Family Welfare, Govt of West BengalSujoyDeNo ratings yet
- AIIMS Syndromic ApproachDocument1 pageAIIMS Syndromic ApproachRagul VNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Management of Covid-19 Algorithm-EngDocument1 pageCritical Care Management of Covid-19 Algorithm-EngMr CROWNo ratings yet
- NIV ProformaDocument10 pagesNIV ProformaWael N Sh GadallaNo ratings yet
- ADRIANO BONDOC ORSOLINO VIADOR - Docx 1Document10 pagesADRIANO BONDOC ORSOLINO VIADOR - Docx 1Luis LazaroNo ratings yet
- Recommendation For The Use of Antibiotics For The Treatment of InfectionDocument5 pagesRecommendation For The Use of Antibiotics For The Treatment of InfectionGem BorjaNo ratings yet
- MX Protocol Book FinalDocument42 pagesMX Protocol Book FinalPawan ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Fluid Therapy: CroupDocument2 pagesNutrition and Fluid Therapy: CroupnasibdinNo ratings yet
- Empirical First Line AntibioticsDocument1 pageEmpirical First Line Antibioticsdiati zahrainiNo ratings yet
- ICU One Pager ARDS v1.1Document1 pageICU One Pager ARDS v1.1Michael LevitNo ratings yet
- BCCA AB in Febrile Neutropenia GuidelinesDocument2 pagesBCCA AB in Febrile Neutropenia GuidelinesAlvy SyukrieNo ratings yet
- WB COVID19 Latest Treatment ProtocolDocument1 pageWB COVID19 Latest Treatment ProtocolRahul AwasthiNo ratings yet
- RFH COVID-19 ICU Resource Pack FULL PDFDocument15 pagesRFH COVID-19 ICU Resource Pack FULL PDFQuique GarciaNo ratings yet
- AHS антибиотики рекомендацDocument42 pagesAHS антибиотики рекомендацMaksym DemianchukNo ratings yet
- Management of Status Epilepticus 2022Document8 pagesManagement of Status Epilepticus 2022albert siraitNo ratings yet
- Croup Summary PDFDocument2 pagesCroup Summary PDFnurfitriaNo ratings yet
- 02-AirwayManage 2021Document26 pages02-AirwayManage 2021Kajanthan SatkunarajahNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument6 pagesPulmonary TuberculosisStefhanie Mae LazaroNo ratings yet
- CASE PRESENTATION PneumoniaDocument13 pagesCASE PRESENTATION PneumoniaHari Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- 00.00 Reference Care Plan Tonsillectomy and Adnoidectomy Post OpDocument5 pages00.00 Reference Care Plan Tonsillectomy and Adnoidectomy Post OpMarya KemmieNo ratings yet
- 00 00 Reference Care Plan Tonsillectomy and Adnoidectomy Post OpDocument5 pages00 00 Reference Care Plan Tonsillectomy and Adnoidectomy Post OpAnita LopokoiyitNo ratings yet
- Streptococcus Pneumoniae Haemophilus Influenzae: Click HereDocument3 pagesStreptococcus Pneumoniae Haemophilus Influenzae: Click HereSiti Hidayatul FitriNo ratings yet
- Asymptomatic Severe Moderate Mild: Comprehensive Guidelines For Management of COVID-19 PatientsDocument9 pagesAsymptomatic Severe Moderate Mild: Comprehensive Guidelines For Management of COVID-19 PatientsVaishnavi JayakumarNo ratings yet
- FluticasoneDocument3 pagesFluticasoneAmberNo ratings yet
- Child With Fits in ED - Srl.Document2 pagesChild With Fits in ED - Srl.azeemNo ratings yet
- BNM Covid FrancesDocument4 pagesBNM Covid FrancesMISSAEL ESPINOZANo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Nursing ResposibilitiesDocument10 pagesDrug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Nursing ResposibilitiesAngelicaNo ratings yet
- Module 9 Mechanical Ventilation PDFDocument46 pagesModule 9 Mechanical Ventilation PDFChabboo SutabrataNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Tract Infections - Med DidacticsDocument59 pagesRespiratory Tract Infections - Med Didacticsapi-649060644No ratings yet
- Guideline For Management Protocol of Children With Fever and Respiratory SymptomsDocument44 pagesGuideline For Management Protocol of Children With Fever and Respiratory SymptomsKushagr GautamNo ratings yet
- TreatmentProtocol 10-4-2021Document3 pagesTreatmentProtocol 10-4-2021Anishk SinghNo ratings yet
- Respirology 2023 FinalDocument127 pagesRespirology 2023 FinalBelinda ELISHANo ratings yet
- General Principles of Antibiotic TherapyDocument44 pagesGeneral Principles of Antibiotic TherapyFadhly SharimanNo ratings yet
- 7698alorithm SeizureDocument3 pages7698alorithm Seizureboromeus abyasa daniswara100% (1)
- Suspected COVID-19 Cases Management in Triage HospitalsDocument6 pagesSuspected COVID-19 Cases Management in Triage HospitalsMuhamed RamadanNo ratings yet
- Management of Acute Respiratory Failure in COVID-PUI Patient - Updated Feb. 2021Document7 pagesManagement of Acute Respiratory Failure in COVID-PUI Patient - Updated Feb. 2021Abhishek GoelNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Therapeutic Guidance COVID-19 Therapeutic Guidance COVID-19 Therapeutic GuidanceDocument1 pageCOVID-19 Therapeutic Guidance COVID-19 Therapeutic Guidance COVID-19 Therapeutic GuidanceAbdullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Hospital ManDocument1 pageAntibiotic Hospital Manarshiya.manasekiNo ratings yet
- Management of CAP in Adults - Ontario GovernmentDocument2 pagesManagement of CAP in Adults - Ontario GovernmentSukhvir AujlaNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia NotesDocument16 pagesAnesthesia NotesJulie Anne AciertoNo ratings yet
- Prone Position Guidelines-2Document14 pagesProne Position Guidelines-2SAMINo ratings yet
- AppendicitisDocument2 pagesAppendicitisYosuaNo ratings yet
- COVID - Management 14 April 2021Document20 pagesCOVID - Management 14 April 2021Zain ZaidiNo ratings yet
- New May2020 PDFDocument7 pagesNew May2020 PDFDoctorMoodyNo ratings yet
- NICU ABX ChartDocument11 pagesNICU ABX ChartdrchiNo ratings yet
- 2021 Final - COVID 19 IN CHILDREN PROTOCOLDocument12 pages2021 Final - COVID 19 IN CHILDREN PROTOCOLSutirtha RoyNo ratings yet
- Differentiating Anesthesia Equipment: Identify and Understand Anesthesia Equipment in 1 Hour (Including the most popular manufacturers and suppliers to buy Anesthesia Equipment)From EverandDifferentiating Anesthesia Equipment: Identify and Understand Anesthesia Equipment in 1 Hour (Including the most popular manufacturers and suppliers to buy Anesthesia Equipment)No ratings yet
- Local Anesthesia Made Easy: Complete Guide on How to make your Local Anesthetic Procedure a Success (Including a List of Anesthetic Equipment and their Uses)From EverandLocal Anesthesia Made Easy: Complete Guide on How to make your Local Anesthetic Procedure a Success (Including a List of Anesthetic Equipment and their Uses)No ratings yet
- Meditation and MindfulnessDocument11 pagesMeditation and MindfulnessmbhangaleNo ratings yet
- Javascript: Introduction To ScriptingDocument26 pagesJavascript: Introduction To ScriptingmbhangaleNo ratings yet
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner-Exam Guide en v1.6Document3 pagesAWS Certified Cloud Practitioner-Exam Guide en v1.6mbhangale0% (1)
- Your Guide To Vitamin PDFDocument34 pagesYour Guide To Vitamin PDFmbhangale100% (1)
- Computer Megamart: # 4 & 5, G.V. Complex, P.P.Lane, S.P. Road Cross, Banglore - 560002Document34 pagesComputer Megamart: # 4 & 5, G.V. Complex, P.P.Lane, S.P. Road Cross, Banglore - 560002mbhangaleNo ratings yet
- Computer Megamart: # 4 & 5, G.V. Complex, P.P.Lane, S.P. Road Cross, Banglore - 560002Document34 pagesComputer Megamart: # 4 & 5, G.V. Complex, P.P.Lane, S.P. Road Cross, Banglore - 560002mbhangaleNo ratings yet
- Kafka Reference ArchitectureDocument12 pagesKafka Reference ArchitecturembhangaleNo ratings yet
- Build Systems: Input File Exec. TaskDocument35 pagesBuild Systems: Input File Exec. TaskmbhangaleNo ratings yet
- Spring Annotations Reference: Spring MVC Spring Boot Spring Data JPA This BlogDocument6 pagesSpring Annotations Reference: Spring MVC Spring Boot Spring Data JPA This BlogmbhangaleNo ratings yet
- LNT PricelistDocument104 pagesLNT PricelistmbhangaleNo ratings yet
- LNT MCCBs Technical CatalogueDocument20 pagesLNT MCCBs Technical CataloguembhangaleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Spring Framework and Dependency Injection: Aaron ZeckoskiDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Spring Framework and Dependency Injection: Aaron ZeckoskimbhangaleNo ratings yet
- Spring Annotations Reference: Spring MVC Spring Boot Spring Data JPA This BlogDocument6 pagesSpring Annotations Reference: Spring MVC Spring Boot Spring Data JPA This BlogmbhangaleNo ratings yet
- Network Standards: ISQS 3349/6341Document9 pagesNetwork Standards: ISQS 3349/6341mbhangaleNo ratings yet
- The Squat-Proper Form, Technique and AdvantagesDocument1 pageThe Squat-Proper Form, Technique and AdvantagesmbhangaleNo ratings yet
- Web Services and Contemporary SOA (Part II: Advanced Messaging, Metadata, and Security)Document60 pagesWeb Services and Contemporary SOA (Part II: Advanced Messaging, Metadata, and Security)mbhangaleNo ratings yet
- Securing Web Services: Application Program SecurityDocument9 pagesSecuring Web Services: Application Program SecuritymbhangaleNo ratings yet
- 05 Multithreadng - Threads and SwingDocument38 pages05 Multithreadng - Threads and SwingmbhangaleNo ratings yet
- WAS On Mainframe Soultion OutlineDocument10 pagesWAS On Mainframe Soultion OutlinembhangaleNo ratings yet
- IntroductionToSCM (Asset)Document53 pagesIntroductionToSCM (Asset)mbhangaleNo ratings yet
- 7 ThreadsDocument19 pages7 ThreadsmbhangaleNo ratings yet
- Seminar On: Software Testing: A Practioner'S ApproachDocument202 pagesSeminar On: Software Testing: A Practioner'S ApproachmbhangaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document22 pagesChapter 8mbhangaleNo ratings yet
- Business Process IntegrationDocument22 pagesBusiness Process IntegrationmbhangaleNo ratings yet
- CorbaDocument962 pagesCorbambhangaleNo ratings yet
- Web Sphere Vs NetDocument17 pagesWeb Sphere Vs NetmbhangaleNo ratings yet
- Suvendu Hota Cowin CertificateDocument1 pageSuvendu Hota Cowin CertificateHemalika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dental PanoramicDocument19 pagesDental Panoramicسعدون بن مساعد العبدالمنعمNo ratings yet
- Press Ganey and PainDocument13 pagesPress Ganey and PainmeganNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Treatment in The Management of Cleft Lip and PalateDocument13 pagesOrthodontic Treatment in The Management of Cleft Lip and PalatecareNo ratings yet
- VaricellaDocument38 pagesVaricellapinanoeNo ratings yet
- Expose-news.com-Deagels Depopulation Forecast Confirmed by Heavily Censored Pfizer DocumentsDocument22 pagesExpose-news.com-Deagels Depopulation Forecast Confirmed by Heavily Censored Pfizer Documentslpamgt_674780425No ratings yet
- 25817-Unit 453 Professional Practice of Sports Massage Syllabus V1Document6 pages25817-Unit 453 Professional Practice of Sports Massage Syllabus V1JackNo ratings yet
- Family and Medical LeaveDocument5 pagesFamily and Medical LeaveGeorge RizkNo ratings yet
- Melio Ebook DKDocument429 pagesMelio Ebook DKStaporn Kasemsripitak100% (1)
- Picot PaperDocument10 pagesPicot PaperFatoumata BayoNo ratings yet
- Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation - Bill & Melinda Gates FoundationDocument7 pagesBill & Melinda Gates Foundation - Bill & Melinda Gates FoundationkelvinkinergyNo ratings yet
- UNIT 16 Spa Treatments Syllabus V2Document7 pagesUNIT 16 Spa Treatments Syllabus V2Jowie SooNo ratings yet
- Managing Covid 19 Patients Nurses Role and ConsiderationsDocument7 pagesManaging Covid 19 Patients Nurses Role and ConsiderationsSimona Marcela ȚibuleacNo ratings yet
- Cheers Statement IsporDocument5 pagesCheers Statement IsporKatherine CuéllarNo ratings yet
- Towards Universal Health Coverage and Sustainable Financing in Afghanistan: Progress and ChallengesDocument5 pagesTowards Universal Health Coverage and Sustainable Financing in Afghanistan: Progress and ChallengesAyu NovitaNo ratings yet
- Dyspepsia PDFDocument14 pagesDyspepsia PDFCdma Nastiti FatimahNo ratings yet
- 3 04 Functions and Disorders of The EarDocument21 pages3 04 Functions and Disorders of The Earapi-181703758No ratings yet
- Ada 2017Document142 pagesAda 2017Ana Maria Ramos Rojas100% (1)
- Mental RetardationDocument27 pagesMental RetardationDiah LouNo ratings yet
- Med Student CV ExampleDocument2 pagesMed Student CV Examplealmas prawotoNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Obturator Design For Partially Edentulous Patients. Part I ClassificationDocument3 pagesBasic Principles of Obturator Design For Partially Edentulous Patients. Part I ClassificationNaveen S Yadav100% (1)
- Siemens SC8000 - Service ManualDocument134 pagesSiemens SC8000 - Service ManualmalucNo ratings yet
- 6 POSTNATAL Case - Book Rupi - OBS p367-534Document168 pages6 POSTNATAL Case - Book Rupi - OBS p367-534piyush0751100% (1)
- Hospital Experiences Responding To The COVID-19 PandemicDocument41 pagesHospital Experiences Responding To The COVID-19 PandemicLaw&CrimeNo ratings yet
- RenalDocument25 pagesRenalCamaligan RockyNo ratings yet
- SGD 10 - Obstetrics & Gynecology and Community HealthDocument4 pagesSGD 10 - Obstetrics & Gynecology and Community HealthBrandonRyanF.MosidinNo ratings yet
- Final End of Life CareDocument38 pagesFinal End of Life CareArchana Panika100% (4)
- Liver Transplant Handbook Contents Introduction 1. Liver Liver Disease 2.Document31 pagesLiver Transplant Handbook Contents Introduction 1. Liver Liver Disease 2.tasarimkutusuNo ratings yet
- Wikipedia - Neonatal Conjunctivitis (CHECKED)Document4 pagesWikipedia - Neonatal Conjunctivitis (CHECKED)pixoguiasNo ratings yet
- Martindale The Extra PharmacopoeiaDocument2 pagesMartindale The Extra PharmacopoeiaMeysiska TrisnaningtyasNo ratings yet