Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Van't Hoff Factor Colligative Properties
Uploaded by
John JosephOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Van't Hoff Factor Colligative Properties
Uploaded by
John JosephCopyright:
Available Formats
We are asked to determine which substance (sucrose or CaCl2) has a greater effect on the boiling
point elevation and freezing point depression.
On adding sucrose and CaCl2 to water, the boiling point and the freezing point of the solution
changes with respect to that of pure water. The change in the boiling point and the freezing point is
due to the number of solute particles in the solvent.
On dissolving sucrose and CaCl2 in water, let ‘i’ be the number of solute particles that will
dissociate into the solvent. This is also called the Van’t Hoff factor
The change in the freezing and boiling point temperatures are given by,
Δ Tb = kb*i*m
Δ Tf = kf*i*m
Where
Δ Tb = boiling point of solution- boiling point of pure solvent
kb = boiling point elevation constant of the solvent. For water it is 0.51 °C/m
m= molality of the solution (moles of solute/kg of solvent)
kf= freezing point depression constant. For water it is 1.86 °C/m
We are given the change in the boiling points and freezing points of the respective solutions.
Therefore we can find ‘i’ by plotting a graph of ΔT on y axis vs k*m on the x axis.
Taking sucrose solution:
The effect of sucrose on the boiling point of water:
Mass of water (g) 100
Mass of sucrose (g) 2.5 5 7.5 10
moles of sucrose 0.007 0.015 0.022 0.029
molality of solution
(m) 0.07 0.15 0.22 0.29
Boiling point
elevation 0.03 0.08 0.11 0.13
kb*m 0.0357 0.0765 0.1122 0.1479
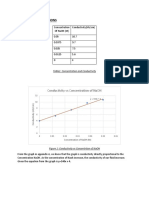
Plotting the graph we get,
Effect of sucrose on BP
0.14
f(x) = 0.89 x + 0
0.12 R² = 0.97
0.1
Boiling point elevation
0.08
bp_elevation
0.06 Linear (bp_elevation)
0.04
0.02
0
0.02 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.1 0.12 0.14 0.16
Kb*m
The trendline of the curve gives us the equation of the line and from the slope, i= 0.89
Similarly for the effect of sucrose on the freezing point of the solution,
Mass of water (g) 100
Mass of sucrose (g) 2.5 5 7.5 10
moles of sucrose 0.007 0.015 0.022 0.029
molality of solution
(m) 0.07 0.15 0.22 0.29
freezing point
depression 0.13 0.26 0.39 0.5
Kf*m 0.1302 0.279 0.4092 0.5394
The graph is
The trendline of the curve gives us the equation of the line and from the slope, i= 0.91
Taking CaCl2 solutions:
Effect of CaCl2 on the boiling point of the solution,
The trendline of the curve gives us the equation of the line and from the slope, i= 2.70
Effect of CaCl2 on the freezing point of the solution,
The trendline of the curve gives us the i value of i = 2.67
Therefore, from the given data it is clear that CaCl2 has a more pronounced effect on the boiling
point elevation and freezing point depression.
From the graph, we see that this is because CaCl2 dissociates into more solute particles in solution
compared to sucrose (greater i values)
You might also like
- MT Example LeachingDocument19 pagesMT Example LeachingAshish RajakNo ratings yet
- Results and DiscussionsDocument8 pagesResults and DiscussionsSalihah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometric Study of Complexes by Job's Method: Report of The Minor UGC Project EntitledDocument19 pagesSpectrophotometric Study of Complexes by Job's Method: Report of The Minor UGC Project EntitledM Irfan Khan100% (1)
- Residence Time Distribution Analysis of A Continuous Stirred Tank ReactorDocument10 pagesResidence Time Distribution Analysis of A Continuous Stirred Tank ReactorNurul IzzahNo ratings yet
- Calculation & Discussion PFR CHE506Document9 pagesCalculation & Discussion PFR CHE506Wahyuningsih YuniNo ratings yet
- MD - Saiful Islam 17... 101Document25 pagesMD - Saiful Islam 17... 101izarul islamNo ratings yet
- Objective:: σ and hasDocument9 pagesObjective:: σ and hasfareeha saeedNo ratings yet
- Analisis Pembahasan Laju ReaksiDocument11 pagesAnalisis Pembahasan Laju ReaksiLia Yuli KusumaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: Aicd-Base TitrationDocument12 pagesLab Report: Aicd-Base TitrationJeff LimNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium - Tutorial-Answersv1Document14 pagesChemical Equilibrium - Tutorial-Answersv1Farah AinaNo ratings yet
- Conductance of SolutionDocument6 pagesConductance of SolutionHatmylifeNo ratings yet
- Collogative Properties: Vapor Pressure LoweringDocument2 pagesCollogative Properties: Vapor Pressure LoweringKryzler KayeNo ratings yet
- NCHE312Document11 pagesNCHE312Charmaine MoyoNo ratings yet
- CSTR 40 L Result Plus Conc, Recommendation, AnalysisDocument8 pagesCSTR 40 L Result Plus Conc, Recommendation, AnalysisFea MeenNo ratings yet
- Results and CalculationsDocument5 pagesResults and CalculationsGriezmann HaziqNo ratings yet
- Iodine LabDocument4 pagesIodine LabHuang ViviNo ratings yet
- Pressure To Decrease Increase The Amount of Power That A Pump Must Deliver To The FluidDocument42 pagesPressure To Decrease Increase The Amount of Power That A Pump Must Deliver To The FluidNixon RamsaranNo ratings yet
- Benzoic - Acid ExperimentDocument7 pagesBenzoic - Acid ExperimentShivani SinghNo ratings yet
- Pressure Decreases Increase The Amount of Power That A Pump Must Deliver To The FluidDocument40 pagesPressure Decreases Increase The Amount of Power That A Pump Must Deliver To The FluidRiaz JokanNo ratings yet
- K Relative PermeabilityDocument13 pagesK Relative PermeabilityTripoli ManoNo ratings yet
- K Relative PermeabilityDocument13 pagesK Relative PermeabilityTripoli ManoNo ratings yet
- TempDocument1 pageTempRobin HoodNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 - CSTR 40LDocument8 pagesLab 3 - CSTR 40Lnur athilahNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry Lab CHDocument22 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Lab CHm.shehroz8898No ratings yet
- Concentration Vs Conductivity: 1.0 Results, Discussion and Analysis 1.1 Calibration CurveDocument9 pagesConcentration Vs Conductivity: 1.0 Results, Discussion and Analysis 1.1 Calibration CurveAhZaiSkyNo ratings yet
- Displacement TDocument1 pageDisplacement TmalchukNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - AdsorptionDocument3 pagesTutorial 3 - AdsorptionKhairul FitryNo ratings yet
- Collogative Properties: Vapor Pressure LoweringDocument3 pagesCollogative Properties: Vapor Pressure LoweringJunell TadinaNo ratings yet
- Lab AnalysisDocument4 pagesLab AnalysisErnestasBlaževičNo ratings yet
- Exercise - 4: Previous Year Jee Advanced Question: Solutions 43Document6 pagesExercise - 4: Previous Year Jee Advanced Question: Solutions 43Shweta AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Exp8 - Lab 5 - Results and Calculations & DiscussionDocument3 pagesExp8 - Lab 5 - Results and Calculations & DiscussionTaslinNo ratings yet
- KimiaaaaaaDocument11 pagesKimiaaaaaaaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Chem Enzyme KineticsDocument2 pagesChem Enzyme KineticsSebastian SmytheNo ratings yet
- 408 Exp 1Document14 pages408 Exp 1goabaone kgopaNo ratings yet
- Results and Data CMT 463 Exp 3Document7 pagesResults and Data CMT 463 Exp 3IzzyanIsaNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Magnetic Susceptibility of Two Noncentrosymmetric Crystals Using Quincke's and Guoy MethodDocument11 pagesEstimation of Magnetic Susceptibility of Two Noncentrosymmetric Crystals Using Quincke's and Guoy Methodsuriya extazeeNo ratings yet
- Kurva Larutan Standar Glukosa: Konsentrasabsorbansi 0 0 0.02 0.017 0.04 0.019 0.06 0.061 0.08 0.08 0.1 0.089Document2 pagesKurva Larutan Standar Glukosa: Konsentrasabsorbansi 0 0 0.02 0.017 0.04 0.019 0.06 0.061 0.08 0.08 0.1 0.089Tiara RiaNo ratings yet
- Aspirin (Conducto) ProductionDocument11 pagesAspirin (Conducto) Productionapi-26797747100% (1)
- PCHEM Lab 3Document9 pagesPCHEM Lab 3api-3868874100% (1)
- Data and Results Exp-5 6Document2 pagesData and Results Exp-5 6esumshunNo ratings yet
- Calculadora Indice de LangelierDocument6 pagesCalculadora Indice de LangelierFábio SenaNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry - Experiment 1Document8 pagesPhysical Chemistry - Experiment 1Ronald Deck Yami0% (1)
- Experiment 2Document18 pagesExperiment 2api-3868874100% (1)
- Appendix A Results For Preparation of Calibration Curve: Concentration of Naoh Vs ConductivityDocument1 pageAppendix A Results For Preparation of Calibration Curve: Concentration of Naoh Vs ConductivityWonda 005No ratings yet
- THE IODINE CLOCK REACTION: Effect of Ionic Strength On Reaction RateDocument6 pagesTHE IODINE CLOCK REACTION: Effect of Ionic Strength On Reaction RateDannah Joy GamilNo ratings yet
- Foster Cole 101230199 Malaïka Zarrouki 2021-01-29Document7 pagesFoster Cole 101230199 Malaïka Zarrouki 2021-01-29Cole FosterNo ratings yet
- Core Practical 1 ChemistryDocument4 pagesCore Practical 1 ChemistryAadharsh NandhakumarNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document8 pagesLab 2Cristel Choquehuayta EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Awc - Proton Ro Null Null 20230927041217Document6 pagesAwc - Proton Ro Null Null 20230927041217Daniel Ortiz GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Analysis of consolidation test data: Observation: Time (Min) 100 σ (KN/m)Document5 pagesAnalysis of consolidation test data: Observation: Time (Min) 100 σ (KN/m)mit ramiNo ratings yet
- Formato SGI-SL-000-LM Mallas Valoradas Huanzala Division: Planta Concentradora Á!rea: Laboratorio Metalurgico Fecha de Vigencia: 27/03/14Document3 pagesFormato SGI-SL-000-LM Mallas Valoradas Huanzala Division: Planta Concentradora Á!rea: Laboratorio Metalurgico Fecha de Vigencia: 27/03/14Luis AlavilNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 (Recovered)Document36 pagesExperiment 7 (Recovered)Manda BaboolalNo ratings yet
- Design SpreadsheetDocument6 pagesDesign SpreadsheetWinnieNo ratings yet
- TSAI HSIANG en Biochemical EngineeringDocument22 pagesTSAI HSIANG en Biochemical EngineeringTSAI, HSIANGEN(대학원학생/일반대학원 화공생명공학) No ratings yet
- L52 Online Assignment Question 1Document3 pagesL52 Online Assignment Question 1Raj PatelNo ratings yet
- Binary LiquidsDocument8 pagesBinary LiquidsSuzanne Clariz M. BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Iodine Clock LabDocument5 pagesIodine Clock LabHuang AmandaNo ratings yet
- JJDocument4 pagesJJEureca ParraNo ratings yet
- Liquidus, Isothermal and Isopleth PlotsDocument1 pageLiquidus, Isothermal and Isopleth PlotsJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- Drug Distribution VolumeDocument1 pageDrug Distribution VolumeJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- Voltaic Cells LabDocument3 pagesVoltaic Cells LabJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- Molar Heat Capacity of AluminumDocument1 pageMolar Heat Capacity of AluminumJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- Focal Length of A LensDocument1 pageFocal Length of A LensJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- Distillation Without Column: Temperature (Celcius)Document2 pagesDistillation Without Column: Temperature (Celcius)John JosephNo ratings yet
- ZrO2-CaO Phase DiagramDocument1 pageZrO2-CaO Phase DiagramJohn Joseph100% (2)
- Koshchmeider EquationDocument1 pageKoshchmeider EquationJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- Czochralski Crystal Growth Technique and Zone RefiningDocument3 pagesCzochralski Crystal Growth Technique and Zone RefiningJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- Antoine and Steam TablesDocument6 pagesAntoine and Steam TablesJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- Electrons in The D OrbitalDocument1 pageElectrons in The D OrbitalJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- Running Shoe LCADocument2 pagesRunning Shoe LCAJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- Fieldbus NetworkDocument1 pageFieldbus NetworkJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- Liquid Nitrogen in StyrofoamDocument1 pageLiquid Nitrogen in StyrofoamJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- 3 Mile Island Case Study - OdtDocument1 page3 Mile Island Case Study - OdtJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Gene TransferDocument1 pageHorizontal Gene TransferJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- Paper Chromatography Lab QuestionsDocument1 pagePaper Chromatography Lab QuestionsJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- Liquid Nitrogen in StyrofoamDocument1 pageLiquid Nitrogen in StyrofoamJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- Distillation Without Column: Temperature (Celcius)Document2 pagesDistillation Without Column: Temperature (Celcius)John JosephNo ratings yet
- Conductivity of Ionic SolutionsDocument1 pageConductivity of Ionic SolutionsJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- Kanaya OkanayamaDocument5 pagesKanaya OkanayamaJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- Analysis of An Alkali Metal Carbonate by Back Titration of Hydrochloric AcidDocument8 pagesAnalysis of An Alkali Metal Carbonate by Back Titration of Hydrochloric AcidJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- Isobaric Expansion ProcessDocument2 pagesIsobaric Expansion ProcessJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- JavaDocument8 pagesJavaJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- Sludge AgeDocument1 pageSludge AgeJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- Titration of CH3NH3+Document3 pagesTitration of CH3NH3+John JosephNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of AspirinDocument2 pagesSynthesis of AspirinJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- Stress Strain Definitions Toughness and ResilienceDocument2 pagesStress Strain Definitions Toughness and ResilienceJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Removal by Air StrippingDocument1 pageAmmonia Removal by Air StrippingJohn JosephNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Biomedical Applications of Shape Memory AlloysDocument16 pagesReview Article: Biomedical Applications of Shape Memory AlloysAntonela-Georgiana MateiNo ratings yet
- Configure Ap Aruba ConsoleDocument2 pagesConfigure Ap Aruba ConsoleKule MemphisNo ratings yet
- Pitcher TemplateDocument1 pagePitcher Templatem.usmanNo ratings yet
- How Torque Converters Work - HowStuffWorksDocument7 pagesHow Torque Converters Work - HowStuffWorksKrishanu ModakNo ratings yet
- DF-760/DF-760 (B) BF-720 MT-720/MT-720 (B) PH-5A/5C/5D: Parts ListDocument83 pagesDF-760/DF-760 (B) BF-720 MT-720/MT-720 (B) PH-5A/5C/5D: Parts ListJose Rojas ValeroNo ratings yet
- Information Data and ProcessingDocument10 pagesInformation Data and ProcessingarshdeepsinghdhingraNo ratings yet
- Casing and Tubing Crossovers: ScopeDocument4 pagesCasing and Tubing Crossovers: Scopeislam atifNo ratings yet
- 12 One Way Ribbed Slab-SlightDocument18 pages12 One Way Ribbed Slab-Slightريام الموسوي100% (1)
- Chapter 20 Surface Area and Volume of A Right Circular ConeDocument19 pagesChapter 20 Surface Area and Volume of A Right Circular ConeMann GosarNo ratings yet
- Correlational ResearchDocument10 pagesCorrelational ResearchSari100% (1)
- Fabry PerotDocument11 pagesFabry PerotG. P HrishikeshNo ratings yet
- RLC-circuits With Cobra4 Xpert-Link: (Item No.: P2440664)Document14 pagesRLC-circuits With Cobra4 Xpert-Link: (Item No.: P2440664)fatjonmusli2016100% (1)
- Airfield Pavement2Document12 pagesAirfield Pavement2molgarNo ratings yet
- 3681 113533 1 SM - , mutasiCVKaroseriLaksanaDocument14 pages3681 113533 1 SM - , mutasiCVKaroseriLaksanataufiq hidayatNo ratings yet
- Beckman Coulter GenomeLab TroubleshootDocument56 pagesBeckman Coulter GenomeLab TroubleshootChrisNo ratings yet
- Jain 2018Document10 pagesJain 2018Pablo Ignacio Contreras EstradaNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Weight 2023Document13 pages2.8 Weight 2023Xinpei ShimNo ratings yet
- Understand Concept of Multi-Rate Signal Processing: (Autonomous College Affiliated To University of Mumbai)Document2 pagesUnderstand Concept of Multi-Rate Signal Processing: (Autonomous College Affiliated To University of Mumbai)nicO neeNo ratings yet
- Edited C Spectra - APT and DEPTDocument4 pagesEdited C Spectra - APT and DEPTKasun RatnayakeNo ratings yet
- Reflective Lesson Plan 4 Pythagorean TheoremDocument9 pagesReflective Lesson Plan 4 Pythagorean Theoremapi-339897912100% (1)
- Chapter Seven: GS Ohlins Installation, Adjustment Tips & TricksDocument29 pagesChapter Seven: GS Ohlins Installation, Adjustment Tips & TricksWhattonNo ratings yet
- Cylindicator Sensor Design GuideDocument2 pagesCylindicator Sensor Design GuideTavo VergaraNo ratings yet
- Free Electricity From The Earth Rotating Through Its Own Magnetic Field Using The Homopolar Generator EffectDocument3 pagesFree Electricity From The Earth Rotating Through Its Own Magnetic Field Using The Homopolar Generator EffectmarcelogiovaneNo ratings yet
- Сравнит. лингвистикаDocument22 pagesСравнит. лингвистикаАнастасия ДобровольскаяNo ratings yet
- Neeraj Pal 2Document1 pageNeeraj Pal 2NeerajPalNo ratings yet
- Comba ODV-065R15E18J-GDocument1 pageComba ODV-065R15E18J-GGaga ChubinidzeNo ratings yet
- DWL-3200AP B1 Manual v2.40 PDFDocument83 pagesDWL-3200AP B1 Manual v2.40 PDFFrank Erick Soto HuillcaNo ratings yet
- DA-100English ManualDocument10 pagesDA-100English ManualGiang TrườngNo ratings yet
- Storage Tanks Vessels Gas LiquidsDocument9 pagesStorage Tanks Vessels Gas Liquidswei wangNo ratings yet
- Heat and Thermodynamics According To KPK Textbook & Sindh TextbookDocument15 pagesHeat and Thermodynamics According To KPK Textbook & Sindh Textbookswatmiandam44No ratings yet