0% found this document useful (0 votes)
853 views3 pagesWEEK 3 LAB EXERCISE Cell Structures and Functions
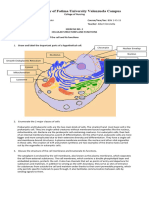
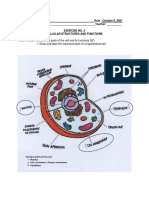
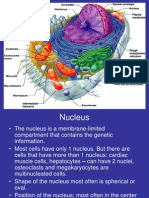
The document discusses the structure and functions of cells. It identifies the two major classes of cells as prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotes lack internal membranes and a nucleus, while eukaryotes have a defined nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane. The cell membrane defines cell boundaries and regulates what enters and exits the cell. The nucleus acts as the control center housing the cell's genetic material and controlling cell growth, reproduction, and gene expression. The cytoplasm contains organelles that perform specialized functions to keep the cell alive, and inclusions that store nutrients, secretions, and pigments.
Uploaded by
Zheldinan Nicole CruzCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
853 views3 pagesWEEK 3 LAB EXERCISE Cell Structures and Functions
The document discusses the structure and functions of cells. It identifies the two major classes of cells as prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotes lack internal membranes and a nucleus, while eukaryotes have a defined nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane. The cell membrane defines cell boundaries and regulates what enters and exits the cell. The nucleus acts as the control center housing the cell's genetic material and controlling cell growth, reproduction, and gene expression. The cytoplasm contains organelles that perform specialized functions to keep the cell alive, and inclusions that store nutrients, secretions, and pigments.
Uploaded by
Zheldinan Nicole CruzCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Exercise No. 2: Cellular Structures and Functions: This section covers exercises related to the cell parts and their respective functions, focusing on comparing prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
- Cell Membrane and Components: Discusses the structure and functions of the cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus detailed in bullet points.
- Cytoplasm and Inclusions: Classifies the formed elements within the cytoplasm and discusses the nucleus' role and function in detail.