Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Zoology Lecture Notes
Uploaded by
Theresa Mae GenovezaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Zoology Lecture Notes
Uploaded by
Theresa Mae GenovezaCopyright:
Available Formats
INTRO: ■ Membranes of adjacent cells
● A multicellular organism is made up of are fused forming continuous
millions of cells belts around cells
● Millions of cells of different kinds ■ Prevent leakage of
● Different structures = different functions extracellular fluid across a
● E- Red blood cells layer of epithelial cells
● D- muscle cells ○ Desmosomes- with an intermediate
● A- neurons filaments of keratin extended to the
● B- cartilage cytoplasm of the two adjacent cells
● C- bone ■ Connects the cells into
● F- WBC extracellular matrix-
● G- adipose tissue hemidesmosomes
● Animal cell types can be grouped into ■ Fasten cells together into
different categories strong sheets, much like
rivets
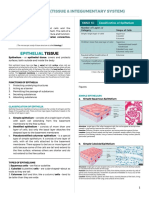
Epithelial tissue ■ Reinforced by intermediate
- Covers the outside of the body and lines filaments of keratin-- anchors
organs and cavities within the body into the cytoplasm allowing
- They have to separate two environment for
that's why ■ Hyper--adhesive state allows
- Compact (nuclei); occurs in sheets and resistance to mechanical
tightly packed cells stress
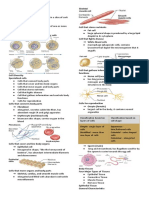
- Little intercellular substance (nuclei) ○ Gap junctions- create channel
- Polarized; meaning there is between cells
- Apical surface ■ Provides cytoplasmic
- Basal surface channels between adjacent
- Basal lamina cells
● Apical or free surface- is exposed to air or ■ Salt ions, sugar, amino acids,
fluid; structures on free surfaces: microvilli, and other small molecules
cilia flagella can pass through the
○ Exposed to the lumen side channels
○ Exposed to the environment
○ Structures for redistributions of any
secretions or might help in trapping Cells joined together in epithelial tissues have
substances that might be floating in different shape
the region ● Squamous- flat like tiles --
● Basal surface- where cells at the base of ● Cuboidal- like dice--
the barrier are attached ● Columnar- like bricks on end --
○ Also called basal lamina and
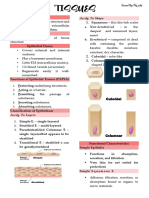
basement membrane Types according to layering
○ Attached to another type of tissue 1. Simple epithelium- made up of a single
Cells are closely joined layer of cells-- C, D, F
● Animals have 3 main types of intercellular 2. Stratified epithelium- made up of many cell
links layers --- B & E
○ Tight junctions- apical part 3. Pseudostratified epithelium- made up of a
■ Looks like a stitching of two single layer of cells but appears stratified---
cells together A; tapered basal ends, gives the
appearance of multilayered, nucleus not in - One layer of columnar cells found on highly
the same layer absorptive surfaces
Layering + shape - Like cuboidal epithelium but cells are taller
A- pseudostratified ciliated columnar because in the - Found on highly absorptive surfaces such
apical surface there is cilia on top as intestinal tract and female reproductive
B- stratified squamous tract
C- simple cuboidal - In some organs, cells may be ciliated
D- simple squamous Stratified columnar epithelium
E- stratified columnar - Consists of at least two layers of cells
F- single columnar - Found along some areas of the anorectal
● Different organizations connected to region and salivary duct
functions - Two layer rings of nucleus
Simple squamous
- Form a continuous delicate lining of blood
capillaries, lungs, and other surfaces
- Permits the passive diffusion of gases and
tissue fluids into and out of cavities
- Structure for more permissive Connective Tissue
- Diffusion will be more difficulties and
slower if columnar Muscular Tissue
Stratified squamous epithelium
- Consists of 2 to many layer of cells Nervous Tissue
- The tissue have this structure for:
- If ever the upper part exposed to external
environment, topmost layer could slogged
off and basal cells undergo continuous
mitotic divisions for more cells on the upper
part
- Adapted to withstand mild mechanical
abrasion
- Basal layer of cells undergo continuous
mitotic divisions
- Lines the oral cavity, esophagus, anal canal,
vagina of mammals, skin
Simple cuboidal epithelium
- Short, boxlike cells
- Usually lines small ducts and tubules
- May have active secretory and absorptive
functions
- Cuboidal cells and columnar are related to
some secretory and absorptive functions
might be because of the presence of
abundant cytoplasm in this type of cell
compared to squamous allowing for much
more intracellular activities
Simple columnar epithelial
You might also like
- Activity 4 - Epithelial TissueDocument4 pagesActivity 4 - Epithelial TissueMay Ann EnoserioNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument13 pagesHistologyangelo davidNo ratings yet
- Animal CellsDocument52 pagesAnimal CellsCally ChanNo ratings yet
- Epithelium Tissues: CellularityDocument6 pagesEpithelium Tissues: CellularityErika VerastigueNo ratings yet
- Tissues: By: Ruth Abigail C. Valdez BSN, RNDocument62 pagesTissues: By: Ruth Abigail C. Valdez BSN, RNrJNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue - Overview PDFDocument9 pagesEpithelial Tissue - Overview PDFAslak TorgersenNo ratings yet
- Histology Lec 1 & 2Document22 pagesHistology Lec 1 & 2Asma Ghazy100% (1)
- Module 2 TissuesDocument3 pagesModule 2 TissuesRaphael SevillaNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument7 pagesTissuesShahina ShayneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 TissuesDocument10 pagesChapter 4 TissuesAl-Shuaib Astami Son100% (1)
- Ep It HeliumDocument24 pagesEp It HeliumKen AkiyamaNo ratings yet
- Module # Epitheleal TransDocument5 pagesModule # Epitheleal TransLara VanessNo ratings yet
- 4 TissuesDocument4 pages4 TissuesCarea CruzNo ratings yet
- Tissues: Cell ConnectionsDocument3 pagesTissues: Cell ConnectionsRalph AlvarezNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Tissue W AnnotationsDocument6 pagesANAPHY Tissue W AnnotationssamanthaNo ratings yet
- Histology & Integumentary SystemDocument12 pagesHistology & Integumentary Systemopingaangelamae.opingaNo ratings yet
- Histology - Epithelial TissuesDocument4 pagesHistology - Epithelial TissuesKrissa OmandamNo ratings yet
- The Tissues: The Four Primary Tissue TypesDocument10 pagesThe Tissues: The Four Primary Tissue TypesgilissaNo ratings yet
- Cells and TissuesDocument5 pagesCells and Tissuesgrafei pennaNo ratings yet
- BODY TISSUES Reviewer 3Document3 pagesBODY TISSUES Reviewer 3Jaira EmmarinaNo ratings yet
- Tissues Glands and Membranes PDFDocument59 pagesTissues Glands and Membranes PDFJE ED100% (1)
- 7 Structural Organisation in Animals - Notes - SampleDocument2 pages7 Structural Organisation in Animals - Notes - SampleManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues 22Document8 pagesAnimal Tissues 22Arleen ColacionNo ratings yet
- Epithelium HÖ 2022-23Document65 pagesEpithelium HÖ 2022-23fiston ishimweNo ratings yet
- Histology Pt. I NotesDocument6 pagesHistology Pt. I Notesmaxpein zein and aceNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document9 pagesCH 7Ruchika Kumari, VIII-A, 3956100% (1)
- Epithelial Tissue (Epithelium) : General Characteristics of EpitheliumDocument22 pagesEpithelial Tissue (Epithelium) : General Characteristics of EpitheliumMahmoud IdlbiNo ratings yet
- Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDocument5 pagesTissues, Glands, and MembranesFrederick ManaigNo ratings yet
- Tissue Histology Types of Tissues: Kylie Jan C. SilvaDocument3 pagesTissue Histology Types of Tissues: Kylie Jan C. SilvaKert trocioNo ratings yet
- Histology Exam I OutlineDocument76 pagesHistology Exam I OutlinePrinceNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 Part 1. TISSUES pART 1Document41 pagesLec 3 Part 1. TISSUES pART 1John Vincent TacalNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Reviewer Tissue and Integumentary SystemDocument7 pagesAnaphy Reviewer Tissue and Integumentary System10. Briol AlvinNo ratings yet
- Forms and Characteristics of Epithelial Cells: Basement MembranesDocument5 pagesForms and Characteristics of Epithelial Cells: Basement MembranesA18- Jessa Mae DayagNo ratings yet
- BBS P03 Four Basic TissuesDocument14 pagesBBS P03 Four Basic TissuesPMIB Matrikulasi FKUI 2018/2019No ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Epithelial Tissue Lagrama - 3B7Document3 pagesChapter 4: Epithelial Tissue Lagrama - 3B7Ella LagramaNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissuesDocument6 pagesEpithelial TissuesPink GreyNo ratings yet
- epiTHITE TissueDocument10 pagesepiTHITE TissueDandel G. GollosoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy and Physiology - Review MaterialDocument7 pagesAnaphy and Physiology - Review MaterialKennethNo ratings yet
- 03 Epithelium 2022Document78 pages03 Epithelium 2022AlkadafeNo ratings yet
- Histology - Week 2 - Epithelium TissueDocument8 pagesHistology - Week 2 - Epithelium TissueHIEL MAALIHANNo ratings yet
- Genzoo Reviewer 1st SemDocument4 pagesGenzoo Reviewer 1st SememilpauloquibilanNo ratings yet
- E1.3 Body TissuesDocument5 pagesE1.3 Body TissueshzntrpNo ratings yet
- Epithelial, Conective and Adipose LECTURE2Document84 pagesEpithelial, Conective and Adipose LECTURE2rideroftorchNo ratings yet
- Histology Notes 2Document13 pagesHistology Notes 2Lukas BüchlerNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5.1: TISSUES - Human Biology (FSM)Document166 pagesLecture 5.1: TISSUES - Human Biology (FSM)Selaina NawadraNo ratings yet
- M4 TiisuesDocument8 pagesM4 TiisuesGemarela Salas CapitenioNo ratings yet
- IV. Chapter 4 (Epithelium)Document9 pagesIV. Chapter 4 (Epithelium)rosalesjirehrNo ratings yet
- Anatomy-The Study of Biological Form Physiology - Study of Bio FunctionsDocument4 pagesAnatomy-The Study of Biological Form Physiology - Study of Bio Functionsizabelle doloresNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues NEW 1Document54 pagesAnimal Tissues NEW 1Jela AgengaNo ratings yet
- Conn. Tissue HemopoiesisDocument14 pagesConn. Tissue HemopoiesischennielafleurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ANAPHY NOTESDocument13 pagesChapter 4 ANAPHY NOTESShannelle SinciocoNo ratings yet
- Cell Types and Cell ModificationDocument29 pagesCell Types and Cell ModificationVictous WarbingerNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy L03Document25 pagesPharmacognosy L03Youssef ElhamamyNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument10 pagesTissuesdenniesjrelefante101622No ratings yet
- EPITHELIUMDocument38 pagesEPITHELIUMAstridNo ratings yet
- Epithelium I (The First of Four Tissues) : Reading Assignment: Junqueira & Carneiro, Chapt. 2&4 Gartner & Hiatt, Chapter 2Document57 pagesEpithelium I (The First of Four Tissues) : Reading Assignment: Junqueira & Carneiro, Chapt. 2&4 Gartner & Hiatt, Chapter 2iramfarazNo ratings yet
- MLS - HISTOLOGY Lec - M2-UNIT1 (Epithelia and Glands)Document22 pagesMLS - HISTOLOGY Lec - M2-UNIT1 (Epithelia and Glands)ataraNo ratings yet
- Structural OrganizationDocument18 pagesStructural OrganizationMSANITYNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY TissuesDocument7 pagesANAPHY TissuesClarence MallariNo ratings yet
- Psych 150 C1-C2Document7 pagesPsych 150 C1-C2Theresa Mae GenovezaNo ratings yet
- Maslow - Holistic - Dynamic TheoryDocument10 pagesMaslow - Holistic - Dynamic TheoryTheresa Mae GenovezaNo ratings yet
- Maslow - Holistic - Dynamic TheoryDocument10 pagesMaslow - Holistic - Dynamic TheoryTheresa Mae GenovezaNo ratings yet
- Psych 150 C1-C2Document7 pagesPsych 150 C1-C2Theresa Mae GenovezaNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 Lesson 1Document7 pagesBio 11 Lesson 1Theresa Mae GenovezaNo ratings yet
- Gravetter - Chapter 1Document8 pagesGravetter - Chapter 1Theresa Mae GenovezaNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 Lesson 2Document2 pagesBio 11 Lesson 2Theresa Mae GenovezaNo ratings yet
- Zoology Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesZoology Lecture NotesTheresa Mae GenovezaNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 Lesson 1Document7 pagesBio 11 Lesson 1Theresa Mae GenovezaNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 Lesson 2Document2 pagesBio 11 Lesson 2Theresa Mae GenovezaNo ratings yet
- Brooks-Et-Al-1984 Principles Methods Cladist PDFDocument106 pagesBrooks-Et-Al-1984 Principles Methods Cladist PDFErika100% (1)
- Intramedullary Spinal Cord TumorsDocument7 pagesIntramedullary Spinal Cord TumorsmutalimNo ratings yet
- G Transport (Plants I)Document18 pagesG Transport (Plants I)luciferNo ratings yet
- Evolutionary Change: A Case Study of Extinct Brachiopod SpeciesDocument26 pagesEvolutionary Change: A Case Study of Extinct Brachiopod SpeciesKlenn Andrea DimalibotNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Zea Mays L EditedDocument34 pagesEvolution of Zea Mays L EditedJaclyn UyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Overview of Cellular EnergyDocument56 pagesLecture 6 Overview of Cellular EnergyMaimouna DialloNo ratings yet
- Pre-Board Examination in Histopathology and Medical Technology Laws (Part 1)Document5 pagesPre-Board Examination in Histopathology and Medical Technology Laws (Part 1)Godofredo Hermosura100% (1)
- Taxonomic Question BankDocument2 pagesTaxonomic Question BankDr-Atin Kumar SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Peter Godfrey-Smith - The Replicator in RetrospectDocument22 pagesPeter Godfrey-Smith - The Replicator in RetrospectKein BécilNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis and Fermentation Worksheet ReviewDocument3 pagesGlycolysis and Fermentation Worksheet ReviewMastentram WidjajaNo ratings yet
- PDF Cell Structure and Function Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesPDF Cell Structure and Function Lesson PlanDaniel Okazaki0% (1)
- CrayfishDocument1 pageCrayfishbroddy1No ratings yet
- KT152 GeNeiPure Plasmid ExtractionDocument11 pagesKT152 GeNeiPure Plasmid ExtractionHemant KawalkarNo ratings yet
- Chetverikov 2019Document26 pagesChetverikov 2019RGNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Science 10Document2 pagesLesson Plan Science 10Khen Francis A. Maceda100% (1)
- GMODocument17 pagesGMOMonina CahiligNo ratings yet
- General Education SecondaryDocument300 pagesGeneral Education Secondaryjorolan.annabelleNo ratings yet
- 10.2305 IUCN - UK.2020-2.RLTS.T5529A111875852.enDocument15 pages10.2305 IUCN - UK.2020-2.RLTS.T5529A111875852.enGeo ZahariaNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes (Lac Operon)Document13 pagesRegulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes (Lac Operon)MUHAMMAD ANEEQ JAVEDNo ratings yet
- Forest Ecosystem (Terrestrial Ecosystem)Document54 pagesForest Ecosystem (Terrestrial Ecosystem)MAHENDERNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-01-11 at 06.23.23Document24 pagesScreenshot 2024-01-11 at 06.23.23victoriaimahndeNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2020: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI1) Paper 2BRDocument16 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2020: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI1) Paper 2BRMilka Rahman100% (1)
- AP Bio COVID Assignment 2Document4 pagesAP Bio COVID Assignment 2Raj RaghuwanshiNo ratings yet
- University of Santo Tomas The Graduate School: An Outcomes-Based Learning ProgramDocument7 pagesUniversity of Santo Tomas The Graduate School: An Outcomes-Based Learning ProgramKathrina Bartido ViescaNo ratings yet
- Adaptations of Cellular Growth & Differentiation: @2022 PreclinicalsDocument27 pagesAdaptations of Cellular Growth & Differentiation: @2022 PreclinicalsJames MubitahNo ratings yet
- Cell Culture: Primary Neural CellsDocument6 pagesCell Culture: Primary Neural CellsJorge QuilumbaNo ratings yet
- HOMEOSTASIS - Lecture (Human Biology)Document22 pagesHOMEOSTASIS - Lecture (Human Biology)dokteraanNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue by Dr. Gironella PDFDocument3 pagesConnective Tissue by Dr. Gironella PDFFatima RadeenaNo ratings yet
- Virtual Mitosis Lab 2015Document3 pagesVirtual Mitosis Lab 2015Terrance TaylorNo ratings yet
- Pigments in Fruits and Vegetables - Genomics and Dietetics (PDFDrive)Document280 pagesPigments in Fruits and Vegetables - Genomics and Dietetics (PDFDrive)abinaya100% (1)