Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Edp: Introduction To Planning: Methods of Representation
Uploaded by
Yang JungwonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Edp: Introduction To Planning: Methods of Representation
Uploaded by
Yang JungwonCopyright:
Available Formats
EDP: INTRODUCTION TO PLANNING
ENGINEERING DRAWING
An engineering drawing is a type of technical drawing used to define the requirements
for engineering products or components. Typically, the purpose of an engineering drawing is to clearly
and accurately capture all geometric features of a product or component so that
a manufacturer or engineer can produce the required item. It may also describe the process of making the
item, may be used to convey engineering ideas during the design process, or may provide a record of an
existing item.
WHAT IS TECHNICAL DRAWING?
The term ‘technical drawing’ has a very broad meaning, referring to any drawing that conveys the
way that something functions or how it is constructed. Technical drawings are intended to convey
one specific meaning, as opposed to artistic drawings which are expressive and may be
interpreted in a number of ways.
Most drawings prepared during the design and construction of buildings might be considered to
be technical drawings.
It is important that the purpose for which technical drawings are being prepared and the people
that will use them are carefully considered to ensure they are properly structured and adopt
appropriate presentational techniques.
The scale at which drawings are prepared should reflect the level of detail of the information they
are required to convey, and graphical techniques such as the use of different line thicknesses and
hatching can help provide greater clarity.
To help convey the precise meaning of information, technical drawings may include title blocks,
dimensions, notation and symbols. To ensure their meaning is concise and unambiguous, it is
important that these are consistent with industry standards.
METHODS OF REPRESENTATION
1. FREEHAND DRAWING
- Lines are sketched without using instruments other than pencils and erasers.
2. MECHANICAL OR INSTRUMENTAL DRAWING
- Drafting instruments are used to draw straight lines, circles and curves concisely thus, the
drawings are usually made to scale. May comprise two-dimensional (orthogonal) plans,
sections and elevations, or may include three-dimensional or exploded projections
EDP: INTRODUCTION TO PLANNING
3. COMPUTER-AIDED DRAWING
- The drawings are usually made by commercial software. Often prepared using Computer
Aided Design (CAD) software. However, increasingly, building information modelling
(BIM) software is being used to create three-dimensional representations of buildings and
their components. BIM models may be described as 'design intent models' during the early
stages of development but then may evolve into 'virtual construction models' (VCM) and
finally 'as-constructed models'
ELEMENTS OF TECHNICAL DRAWING
GRAPHIC LANGUAGE (LINES)
WORD LANGUAGE (LETTERING)
DRAWINGS CONVEY THE FOLLOWING CRITICAL INFORMATION:
Geometry Diameter Scale
Dimensions Radius Full size
Linear Tolerances Reduced size
Aligned Materials Enlarged size
Angular Finish
UNITS OF MEASUREMENT
You might also like
- DrawDocument36 pagesDrawHassan XoghayeNo ratings yet
- Assignment Drafting Topic 1Document2 pagesAssignment Drafting Topic 1Jc SantosNo ratings yet
- FUNDAMENTAL ELEMENTS (Working Drawing) Nadiya Nazir and Ayman BashirDocument6 pagesFUNDAMENTAL ELEMENTS (Working Drawing) Nadiya Nazir and Ayman Bashirsyed mohsinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EGDocument29 pagesIntroduction To EGambika1969inNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Part OneDocument78 pagesLecture 1 Part Onewubied100% (1)
- CSS Report 2.1 Interpret Technical DrawingDocument41 pagesCSS Report 2.1 Interpret Technical DrawingTrexy HerederoNo ratings yet
- 112 Concept of Engineering DrawingDocument3 pages112 Concept of Engineering DrawingtalhaNo ratings yet
- The Art and Science of Technical Drawing PDFDocument2 pagesThe Art and Science of Technical Drawing PDFdavidguderianNo ratings yet
- Modul English For Engineering II UnlockedDocument11 pagesModul English For Engineering II UnlockedRikko PutraNo ratings yet
- ED Lecture 01Document35 pagesED Lecture 01Ateeq-Ur-Rehman ShaheenNo ratings yet
- Drafting PDFDocument36 pagesDrafting PDFJc SantosNo ratings yet
- Cad Cam Full Detail PracticalDocument45 pagesCad Cam Full Detail PracticalSamarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 CadDocument23 pagesLesson 1 CadBlank UndefeatedNo ratings yet
- Technical Drawing, Drafting or Drawing, Is The Act andDocument11 pagesTechnical Drawing, Drafting or Drawing, Is The Act andAjhay BonghanoyNo ratings yet
- Kamal CPCE2Document30 pagesKamal CPCE2kamalkumarbal77No ratings yet
- Unit-I ADocument41 pagesUnit-I ALakshmi Narayana SNo ratings yet
- Abs Trac Final 2Document39 pagesAbs Trac Final 2DIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENo ratings yet
- WST04101 Technical Drawing: Reference BooksDocument10 pagesWST04101 Technical Drawing: Reference Booksjoshua stevenNo ratings yet
- DraftingDocument4 pagesDraftingJenny TingsonNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2020-21 MEE3501 ETH VL2020210100431 Reference Material I 16-Jul-2020 Introduction To Freehand Sketches Layouts SymbolsDocument38 pagesFALLSEM2020-21 MEE3501 ETH VL2020210100431 Reference Material I 16-Jul-2020 Introduction To Freehand Sketches Layouts SymbolsJawa freakNo ratings yet
- TD 1Document1 pageTD 1joshNo ratings yet
- Technical Drawing - WikipediaDocument45 pagesTechnical Drawing - WikipediaAngelee PaskieNo ratings yet
- Pendahuluan GamtekDocument10 pagesPendahuluan GamtekAlfan MunawarNo ratings yet
- TNPSC Fs Unit-10 Building Drawing Part-1Document13 pagesTNPSC Fs Unit-10 Building Drawing Part-1அருண்குமார் அமைப்பியல்No ratings yet
- Cec 209 - Civil Engineering Drawing IDocument44 pagesCec 209 - Civil Engineering Drawing IVietHungCao89% (9)
- Technical DrawingDocument10 pagesTechnical DrawingDanica Nicole BuhatNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing (Graphics) Technical DrawingDocument47 pagesEngineering Drawing (Graphics) Technical DrawingErhan TokNo ratings yet
- Interior Design Student Handbook PDFDocument56 pagesInterior Design Student Handbook PDFJose NavarroNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Technical DrawingDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Technical Drawingcadhub4uNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Engineering Graphics Book TPA ExamDocument150 pagesComputer Aided Engineering Graphics Book TPA Examfun and learnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Blueprint ReadingDocument44 pagesLesson 2 - Blueprint Readingmakoto kirishimaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Notes 2Document1 pageEngineering Drawing Notes 2temp manNo ratings yet
- Technical Drawing or Drafting: Methods SketchingDocument10 pagesTechnical Drawing or Drafting: Methods SketchingMark BalbuenaNo ratings yet
- Engg DRW I Lecture NotesDocument71 pagesEngg DRW I Lecture NotesmujahidlawanfalgoreNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing: Unlocking Visual Perception in Engineering DrawingFrom EverandEngineering Drawing: Unlocking Visual Perception in Engineering DrawingNo ratings yet
- Dasar Gambar TeknikDocument146 pagesDasar Gambar Teknikhanifhakim2311No ratings yet
- Chapter 01 EGDocument50 pagesChapter 01 EGaneesh19inNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1.3-3 Architectural Working DrawingsDocument4 pagesInformation Sheet 1.3-3 Architectural Working DrawingsNico C GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided DesignDocument26 pagesComputer Aided DesignEngr Fazal AkbarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Plan and Work Drawings Level 1Document21 pagesIntroduction To Plan and Work Drawings Level 1zerihungezie6No ratings yet
- Not To Be Confused With Technical DrawDocument3 pagesNot To Be Confused With Technical DrawBryan PanilaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Course BookDocument48 pagesEngineering Drawing Course Bookgirishkaundinya100% (15)
- The Role of Engineering Drawing Production ReviewDocument2 pagesThe Role of Engineering Drawing Production ReviewSafira ApriliaNo ratings yet
- Engineering GraphicsDocument21 pagesEngineering GraphicsLakshwanath JaganathNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Basic Drafting: Types of Basic Engineering GraphicsDocument4 pagesLecture On Basic Drafting: Types of Basic Engineering GraphicsasifNo ratings yet
- Technical Drawing: Unlocking Computer Vision Through Technical DrawingFrom EverandTechnical Drawing: Unlocking Computer Vision Through Technical DrawingNo ratings yet
- Technical Drawing: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesTechnical Drawing: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaShiela Mae Falsis SalesNo ratings yet
- Drawing Standards Protocols ConventionsDocument6 pagesDrawing Standards Protocols ConventionsJack JimeneNo ratings yet
- Engineering DrawingDocument49 pagesEngineering DrawingSãröj Shâh100% (2)
- Digital Assignment-1: Product Development and ManagementDocument9 pagesDigital Assignment-1: Product Development and ManagementSanjit RameshNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Technical DrawingDocument22 pagesFundamentals of Technical Drawingdavid78% (9)
- Engineering Drawing and Graphics A First Year Engineering Drawing Lecture 1Document23 pagesEngineering Drawing and Graphics A First Year Engineering Drawing Lecture 1Talha RajaNo ratings yet
- Progressive Steps in Architectural Drawing - A Step-by-Step Method for Student Draughtsmen Together with Details of Construction and DesignFrom EverandProgressive Steps in Architectural Drawing - A Step-by-Step Method for Student Draughtsmen Together with Details of Construction and DesignRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- JGB20203 (P) WW1 Projection ViewsDocument46 pagesJGB20203 (P) WW1 Projection ViewsMuhammad IzzuanNo ratings yet
- VisCom ReviewerDocument10 pagesVisCom ReviewerAron BagaforoNo ratings yet
- Notes on Mechanical Drawing - Prepared for the Use of Students in Mechanical, Electrical and Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandNotes on Mechanical Drawing - Prepared for the Use of Students in Mechanical, Electrical and Chemical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Structural Drafting - A Practical Presentation of Drafting and Detailed Methods used in Drawing up Specifications for Structural Steel WorkFrom EverandStructural Drafting - A Practical Presentation of Drafting and Detailed Methods used in Drawing up Specifications for Structural Steel WorkRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Mechanical Drawing - Projection Drawing, Isometric and Oblique Drawing, Working DrawingsFrom EverandMechanical Drawing - Projection Drawing, Isometric and Oblique Drawing, Working DrawingsNo ratings yet
- Potato Starch Bioplastic 2Document31 pagesPotato Starch Bioplastic 2Yang JungwonNo ratings yet
- Potato Starch Bioplastic 1Document11 pagesPotato Starch Bioplastic 1Yang Jungwon0% (1)
- Academic Involvement of G12 Students in An Air-Conditioned RoomDocument47 pagesAcademic Involvement of G12 Students in An Air-Conditioned RoomYang JungwonNo ratings yet
- Filling in The Gaps - The Role of Peers To Adolescents From Broken FamiliesDocument23 pagesFilling in The Gaps - The Role of Peers To Adolescents From Broken FamiliesYang JungwonNo ratings yet
- A Study On The Gender Differences Among SHS Students in Budget AllocationDocument15 pagesA Study On The Gender Differences Among SHS Students in Budget AllocationYang JungwonNo ratings yet
- Watergems Product Data SheetDocument2 pagesWatergems Product Data SheetVinayak PotdarNo ratings yet
- Whats New SmartPlant PID Product SheetDocument2 pagesWhats New SmartPlant PID Product SheetDuran ShNo ratings yet
- Lenoir FlowProcessFold PDFDocument29 pagesLenoir FlowProcessFold PDFMohammed Gism AllahNo ratings yet
- A Report On Student Industrial Work Experience Scheme (Siwes) Training Programme (May 2016 - October 2016)Document36 pagesA Report On Student Industrial Work Experience Scheme (Siwes) Training Programme (May 2016 - October 2016)Nachi ManuelNo ratings yet
- How To Draw Good-Looking Bolts (From The Trenches Tutorial) : AutocadDocument5 pagesHow To Draw Good-Looking Bolts (From The Trenches Tutorial) : AutocadNrl SyafiniNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 - CAD - V02Document21 pagesUnit-1 - CAD - V02muthupuviNo ratings yet
- Tech For Good Guidebook 2021Document46 pagesTech For Good Guidebook 2021Hendrikus MipayauNo ratings yet
- Cloud-Based Design and Manufacturing Status and PromiseDocument24 pagesCloud-Based Design and Manufacturing Status and PromiseindrabudhiNo ratings yet
- FastCAM TutorialDocument137 pagesFastCAM Tutorialovidiughita88% (8)
- 7dimension PortfolioDocument45 pages7dimension Portfoliochirag chhotwaniNo ratings yet
- Accord 25 FX - Rev00 - Mag17 - Ing - 00L0372819LDocument24 pagesAccord 25 FX - Rev00 - Mag17 - Ing - 00L0372819Lakcelerator100% (1)
- Shams Ur RehmanDocument2 pagesShams Ur RehmanShAms KhAn100% (1)
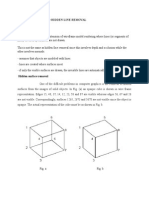
- Hidden Surface RemovalDocument8 pagesHidden Surface RemovalAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- 2, 3 Configurations Receptacle Connector Assembly Molex InterfaceDocument6 pages2, 3 Configurations Receptacle Connector Assembly Molex InterfaceJESUS CERVERANo ratings yet
- Autocad 2D: Lesson 2 - EditingDocument16 pagesAutocad 2D: Lesson 2 - EditingJaydipPatelNo ratings yet
- Design Modeler TutorialDocument360 pagesDesign Modeler TutorialYoung Jun ChoNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Overview Mechanical Is Your SolutionDocument2 pagesMechanical Overview Mechanical Is Your SolutionVijay KadliNo ratings yet
- Aerospace Science and Technology: Abdelkader Benaouali, Stanisław KachelDocument11 pagesAerospace Science and Technology: Abdelkader Benaouali, Stanisław KachelHoàng DavidNo ratings yet
- Flowizard 3.1Document4 pagesFlowizard 3.1Antonio MezzopreteNo ratings yet
- Cost Reduction in Cast Components ManufacturingDocument4 pagesCost Reduction in Cast Components ManufacturingNaveen TiwariNo ratings yet
- Project Name P22-02 Project Code - : P22-XX-XX-SP-K-BEP Pre - Contract BIM Execution Plan (BEP)Document29 pagesProject Name P22-02 Project Code - : P22-XX-XX-SP-K-BEP Pre - Contract BIM Execution Plan (BEP)Juan PNo ratings yet
- Pranav Jadhav Resume YoE 3.3 Design EnggDocument2 pagesPranav Jadhav Resume YoE 3.3 Design EnggRahul PatankarNo ratings yet
- Products Guide CRADLEDocument16 pagesProducts Guide CRADLEdddidsNo ratings yet
- BIM - A Platform To The Future of ArchitectureDocument30 pagesBIM - A Platform To The Future of ArchitectureHasan KothariNo ratings yet
- Flyer RAMSIS Modul SeatBeltDesign 2013e HSIDocument2 pagesFlyer RAMSIS Modul SeatBeltDesign 2013e HSIpmm05479No ratings yet
- CAD-CAM LAB MANUAL 2021-22manualDocument59 pagesCAD-CAM LAB MANUAL 2021-22manualShashankNo ratings yet
- Escalator: Installation ManualDocument53 pagesEscalator: Installation ManualSamih AlraghbanNo ratings yet
- Roboguide Brochure enDocument5 pagesRoboguide Brochure enViktor BalogNo ratings yet
- Djj5032: Mechanical Workshop Practice 4: Cadcam ReportDocument13 pagesDjj5032: Mechanical Workshop Practice 4: Cadcam ReportKosigar ChelladoraiNo ratings yet
- Building Massing Optimization in The Conceptual Design PhaseDocument12 pagesBuilding Massing Optimization in The Conceptual Design PhaseliupeiNo ratings yet