Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biogeosphere Bilingual Biology and Geology I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
Uploaded by
JavierOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biogeosphere Bilingual Biology and Geology I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
Uploaded by
JavierCopyright:
Available Formats
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOLOGY AND GEOLOGY 3rd ESO
Unit 8: The reproductive system 1 2 3
3. Physiology of reproduction
3.1. Formation of gametes
Gametes are formed by a process called gametogenesis.
This process takes place in gonads (ovaries and testicles).
Gametes form from germ cells which like other human cells have 46
chromosomes. However when gametes are formed the number of chromosomes is
halved through a special type of cell division called meiosis. The resulting cells
therefore only have 23 chromosomes.
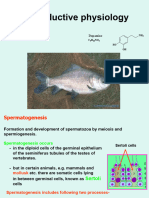
a) Spermatogenesis
This is the male gametogenesis. It takes place in the walls of the seminiferous
tubules of the testicles.
The process takes about two months and after puberty it occurs continuously
throughout the man’s lifetime. Spermatozoa are produce in large quantities
(millions) each day.
After meiosis the cells become spermatozoa, male gametes, through a process of
cellular specialisation during which they change their shape.
- They reduce their volume
- The organelles disappear except the nucleus and the acrosome.
- The flagellum develops.
A spermatozoon has three parts:
- Head. This contains the nucleus (genetic material)
and the acrosome (organelle that contains digestive
enzymes to dissolve
the outer layer of the ovum)
- Midpiece. This part is located between
the head and the tail. It contains lots of
mitochondria that provide the energy
required to move the flagellum.
- Tail. It is a flagellum which enables
the spermatozoon to move.
b) Oogenesis
This is the female gametogenesis. It takes place in ovaries, inside structures called
follicles.
After puberty, oogenesis takes place regularly in woman, approximately every 28
days. An ovum develops, mature and is released each time.
As spermatozoa, ova change after
meiosis to become a specialised cell.
Its size increases because of the
accumulation of nutritive substances
which will be the support of the
embryo during the first few days after
fertilisation.
In addition, ovum is covered by two
protective layers the zona pellucida
(mucous substance) and the corona
radiate (remains of follicular cells).
ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions
into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
3.1. Answer these questions:
a. How do ovum and spermatozoon differ?
b. What are the differences between the production of male and female
gametes?
1 2 3
Aviso legal | Política de privacidad | Mapa del sitio
Esta página web ha sido creada con Jimdo. ¡Regístrate ahora gratis en https://es.jimdo.com
You might also like
- BIOL 1700 - Test 1 - Important InformationDocument4 pagesBIOL 1700 - Test 1 - Important InformationSophie100% (1)
- 10class Biology Bits - (Em) RRDocument35 pages10class Biology Bits - (Em) RRsekkharchandra50% (2)
- Bootstrapping PRESENTATION BY GROUP 4Document31 pagesBootstrapping PRESENTATION BY GROUP 4Aditi Mohan100% (3)
- Biology Lectures Finals-2Document12 pagesBiology Lectures Finals-2Jaina Alexandra MendozaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physics: Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physics: Reproductive SystemDenise CalderonNo ratings yet
- Phylogenetics Is The Study of Evolutionary Relationships Among Biological EntitiesDocument14 pagesPhylogenetics Is The Study of Evolutionary Relationships Among Biological EntitiesThuvishka PrabagarNo ratings yet
- Adrián Lois Illana - Representation of The Human Reproductive Cycle (Unit 7)Document2 pagesAdrián Lois Illana - Representation of The Human Reproductive Cycle (Unit 7)Adrián Lois IllanaNo ratings yet
- Midterm GenHisto ReviewerDocument12 pagesMidterm GenHisto ReviewerNATALIE NICOLE GABASNo ratings yet
- Developmental Anatomy: VeterinaryDocument87 pagesDevelopmental Anatomy: VeterinaryLulus KisworoNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Developmental Anatomy: Veterinary Embryology Class NotesDocument82 pagesVeterinary Developmental Anatomy: Veterinary Embryology Class NotesMadhav KiranNo ratings yet
- Tanya Jawab LO S1Document21 pagesTanya Jawab LO S1AS RNo ratings yet
- Insect Physiology: Developmental SystemsDocument47 pagesInsect Physiology: Developmental SystemstariNo ratings yet
- B2603 ANIMAL DEVELOPMENT - Post Fertilization EventsDocument13 pagesB2603 ANIMAL DEVELOPMENT - Post Fertilization EventssispulieNo ratings yet
- Apigo 3Document11 pagesApigo 3Ms. Jia Mae CasimoNo ratings yet
- Early EmbryogenesisDocument13 pagesEarly Embryogenesisolawandeilo123No ratings yet
- Open Book Exam Muzzammil HussainDocument22 pagesOpen Book Exam Muzzammil HussainRIFAT RAKIBUL HASANNo ratings yet
- As Biology: Unit 2 Notes (Edexcel)Document21 pagesAs Biology: Unit 2 Notes (Edexcel)Charity Owo100% (1)
- CH 47 - Animal DevelopmentDocument70 pagesCH 47 - Animal DevelopmentSofiaNo ratings yet
- Embryology 2020Document8 pagesEmbryology 2020A-Naeem To'mah Al-sawaieNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 3 Edexcel (A) Biology A-Level PDFDocument8 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 3 Edexcel (A) Biology A-Level PDFmohammedNo ratings yet
- Reproductive PhysiologyDocument13 pagesReproductive PhysiologyfacultyfisheriesNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Cycle and Implantation)Document19 pagesMenstrual Cycle and Implantation)Ragdha MehdawiNo ratings yet
- Pembentukan Lapisan-Lapisan Bakal Dan SelomDocument35 pagesPembentukan Lapisan-Lapisan Bakal Dan SelomRosihan Husnu MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Vertebrate DevelopmentDocument16 pagesGroup 5 Vertebrate DevelopmentannaMariaGracia EstardoNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Developmental Anatomy: Veterinary Embryology Class NotesDocument76 pagesVeterinary Developmental Anatomy: Veterinary Embryology Class NotesHanaNo ratings yet
- Embryology Kul FKDocument65 pagesEmbryology Kul FKFahreza ArraisyNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Development: Lesson 2Document10 pagesPlant and Animal Development: Lesson 2hellohelloworldNo ratings yet
- 1st To 3rd Weeks of DevelopmentDocument60 pages1st To 3rd Weeks of DevelopmentJérômeLkNo ratings yet
- Human Development Days 1-4Document43 pagesHuman Development Days 1-4Kriztine Mae GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Developmental Anatomy: Veterinary Embryology Class NotesDocument76 pagesVeterinary Developmental Anatomy: Veterinary Embryology Class NotesgirishNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Biology AS Level Unit 2 Sample NotesDocument4 pagesEdexcel Biology AS Level Unit 2 Sample NotesMariam AhmedNo ratings yet
- ProtozoologyDocument51 pagesProtozoologySagar AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Sperm Maturation:: FertilizationDocument4 pagesSperm Maturation:: FertilizationMuhammet Fatih CantepeNo ratings yet
- Science JournalDocument3 pagesScience JournalShirley AngNo ratings yet
- FertlizationDocument5 pagesFertlizationgallardo.bettinarose.iNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesOverview of The Female Reproductive SystemMonica J Ortiz PereiraNo ratings yet
- Human Cloning - 1Document3 pagesHuman Cloning - 1surendracrysisNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of ReproductionDocument4 pagesFundamentals of ReproductionHalo Ini JeskryNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Reproduction (2019) Notes:: Provided by Yvonne HodgsonDocument14 pagesPhysiology of Reproduction (2019) Notes:: Provided by Yvonne HodgsonBảoChâuNo ratings yet
- Fetal Development Occurs in 3 Stages:: BlastomeresDocument7 pagesFetal Development Occurs in 3 Stages:: BlastomeresSofiaLopezNo ratings yet
- Dkp1 Imam Agus Faisal 1.A. Stage or Phase Embriogenesis and OrganogenesisDocument3 pagesDkp1 Imam Agus Faisal 1.A. Stage or Phase Embriogenesis and OrganogenesisImam Agus FaisalNo ratings yet
- Developmental GeneticsDocument20 pagesDevelopmental GeneticsProjjal SanyalNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Zoology (Psych 1B)Document14 pagesGroup 1 Zoology (Psych 1B)annaMariaGracia EstardoNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Anatomy and EmbryologyDocument77 pagesVeterinary Anatomy and EmbryologyFor AstroNo ratings yet
- KM GametogenesisDocument42 pagesKM GametogenesisKALAMYA BRIAN BWAYONo ratings yet
- WWW - Studyguide.pk: Aspects of Human Reproduction Key ObjectivesDocument9 pagesWWW - Studyguide.pk: Aspects of Human Reproduction Key ObjectivesP.P.KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Animal - Development (Kel 1-5)Document83 pagesAnimal - Development (Kel 1-5)MelatiNo ratings yet
- Stages of Fetal (Prenatal) Development Prof. Dymphna CasquejoDocument3 pagesStages of Fetal (Prenatal) Development Prof. Dymphna CasquejoLynnelljhyen MALUBAYNo ratings yet
- Applications of Biology 9700 - Nos - As - 5Document9 pagesApplications of Biology 9700 - Nos - As - 5Nana_Banana_94No ratings yet
- Embryology Made Ridiculously Simple Handout PDFDocument15 pagesEmbryology Made Ridiculously Simple Handout PDFAsma SaleemNo ratings yet
- Embriologie 2017Document100 pagesEmbriologie 2017Irina LutcanNo ratings yet
- Animal Diversity: Zarah Alaska-VillalonDocument68 pagesAnimal Diversity: Zarah Alaska-VillalonGabrielle Salamanca CastuloNo ratings yet
- Beginning)Document7 pagesBeginning)Jaina Alexandra MendozaNo ratings yet
- Gametogenesis of Drosophila MelanogasterDocument2 pagesGametogenesis of Drosophila MelanogasterTricia Barot0% (1)
- EmbryologyDocument101 pagesEmbryologytawandarukwavamadisonNo ratings yet
- Human Embryonic DevelopmentDocument8 pagesHuman Embryonic DevelopmentGargi BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Process of Conception and Stage of Fetal DevelopmentDocument25 pagesModule 2 - Process of Conception and Stage of Fetal DevelopmentKatie HolmesNo ratings yet
- EMBRYOLOGY - First Week of Human DevelopmentDocument7 pagesEMBRYOLOGY - First Week of Human DevelopmentMeow CattoNo ratings yet
- Bsp1a - Gr.a - ReportingDocument14 pagesBsp1a - Gr.a - ReportingannaMariaGracia EstardoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction and Embryonic Development in Plants and AnimalsDocument3 pagesReproduction and Embryonic Development in Plants and AnimalsJoy BoyNo ratings yet
- Animal Development 2Document7 pagesAnimal Development 2dewiNo ratings yet
- Camp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- The Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- How Birds Evolved From Dinosaurs 20150602Document8 pagesHow Birds Evolved From Dinosaurs 20150602Niranjana Prasanna VenkateswaranNo ratings yet
- Ne-Slet Mock Test 1Document28 pagesNe-Slet Mock Test 1ShivangNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 15.1 Comparing Continuous and Discontinuous VariaDocument2 pagesWORKSHEET 15.1 Comparing Continuous and Discontinuous VariaSiti Nor Aishah100% (1)
- Nature Vs Nurture AssignmentDocument3 pagesNature Vs Nurture AssignmentKaiya K HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Indian Council of Agricultural Research Krishi Bhawan, New DelhiDocument14 pagesIndian Council of Agricultural Research Krishi Bhawan, New DelhiSripathy KudekalluNo ratings yet
- 3.4Document13 pages3.4Lia BodoyanNo ratings yet
- Informes de LaboratorioDocument17 pagesInformes de Laboratoriojessica vanessaNo ratings yet
- Biological Databases GenbankDocument31 pagesBiological Databases GenbankjaineemNo ratings yet
- Mahajan 2018Document14 pagesMahajan 2018nguyenvinh daoNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument228 pagesBiologyKanchan AgasheNo ratings yet
- Thesis ElementsDocument7 pagesThesis Elementsgj84st7d100% (2)
- PBT Pre University 2019-20Document1 pagePBT Pre University 2019-20Vanshika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bioinformatics in PAM AND BLOSUMDocument17 pagesBioinformatics in PAM AND BLOSUMgladson100% (15)
- 22 10 Human Genetics CIBID 2014Document98 pages22 10 Human Genetics CIBID 2014Малиша МанићNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering and Recombinant DNADocument33 pagesGenetic Engineering and Recombinant DNAElton John TubaNo ratings yet
- (Ap & TS) SR Elite Neet Grand Test - 3 Paper (15-03-2022)Document22 pages(Ap & TS) SR Elite Neet Grand Test - 3 Paper (15-03-2022)srsoumyaranjantareiNo ratings yet
- Final Requirement in SCI 402Document3 pagesFinal Requirement in SCI 402Divine Via DaroyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ArchaebacteriaDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Archaebacteriakanchan sharmaNo ratings yet
- Bio Topic 1.5 Worksheet (Answers)Document2 pagesBio Topic 1.5 Worksheet (Answers)Mahina WongNo ratings yet
- Plant TaxonomyDocument7 pagesPlant TaxonomySiaNo ratings yet
- School Job Application LetterDocument2 pagesSchool Job Application LetterHalidah BamejbourNo ratings yet
- EarthLifeSci PPT Q2W2Document26 pagesEarthLifeSci PPT Q2W2arvin paruliNo ratings yet
- Stem Jeopardy 2023 Study GuideDocument4 pagesStem Jeopardy 2023 Study Guideapi-653192298No ratings yet
- Lecture 6 (Week 3) : BIOLOGY 201/winter 2018 Dr. Ian FergusonDocument3 pagesLecture 6 (Week 3) : BIOLOGY 201/winter 2018 Dr. Ian FergusonMohammad FotovatNo ratings yet
- MANGO ReferenceDocument15 pagesMANGO ReferenceN S Arun KumarNo ratings yet
- Frederick and Haselton PSPB 2007Document17 pagesFrederick and Haselton PSPB 2007Hacker GuduNo ratings yet
- Biology and Genetics PDFDocument8 pagesBiology and Genetics PDFPrincess Angie GonzalesNo ratings yet