Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Guidelines of Substance Data Acquisation
Uploaded by
NeybilCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Guidelines of Substance Data Acquisation
Uploaded by
NeybilCopyright:
Available Formats
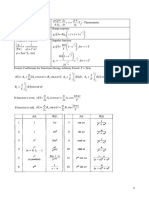
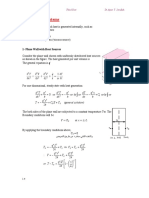
THERMODYNAMIC
DATA ACQUISATION
Data from YES
Property Tables PROPERTY
(eg. h, u, v, s) TABLE?
NO
h h h 2 1
u u u 2 1
PHASE?
v v v 2 1
s s s 2 1
SOLIDS GASES LIQUIDS
Specific heats YES NO Specific heats
Equation Equation
C C C IDEAL GAS? C C C
P V
Pv RT Pv ZRT P V
(Z from
compressibility
Enthalpy and internal Internal energy
Specific heats chart)
energy
C P a bT cT 2 dT 3 u CT
h u CT
and, C P CV R
Entropy
Entropy CdT T
Enthalpy and internal energy s
1
C ln 2
u C T dT
CdT T 2
T T
s
1 2
C ln 2
V
1
T 2
T 1
h C T dT
1
2
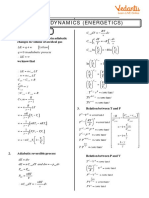
P Boundary work
Enthalpy
1
W PdV
2
b
1 h CT vP
Entropy
Isentropic process, k=CP/CV T2 v
k 1 k k 1
s C P ln R ln 2 Isobaric process
T2 P2 v T1 v1
(eg. in heaters)
1 T2 P
T1 P1 v2 or, s C P ln R ln 2 h CT
T1 P1
Isothermal
process
Polytropic process PVn=constant Isochoric process Isobaric process Isothermal process (eg. in pumps)
P2V2 P1V1 W 0 Wb Po (V2 V1 ) Wb mRTo ln
V2
h vP
Wb , for n 1
b
V1
1 n
V Polytropic and ideal gas
PV ln 2 , for n 1
V1 mR (T2 T1 )
Wb , for n 1
1 n
V
mRT ln 2 , for n 1
V1
Abdullah et al. (2013). Challenges in teaching and learning fundamentals of thermodynamics in engineering. J. of Engineering and Applied Sciences. 8(1):29-37
You might also like
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Formulasheetforquiz1 PDFDocument2 pagesFormulasheetforquiz1 PDFDheeraj Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- FormulaeDocument1 pageFormulaeAna Paula BittencourtNo ratings yet
- Scroll of Seals 1Document25 pagesScroll of Seals 1Anthony MacalindongNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Review SheetDocument2 pagesThermodynamics Review SheetAbinashSahooNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Converters: Step-Down Operation and ModesDocument20 pagesDC-DC Converters: Step-Down Operation and Modesحسن علي جاسمNo ratings yet
- RLC Circuits: Series and Parallel CombinationsDocument69 pagesRLC Circuits: Series and Parallel CombinationsPenziiNo ratings yet
- THERMODYNAMICS & THERMO CHEMISTRY Level 5 Quest & SolnDocument32 pagesTHERMODYNAMICS & THERMO CHEMISTRY Level 5 Quest & Solnproud vedan laxmiNo ratings yet
- Light Scattering: Basics: R K T E EDocument18 pagesLight Scattering: Basics: R K T E ESimo SoreNo ratings yet
- 102MAE Thermodynamics Formula SheetDocument2 pages102MAE Thermodynamics Formula SheetBogdan ProfirNo ratings yet
- KinjutsuDocument21 pagesKinjutsuLocus Jhun MichaelNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Converter Guide: Step-Down Operation & AnalysisDocument22 pagesDC-DC Converter Guide: Step-Down Operation & AnalysiskanithanNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems, 5e: Chapter 11: Baseband Digital Transmission A. Bruce Carlson Paul B. CrillyDocument48 pagesCommunication Systems, 5e: Chapter 11: Baseband Digital Transmission A. Bruce Carlson Paul B. CrillySara JEBRINo ratings yet
- Formulario Termodinamica Equaciones BasicasDocument1 pageFormulario Termodinamica Equaciones BasicasDivad_28No ratings yet
- Formula ListDocument3 pagesFormula ListRaihanNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Field SolutionsDocument14 pagesTransmission Line Field SolutionsBadai TimurNo ratings yet
- Ideal GasDocument1 pageIdeal GasMike Raphy T. VerdonNo ratings yet
- Chapt 4Document33 pagesChapt 4Ahmed AL-HarthiNo ratings yet
- Second Law of Thermodynamics: Spontaneous Direction of ChangeDocument24 pagesSecond Law of Thermodynamics: Spontaneous Direction of ChangeMichael Conan MaglaqueNo ratings yet
- Midterm I Formula SheetDocument5 pagesMidterm I Formula Sheeta0909665916No ratings yet
- Facts and Formulae SheetDocument7 pagesFacts and Formulae SheethenryNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet DSP FullDocument13 pagesFormula Sheet DSP FullMehmetNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering-Ii: BSC Civil Engineering - 5 SemesterDocument6 pagesGeotechnical Engineering-Ii: BSC Civil Engineering - 5 SemesterSaid-Mansour MohamedNo ratings yet
- Formularium R1-R2Document2 pagesFormularium R1-R2Marie De KerpelNo ratings yet
- Revision of Thermodynamics: Chapter 2. EngineDocument35 pagesRevision of Thermodynamics: Chapter 2. EngineYang Woo SeongNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Lab - Determination of Jet Velocity and Nozzle EfficiencyDocument9 pagesThermodynamics Lab - Determination of Jet Velocity and Nozzle EfficiencyfaezahjalalNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 5: Electromagnetic Waves in Vacuum The Wave Equation (S) For E and BDocument33 pagesLecture Notes 5: Electromagnetic Waves in Vacuum The Wave Equation (S) For E and BZhenhua HuangNo ratings yet
- Digital Control in Power Electronics, 2nd EditionDocument232 pagesDigital Control in Power Electronics, 2nd Editiontj.lin1024No ratings yet
- Seminar 'Signals and Systems 1': Properties of Signals in Time- and Frequency DomainDocument8 pagesSeminar 'Signals and Systems 1': Properties of Signals in Time- and Frequency DomainUmmu Abiha AssociatesNo ratings yet
- Physics 132 Midterm II Equation Sheet: Capacitors, EnergyDocument1 pagePhysics 132 Midterm II Equation Sheet: Capacitors, EnergyajdfhjNo ratings yet
- 2 SignalsDocument50 pages2 Signalskaganerkek98No ratings yet
- Ocw Chapter 4Document48 pagesOcw Chapter 4Agam HanasichulaNo ratings yet
- THERMODYNAMICS EQUATIONSDocument11 pagesTHERMODYNAMICS EQUATIONSAnthony MacalindongNo ratings yet
- Thermal Equation NotesDocument3 pagesThermal Equation NotesIsaac PittmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7.3 - EntropyDocument11 pagesChapter 7.3 - EntropyhudarusliNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6: The Greeks and Basic Hedging: Sources Avellaneda and Laurence J HullDocument20 pagesLecture 6: The Greeks and Basic Hedging: Sources Avellaneda and Laurence J HullJNo ratings yet
- Signals and Spectra (All Sections, Except Section 8, Are Covered.)Document49 pagesSignals and Spectra (All Sections, Except Section 8, Are Covered.)Nathan GossieauxNo ratings yet
- Week04Module03 FourierTransformsDocument13 pagesWeek04Module03 FourierTransformsrra127No ratings yet
- 3920614Document21 pages3920614Agam HanasichulaNo ratings yet
- Entropy View of Theoretical Processes .Document11 pagesEntropy View of Theoretical Processes .Muket AgmasNo ratings yet
- Formulario 3rd Winter 2018Document1 pageFormulario 3rd Winter 2018Oscar Daniel Martinez HuartadoNo ratings yet
- Reversed CurvesDocument7 pagesReversed CurvesRichiemay ValerianoNo ratings yet
- A B C D E: H P o L M CDocument1 pageA B C D E: H P o L M CMaiko Laine CarbonelNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics PDFDocument83 pagesThermodynamics PDFAbdel ElhamimiNo ratings yet
- BEF 12503 - Week 9 - AC Circuit Analysis Using Phasors and Equivalent Impedance ConceptDocument61 pagesBEF 12503 - Week 9 - AC Circuit Analysis Using Phasors and Equivalent Impedance Conceptfullmetal AesirNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 13 Coastal ProcessesDocument39 pagesKuliah 13 Coastal Processesberry mirazNo ratings yet
- Ramktne Qcle: Ha-H H) (B, - Ha)Document10 pagesRamktne Qcle: Ha-H H) (B, - Ha)Mr I S A MNo ratings yet
- Plane Wall 1-D Steady State Conduction W/O Heat GenerationDocument1 pagePlane Wall 1-D Steady State Conduction W/O Heat GenerationI Gede Darma SusilaNo ratings yet
- MSE 3002-Exam-1a-2a-Useful-Relations-2-19 - 3-25-2020Document2 pagesMSE 3002-Exam-1a-2a-Useful-Relations-2-19 - 3-25-2020hg lg jhgNo ratings yet
- Diatomic Ideal Gas 1Document36 pagesDiatomic Ideal Gas 1manurihimalshaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document23 pagesChapter 7sinabghbghNo ratings yet
- Form AstroDocument2 pagesForm AstroVictor De Paula VilaNo ratings yet
- Penurunan 2Document5 pagesPenurunan 2Fadli PunyeNo ratings yet
- Heat Conduction (导热) : Chapter 2 Heat conduction equations Chapter 2 Heat conduction equationsDocument20 pagesHeat Conduction (导热) : Chapter 2 Heat conduction equations Chapter 2 Heat conduction equationsVinod KhokharNo ratings yet
- Formulario 3rd Fall 2019Document1 pageFormulario 3rd Fall 2019Travis BickleNo ratings yet
- Heat Source Systems: 1-Plane Wall With Heat SourcesDocument5 pagesHeat Source Systems: 1-Plane Wall With Heat SourcesAnonymous 2BJgxbxJNo ratings yet
- Es3b5 - Revision Session - WK31 - Special Examinations PDFDocument46 pagesEs3b5 - Revision Session - WK31 - Special Examinations PDFPaul TanuNo ratings yet
- New IHR IGBT TechnologyDocument4 pagesNew IHR IGBT TechnologyvittorioNo ratings yet
- Reversed Curves GuideDocument7 pagesReversed Curves GuideBenidick Santos BernardinoNo ratings yet
- SI - Heat - 4e - Chap11 - Lecture WITH TUTORIAL Student COPY (Compatibility Mode)Document40 pagesSI - Heat - 4e - Chap11 - Lecture WITH TUTORIAL Student COPY (Compatibility Mode)NeybilNo ratings yet
- B9780123820983000032Document1 pageB9780123820983000032NeybilNo ratings yet
- cpt10 Case Studies Related To Safety in Process IndustryDocument17 pagescpt10 Case Studies Related To Safety in Process IndustryNeybilNo ratings yet
- Hysys SimulationDocument24 pagesHysys SimulationNeybil100% (1)
- B9780128009406000046Document1 pageB9780128009406000046NeybilNo ratings yet
- Property Tables and Charts (Si Units)Document50 pagesProperty Tables and Charts (Si Units)Q_TNo ratings yet
- Transient Heat Conduction: Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals & ApplicationsDocument44 pagesTransient Heat Conduction: Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals & ApplicationsNeybilNo ratings yet
- Ideology Doping and The Spirit of SportDocument18 pagesIdeology Doping and The Spirit of SportNeybilNo ratings yet
- Preparation Outline FormatDocument2 pagesPreparation Outline FormatNeybilNo ratings yet
- Flow Measurement Device Part 1Document1 pageFlow Measurement Device Part 1NeybilNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - Eh2203d - Properties Measurement PVTDocument14 pagesGroup 4 - Eh2203d - Properties Measurement PVTNeybilNo ratings yet
- Property Tables and Charts (Si Units)Document50 pagesProperty Tables and Charts (Si Units)Q_TNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Agitation Power Number and Scale Up 2020Document26 pages6.1 Agitation Power Number and Scale Up 2020Neybil100% (1)
- Qdoc - Tips - th11 Experimental ManualpdfDocument46 pagesQdoc - Tips - th11 Experimental ManualpdfNeybilNo ratings yet
- Property Tables and Charts (Si Units)Document50 pagesProperty Tables and Charts (Si Units)Q_TNo ratings yet
- Flow Measurement Devices Part 2 Inc AnsDocument3 pagesFlow Measurement Devices Part 2 Inc AnsNeybilNo ratings yet
- Guidelines of Substance Data AcquisationDocument1 pageGuidelines of Substance Data AcquisationNeybilNo ratings yet
- Equipment For Fluid Mechanics 2019aDocument30 pagesEquipment For Fluid Mechanics 2019aNeybilNo ratings yet
- Equipment For Fluid Mechanics 2019aDocument30 pagesEquipment For Fluid Mechanics 2019aNeybilNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.2 - Integration by Trigo FunctionsDocument19 pagesLesson 1.2 - Integration by Trigo FunctionsNeybilNo ratings yet
- cpt10 Case Studies Related To Safety in Process IndustryDocument17 pagescpt10 Case Studies Related To Safety in Process IndustryNeybilNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Agitation Power Number and Scale Up 2020Document26 pages6.1 Agitation Power Number and Scale Up 2020Neybil100% (1)
- Continuity and Bernoulli EqnDocument20 pagesContinuity and Bernoulli EqnNeybilNo ratings yet
- Continuity and Bernoulli EqnDocument20 pagesContinuity and Bernoulli EqnNeybilNo ratings yet
- Continuity & Bernoulli's Eqn Part 1Document1 pageContinuity & Bernoulli's Eqn Part 1NeybilNo ratings yet
- Measure and Calculate Fluid Flow Using Orifice, Venturi & Pitot Tube MetersDocument33 pagesMeasure and Calculate Fluid Flow Using Orifice, Venturi & Pitot Tube MetersAeyrul KhairulNo ratings yet
- Laminar Flow in ChannelsDocument15 pagesLaminar Flow in ChannelsNeybilNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Agitation Power Number and Scale Up 2020Document26 pages6.1 Agitation Power Number and Scale Up 2020Neybil100% (1)
- Experimental Analysis of Heat Transfer Performance of Wavy Fin Heat Sink With Different OrientationDocument5 pagesExperimental Analysis of Heat Transfer Performance of Wavy Fin Heat Sink With Different OrientationMADDI MADHAV.No ratings yet
- Cider Process and Process SimulationDocument41 pagesCider Process and Process SimulationRenzo Jose Canro CalderonNo ratings yet
- Air Based Hazards Sources of Air PollutantsDocument14 pagesAir Based Hazards Sources of Air PollutantslithaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: I Puc - Chemistry Chapter - 06Document11 pagesThermodynamics: I Puc - Chemistry Chapter - 06Udaybhaskar LalamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18: Nursing Care of A Family With A NewbornDocument32 pagesChapter 18: Nursing Care of A Family With A NewbornAlyssaGrandeMontimor100% (1)
- Thermo-economic optimization of waste heat recovery Organic Rankine CyclesDocument9 pagesThermo-economic optimization of waste heat recovery Organic Rankine CyclesKarla RezendeNo ratings yet
- 1.thermodynamics 21 30Document10 pages1.thermodynamics 21 30Aqsa KanwalNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Methods QuizDocument5 pagesHeat Transfer Methods QuizLoiweza AbagaNo ratings yet
- Concentric TubeDocument34 pagesConcentric TubeNajwa NaqibahNo ratings yet
- Ammonia PipelineDocument6 pagesAmmonia PipelineCesar Ricardo Lopez ValerioNo ratings yet
- Industrial - Elements NO ANSWERDocument78 pagesIndustrial - Elements NO ANSWERMark John RosalesNo ratings yet
- Alfa Laval Heat ExchangerDocument6 pagesAlfa Laval Heat Exchangersumit11235No ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer (MCC 15102) Assignmnet - 1: A F B C D EDocument4 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer (MCC 15102) Assignmnet - 1: A F B C D ERotten AppleNo ratings yet
- CT2 Grade 7 EditedDocument3 pagesCT2 Grade 7 EditedshamshadNo ratings yet
- M.tech Dissertation PPT FormatDocument4 pagesM.tech Dissertation PPT FormatWriteMyPaperIn3HoursSingapore100% (1)
- Management and Engineering of Fire Safety and Loss Prevention Onshore and OffshoreDocument295 pagesManagement and Engineering of Fire Safety and Loss Prevention Onshore and OffshoreAda Darmon100% (2)
- Pump Installation, Operation and MaintenanceDocument25 pagesPump Installation, Operation and Maintenancebayu kusumaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 The First Law of Thermodynamics (PP 59-81)Document23 pagesChapter 03 The First Law of Thermodynamics (PP 59-81)Muhammad Ashfaq Ahmed100% (1)
- SAPDocument16 pagesSAPsourav84No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction - 2012 - Applied Welding EngineeringDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Introduction - 2012 - Applied Welding EngineeringJames LeonNo ratings yet
- تقارير مختبر محركات احتراق داخليDocument19 pagesتقارير مختبر محركات احتراق داخليwesamNo ratings yet
- CFD Analysis of RadiatorDocument5 pagesCFD Analysis of RadiatorjournalNo ratings yet
- BIOE 332 Quiz Questions InsightsDocument31 pagesBIOE 332 Quiz Questions InsightsLina MaeNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1359836817335825 MainDocument15 pages1 s2.0 S1359836817335825 MainYineth PinzonNo ratings yet
- IEEE Document Superheated Steam Generator by Induction HeatingDocument4 pagesIEEE Document Superheated Steam Generator by Induction HeatingVarun ThakurNo ratings yet
- MEC 189.2 Thermal ScienceDocument4 pagesMEC 189.2 Thermal ScienceSyh TfkNo ratings yet
- PGS2 1997Document184 pagesPGS2 1997Pieter GrendelNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Assessment of The Fiji Islands - An Overview - NZWorkshop - 1982Document7 pagesGeothermal Assessment of The Fiji Islands - An Overview - NZWorkshop - 1982Ricardo PobleteNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Biochemistry 4th Edition DonaldDocument25 pagesTest Bank For Biochemistry 4th Edition DonaldUsman HaiderNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics ExamDocument2 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics ExamNiban IlawurNo ratings yet