Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 2-Focus On Laerner: Module Overview
Uploaded by
Jed GarciaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 2-Focus On Laerner: Module Overview
Uploaded by
Jed GarciaCopyright:
Available Formats
Study Guide in Prof.Ed.
103-Facilitating Learner Centered-Teaching Module 2: Unit 2- Focus on Learner
Module No.2
Unit 2- Focus on Laerner
MODULE OVERVIEW
Development is the series of age-related changes that happen throughout a life span.
Several famous psychologists, including Sigmund Freud, Erik Erikson, Jean Piaget, and Lawrence
Kohlberg, describe development as a series of stages. A Stage is a period in development in which
people exhibit typical behavior patterns and establish particular capacities. The various stage
theories share three assumptions:
People pass through stages in a specific order, with each stage building on capacities developed in
the previous stage. Stages are related to age. Development is discontinuous, with qualitatively
different capacities emerging in each stage.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
1. Give the 14 psychological principles?
2.. Define the meaning of the learning process?
LEARNING CONTENTS
A. REVIEW Of THE DEVELOPMENT THEORIES
Piaget's Stages of cognitive theories
Jean Piaget's theory of cognitive development suggests that children move through four
different stages of mental development. His theory focuses not only on understanding how children
acquire knowledge, but also on understanding the nature of intelligence.
• Sensorimotor stage: birth to 2 years
• Preoperational stage: ages 2 to 7
• Concrete operational stage: ages 7 to 11
• Formal operational stage: ages 12 and up
Erik Erikson's Stages of Psychosocial Development
Erik Erikson was an ego psychologist who developed one of the most popular and
influential theories of development. While his theory was impacted by psychoanalyst Sigmund
Freud's work, Erikson's theory centered on psychosocial development rather than psychosexual
development.
The stages that make up his theory are as follows:1
Stage 1: Trust vs. Mistrust
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 1
Study Guide in Prof.Ed.103-Facilitating Learner Centered-Teaching Module 2: Unit 2- Focus on Learner
Stage 2: Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt
Stage 3: Initiative vs. Guilt
Stage 4: Industry vs. Inferiority
Stage 5: Identity vs. Confusion
Stage 6: Intimacy vs. Isolation
Stage 7: Generativity vs. Stagnation
Stage 8: Integrity vs. Despair
Vygotsky's Sociocultural Theory
The work of Lev Vygotsky (1934) has become the foundation of much research and theory
in cognitive development over the past several decades, particularly of what has become known as
sociocultural theory.
Vygotsky's sociocultural theory views human development as a socially mediated process
in which children acquire their cultural values, beliefs, and problem-solving strategies through
collaborative dialogues with more knowledgeable members of society. Vygotsky's theory is
comprised of concepts such as culture-specific tools, private speech, and the Zone of Proximal
Development.
B. Student Diversity
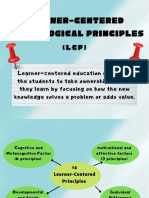
The following 14 psychological principles pertain to the learner and the learning process.
The 14 principles are divided into those referring to
- Cognitive and metacognitive
- Motivational and affective
- Developmental and social
- Individual difference factors
A. Cognitive and Metacognitive
Nature of Learning Process
> the learning of complex subject matter is most effective when it is
aninternational process of constructing meaning from information andexperience.
2. Goals of the Learning Process
> the successful learner, over time and with support and instructional guidance,can create
meaningful, coherent representations of knowledge.
3. Construction of Knowledge
> the successful learner can link new information with existing knowledge inmeaningful ways.
Knowledge widens and deepens as students continue to build links betweennew information and
experiences and their existing knowledge base.
4. Strategic Thinking
> the successful learner can create and use a repertoire of thinking and reasoningstrategies to
achieve complex learning goals. Successful learners use in their approach to learning
reasoning, problemsolving, and concept learning
5. Thinking about thinking
> Successful learners can reflect on how they think and learn, set reasonablelearning or
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 2
Study Guide in Prof.Ed.103-Facilitating Learner Centered-Teaching Module 2: Unit 2- Focus on Learner
performances goals, select potentially appropriate learningstrategies or methods, and monitor
their progress towards these goals.
6. Context of Learning
> Learning is influenced by environmental factors, including culture, technologyand instructional
practices.
B. Motivational and Affective Factors
FACILITATING LEARNING INTRODUCTION
7. Motivational and emotional influences on learning
> the rich internal world of thoughts, beliefs, goals, and expectation for successor failure can
enhance or interfere with the learner’s quality of thinking andinformation processing
8. Intrinsic motivation to learn
> Intrinsic motivation is stimulated by tasks of optimal novelty and difficulty,relevant to
personal interests, and providing for personal choice andcontrol.
9. Effects of motivation on effort
> Effort is another major indicator of motivation to learn. The acquisition ofcomplex knowledge
and skills demands the investment of considerablelearner energy and strategic effort, along
with persistence over time.
C. Developmental and Social Factors
10. Developmental influences on learning
> learning is most effective when differential developmental within and acrossphysical,
intellectual, emotional, and social domains is taken into account.
> Individuals learn best when material is appropriate to their developmentallevel and is presented
in an enjoyable and interesting way.
11. Social influence on learning
> Learning can be enhanced when the learner has an opportunity to interact and tocollaborate with
others on instructional tasks.
D. Individual Differences Factors
12. Individual differences in learning
> Individuals are born with and develop their own capabilities and talents.
> Educators need to help students examine their learning preferences andexpand or
modify them, if necessary.
13. Learning and diversity
> the same basic principles of learning, motivation, and effective instructionapply to all learners.
14. Standards and assessment
> Assessment provides important information to both the learner and teacher atall stages of the
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 3
Study Guide in Prof.Ed.103-Facilitating Learner Centered-Teaching Module 2: Unit 2- Focus on Learner
learning process.
LEARNING POINTS
A learning continuity plan seeks to ensure that students’ learning progresses even amidst
disasters such as natural calamities, storms, fires, and pandemics. This plan overcomes obstacles
created by the disasters through innovative means of teaching and learning, keeping students on
track with their courses. With today’s COVID-19 pandemic, the main obstacle that has to be
overcome is the need for social distancing, making face-to-face interaction impossible. Therefore,
any learning continuity plan to be implemented today has to account for this limitation.
A widely applied approach to second or foreign language teaching and training that
addresses immediate and very specific needs of learners who need that language as a tool in their
education, training, or job. Needs analysis is the underlying "driver" for the development of LSP
programs. For example, English native speaking nurses who work in hospitals with a high
percentage of patients whose native language is Spanish might have to study Spanish for the very
specific purpose of communication between nurses and patients. Students are encouraged to take
active roles in their learning and question what they have been taught. This is likened to negotiated
syllabus about which Hyland (2009) writes, "A negotiated syllabus means that the content of a
particular course is a matter of discussion between teacher and students, according to the wishes
and needs of the learners in conjunction with the expertise, judgment, and advice of the teacher"
LEARNING ACTIVITIES
Review Exercises
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 4
Study Guide in Prof.Ed.103-Facilitating Learner Centered-Teaching Module 2: Unit 2- Focus on Learner
Name: _________________________________ Date: _________
Year & Section__________________________ Score: __________
Essay
1. Examine the meaning of learner and applied it to the Centered Psychological Principle?
2. What are the focuses of the Centered Psychological Principle?
3. Explain each theory based on what you read in this module
REFERENCES
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 5
Study Guide in Prof.Ed.103-Facilitating Learner Centered-Teaching Module 2: Unit 2- Focus on Learner
Maryellen Weimer
Learner-Centered Teaching: Five Key Changes to Practice
By Erik H. Erikson Childhood and Society
Dale H. Schunk
Learning Theories: An Educational Perspective
edited by Robert W. Cole W. Cole Educating Everybody's Children: Diverse Teaching
Strategies for Diverse GTeaching Strategies
Prepared by : DR. GLORIA M. CAPANANG
Faculty, professional Education Dept.
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY 6
You might also like
- Part 1: IntroductionDocument10 pagesPart 1: IntroductionStacy Ann Dorado CoEdNo ratings yet
- Module 1 FaciDocument6 pagesModule 1 FaciAllysa Shane Paningbatan RascoNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 1Document3 pagesAssignment No. 1ruby lyn orejudosNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Psychological Principles: Vision MissionDocument9 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological Principles: Vision MissionCesar Dave PresentacionNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed ReviewerDocument54 pagesProf Ed ReviewerAniah OdinNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Module 1 FLCT The Learning Principles.Document6 pagesActivity 1 Module 1 FLCT The Learning Principles.Juedy Lala PostreroNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Introduction: Module OverviewDocument8 pagesUnit 1 - Introduction: Module OverviewJed GarciaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 FaciDocument6 pagesModule 1 FaciALLYSA RASCONo ratings yet
- Ed 101 - Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles Module 1: Learner - Centered Psychological Principles (LCP OverviewDocument9 pagesEd 101 - Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles Module 1: Learner - Centered Psychological Principles (LCP OverviewReana Bea Alquisada Leysa - CoedNo ratings yet
- Ed 101 - Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles Module 1: Learner - Centered Psychological Principles (LCP) OverviewDocument8 pagesEd 101 - Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles Module 1: Learner - Centered Psychological Principles (LCP) OverviewLino jay Ombega 2BNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University IslamabadDocument28 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University IslamabadZainab GameplaysNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Leaner Centered TeachingDocument27 pagesFacilitating Leaner Centered TeachingBann Ayot100% (1)
- Written Report Unit 2 Bsed Fil 1aDocument13 pagesWritten Report Unit 2 Bsed Fil 1aaira mambagNo ratings yet
- PROFED611Document14 pagesPROFED611PRINCESS MAE B. ARESNo ratings yet
- 1 The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles 1Document8 pages1 The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles 1Arianne Rose FangonNo ratings yet
- Unit 5-Integration: Module OverviewDocument5 pagesUnit 5-Integration: Module OverviewMAYLENE CALICDANNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learner-Centered TeachingDocument5 pagesFacilitating Learner-Centered TeachingHelna CachilaNo ratings yet
- Ed 101 - Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles Module 1: Learner - Centered Psychological Principles (LCP) OverviewDocument10 pagesEd 101 - Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles Module 1: Learner - Centered Psychological Principles (LCP) OverviewShaira B. Anonat CoedNo ratings yet
- Educ 3Document10 pagesEduc 3Lhoixhie BernardNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of The Physical Cognitive An Socio-Emotional Development of Pre-SchoolersDocument6 pagesSynthesis of The Physical Cognitive An Socio-Emotional Development of Pre-SchoolersGerome Anthon BritonNo ratings yet
- In Child and Adolescent Development: Colegio de San Sebastian College Department Sablayan, Occidental MindoroDocument14 pagesIn Child and Adolescent Development: Colegio de San Sebastian College Department Sablayan, Occidental MindoroDivyne BonaventeNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument4 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesHariette Mae OnofreNo ratings yet
- Module 5 FaciDocument5 pagesModule 5 FaciAngelo CaoileNo ratings yet
- Learner: Motivational and Affective Factors (3 Principles) Cognitive and Metacognitive Factor (6 Principles)Document3 pagesLearner: Motivational and Affective Factors (3 Principles) Cognitive and Metacognitive Factor (6 Principles)Sherwin Gipit100% (2)
- ES-332 Block1Document60 pagesES-332 Block1Subbaraju Gv100% (1)
- Barboza Bryan m5 Activity 1 2ced 3Document20 pagesBarboza Bryan m5 Activity 1 2ced 3Trisha Anne BataraNo ratings yet
- Learner Centered Psychological Principles Child AdoDocument25 pagesLearner Centered Psychological Principles Child Adobalanemaryjoy4No ratings yet
- Educational PsychologyDocument24 pagesEducational PsychologyBích NgọcNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learning Introduction 2222222222222Document16 pagesFacilitating Learning Introduction 2222222222222Roma RosarioNo ratings yet
- English 004Document20 pagesEnglish 004Charmen BontuyanNo ratings yet
- 01 Learner - Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument4 pages01 Learner - Centered Psychological PrinciplesKristine Saron GalaNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learner - Centered TeachingDocument21 pagesFacilitating Learner - Centered TeachingRicamae BalmesNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University Islamabad: Course Name M.EdDocument23 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University Islamabad: Course Name M.EdChemo PhobiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Ed123Document7 pagesLesson 5 Ed123Julie Ann Arenasa PiscosNo ratings yet
- SG1 Learner Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument5 pagesSG1 Learner Centered Psychological PrinciplesFate VargasNo ratings yet
- Acilitating: University of Mindanao Tagum CampusDocument25 pagesAcilitating: University of Mindanao Tagum CampusClara ArejaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - The Learner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP)Document31 pagesMODULE 1 - The Learner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP)Tintin Llauderes LloricoNo ratings yet
- Teaching Aptitude 1Document6 pagesTeaching Aptitude 1hampamNo ratings yet
- FLCL Mod 1Document9 pagesFLCL Mod 1Ana Carmela Salazar LaraNo ratings yet
- Learning TheoriesDocument10 pagesLearning Theoriesyonaseskezia8No ratings yet
- Ed1 Module 1 NotesDocument3 pagesEd1 Module 1 NotesChristhie RobleNo ratings yet
- PS 5 Module 1 PrelimDocument8 pagesPS 5 Module 1 Prelimblssm AbenesNo ratings yet
- Week 4-5 Psychological Principles and TheoriesDocument30 pagesWeek 4-5 Psychological Principles and TheoriesTrisha Mae VaguchayNo ratings yet
- Attributes and Distinctive Features of Adult Learning and (Autosaved) (Autosaved)Document32 pagesAttributes and Distinctive Features of Adult Learning and (Autosaved) (Autosaved)Mericar EsmedioNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learner ActivityDocument7 pagesFacilitating Learner ActivityLeslyn Bangibang DiazNo ratings yet
- The Learning of A Complex Subject Matter Is Most Effective When It Is Intentional Process of Constructing Meaning From Information and ExperienceDocument6 pagesThe Learning of A Complex Subject Matter Is Most Effective When It Is Intentional Process of Constructing Meaning From Information and ExperienceAbhey Abellera Barcena100% (2)
- Active Learning ConceptsDocument92 pagesActive Learning ConceptsAnh leNo ratings yet
- Module 4 FLCTDocument6 pagesModule 4 FLCTJerico VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Ed 123Document4 pagesLesson 4 Ed 123Julie Ann Arenasa PiscosNo ratings yet
- Facilitating LearningDocument16 pagesFacilitating LearningMa Iris Paula Talaga100% (3)
- Module 1Document5 pagesModule 1Dhaze OjanoNo ratings yet
- ED123 - Unit-1 - Lesson-3 Nov. 2022Document9 pagesED123 - Unit-1 - Lesson-3 Nov. 2022Hezel CabunilasNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 - Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument13 pagesUNIT 4 - Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesZarry ZackNo ratings yet
- Educ 111Document34 pagesEduc 111Jheufelle Ausa BocoNo ratings yet
- Course EnhancementDocument7 pagesCourse EnhancementPraxedes NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument37 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesJanny DiezNo ratings yet
- IMD - Educ101 Module PDFDocument67 pagesIMD - Educ101 Module PDFKarla G. AbadNo ratings yet
- Fs 1 Module 1 9 OutlineDocument13 pagesFs 1 Module 1 9 OutlineDONNA FEI MORENONo ratings yet
- Garcia, Jed D. Bee-Ege II-1 - ttl1 - Module 1-30pointsDocument8 pagesGarcia, Jed D. Bee-Ege II-1 - ttl1 - Module 1-30pointsJed GarciaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument13 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in ScienceJed GarciaNo ratings yet
- DLL W7 Q3 English 5Document6 pagesDLL W7 Q3 English 5Jed GarciaNo ratings yet
- DLL Week 7-Q3 Science 5Document6 pagesDLL Week 7-Q3 Science 5Jed GarciaNo ratings yet
- Life Without ComputerDocument1 pageLife Without ComputerJed GarciaNo ratings yet
- 5E Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument9 pages5E Lesson Plan in ScienceJed GarciaNo ratings yet
- WRITTEN REPORT Ft. CONTENT OFDocument4 pagesWRITTEN REPORT Ft. CONTENT OFJed GarciaNo ratings yet
- Garcia, Jed D. BEE-EGE II-1 - Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesGarcia, Jed D. BEE-EGE II-1 - Lesson PlanJed GarciaNo ratings yet
- Gde (Ege 4) SG Unit 6Document26 pagesGde (Ege 4) SG Unit 6Jed GarciaNo ratings yet
- Garcia, Jed D. - bee-EGE I-1 - Compilation of ModulesDocument23 pagesGarcia, Jed D. - bee-EGE I-1 - Compilation of ModulesJed GarciaNo ratings yet
- Popular Advertisement in The PhilppinesDocument25 pagesPopular Advertisement in The PhilppinesJed GarciaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3-Focus On Learning: Module OverviewDocument6 pagesUnit 3-Focus On Learning: Module OverviewJed GarciaNo ratings yet
- Life Without ComputerDocument1 pageLife Without ComputerJed GarciaNo ratings yet
- Popular Advertisements in The Philippines: Pangasinan State UniversityDocument19 pagesPopular Advertisements in The Philippines: Pangasinan State UniversityJed GarciaNo ratings yet
- Jed D. Garcia: Maigpa, Bayambang, Pangasinan 09287517497Document1 pageJed D. Garcia: Maigpa, Bayambang, Pangasinan 09287517497Jed GarciaNo ratings yet
- Title of The Unit/Chapter: Study Guide For Module No.Document8 pagesTitle of The Unit/Chapter: Study Guide For Module No.Jed GarciaNo ratings yet
- It EraDocument2 pagesIt EraJed GarciaNo ratings yet
- FinaltableofcontentsDocument3 pagesFinaltableofcontentsJed GarciaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument1 pageDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesJed GarciaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument1 pageDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesJed GarciaNo ratings yet
- Presidential PowersDocument8 pagesPresidential PowersJed GarciaNo ratings yet
- Reflection EssayDocument2 pagesReflection EssayJed GarciaNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Child Protection Policy in School As Perceived by Grade 12 StudentsDocument39 pagesEffectiveness of Child Protection Policy in School As Perceived by Grade 12 StudentsJed Garcia100% (1)
- Culminating Activity (Humss) : Department of EducationDocument5 pagesCulminating Activity (Humss) : Department of EducationJed GarciaNo ratings yet
- IndustrializtaionDocument2 pagesIndustrializtaionJed GarciaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3-Focus On Learning: Module OverviewDocument6 pagesUnit 3-Focus On Learning: Module OverviewJed GarciaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Introduction: Module OverviewDocument8 pagesUnit 1 - Introduction: Module OverviewJed GarciaNo ratings yet
- Thesis Report KapilDocument66 pagesThesis Report Kapilkapilsharma2686100% (1)
- The Allied Valve Spares Manufacturer Company Maharashtra IndiaDocument10 pagesThe Allied Valve Spares Manufacturer Company Maharashtra IndiaThe Allied Valve Spares Manufacturer CompanyNo ratings yet
- Dirty Dozen List of Endocrine DisruptorsDocument4 pagesDirty Dozen List of Endocrine DisruptorsMariuszNo ratings yet
- QRG-DC-004 Procedure and Regulation Governing The Requirements For CPWDocument56 pagesQRG-DC-004 Procedure and Regulation Governing The Requirements For CPWKarthi Keyan100% (2)
- Keith UrbanDocument2 pagesKeith UrbanAsh EnterinaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Evaluation and Management of The Solitary Pulmonary NoduleDocument21 pagesDiagnostic Evaluation and Management of The Solitary Pulmonary NoduleGonzalo Leal100% (1)
- Time Sheets CraneDocument1 pageTime Sheets CraneBillie Davidson100% (1)
- Basic Concepts and Applied Aspect of Sharir RachnaDocument122 pagesBasic Concepts and Applied Aspect of Sharir RachnaRam Krish100% (1)
- UntitledDocument18 pagesUntitledSpace HRNo ratings yet
- தமிழ் உணவு வகைகள் (Tamil Cuisine) (Archive) - SkyscraperCityDocument37 pagesதமிழ் உணவு வகைகள் (Tamil Cuisine) (Archive) - SkyscraperCityAsantony Raj0% (1)
- Julie Trimarco: A Licensed Speech-Language PathologistDocument5 pagesJulie Trimarco: A Licensed Speech-Language PathologistJulie TrimarcoNo ratings yet
- Northbrook CollegeDocument10 pagesNorthbrook CollegeDaniyal AsifNo ratings yet
- Continuous Microbiological Environmental Monitoring For Process Understanding and Reduced Interventions in Aseptic ManufacturingDocument44 pagesContinuous Microbiological Environmental Monitoring For Process Understanding and Reduced Interventions in Aseptic ManufacturingTorres Xia100% (1)
- Mrunal Handout 12 CSP20Document84 pagesMrunal Handout 12 CSP20SREEKANTHNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 2020 (Notes, PBD, Exercise) : Chapter: 8 RadioactivityDocument19 pagesScience Form 3 2020 (Notes, PBD, Exercise) : Chapter: 8 Radioactivitysakinah100% (1)
- Damasco - Cpi - Activity No. 10Document18 pagesDamasco - Cpi - Activity No. 10LDCU - Damasco, Erge Iris M.No ratings yet
- The Mystique of The Dominant WomanDocument8 pagesThe Mystique of The Dominant WomanDorothy HaydenNo ratings yet
- ReclosersDocument28 pagesReclosersSteven BeharryNo ratings yet
- Legg Calve Perthes DiseaseDocument97 pagesLegg Calve Perthes Diseasesivaram siddaNo ratings yet
- Molarity, Molality, Normality, and Mass Percent Worksheet II Answer Key 11-12 PDFDocument3 pagesMolarity, Molality, Normality, and Mass Percent Worksheet II Answer Key 11-12 PDFGerald KamulanjeNo ratings yet
- MCQ Cell InjuryDocument19 pagesMCQ Cell InjuryMoaz EbrahimNo ratings yet
- Summative Test SolutionsDocument1 pageSummative Test SolutionsMarian Anion-GauranoNo ratings yet
- Windows Perfectpath: Promise Multipath DriverDocument3 pagesWindows Perfectpath: Promise Multipath Driverpd904526No ratings yet
- 7B Form GRA Original - Part499 PDFDocument1 page7B Form GRA Original - Part499 PDFRicardo SinghNo ratings yet
- Inversor Abb 3 8kwDocument2 pagesInversor Abb 3 8kwapi-290643326No ratings yet
- WP DeltaV Software Update Deployment PDFDocument8 pagesWP DeltaV Software Update Deployment PDFevbaruNo ratings yet
- Period of Intuitive NursingDocument4 pagesPeriod of Intuitive NursingJhey-ar Toledo100% (1)
- MN - 2019 01 29Document28 pagesMN - 2019 01 29mooraboolNo ratings yet
- Sore Throat, Hoarseness and Otitis MediaDocument19 pagesSore Throat, Hoarseness and Otitis MediaainaNo ratings yet
- Hydroprocessing Pilot PlantsDocument4 pagesHydroprocessing Pilot PlantsNattapong PongbootNo ratings yet