Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WWW - Learnengineering.In: Me Echan Nism
Uploaded by
T COriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
WWW - Learnengineering.In: Me Echan Nism
Uploaded by
T CCopyright:
Available Formats
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.
in
Me
echan
nism
S K Moondal’s Chaptter 1
Number of Innstantan
neous centres
s in Mechanism and
Kenne edy The
eorem
GATE-26.. In the figure shown,
s th
he relative e
velocity of
o link 1 with
w respecct to link 2
is 12 m/seec. Link 2 rotates
r at a constannt
speed of 120 rpm.. The mag gnitude ofo
Carioles componen nt of accelleration ofo
link 1 is
.in
(a) 302m/s2 (b) 604 m/s
m 2
(c) 906m/s2 (d) 1208 m/s2
ng
eri
[GATE-20
004]
GATE-26.. Ans. (a) e
gin
En
arn
Le
Velocity off link 1 with
h respect to 2
w.
V1 2 = 12m s
2πN 2π × 120
ω= =
60 60
ww
= 12.566rad / s
∴Corioli’s componentt of accelera
ation
= 2V1 2 ω
= 2 × 12 × 12.566
= 302 m s2
GATE-27.. The Cario oles compo
onent of acccelerationn is presennt [GATE--2002]
(a) 4-bar mechanisms
m with 4 turn
ning pairs (b) shaperr mechanism
m
(c) slider-crrank mecha
anism (d) Scotch
h Yoke mechhanism
GATE-27.. Ans. (b)
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
Mechanism
S K Mondal’s Chapter 1
Hooke’s Joint (Universal Joint)
GATE-28. The coupling used to connect two shafts with large angular misalignment
is
(a) a Flange coupling (b) an Oldham's coupling [GATE-2002]
(c) a Flexible bush coupling (d) a Hooker’s joint
GATE-28. Ans. (d)
Previous 20-Years IES Questions
.in
Kinematic pair
ng
IES-1. Match List I with List II and select the correct answer [IES-2002]
eri
List I (Kinematic pairs) List II (Practical example)
A.Sliding pair 1. A road roller rolling over the ground
B. Revolute pair 2. Crank shaft in a journal bearing in an
C. Rolling pair
e
engine
gin
D. Spherical pair 3. Ball and socket joint
4. Piston and cylinder
5. Nut and screw
En
A B C D A B C D
(a) 5 2 4 3 (b) 4 3 1 2
(c) 5 3 4 2 (d) 4 2 1 3
IES-1. Ans. (d)
arn
Le
Sliding pair→ piston and cylinder
w.
Revolute pair → Crank shaft in a journal
bearing in an engine
Rolling →A road roller rolling over
ww
the ground
Spherical pair→ Ball and socket joint
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
Me
echan
nism
S K Moondal’s Chaptter 1
IES-2. A round bar A passes s through h
the cylindrical holle in B ass
shown in n the givven figuree.
Which on ne of the following g
statementts is correect in thiss
regard?
(a) The twwo links sho
own form a
kinematic pair.
p
(b) The pair is completely y
constrained
d.
.in
(c) The pair has incompletee
constraint.
(d) The pair is successfully y [IES-1
1995]
ng
constrained
d.
IES-2. An
ns. (c)
e eri
gin
When twoo elements or links are
a connectted in such h a way th hat their reelative mottion is
constrained
d they form
m a kinematiic pair. The relative mootion of a kin
nematic paiir may
be completely, incomp
pletely or successfully coonstrained
En
IES-3. Consider the following statem ments [IES--2000]
1. A round d bar in a round
r holee form a tuurning pairr.
2. A squar re bar in a square ho ole forms a sliding pa
air.
3. A verticcal shaft in
n a footstepp bearing forms
f a su
uccessful co
onstraint.
arn
Of these statements
s s
(a) 1 and 2 are correct (b) 1 andd 3 are correect
(c) 2 and 3 are correct (d) 1, 2 and
a 3 are corrrect
IES-3. An
ns. (c)
Le
IES-4. Match List-I with List-II
L and
d select th
he correct answer using
u the codes
given belo
ow the Listts: [IES--1999]
w.
List-I List-III
A. 4 links,, 4 turning
g pairs 1. Complete connstraint
B. 3 links,, 3 turning
g pairs 2. Successful co
onstraint
ww
C. 5 links,, 5 turning
g pairs 3. Rig
gid frame
D. Footsteep bearing g 4. Inc
complete cconstraint
Code: A B C D A B C D
(a) 3 1 4 2 (b
b) 1 3 2 4
(c) 3 1 2 4 (d
d) 1 3 4 2
IES-4. An
ns. (d)4
3
links and 4 turning pairs
p satisfy
y the equatiion L = (jj + 2); It is case of com
mplete
2
constraint. 3 links and
d 3 turning pairs form rigid
r frame. Foot step bearing
b resu
ults in
successful constraint and
a 5 links and 5 turniing pairs proovide incom
mplete constrraint.
IES-5. Consider the following statem
ments: [IES--2005]
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
Mechanism
S K Mondal’s Chapter 1
1. The degree of freedom for lower kinematic pairs is always equal to
one.
2. A ball-and-socket joint has 3 degrees of freedom and is a higher
kinematic pair
3.Oldham's coupling mechanism has two prismatic pairs and two revolute
pairs.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3 (b) 1 only (c) 2 and 3 (d) 3 only
IES-6. Ans. (a)
.in
IES-7. Which of the following are examples of forced closed kinematic pairs?
1. Cam and roller mechanism 2. Door closing mechanism [IES-2003]
3. Slider-crank mechanism 4. Automotive clutch operating mechanism
ng
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Codes:
(a) 1, 2 and 4 (b) 1 and 3 (c) 2, 3 and 4 (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
eri
IES-7. Ans. (a)
IES-8. Assertion (A): Hydraulic fluid is one form a link. [IES-1996]
e
Reason (R): A link need not necessarily be a rigid body but it must be a
gin
resistant body.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
En
IES-8. Ans. (a)
IES-9 Assertion (A): When a link has pure translation, the resultant force must
arn
pass through the centre of gravity. [IES-1994]
Reason (R): The direction of the resultant force would be in the direction
of acceleration of the body.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A
Le
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
IES-9. Ans. (b)
w.
Lower pair
ww
IES-10. Consider the following statements: [IES-2006]
1. Lower pairs are more resistant than the higher pairs in a plane
mechanism.
2. In a 4-bar mechanism (with 4 turning pairs), when the link opposite to
the shortest link is fixed, a double rocker mechanism results.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) Only 1 (b) Only 2 (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2
IES-10. Ans. (c)
Higher pair
IES-11. Consider the following pairs of parts: [IES-2000]
1. Pair of gear in mesh 2. Belt and pulley
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
Mechanism
S K Mondal’s Chapter 1
3. Cylinder and piston 4. Cam and follower
Among these, the higher pairs are
(a) 1 and 4 (b) 2 and 4 (c) 1, 2 and 3 (d) 1, 2 and 4
IES-11. Ans. (d)
IES-12. Assertion (A): The elements of higher pairs must be force closed.
Reason (R): This is required in order to provide completely constrained
motion.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of
A
.in
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation
of A
(c) A is true but R is false
ng
(d) A is false but R is true [IES-1995]
IES-12. Ans. (a)
eri
Elements of higher pairs must be force closed to provide completely constrained
motion.
Kinematic chain
IES-13. e
In a Kinematic chain, a quaternary joint is equivalent to: [IES-2005]
gin
(a) One binary joint (b) Two binary joints
(c) Three binary joints (d) Four binary joints
IEA-13. Ans. (c)
when ‘l’ number of links are joined at the same connection, the joint is equivalent to
En
(l - 1) binary joints.
IES-14. The kinematic
arn
chain shown in
the above
figure is a
(a) structure
Le
(b) mechanism
with one degree
of freedom
w.
(c) mechanism
[IES-2000]
with two degree
of freedom
ww
(d) mechanism
with more than
two degrees of
freedom
IES-14. Ans. (b)
IES-15. Which of the following are examples of a kinematic chain? [IES-1998]
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
Mechanism
S K Mondal’s Chapter 1
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Codes: (a) 1, 3 and 4 (b) 2 and 4 (c) 1, 2 and 3 (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
.in
IES-15. Ans. (d)
IES-16. A linkage is shown
below in the figure
ng
in which links ABC
and DEF are
ternary Jinks
eri
whereas AF, BE
and CD are binary
links.
The
freedom
degrees
of
of
the e
gin
linkage when link [IES-2002]
ABC is fixed are
(a) 0 (b) 1
(c) 2 (d) 3
En
IES-16. Ans. (a)
arn
Degrees of freedom
IES-18. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes
given below the lists:
Le
[IES-2001]
List-I List-II
A. 6 d.o.f. system 1. Vibrating beam
w.
B. 1 d.o.f. system 2. Vibration absorber
C. 2 d.o.f. system 3. A rigid body in space
D. Multi d.o.f. system 4. Pure rolling of a cylinder
ww
Codes: A B C D A B C D
(a) 1 2 4 3 (b) 1 4 2 3
(c) 3 2 4 1 (d) 3 4 2 1
IES-18. Ans. (d)
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
Mechanism
S K Mondal’s Chapter 1
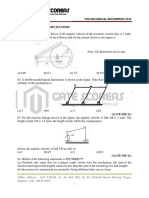
IES-19. The two-link system, shown in the
given figure, is constrained to
move with planar motion. It
possesses
(a) 2-degrees of freedom
(b) 3-degrees of freedom
(c) 4-degrees of freedom
(d) 6-degrees of freedom
.in
[IES-1994]
IES-19. Ans. (a) Two link system shown in the above figure has 2 degrees of freedom.
ng
IES-20. When supported on three points, out of the 12 degrees of freedom the
number of degrees of reedom arrested in a body is [IES-1993]
eri
(a) 3 (b) 4 (c) 5 (d) 6
IES-20. Ans. (d) When supported on three points, following six degrees of freedom are
arrested (two line movements along y-axis, two rotational movements each along x-
axis and z-axis.)
e
gin
Grubler criterion
IES-21. f = 3 (n - 1) - 2j. In the Grubler's equation for planar mechanisms given, j is
En
the [IES-2003]
(a) Number of mobile links (b) Number of links
(c) Number of lower pairs (d) Length of the longest link
arn
IES-21. Ans. (c)
IES-22. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes
given below the lists:
Le
List-I List-II
A.Cam and follower 1. Grubler's rule
B. Screw pair 2. Grashof's linkage
w.
C. 4-bar mechanism 3. Pressure angle
D. Degree of freedom of planar 4. Single degree of freedom
mechanism
ww
Codes: A B C D A B C D
(a) 3 4 2 1 (b) 1 2 4 3
(c) 1 4 2 3 (d) 3 2 4 1
IES-23. Ans. (a)
Grashof’s law
IES-24. Inversion of a mechanism is [IES-1992]
(a) changing of a higher pair to lower pair
(b) obtained by fixing different links in a kinematic chain
(b) turning it upside down
(d) obtained by reversing the input and output motion
For More Visit : www.LearnEngineering.in
You might also like
- WWW - Learnengineering.In: MechanismDocument7 pagesWWW - Learnengineering.In: MechanismT CNo ratings yet
- PW - AITS - NT-18: PhysicsDocument21 pagesPW - AITS - NT-18: PhysicsShivanshu ShivamNo ratings yet
- Engineering Academy: (Questions Based On Memory of Students) SET - 1 (31 January Forenoon Session)Document14 pagesEngineering Academy: (Questions Based On Memory of Students) SET - 1 (31 January Forenoon Session)rohithNo ratings yet
- (PDF) Download Disha Target VITEEE 2021 - Past 14 Years (2019 - 2006) Solved Papers + 10 Mock Tests 10th (IIT-NEET - Xyz)Document600 pages(PDF) Download Disha Target VITEEE 2021 - Past 14 Years (2019 - 2006) Solved Papers + 10 Mock Tests 10th (IIT-NEET - Xyz)ANDREW JOHNNo ratings yet
- DPP (30-32) 12th Physics - E - WADocument6 pagesDPP (30-32) 12th Physics - E - WAMeena ChakrabartyNo ratings yet
- Gate Paper Solution - 2007 - 2018Document313 pagesGate Paper Solution - 2007 - 2018Raddical IndianNo ratings yet
- WWW - Learnengineering.In: MechanismDocument7 pagesWWW - Learnengineering.In: MechanismT CNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapterwise Objective QuestionsDocument24 pagesPhysics Chapterwise Objective QuestionsNafisha KNo ratings yet
- HT TP: //qpa Pe R.W But .Ac .In: 2011 Solid State DevicesDocument4 pagesHT TP: //qpa Pe R.W But .Ac .In: 2011 Solid State DevicesSoumitra BhowmickNo ratings yet
- A Pxe B) O) E: Bvoltldoule) Volt/metreDocument5 pagesA Pxe B) O) E: Bvoltldoule) Volt/metreassentialNo ratings yet
- BendingStressInBeam GATEDocument15 pagesBendingStressInBeam GATEParth PatelNo ratings yet
- Phy Sample Paper 1Document8 pagesPhy Sample Paper 1nidha.jasmine21No ratings yet
- 2 Jeem 2022 July 25 Second Shift PaperDocument37 pages2 Jeem 2022 July 25 Second Shift PaperAtharva Sheersh PandeyNo ratings yet
- ME 2012 Solved PDFDocument22 pagesME 2012 Solved PDFTavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Questions Chap4 de Strength of Materials 1 CopierDocument36 pagesQuestions Chap4 de Strength of Materials 1 CopierAnge Miniminione Sims SimoNo ratings yet
- Cce RR: - Moêfi) - Msê¿Document9 pagesCce RR: - Moêfi) - Msê¿Michael VladislavNo ratings yet
- PHY1Document6 pagesPHY1Sagar NyaupaneNo ratings yet
- Design of Friction Drives: Selection of V-Belt DriveDocument5 pagesDesign of Friction Drives: Selection of V-Belt DriveJai SharmaNo ratings yet
- SQP 20 Sets PhysicsDocument163 pagesSQP 20 Sets Physicsparam.bhathal09100% (1)
- Theory of Machines - by LearnEngineering - inDocument137 pagesTheory of Machines - by LearnEngineering - inuserhoverwatch184No ratings yet
- Simulation Analysis of Petroleum Premium Casing Connection: Procedia EngineeringDocument8 pagesSimulation Analysis of Petroleum Premium Casing Connection: Procedia EngineeringWilliam OmgbaNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity PYQ SDocument5 pagesCurrent Electricity PYQ Spatiminati2020No ratings yet
- Board Question Paper: March 2016: PhysicsDocument8 pagesBoard Question Paper: March 2016: PhysicsRavindra YadavNo ratings yet
- Ese 2021: Prelims Exam: MechanicalDocument12 pagesEse 2021: Prelims Exam: MechanicalSheelendra kumarNo ratings yet
- Design of Friction Drives: Self Locking ScrewDocument5 pagesDesign of Friction Drives: Self Locking ScrewJai SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cblephpu 10Document7 pagesCblephpu 10HwhaibNo ratings yet
- Pathfinder WBJEE 2014 Physics SolutionDocument12 pagesPathfinder WBJEE 2014 Physics SolutionafasdfasdNo ratings yet
- ME Theory of MachinesDocument54 pagesME Theory of MachinesShah GhanimNo ratings yet
- 12th Physics Sahodaya Set2 QPDocument12 pages12th Physics Sahodaya Set2 QPAdiboiiiNo ratings yet
- XII Physics EveningDocument12 pagesXII Physics EveningPiyush Kumar JhaNo ratings yet
- Dimensional & Model Analysis GATE PDFDocument13 pagesDimensional & Model Analysis GATE PDFYashwanth VudathuNo ratings yet
- AITS 2324 FT V JEEM LD SolDocument17 pagesAITS 2324 FT V JEEM LD SolVishnuNo ratings yet
- Ai Aieee Modeltest 10Document22 pagesAi Aieee Modeltest 10api-26165439No ratings yet
- 9.nuclear and Particle Physics - GATEDocument14 pages9.nuclear and Particle Physics - GATEDeepneel KunduNo ratings yet
- PH Sample Paper 1 UnsolvedDocument11 pagesPH Sample Paper 1 Unsolvedudit anandNo ratings yet
- Gate Solved Paper - Ce: List I List IIDocument21 pagesGate Solved Paper - Ce: List I List IIsaithejaNo ratings yet
- Paper 9Document8 pagesPaper 9zeeltarpara97560No ratings yet
- Csir - Net Physical Sciences Nuclear & Particle Physics JUNE - 2011Document5 pagesCsir - Net Physical Sciences Nuclear & Particle Physics JUNE - 2011ken adamsNo ratings yet
- O Q (Gate, Ies, Ias) : Bjective Uestions Previous 20-Years GATE Questions Helical SpringDocument16 pagesO Q (Gate, Ies, Ias) : Bjective Uestions Previous 20-Years GATE Questions Helical SpringharshdeepNo ratings yet
- Jee Main 2020 Sept 4 Second Shift PaperDocument35 pagesJee Main 2020 Sept 4 Second Shift PaperRIYA KUMARINo ratings yet
- Vedantu - JEE Main Simulator: 1. in A Circuit Consisting of A Capacitance and A Generator With Alternating Emf EDocument53 pagesVedantu - JEE Main Simulator: 1. in A Circuit Consisting of A Capacitance and A Generator With Alternating Emf EPandu KpNo ratings yet
- IIT-JEE - 2007 Paper - 1 SolutionsDocument34 pagesIIT-JEE - 2007 Paper - 1 Solutionsmintuphy100% (1)
- 19.06.23 Sankalp24 Paper SolutionsDocument36 pages19.06.23 Sankalp24 Paper SolutionsworkspaceformyselfNo ratings yet
- Vedantu - JEE Main Simulator: 1. The Value of Current in TheDocument44 pagesVedantu - JEE Main Simulator: 1. The Value of Current in ThechaitubudatiNo ratings yet
- MT-87 QueDocument12 pagesMT-87 QuePriyansh RastogiNo ratings yet
- ME 2003 Unsolved PDFDocument18 pagesME 2003 Unsolved PDFSathya ThyaguNo ratings yet
- 09 01 24 SR Star Co Scmodel A, B&C Jee Main GTM 11n QPDocument20 pages09 01 24 SR Star Co Scmodel A, B&C Jee Main GTM 11n QPReddyNo ratings yet
- 2022 JEE Main Home Practice Test - 8 - Solutions (@vmclectures On Telegram)Document13 pages2022 JEE Main Home Practice Test - 8 - Solutions (@vmclectures On Telegram)cosmicbot2k06No ratings yet
- VGADocument40 pagesVGAmaheshNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics DPP-02 Lec-03 @physicswallahlakshyavideos PhysicswallahlakshyavideosDocument4 pagesRay Optics DPP-02 Lec-03 @physicswallahlakshyavideos PhysicswallahlakshyavideosSR PHYSICSNo ratings yet
- JIPMER Sample Paper: JIPMER Set 2 JIPMER Set 2Document36 pagesJIPMER Sample Paper: JIPMER Set 2 JIPMER Set 2Rohit ChattopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Test Series Full Test-2332002Document11 pagesTest Series Full Test-2332002Mayank KoshtaNo ratings yet
- HSC 2016 March PhysicsDocument8 pagesHSC 2016 March Physicsaryxn123No ratings yet
- Cblephpl 14Document6 pagesCblephpl 14Harishni ArulvasagamNo ratings yet
- Ternary Chalcopyrite Semiconductors: Growth, Electronic Properties, and Applications: International Series of Monographs in The Science of The Solid StateFrom EverandTernary Chalcopyrite Semiconductors: Growth, Electronic Properties, and Applications: International Series of Monographs in The Science of The Solid StateRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- An Introduction to Field Quantization: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyFrom EverandAn Introduction to Field Quantization: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyNo ratings yet
- Theory of Dielectric Optical Waveguides 2eFrom EverandTheory of Dielectric Optical Waveguides 2ePaul LiaoNo ratings yet
- LKJGGDVVJHDocument6 pagesLKJGGDVVJHT CNo ratings yet
- GHJJFFDFVHDocument6 pagesGHJJFFDFVHT CNo ratings yet
- CVNNXSDFDocument6 pagesCVNNXSDFT CNo ratings yet
- FhhgtuffDocument6 pagesFhhgtuffT CNo ratings yet
- VBNMXXSGGDFDocument6 pagesVBNMXXSGGDFT CNo ratings yet
- PrefaceDocument6 pagesPrefaceT CNo ratings yet
- WWW - Learnengineering.In: MechanismDocument7 pagesWWW - Learnengineering.In: MechanismT CNo ratings yet
- 2.4.2 Specific Volume and Density: Thermal Principles-A Review of FundamentalsDocument6 pages2.4.2 Specific Volume and Density: Thermal Principles-A Review of FundamentalsT CNo ratings yet
- 2.11 Third Law of Thermodynamics: PT S VDocument6 pages2.11 Third Law of Thermodynamics: PT S VT CNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning: 1.3.6 Solar Energy Based Refrigeration SystemsDocument7 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning: 1.3.6 Solar Energy Based Refrigeration SystemsT CNo ratings yet
- Evaporator.: Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument6 pagesEvaporator.: Refrigeration and Air ConditioningT CNo ratings yet
- First Toss Second Toss Third Toss Outcome H T: Uniform DistributionDocument6 pagesFirst Toss Second Toss Third Toss Outcome H T: Uniform DistributionT CNo ratings yet
- Continuous Probability Densities: 2.1 Simulation of Continuous ProbabilitiesDocument6 pagesContinuous Probability Densities: 2.1 Simulation of Continuous ProbabilitiesT CNo ratings yet
- WWW - Learnengineering.In: MechanismDocument7 pagesWWW - Learnengineering.In: MechanismT CNo ratings yet
- WWW - Learnengineering.In: MechanismDocument7 pagesWWW - Learnengineering.In: MechanismT CNo ratings yet
- Possible Questions Exam Non-Equilibrium Statistical MechanicsDocument4 pagesPossible Questions Exam Non-Equilibrium Statistical MechanicsEgop3105No ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Test For Dimensions and Tolerance of Burnt Clay BricksDocument2 pagesExperiment 4 Test For Dimensions and Tolerance of Burnt Clay BricksJigme SingyeNo ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantsDocument18 pagesSteam Power Plantscan canNo ratings yet
- Cationic Polymerization: From Photoinitiation To PhotocontrolDocument10 pagesCationic Polymerization: From Photoinitiation To Photocontrol章晴昱No ratings yet
- Expansion Joint in CAESARDocument5 pagesExpansion Joint in CAESARkaruna346No ratings yet
- 00 IntroductionDocument2 pages00 IntroductionRK MEHTANo ratings yet
- TB50SE13Document11 pagesTB50SE13Novianto RachmadNo ratings yet
- WPS P1 Group Any To P1 Group Any GTAW-FCAW (Manual-Machine)Document2 pagesWPS P1 Group Any To P1 Group Any GTAW-FCAW (Manual-Machine)Prasad ChakkrapaniNo ratings yet
- 3) Actuator Valve - Johnson Control VG8000NDocument4 pages3) Actuator Valve - Johnson Control VG8000Nfaris.tlksNo ratings yet
- Stored EnergyDocument38 pagesStored EnergySajid SattarNo ratings yet
- Lecture Nine: Best Vision Sphere (BVS) and Stenopaeic SlitDocument24 pagesLecture Nine: Best Vision Sphere (BVS) and Stenopaeic Slithenok birukNo ratings yet
- Limits Fits and ToleranceDocument47 pagesLimits Fits and TolerancePranjali SinhaNo ratings yet
- A Computer Program For The Aerodynamic Design of Axisymmetric and Planar Nozzles For Supersonic and Hypersonic Wind TunnelsDocument151 pagesA Computer Program For The Aerodynamic Design of Axisymmetric and Planar Nozzles For Supersonic and Hypersonic Wind TunnelsBlackFootNo ratings yet
- 8989 Ijmme IjensDocument16 pages8989 Ijmme IjensjeovanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Standards Manual ISD 341-2 Chapter 13, Welding & Joining GWS 1-07 - Consumable MaterialsDocument2 pagesEngineering Standards Manual ISD 341-2 Chapter 13, Welding & Joining GWS 1-07 - Consumable MaterialsMUHAMMAD WARIS SQNo ratings yet
- Studio Photography PresentationDocument16 pagesStudio Photography Presentationapi-248078730No ratings yet
- SCC SeminarDocument20 pagesSCC SeminarManas SinghNo ratings yet
- Dialab Autolyzer 450Document2 pagesDialab Autolyzer 450Niraj Silwal100% (1)
- The Reinforcement of Steel ColumnsDocument5 pagesThe Reinforcement of Steel Columnsprinkesh barodiyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Chapter7 2020 Part1Document45 pagesLecture - Chapter7 2020 Part1Qassem MohaidatNo ratings yet
- LNGC Methane Kari Elin - Imo 9256793 - Machinery Operating Manual - 2005Document388 pagesLNGC Methane Kari Elin - Imo 9256793 - Machinery Operating Manual - 2005seawolf50No ratings yet
- RGPV Syllabus Grading Me 403 Theory of MC and MechanismDocument1 pageRGPV Syllabus Grading Me 403 Theory of MC and MechanismSagar DhruvaNo ratings yet
- Coasts Revision BookDocument31 pagesCoasts Revision Bookapi-261914272No ratings yet
- Theories Behind Shear Thinning BehaviorDocument4 pagesTheories Behind Shear Thinning Behaviorengineer bilalNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil - Petroleum ProductsDocument10 pagesCrude Oil - Petroleum ProductsGeorge_Wabag_2014No ratings yet
- 12 Passed Leader Asat SyllabusDocument1 page12 Passed Leader Asat SyllabusprinceNo ratings yet
- 7 EFv NPBL RS9 BV 6 J 37 Ux LTZgiqa R6 E6 R 1 C Osu TRC XDocument18 pages7 EFv NPBL RS9 BV 6 J 37 Ux LTZgiqa R6 E6 R 1 C Osu TRC XAbhishekNo ratings yet
- Evaporation NotesDocument151 pagesEvaporation NotesIreneNo ratings yet
- Weld Modeling With MSC - NastranDocument14 pagesWeld Modeling With MSC - Nastransumatrablackcoffee453No ratings yet
- LPG Blackmer PumpsDocument16 pagesLPG Blackmer Pumpssizweh100% (1)