Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rrlmatirx
Uploaded by
John Linard Aningga0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views4 pagesThe document discusses mobility challenges faced by persons with disabilities (PWDs) and efforts to make transportation facilities more disability inclusive and accessible. Key points include:
1) PWDs face challenges using public transportation due to lack of accessibility features like ramps, accessible toilets, and designated seating.
2) Laws and bills aim to mandate upgrades to public utility vehicles to better accommodate PWDs, including wheelchair spaces and safety accessories.
3) Groups audit transportation facilities to identify accessibility gaps and work with agencies to implement inclusive designs like audio signals and wider doors at stations.
Original Description:
Original Title
rrlmatirx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses mobility challenges faced by persons with disabilities (PWDs) and efforts to make transportation facilities more disability inclusive and accessible. Key points include:
1) PWDs face challenges using public transportation due to lack of accessibility features like ramps, accessible toilets, and designated seating.
2) Laws and bills aim to mandate upgrades to public utility vehicles to better accommodate PWDs, including wheelchair spaces and safety accessories.
3) Groups audit transportation facilities to identify accessibility gaps and work with agencies to implement inclusive designs like audio signals and wider doors at stations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views4 pagesRrlmatirx
Uploaded by
John Linard AninggaThe document discusses mobility challenges faced by persons with disabilities (PWDs) and efforts to make transportation facilities more disability inclusive and accessible. Key points include:
1) PWDs face challenges using public transportation due to lack of accessibility features like ramps, accessible toilets, and designated seating.
2) Laws and bills aim to mandate upgrades to public utility vehicles to better accommodate PWDs, including wheelchair spaces and safety accessories.
3) Groups audit transportation facilities to identify accessibility gaps and work with agencies to implement inclusive designs like audio signals and wider doors at stations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
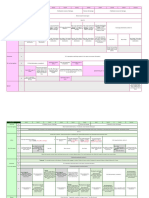
Keywords: Mobility challenges, PWDs, Transportation Facilities, Disability inclusive, Accessibility
Related Literature
Author Mobility Challenges PWDs Transportation Facilities Disability Inclusive Accessibility
The measures also take The road safety advocate We started our auditing in Above all, Fullo, Malinao and According to Barba,
Ting, K. (2019) into account the said Batas Pambansa 344 or some bus stations in Cubao. Barba agree that teaching transport should be
vulnerability of people the 35-year-old Act which There have to be toilets and road safety should be a accessible for all, non –
around or those who assist calls for the enhancement of ramps in buses. In the priority in homes and disabled and disabled
PWDs. “If one of the people mobility for PWDs serve as Paranaque Integrated schools. individuals, but can’t be
assisting you slips while their guide in PWD-friendly Terminal Exchange (PITX), “You have to start them easily achieve straightaway.
carrying you, you fall. You infrastructure. But while before we checked, there young,” said Barba, who Presently, the accessibility
can get injured. That’s why there is an existing law, a lot were no accessibility plans. cited the Paranaque guidelines in public utility
we are giving solutions to more can be done to Good thing we checked it Elementary School and the vehicles (PUV)
buses to get a movable improve the set standards, just time while construction nearby San Dionisio modernization programs
ramp. It is still in the he said. was still going on.” Elementary School as good aren’t completely prepared
production stage so it will Last July, a bill was filed in “We believe that if (roads) examples because they yet.
take time to fully develop the House of Representative are accessible, they are safe teach kids about road safety.
many of them.” aiming to institutionalize not just for commuters and “They teach them to have
“Everything we do is PWD-friendly transportation pedestrians, but also for road safety commitments so
concerned with disability,” programs to address the cars, and establishments,” they know better when they
he said, adding that many needs of PWDs as he said. grow older.”
among the elderly have commuters. Their group, formed in Malinao agrees it is
some kind of disability, Under the proposed House March 2019, is responsible important to teach not only
whether due to hearing or Bill No. 2224 or the ‘PWD- for assessing the quality of road safety to students but
sight,” said Barba. friendly and Safe transport and road also about inclusivity of
There are 1.4 million PWDs Transportation Act’ conditions for PWDs. PWDs. “Not all roads are
across the country based authored by For the pilot testing, some accessible to PWDs so
on the 2010 Population Congresswoman Ma. hybrid buses already have people should be more
Census of the Philippine Lourdes Arroyo, all PUV labels designating seats for considerate.”
Statistics Authority. operators and owners are senior citizens, small Fullo thinks while there have
mandated to upgrade their children, and pregnant been moves towards greater
PUVs by providing passenger women. For PWDs, they inclusivity, more needs to be
boarding ramps or lifts, will have a space to park done to better aid them.
spaces for wheelchairs and their wheelchairs in the
other safety accessories center.
such as seatbelts, clamps, “We designed it with the
and grab bars to provide DOTr. The doors will also be
safety and comfort to PWD bigger to accommodate
commuters. wheelchair users,” Barba
The bill also requires the said in an interview.
Department of Public Works The task force is building
and Highways to designate a ‘special tools’ for the blind,
certain portion of roadway such as stop lights with
or highway as pick-up points sounds to signal the blind if
for PWDs. they can cross the roads.
Around the same time,
Senator Leila de Lima filed
Senate Bill 188, which aims
to transform the National
Council on Disability Affairs
into a National Commission
for Disability Affairs. The
shift is designed to “further
strengthen its role as the
primary agency responsible
for the implementation of
policies aimed at fulfilling
the rights of the PWD
sector.”
Mobility challenges PWDs Transportation Facilities Disability Inclusive Accessibility
Ola Mobility Institute(2021) Before the time of the covid- Amidst of the pandemic, According to the
19 pandemic, Persons with India has set its goal to International Labour
Disabilities (PwDs) are achieve a more resilient and Organization, India’s GDP
continuing living the successful economy. The can increase to 7 percent
challenges in public country encourages its when the cost of Persons
transportation. In Mumbai, citizen to grasp their full with Disability is excluded.
a student using a wheelchair potential, and to accomplish With an approximate $2.8
can’t enter local train that the country should first trillion estimation of 2021-
stations because of the focus to its transport 22 GDP, which could lost a
stairs in the transportation systems, wherein it is the break of approximately $232
facility, and the accessible life arteries of any economy billion.
buses are not always from any countries, because
available, making it more it inhibits its progression and
difficult. Similarly, a visually advancement. Hence, the
impaired teacher named transport systems should
Usha, from Delhi and her pass its accessibility and
student with a disability is inclusivity standards for all,
infuriated when buses don’t not only for non-disabled
stop for them. individuals but for the 100
million+ Persons with
Disabilities as well.
Mobility challenges PWDs Transportation Facilities Disability Inclusive Accessibility
Alexiou, G. (2021) The priority regarding public According to Alexiou, the According to Alexiou, the
transport and road objective is not to create report note some significant
infrastructure is its physical specific suggestions but to data points, says that 80 out
accessibility, but in the extract several emotional of the 270 stations in London
world of the disabled people and psychological drivers Underground which has a
it is only a fraction of their describing inaccessibility step – free access and 65%
problem, which leads to from the perception of a of persons with disabilities
many challenges faced by disabled person. The report used public transportation at
people with disability. also creates on the idea of least once a week in the
The report’s annotations “mobility justice,” which all report in 2017, wherein the
from the interviews taken people should have a fair transport accessibility is
from the five interviewees and equal opportunity to anything but a dry statistical
with mobility deficiencies access and use public analysis.
with no relation to their spaces.
demographic status, yet all
interviewees are similar to
one, and that is the degree
of anxiety experienced of
disabled people in using
public transportation and its
premises.
Mobility challenges PWDs Transportation Facilities Disability Inclusive Accessibility
Geronia, E.(2017) Persons with Disabilities still In the Philippines, several Many centuries have passed, In London, the buses have
experienced most laws concerning people with the world and even the hydraulics that lowers the
architectural barriers every disabilities are designed to Philippines develops vehicle to curb level while a
day, such as steep and ensure the health, safety continuously, yet in some ramp deploys so you can
narrow ramps, that is too and security of disabled other parts, especially in smoothly roll in and out.
difficult for wheelchair – people, and also to improve handling the problems Most buildings in Japan have
bound individuals, non – accessibility in various regarding people with automatic doors for easy
disabled individuals that spaces. Though these laws, disabilities, which comprises access, walkalators and
takes the area of parking regardless of the quantity, mostly of physical escalators have interactive
slots made for persons with there is no guarantee that it disabilities, sensory voice response (IVR)
disabilities, toilets for will inevitably develop the impairments, and mental systems, and you are always
disabled users that are everyday life of a person retardation. Thus, in the the priority in line without
closed, elevator switches with a disability. perception of a disabled asking for it. If there is a lack
without Braille markings, A modified vehicle for person, this world and of accessibility in the area,
and pavements that lacks persons with disabilities is country is all designed for the handlers are the one at
detectable warning surfaces. quite expensive, because able – bodied individuals. fault and are extremely
only few companies accept apologetic, because of the
modifications in vehicles inconvenience that the
that are accessible for person had experienced.
disabled persons, and also
the lack of demand, that is
why a person with
disabilities in the Philippines
is difficult, because of the
financial challenges to
acquire this modified
vehicles.
Links:
https://verafiles.org/articles/accessibility-sensitivity-toward-pwd-commuters
https://www.cnbctv18.com/views/accessible-inclusive-transport-must-to-unlock-potential-of-100-million-indians-with-disabilities-11486282.htm
https://www.forbes.com/sites/gusalexiou/2021/02/17/for-disabled-people-inclusive-transportation-is-about-much-more-than-lifts-and-ramps/?sh=47521b8b2b08
https://www.esquiremag.ph/life/health-and-fitness/the-life-of-a-pwd-in-the-philippines-a1760-20170810-lfrm?fbclid=IwAR3uxd5lV6B2FWr8zUTMRfvxVEZflYYz1Jw-ye4CCui09IRtSGBbh2Fdm7E
You might also like
- MK6 Golf GTI Wiring Diagrams & Component Locations PDFDocument1,165 pagesMK6 Golf GTI Wiring Diagrams & Component Locations PDFMorarescu Andrei100% (5)
- Skilltest A320Document8 pagesSkilltest A320Lohrasp SuraliwalaNo ratings yet
- Arctic Marine Operations Report PDFDocument463 pagesArctic Marine Operations Report PDFfergerson100% (1)
- Genset WD Tp6146Document28 pagesGenset WD Tp6146andrea lizeth martinez camachoNo ratings yet
- Merchant Shipping Crew Agreement RegulationsDocument6 pagesMerchant Shipping Crew Agreement RegulationsMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Matrix of Related LiteratureDocument19 pagesMatrix of Related LiteratureJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Research DocumentationDocument58 pagesResearch Documentationapi-468315946No ratings yet
- Bulawayo safe & inclusive cities newsletter promotes youth participationDocument8 pagesBulawayo safe & inclusive cities newsletter promotes youth participationPraise NkalaNo ratings yet
- Abina Omarova (Problem of Public During A Pandemic)Document58 pagesAbina Omarova (Problem of Public During A Pandemic)Albina OmarovaNo ratings yet
- Canvas de Modelo de Negocio Tabla para Estrategia Planeación Negocio Pastel ModernoDocument3 pagesCanvas de Modelo de Negocio Tabla para Estrategia Planeación Negocio Pastel ModernoSelene Tamara Bravo PingoNo ratings yet
- Harmonized Gender and Development Guideline andDocument7 pagesHarmonized Gender and Development Guideline andJulia Katherine MoplaNo ratings yet
- TableDocument8 pagesTableDEANNA DANIELLE REYESNo ratings yet
- FT AspxDocument9 pagesFT AspxAndrea Guzmán GálvezNo ratings yet
- Pelayanan Publik Bidang Transportasi Bagi Difabel Di Daerah Istimewa YogyakartaDocument12 pagesPelayanan Publik Bidang Transportasi Bagi Difabel Di Daerah Istimewa Yogyakartasiti maisarohNo ratings yet
- Dadaab Project ReportDocument17 pagesDadaab Project ReportShivraj SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- Be A Kidult' and Be With Children - Some Thoughts On Active and Public Transportation - PUTSPACEDocument6 pagesBe A Kidult' and Be With Children - Some Thoughts On Active and Public Transportation - PUTSPACEAlessander MarcondesNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Universally Accepted Public Transport - A Before and After StudyDocument8 pagesThe Impact of Universally Accepted Public Transport - A Before and After StudyAaron BennettNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS PRESENTATION ENGLISH 3 | Marginingsih,S.Pd.,M.PdDocument16 pagesBUSINESS PRESENTATION ENGLISH 3 | Marginingsih,S.Pd.,M.PdPipin AnjarwatiNo ratings yet
- Free Developmental and Autism Screenings To Be Offered in OKCDocument2 pagesFree Developmental and Autism Screenings To Be Offered in OKCSloane WellnerNo ratings yet
- A Practice of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)Document11 pagesA Practice of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)Leslie Monica MacaisaNo ratings yet
- Empath and Research WorksheetDocument3 pagesEmpath and Research Worksheetapi-664240486No ratings yet
- Terms of Reference - GESICDocument6 pagesTerms of Reference - GESICsanjay prasadNo ratings yet
- Josephetal.2021-ChangesinmobilityexperiencesandperceptionsafterBRTimplementationDocument10 pagesJosephetal.2021-ChangesinmobilityexperiencesandperceptionsafterBRTimplementationBenson NkyaNo ratings yet
- Public Transport Accessibility For WheelchairDocument11 pagesPublic Transport Accessibility For WheelchairdangerousmalwpNo ratings yet
- Gender Equality and Disability Inclusion in WASHDocument16 pagesGender Equality and Disability Inclusion in WASHHabtamNo ratings yet
- OARS 1st IssueDocument5 pagesOARS 1st IssueRachit JainNo ratings yet
- NO Nama Judul Metode Kesimpulan: Kemis Martono, Sandriana Marina, Aditya WardanaDocument5 pagesNO Nama Judul Metode Kesimpulan: Kemis Martono, Sandriana Marina, Aditya WardanaMuhammad FarizalNo ratings yet
- September 2018 Connects SpecialDocument16 pagesSeptember 2018 Connects Specialbotta bhavnaNo ratings yet
- Transport Industry Chapter 1Document9 pagesTransport Industry Chapter 1alcrishr19No ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument5 pages1 PBSekar DwijayantiNo ratings yet
- Mateo Babiano2015Document17 pagesMateo Babiano2015Ayako KurobaNo ratings yet
- PAP126Document8 pagesPAP126Allan AmilcarNo ratings yet
- Safe Routes To School in Brazil: Current ConditionsDocument4 pagesSafe Routes To School in Brazil: Current ConditionsPostcrestNo ratings yet
- Final-Term-Major-Requirement_Research-Paper-in-Journal-Format_TESIORNA-KINSHEN-S.-1Document8 pagesFinal-Term-Major-Requirement_Research-Paper-in-Journal-Format_TESIORNA-KINSHEN-S.-1Cheska ChangcoNo ratings yet
- Public Transport Ebook Milestone SystemsDocument21 pagesPublic Transport Ebook Milestone SystemsStar BreakerNo ratings yet
- IT PedestrianDocument1 pageIT PedestrianEdreen Mae GalangNo ratings yet
- University of Southern Mindanao Senior High SchoolDocument33 pagesUniversity of Southern Mindanao Senior High SchoolKoleen Lopez Ü100% (1)
- HPBS PUJ ConsultationDocument1 pageHPBS PUJ ConsultationAndi ChinaNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id4175764Document12 pagesSSRN Id4175764Bryan LazoNo ratings yet
- FERRYGO: Mobile App for Maritime Transport Booking in Alabat IslandDocument53 pagesFERRYGO: Mobile App for Maritime Transport Booking in Alabat IslandBanjo De los SantosNo ratings yet
- Existing HYPAR ResourcesDocument5 pagesExisting HYPAR Resourcesapi-3742131No ratings yet
- Willamette Pedestrian Coalition: Annual ReportDocument4 pagesWillamette Pedestrian Coalition: Annual ReportStephanie RouthNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0965856422002361 MainDocument14 pages1 s2.0 S0965856422002361 MainMaria AnaNo ratings yet
- Free Developmental and Autism Screenings Offered: Clip Resized 52%Document1 pageFree Developmental and Autism Screenings Offered: Clip Resized 52%Sloane WellnerNo ratings yet
- 1909.11604Document4 pages1909.11604kkeerthi595No ratings yet
- Volume 46 Number 4Document23 pagesVolume 46 Number 4Bryan High School NorsemanNo ratings yet
- Assessing Bus Transit Service From The Perspective of Elderly Passengers in Harbin, ChinaDocument17 pagesAssessing Bus Transit Service From The Perspective of Elderly Passengers in Harbin, ChinaYalong YuanNo ratings yet
- PART A - Ballarat Integrated Transport Action Plan - Community ConsultationDocument26 pagesPART A - Ballarat Integrated Transport Action Plan - Community ConsultationAlexNo ratings yet
- Gender and Transport: Key Issues and Good Practices For ADB OperationsDocument43 pagesGender and Transport: Key Issues and Good Practices For ADB OperationsADBGADNo ratings yet
- Keep To The Left and Stay Alert - Singapore's First-Ever Code of Conduct For Pedestrians Kicks In, Transport News & Top Stories - The Straits TimesDocument4 pagesKeep To The Left and Stay Alert - Singapore's First-Ever Code of Conduct For Pedestrians Kicks In, Transport News & Top Stories - The Straits TimesShivani VNo ratings yet
- Roundtable Transport CORP Agenda 2 9thsept MAHSRTCDocument6 pagesRoundtable Transport CORP Agenda 2 9thsept MAHSRTCVinay NamdeoNo ratings yet
- Travelling in A Womans ShoesDocument90 pagesTravelling in A Womans ShoesAishwarya IshaNo ratings yet
- TeacherGuide BoosterClubDocument24 pagesTeacherGuide BoosterClubapi-3850559100% (1)
- Executive Summary Toward Universal Mobility For Web ShareDocument20 pagesExecutive Summary Toward Universal Mobility For Web ShareAnonymous 8v54VwOGtNo ratings yet
- 04 TargetGroup Group6Document1 page04 TargetGroup Group6siegaralphNo ratings yet
- ADA Case StudyDocument3 pagesADA Case StudySokhoeurn MourNo ratings yet
- Covid-19:Resuming Public Transport Post Lockdown: Team KUET - ImperioDocument11 pagesCovid-19:Resuming Public Transport Post Lockdown: Team KUET - ImperioAsif SaadNo ratings yet
- Metro Manila and Public Transport: A Study of Its Economic Impact Towards CommutersDocument9 pagesMetro Manila and Public Transport: A Study of Its Economic Impact Towards CommutersMaria Elena AquinoNo ratings yet
- Barriers To Inclusion of Children With Disabilities: July 2020Document9 pagesBarriers To Inclusion of Children With Disabilities: July 2020pratamamelani717No ratings yet
- ITU Guidelines For Children On Child Online ProtectionDocument86 pagesITU Guidelines For Children On Child Online ProtectionJohn J. MacasioNo ratings yet
- EmpowerABILITYDocument32 pagesEmpowerABILITYipshigoyal4No ratings yet
- Sustainable Transportation and Mobility System in Kabul City SpringerLinkDocument10 pagesSustainable Transportation and Mobility System in Kabul City SpringerLinkMohammad Zamir TaqwaNo ratings yet
- Mobility for Empowerment in Remote Himalayan RegionsDocument8 pagesMobility for Empowerment in Remote Himalayan Regionsshadab0123No ratings yet
- NSTP Development PlanDocument1 pageNSTP Development PlanCHAD JENREX HAPINNo ratings yet
- Application FormDocument6 pagesApplication FormJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Ch3 - Methodology - CE4-3 - Aningga-Manalo-San Jose-VillafuerteDocument12 pagesCh3 - Methodology - CE4-3 - Aningga-Manalo-San Jose-VillafuerteJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Death BedDocument2 pagesDeath BedJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Year at A GlanceDocument4 pagesYear at A GlanceJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- ReactionsDocument6 pagesReactionsJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- F-0349-15 - Information SheetDocument2 pagesF-0349-15 - Information SheetJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Test D PlansDocument6 pagesTest D PlansJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Test C PlansDocument7 pagesTest C PlansJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Sample CADsDocument4 pagesSample CADsJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Test A PlansDocument8 pagesTest A PlansJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Sy 2 + Associates Inc. - Application FormDocument3 pagesSy 2 + Associates Inc. - Application FormJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Test B PlansDocument5 pagesTest B PlansJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- TasksDocument1 pageTasksJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- STAAD SteelDocument1 pageSTAAD SteelJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesQuestionnaireJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Practical Steps To Making Public Transport Disability InclusiveDocument25 pagesPractical Steps To Making Public Transport Disability InclusiveJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Laws in The CE ProfessionDocument4 pagesLaws in The CE ProfessionJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- BP 344 - DPWHDocument11 pagesBP 344 - DPWHJabriellaSanMiguelNo ratings yet
- IRR of BP 344Document12 pagesIRR of BP 344VERA FilesNo ratings yet
- APA Format: A Quick GuideDocument4 pagesAPA Format: A Quick GuideJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Disability, Mobility and Transport in Low-And Middle-Income Countries: A Thematic ReviewDocument18 pagesDisability, Mobility and Transport in Low-And Middle-Income Countries: A Thematic ReviewCliff LowanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Examples Dynamic Magnification FactorDocument4 pagesUnit 3 - Examples Dynamic Magnification FactorJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- CE Laws, Codes and EthicsDocument30 pagesCE Laws, Codes and EthicsJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- 2TitleProposal - CE-4-3 - Aningga, Manalo, San Jose, VillafuerteDocument2 pages2TitleProposal - CE-4-3 - Aningga, Manalo, San Jose, VillafuerteJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- SOLUTION: Thiessen-Polygon Method: Area (A) Area (B) Area (C)Document2 pagesSOLUTION: Thiessen-Polygon Method: Area (A) Area (B) Area (C)John Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Examples SDOF Forced VibrationDocument10 pagesUnit 3 - Examples SDOF Forced VibrationJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- 2TitleProposal - CE-4-3 - Aningga, Manalo, San Jose, VillafuerteDocument2 pages2TitleProposal - CE-4-3 - Aningga, Manalo, San Jose, VillafuerteJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- 2TitleProposal - CE-4-3 - Aningga, Manalo, San Jose, VillafuerteDocument2 pages2TitleProposal - CE-4-3 - Aningga, Manalo, San Jose, VillafuerteJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Fassi Crane Use and Maintenance Manual Translation of The Original Instructions UM001Document214 pagesFassi Crane Use and Maintenance Manual Translation of The Original Instructions UM001MANUEL CASTILLONo ratings yet
- Wind Tunnel Test Specification for Honshu-Shikoku Bridges (2001Document15 pagesWind Tunnel Test Specification for Honshu-Shikoku Bridges (2001Michael HiiNo ratings yet
- Outer Rim Character Solo Decks v2.3 Modified Chart LayoutDocument9 pagesOuter Rim Character Solo Decks v2.3 Modified Chart LayoutjanunezmendozaNo ratings yet
- Gates DatasheetDocument2 pagesGates DatasheetWilson DavaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Traffic Reduction System OriginalDocument8 pagesHydraulic Traffic Reduction System OriginalChandra shekar RaoNo ratings yet
- Meghana Travels - Online Bus Tickets To Hyderbad, Visakhapatnam, Tirupati, Kadapa, Nandyala, Kurnool, Giddalur..Document2 pagesMeghana Travels - Online Bus Tickets To Hyderbad, Visakhapatnam, Tirupati, Kadapa, Nandyala, Kurnool, Giddalur..Yogeeswar ReddyNo ratings yet
- RegistrosDocument23 pagesRegistrosSilvianny BotelloNo ratings yet
- DocsDocument6 pagesDocsMary Margaret FuentesNo ratings yet
- Saima Mangi Reg # 1935153 Course: Strategic Management Final Project Report Organization: PIA Pakistan International AirportDocument15 pagesSaima Mangi Reg # 1935153 Course: Strategic Management Final Project Report Organization: PIA Pakistan International AirportJamshed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ship RepairDocument5 pagesShip Repairycgoyal100% (1)
- Asia's Largest Travel Network in a Single ClickDocument6 pagesAsia's Largest Travel Network in a Single ClickjrduronioNo ratings yet
- Blue and White Modern Technology Portfolio PresentationDocument15 pagesBlue and White Modern Technology Portfolio PresentationYanella Seneth Salas ParodiNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Road Infrastructure in Road Safety: Performance IndicatorsDocument9 pagesThe Influence of Road Infrastructure in Road Safety: Performance IndicatorsluizaNo ratings yet
- DEPT of Mechanical Engineering JNNCE, ShivamoggaDocument23 pagesDEPT of Mechanical Engineering JNNCE, ShivamoggaAkshayNo ratings yet
- Axe Bow Concept - Gelling 2005Document44 pagesAxe Bow Concept - Gelling 2005haujesNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating ProcedureDocument5 pagesStandard Operating ProcedurekstapletNo ratings yet
- Shale Gas Play Screening and Evaluation CriteriaDocument14 pagesShale Gas Play Screening and Evaluation CriteriaLulut Fitra FalaNo ratings yet
- All Terrain Crane SpecsDocument3 pagesAll Terrain Crane SpecsSaul TobonNo ratings yet
- 804-Automotive - Handbook Xii ClassDocument157 pages804-Automotive - Handbook Xii ClassAyush SoniNo ratings yet
- Practice 3 HDTTX Ar2Document15 pagesPractice 3 HDTTX Ar2Quang PhùngNo ratings yet
- Agc Lcep Project Team Course FinalDocument92 pagesAgc Lcep Project Team Course FinalPiereSalas100% (1)
- BT Road From R&B Road Lankalapalli in ButtayagudemDocument62 pagesBT Road From R&B Road Lankalapalli in Buttayagudempilli hemanthNo ratings yet
- CV Yogi SianiparDocument2 pagesCV Yogi SianiparArdiansyahNo ratings yet
- A320LEAP1A-B12-0008.6, Exhaust, R1 220517Document28 pagesA320LEAP1A-B12-0008.6, Exhaust, R1 220517simsimsom100% (1)
- Chapter 5 - Product SpecificationsDocument23 pagesChapter 5 - Product Specificationshisham_eyes100% (1)