Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Middle East Technical University Department of Chemical Engineering Ch.E. 204-Thermodynamics I (Section 02) Dr. N. Sezgi, M. Sarıyer
Uploaded by
GG MMOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Middle East Technical University Department of Chemical Engineering Ch.E. 204-Thermodynamics I (Section 02) Dr. N. Sezgi, M. Sarıyer
Uploaded by
GG MMCopyright:
Available Formats
MIDDLE EAST TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
Ch.E. 204- Thermodynamics I (Section 02)
Dr. N. Sezgi, M. Sarıyer
PROBLEM SET I
(Date Due: October 30, 2018)
Problem 1. For each of the following systems, indicate whether the system is isolated,
closed, or open and explain briefly a) A closed bottle of wine, b) A lake, c) A pressure
cooker, d) A thermos flask, e) A human body, f) A car radiator.
Problem 2. A mercury thermometer is calibrated at the ice and steam points. Using
the following data, calculate the reading of this thermometer at 200°C. Indicate your
assumptions.
T(°C) ρ(g/cm3 ) T(°C) ρ(g/cm3 )
0 13.5955 150 13.2330
50 13.4729 200 13.1148
100 13.3522 250 12.9975
Problem 3. A rigid tank initially contains air at 60 bar. A valve is opened and the
pressure in the tank falls rapidly to 35 bar. To calculate the air temperature at the final
state it is convenient to choose “air remaining in the tank when the pressure reaches
35 bar” as the system. Is this an open or a closed system?
Problem 4. State the direction of the heat transfer Q and work W for each of the
following processes. The systems to be considered are underlined.
a) The air in a tyre and connected pump. The pump plunger is pushed down,
forcing air into the tyre. Assume tyre, pump walls, plunger and connecting tube
to be non-conducting.
b) Steam in a closed rigid vessel at a temperature of 150°C is left standing in an
atmosphere which is at a temperature of 25°C.
c) Gas in an insulated cylinder expans as the piston is moved slowly outwards.
Problem 5. A cylinder fitted with a piston contains a gas at a given temperature and
pressure. The gas cools at constant pressure to a new volume by the transfer of heat.
How would you define the system to determine the amount of work done and heat
transferred? Also show the process path in a P-V diagram.
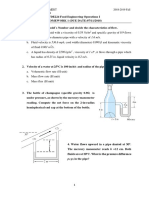
Problem 6. A gas is compressed from an initial volume of 0.42 m3 to a
final volume of 0.12 m3. During the quasi-equilibrium process, the
pressure changes with volume according to the relation P = aV + b,
where a = -1200 kPa/m3 and b = 600 kPa. Calculate the work done
during this process (a) by plotting the process on a P–V diagram and
finding the area under the process curve and (b) by performing the
necessary integrations.
You might also like
- Rac Solution Set BDocument12 pagesRac Solution Set BxofigoNo ratings yet
- Problem Chapter 9Document48 pagesProblem Chapter 9Syahid ZamaniNo ratings yet
- Transient Heat TransferDocument10 pagesTransient Heat TransferRimaz RameezNo ratings yet
- HW 4 3.12Document33 pagesHW 4 3.12Anonymous U3DpVvqVWx0% (3)
- Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics ReviewDocument5 pagesChemical Engineering Thermodynamics ReviewGeorge Isaac McQuiles100% (2)
- Is 600 MM Sufficient To Keep BDV FunctionalDocument0 pagesIs 600 MM Sufficient To Keep BDV Functionalsachin2010No ratings yet
- Me2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - May June 2016Document4 pagesMe2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - May June 2016BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Quiz No. 3Document1 pageQuiz No. 3Remae GarciNo ratings yet
- 10.213 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Spring 2002 Problem Set GDocument2 pages10.213 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Spring 2002 Problem Set GPM SHNo ratings yet
- Qbank 18me32 BTDDocument6 pagesQbank 18me32 BTDAmaresh Movies ASNo ratings yet
- Adibatik Gas LawDocument14 pagesAdibatik Gas LawAsiyahBeybehNo ratings yet
- ChE 122 LE1 Samplex 2Document3 pagesChE 122 LE1 Samplex 2googley71No ratings yet
- PART-I Numerical Problem Type QuestionsDocument3 pagesPART-I Numerical Problem Type QuestionsByisa BgaleNo ratings yet
- Rac Assignment 1Document4 pagesRac Assignment 1Guru Ravindra ReddyNo ratings yet
- CHEE220 Heat Engine Lab Jan2014Document4 pagesCHEE220 Heat Engine Lab Jan2014mfuzdnldNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 11 Cyclepad - Thermodynamic Properties of Air: 1. BuildDocument2 pagesTutorial 11 Cyclepad - Thermodynamic Properties of Air: 1. BuildAbdul HafizNo ratings yet
- RAC April-May 2013 PDFDocument3 pagesRAC April-May 2013 PDFShashi Bhushan PatelNo ratings yet
- ChE204 20181HWIIDocument1 pageChE204 20181HWIIGG MMNo ratings yet
- MAE 3223-Tulsa HW 1 Text - First Law Ver 07Document2 pagesMAE 3223-Tulsa HW 1 Text - First Law Ver 07Yep IdidthisNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Air Conditioning Nme604Document3 pagesRefrigeration Air Conditioning Nme604Mayank Vasisth GandhiNo ratings yet
- MMAN2700 Laboratory T1 2014Document4 pagesMMAN2700 Laboratory T1 2014Abhishek SharanNo ratings yet
- AE May 2013 04 BS 10Document4 pagesAE May 2013 04 BS 10Amber HarrisNo ratings yet
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics May June 2014Document4 pagesMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics May June 2014BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Code: 9A03302 B.Tech II Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14Document4 pagesCode: 9A03302 B.Tech II Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14sivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Is 600 MM Sufficient To Keep BDV FunctionalDocument4 pagesIs 600 MM Sufficient To Keep BDV FunctionalkronafNo ratings yet
- ME 417 ProblemsDocument5 pagesME 417 ProblemsReina Grace PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 SolutionDocument3 pagesAssignment 2 SolutionJacob Johnston100% (1)
- Problem Sheet 3 Heat, Work and The First Law of Thermodynamics PDFDocument4 pagesProblem Sheet 3 Heat, Work and The First Law of Thermodynamics PDFS DNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document7 pagesSheet 1Bahaa RaghebNo ratings yet
- Maae 3400: Applied Thermodynamics Problem Set 1Document4 pagesMaae 3400: Applied Thermodynamics Problem Set 1minyoun0% (1)
- Theoretical Analysis Report: Problem DefinitionDocument6 pagesTheoretical Analysis Report: Problem Definitionwtt1640No ratings yet
- Tutorial QuestionsDocument6 pagesTutorial QuestionsLadnilrebNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics - هيرارح اكيمانيدDocument16 pagesThermodynamics - هيرارح اكيمانيدHafiz Mahar28No ratings yet
- Work Sheet.1Document6 pagesWork Sheet.1tfkthe46No ratings yet
- Vm235: Thermodynamics Homework 6: Assigned Fri Jun 24, 2016 Due Thur July 7 at The Start of ClassDocument3 pagesVm235: Thermodynamics Homework 6: Assigned Fri Jun 24, 2016 Due Thur July 7 at The Start of Classtony960129No ratings yet
- Colling Tower: Mechanical Lab / Exp. NO.Document10 pagesColling Tower: Mechanical Lab / Exp. NO.Dalal Salih100% (1)
- BTD Question Bank1Document16 pagesBTD Question Bank1Mahantesh ChulakiNo ratings yet
- RAC Assign 1Document2 pagesRAC Assign 1Arun BeniwalNo ratings yet
- บทที่ 3 thermodynamicsDocument11 pagesบทที่ 3 thermodynamicsAnonymous nveiFINo ratings yet
- PomeDocument17 pagesPomeAnirudh KaushikNo ratings yet
- Refrigerant in Capillary Tube PDFDocument6 pagesRefrigerant in Capillary Tube PDFMayank Kumar100% (2)
- Test 3-2016-1-bsDocument5 pagesTest 3-2016-1-bsBladimir FSNo ratings yet
- Sheets 1 TO 6Document13 pagesSheets 1 TO 6Tito HeshamNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Soln PDFDocument13 pagesAssignment 1 Soln PDFJawahar Khetan100% (1)
- Hes 3334Document12 pagesHes 3334siamak1438No ratings yet
- Instruction: Answer All Questions, Submit Within 1 Week After The Issuance DateDocument2 pagesInstruction: Answer All Questions, Submit Within 1 Week After The Issuance DateMuhammad Adrian ThomasNo ratings yet
- Test 1 With AnsDocument4 pagesTest 1 With AnsKavinesh GanesanNo ratings yet
- Vapor Compression Refrigeration CycleDocument9 pagesVapor Compression Refrigeration CycleNisha KuttanNo ratings yet
- ME6301 Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument19 pagesME6301 Engineering ThermodynamicsJeevanandam ShanmugaNo ratings yet
- 4c Lab3 Heat EnginesDocument4 pages4c Lab3 Heat EnginesAiza AliNo ratings yet
- Heating VentilationDocument20 pagesHeating VentilationAshan LiaqatNo ratings yet
- RefrigeratorDocument6 pagesRefrigeratorChooi San LaiNo ratings yet
- SMA1 Boilers 2010finDocument13 pagesSMA1 Boilers 2010finSandep BhatiaNo ratings yet
- AE May 2013 07 Mec A1Document6 pagesAE May 2013 07 Mec A1Hariz BayuNo ratings yet
- Questionaire Requested PIPEDocument7 pagesQuestionaire Requested PIPERhizhailNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - Module 2Document3 pagesQuestion Bank - Module 2Mohammed ElsheikhNo ratings yet
- The Economic Order Quantity CalculationDocument2 pagesThe Economic Order Quantity CalculationAdnan AzizNo ratings yet
- ChE204 20181HWIV-2Document1 pageChE204 20181HWIV-2GG MMNo ratings yet
- Middle East Technical University Department of Chemical Engineering Ch.E. 204-Thermodynamics I (Section 02) Dr. N. Sezgi, M. SarıyerDocument1 pageMiddle East Technical University Department of Chemical Engineering Ch.E. 204-Thermodynamics I (Section 02) Dr. N. Sezgi, M. SarıyerGG MMNo ratings yet
- Listening Week: The Aims of The Listening Self-Study Programme Are That You - .Document3 pagesListening Week: The Aims of The Listening Self-Study Programme Are That You - .Natalia Velardi0% (1)
- How To Use This Self-Study Programme For IELTS Preparation: Which IELTS Test Should I Take: Academic or General Training?Document1 pageHow To Use This Self-Study Programme For IELTS Preparation: Which IELTS Test Should I Take: Academic or General Training?No tengo nombreNo ratings yet
- Middle East Technical University Department of Chemical Engineering Ch.E. 204-Thermodynamics I (Section 02) Dr. N. Sezgi, M. SarıyerDocument1 pageMiddle East Technical University Department of Chemical Engineering Ch.E. 204-Thermodynamics I (Section 02) Dr. N. Sezgi, M. SarıyerGG MMNo ratings yet
- ChE204 20181HWIIDocument1 pageChE204 20181HWIIGG MMNo ratings yet
- Tens EgrityDocument1 pageTens EgrityGG MMNo ratings yet
- 19-20 Spring PS11Document2 pages19-20 Spring PS11GG MMNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Vii: Problem 1. One Hundred Moles of A Gas at 400 K Is Compressed Reversibly andDocument2 pagesProblem Set Vii: Problem 1. One Hundred Moles of A Gas at 400 K Is Compressed Reversibly andGG MMNo ratings yet
- 19-20 Spring PS12Document2 pages19-20 Spring PS12GG MMNo ratings yet
- 19-20 Spring PS10Document2 pages19-20 Spring PS10GG MMNo ratings yet
- 2.115 G/L Exit Cell Concentration 4.73 G Cell/ L) )Document2 pages2.115 G/L Exit Cell Concentration 4.73 G Cell/ L) )GG MMNo ratings yet
- Reinforcing Strategies: Learning ResourceDocument1 pageReinforcing Strategies: Learning ResourceTrevor G. SamarooNo ratings yet
- Lines of Force & Stresses: Learning ResourceDocument1 pageLines of Force & Stresses: Learning ResourceGG MMNo ratings yet
- Instructor: Prof. Dr. Behiç Mert 2018-2019 Fall TA: Res - Asst. Kübra ERTANDocument2 pagesInstructor: Prof. Dr. Behiç Mert 2018-2019 Fall TA: Res - Asst. Kübra ERTANGG MMNo ratings yet
- 1st Span Vocab ListsDocument5 pages1st Span Vocab ListsGG MMNo ratings yet
- General Training Reading Week: Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesGeneral Training Reading Week: Page 1 of 2No tengo nombreNo ratings yet
- 1st Span Vocab ListsDocument5 pages1st Span Vocab ListsGG MMNo ratings yet
- 1st Span Vocab ListDocument5 pages1st Span Vocab ListGG MMNo ratings yet
- 3-Writing Task 1 Week PDFDocument3 pages3-Writing Task 1 Week PDFNo tengo nombreNo ratings yet
- 224 - HW2Document1 page224 - HW2GG MMNo ratings yet
- Homework Format ChE204Document1 pageHomework Format ChE204GG MMNo ratings yet
- 224 Problem Set-1Document2 pages224 Problem Set-1GG MMNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Spring 20181CHE204Document3 pagesSyllabus Spring 20181CHE204GG MMNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Vii: Problem 1. One Hundred Moles of A Gas at 400 K Is Compressed Reversibly andDocument2 pagesProblem Set Vii: Problem 1. One Hundred Moles of A Gas at 400 K Is Compressed Reversibly andGG MMNo ratings yet
- ChE204 20181HWIV-2Document1 pageChE204 20181HWIV-2GG MMNo ratings yet
- ChE204 20181HWIIDocument1 pageChE204 20181HWIIGG MMNo ratings yet
- Middle East Technical University Department of Chemical Engineering Ch.E. 204-Thermodynamics I (Section 02) Dr. N. Sezgi, M. SarıyerDocument1 pageMiddle East Technical University Department of Chemical Engineering Ch.E. 204-Thermodynamics I (Section 02) Dr. N. Sezgi, M. SarıyerGG MMNo ratings yet
- ChE20420181HWV 2Document1 pageChE20420181HWV 2GG MMNo ratings yet