Professional Documents
Culture Documents
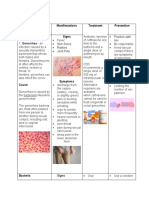
Gonorrhea
Uploaded by
Parul RajOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gonorrhea
Uploaded by
Parul RajCopyright:
Available Formats
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It’s caused by the bacterium Neisseria
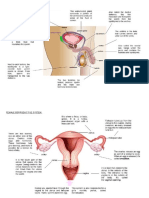
gonorrhoeae. It tends to target warm, moist areas of the body, including
the:urethra,eyes,throat,vagina,anus,female reproductive tract.
Gonorrhea passes from person to person through oral, anal, or vaginal sex without a
condom or other barrier method. The best protections against transmission are abstinence
and proper condom or barrier method usage.
SYMPTOMS
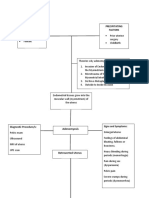
Symptoms usually occur within 2 to 14 days after exposure.
However, some people who acquire gonorrhea never develop
noticeable symptoms.
Symptoms in men
The first noticeable symptom in men is often a burning or painful
sensation during urination.As it progresses, other symptoms may
include:
greater frequency or urgency of urination
a pus-like discharge (or drip) from the penis (white, yellow, beige, or
greenish)
swelling or redness at the opening of the penis or pain in the testicles
Symptoms in women
Gonorrhea symptoms can appear much like common vaginal yeast
or bacterial infections.
discharge from the vagina (watery, creamy, or slightly green),pain or
burning sensation while urinating,urge to urinate more
frequently,heavier,periods or spotting,sore throat,pain during sexual
intercourse,sharp pain in the lower abdomen
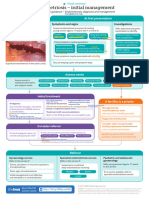
Complications of gonorrhea
PEOPLE WITH A VAGINA ARE AT GREATER RISK FOR LONG-TERM
COMPLICATIONS FROM AN UNTREATED TRANSMISSION.
UNTREATED, THE BACTERIA MAY ASCEND UP THE REPRODUCTIVE
TRACT AND INVOLVE THE UTERUS, FALLOPIAN TUBES, AND
OVARIES.
WOMEN MAY ALSO DEVELOP BLOCKING OR SCARRING OF THE
FALLOPIAN TUBES, WHICH CAN PREVENT FUTURE PREGNANCY OR
CAUSE ECTOPIC PREGNANCY. AN ECTOPIC PREGNANCY IS WHEN A
FERTILIZED EGG IMPLANTS OUTSIDE THE UTERUS.
People with a vagina are at greater risk for long-term complications from an untreated transmission. Untreated, the bacteria may ascend up the reproductive tract and involve the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries.
PREVENTION
The safest way to prevent gonorrhea or other STIs is through abstinence. If you do engage in sexual activities, always use a condom or other
barrier method.
It’s important to be open with your sexual partners, get regular testing, and find out if they’ve been tested.
If your partner is showing any symptoms, avoid any sexual contact. Ask them to seek medical attention to rule out any possible conditions that
could be passed on.
You’re at a higher risk for acquiring gonorrhea if you’ve already had it or any other STIs. You’re also at a higher risk if you have multiple
sexual partners or a new partner.
You might also like
- The Powerful Doula HandbookDocument12 pagesThe Powerful Doula HandbookKimberly L Curette75% (4)
- Eureka Wow - Money-And-Financial-MarketsDocument208 pagesEureka Wow - Money-And-Financial-MarketsParul RajNo ratings yet
- Hydatidiform MoleDocument23 pagesHydatidiform MoleKristel Rivamonte100% (1)
- Poster GonorrheaDocument1 pagePoster GonorrheazacgoezNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 - GajoDocument3 pagesActivity 3 - GajoSanti HukomNo ratings yet
- Gonorrhea Symptoms and TreatmentDocument2 pagesGonorrhea Symptoms and TreatmentEnding HIV OklahomaNo ratings yet
- Fever Skin Sores Rashes Joint Pain Practice Safe SexDocument13 pagesFever Skin Sores Rashes Joint Pain Practice Safe SexMc MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Yayin Ob: 2. Trichomonas VaginalisDocument3 pagesYayin Ob: 2. Trichomonas VaginalisYayin PestañoNo ratings yet
- Sexual Transmitted Diseases: Chlamydia TrachomatisDocument3 pagesSexual Transmitted Diseases: Chlamydia TrachomatisNur SetsuNo ratings yet
- Chain of Infection, Dengue, and UtiDocument4 pagesChain of Infection, Dengue, and UtiArnold ZamoroNo ratings yet
- VaginitisDocument2 pagesVaginitisFilip JovanovskiNo ratings yet
- STDs and STIs Brochure - Benedict H. Dipaculang (BSMT-T3)Document2 pagesSTDs and STIs Brochure - Benedict H. Dipaculang (BSMT-T3)DipacsNo ratings yet
- MeilindaDocument2 pagesMeilindasenjamartiaNo ratings yet
- NameDocument2 pagesNamekorikonglibatNo ratings yet
- BIO-diseases PDFDocument1 pageBIO-diseases PDFmonfoxNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Health and Responsible Parenthood and Birth Control Methods by Joshua SiegaDocument21 pagesReproductive Health and Responsible Parenthood and Birth Control Methods by Joshua SiegaJoshua SiegaNo ratings yet
- Flyer de Sustentabilidad Ilustrado Divertido ColoridoDocument2 pagesFlyer de Sustentabilidad Ilustrado Divertido ColoridoHobi -ahNo ratings yet
- A UTI, or Urinary Tract Infection, Is An Infection of The Parts of The Urinary System, Usually Affecting Women in The Bladder or UrethraDocument2 pagesA UTI, or Urinary Tract Infection, Is An Infection of The Parts of The Urinary System, Usually Affecting Women in The Bladder or Urethraapi-344416218No ratings yet
- The Thing For Sunday Pneumonia FlavouredDocument3 pagesThe Thing For Sunday Pneumonia FlavouredkasjdkasNo ratings yet
- STI AwarenessDocument7 pagesSTI AwarenessMarcus RossNo ratings yet
- Presentación3 2Document4 pagesPresentación3 2hp5by8bvb2No ratings yet
- Women's HealthDocument8 pagesWomen's HealthkellyjackykjNo ratings yet
- Oral SexDocument18 pagesOral SexVerlana Garcia100% (1)
- GonorrheaDocument9 pagesGonorrheaWulan DayuNo ratings yet
- The Diagnosis of Upadamsa (Penile and Venereal Diseases) NidhanamDocument10 pagesThe Diagnosis of Upadamsa (Penile and Venereal Diseases) NidhanamVenkatesan VidhyaNo ratings yet
- ExamguideDocument6 pagesExamguideJuan Moreno BasurtoNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Vagina DischargeDocument6 pagesAbnormal Vagina DischargeShafiqMtKamilNo ratings yet
- Ims-Kelompok 7 (Xi-S2)Document15 pagesIms-Kelompok 7 (Xi-S2)hyunkyu 12No ratings yet
- 9th STD'sDocument7 pages9th STD'sxxonlyjupiterNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIODocument3 pagesPATHOPHYSIONobby FulgencioNo ratings yet
- STI - HerpesDocument1 pageSTI - HerpesDanii LuvNo ratings yet
- HerpesDocument3 pagesHerpesNizam UddinNo ratings yet
- In WomenDocument6 pagesIn Womenkayeemperado997No ratings yet
- g5 Science Reporting GonorrheaDocument12 pagesg5 Science Reporting GonorrheaJoy VillafloresNo ratings yet
- Neurogenic Bladder UrethritisDocument2 pagesNeurogenic Bladder UrethritisOlivia LowellNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument1 pageUrinary Tract InfectionMarieta CañedaNo ratings yet
- Vulvovaginitis BritSPAG Information Leaflet 2018Document2 pagesVulvovaginitis BritSPAG Information Leaflet 2018Budi AntoNo ratings yet
- Blue Colorful Pastel Ice Breaker Class Activity Show and Tell Education PresentationDocument7 pagesBlue Colorful Pastel Ice Breaker Class Activity Show and Tell Education PresentationPutri Ayu NathasyaNo ratings yet
- Gonorrhea: Fact SheetDocument8 pagesGonorrhea: Fact SheetViona HardiantiNo ratings yet
- UTI Patient Leaflet SpanishDocument1 pageUTI Patient Leaflet Spanishovidioch760No ratings yet
- Safe Sex No Regrets BookletDocument9 pagesSafe Sex No Regrets BookletThat Cat in the Hat.No ratings yet
- Bacterial Vaginosis Vs Chlamydia Vs Gonorrhea Vs Trichomoniasis - Conditions Com.Document9 pagesBacterial Vaginosis Vs Chlamydia Vs Gonorrhea Vs Trichomoniasis - Conditions Com.mikezNo ratings yet
- Prepared By-V.S. Krishna Prasad Slot B1: Ethics and Values Prof. Sivakumar SDocument23 pagesPrepared By-V.S. Krishna Prasad Slot B1: Ethics and Values Prof. Sivakumar SduddeanudeepNo ratings yet
- Nama: - Haura Nafisah - Nasywa Jihan AqillahDocument11 pagesNama: - Haura Nafisah - Nasywa Jihan AqillahEVINo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument11 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseasesDavid PerezNo ratings yet
- Herpes: Sherillyn Ternera Mayra Calabria GRADE 11° 2021Document8 pagesHerpes: Sherillyn Ternera Mayra Calabria GRADE 11° 2021sherillyn de armasNo ratings yet
- 5 Birth Control Methods Available in Philippines Birth Controls CondomsDocument5 pages5 Birth Control Methods Available in Philippines Birth Controls CondomsKyle HermosillaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationJenny Rose AnieteNo ratings yet
- Urinary System 1Document17 pagesUrinary System 1Mc MagtibayNo ratings yet
- STD Comparison ChartDocument4 pagesSTD Comparison Chartabu ubaidahNo ratings yet
- CHN ReportDocument15 pagesCHN ReportBryan Cruz VisarraNo ratings yet
- GonorrheaDocument4 pagesGonorrheaNader Smadi100% (1)
- Preventing Coronavir US: Who Is at RISK?Document2 pagesPreventing Coronavir US: Who Is at RISK?mark encilayNo ratings yet
- Gonorrhe A: Kayleigh H-Mahedy, Javier Woo, ConnorDocument8 pagesGonorrhe A: Kayleigh H-Mahedy, Javier Woo, ConnorkayleighNo ratings yet
- GonoraeDocument16 pagesGonoraeOkta KendaNo ratings yet
- Vaginal InfectionsDocument35 pagesVaginal InfectionsAxl SalimoNo ratings yet
- Treating Your Infection UtiDocument1 pageTreating Your Infection UtiJames 'jps' SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- BIO 271 - Study Questions For Chapter 19 Reproductive System DisordersDocument5 pagesBIO 271 - Study Questions For Chapter 19 Reproductive System Disorderskelsey jacksonNo ratings yet
- Genital Herpes: Looking After Your Sexual HealthDocument9 pagesGenital Herpes: Looking After Your Sexual HealthGrace ArganaNo ratings yet
- Ec2 UrinaryDocument4 pagesEc2 UrinaryDiana Marie ReyesNo ratings yet
- Uti Brochure WomenDocument2 pagesUti Brochure WomenPABLO, JACKSON P.No ratings yet
- Quick Natural Cure for White Discharge (Leucorrhoea) in WomenFrom EverandQuick Natural Cure for White Discharge (Leucorrhoea) in WomenRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Vulvovaginitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandVulvovaginitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- MA Economics 2020 - SSF JMIDocument21 pagesMA Economics 2020 - SSF JMIParul RajNo ratings yet
- 2301 Detail - 230331 - 103550Document35 pages2301 Detail - 230331 - 103550Parul RajNo ratings yet
- Rca Jmi 2019 - SSF JmiDocument16 pagesRca Jmi 2019 - SSF JmiParul RajNo ratings yet
- Kolstad Efficiency and Competitive MarketsDocument7 pagesKolstad Efficiency and Competitive MarketsParul RajNo ratings yet
- JMI RCA Entrance SyllabusDocument3 pagesJMI RCA Entrance SyllabusParul RajNo ratings yet
- Jamia Rca 2017Document14 pagesJamia Rca 2017Parul RajNo ratings yet
- IUKYF Speak Up For Progress Talk 2 AttendeesDocument3 pagesIUKYF Speak Up For Progress Talk 2 AttendeesParul RajNo ratings yet
- DE 2 Unit 1Document48 pagesDE 2 Unit 1Parul RajNo ratings yet
- Dev Eco 2 Chapter 11 (Unit 2)Document26 pagesDev Eco 2 Chapter 11 (Unit 2)Parul RajNo ratings yet
- Kolstad Chapter1Document39 pagesKolstad Chapter1Parul RajNo ratings yet
- ChlamydiaDocument1 pageChlamydiaParul RajNo ratings yet
- Indias Stalled RiseDocument12 pagesIndias Stalled RiseParul RajNo ratings yet
- Project Seed: (Socio Economic Empowerment and Development)Document15 pagesProject Seed: (Socio Economic Empowerment and Development)Parul RajNo ratings yet
- The Kashmir Conflict: A Kashmiri Perspective: by Mehraj HajniDocument3 pagesThe Kashmir Conflict: A Kashmiri Perspective: by Mehraj HajniParul RajNo ratings yet
- Du Question Paper of UseDocument165 pagesDu Question Paper of UseParul RajNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter - IFPDDocument2 pagesCover Letter - IFPDParul RajNo ratings yet
- MSB CV WorksheetDocument1 pageMSB CV WorksheetParul RajNo ratings yet
- m1 Psychological and Physiologic Changes of PregnancyDocument8 pagesm1 Psychological and Physiologic Changes of PregnancyShermaigne Ananayo BuyaNo ratings yet
- Nau Pai Lai Te Tan DR TeteaDocument4 pagesNau Pai Lai Te Tan DR TeteaAugust ChiaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Health Questions With AnswersDocument3 pagesReproductive Health Questions With AnswersPrajwal d100% (1)
- Employees' State Insurance Corporation: Strike Out If Not ApplicableDocument1 pageEmployees' State Insurance Corporation: Strike Out If Not Applicablenasir ahmedNo ratings yet
- Gynecology & Obstetrics (Questions 1)Document3 pagesGynecology & Obstetrics (Questions 1)marouf elgoulNo ratings yet
- Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument10 pagesHyperemesis GravidarumFarxan Da Napolian BwoyNo ratings yet
- Sample Obstetric CaseDocument46 pagesSample Obstetric CasemelissaoljoyNo ratings yet
- Review of StudiesDocument1 pageReview of StudiesThian Yong YapNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 NotesDocument7 pagesChapter 25 NotesJori Domini Llacuna AwayanNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of Amniotic Fluid: Presented by Ms. K.D. Sharon Final Year MSC (N) Obstetrics and Gynaecology NursingDocument32 pagesAbnormalities of Amniotic Fluid: Presented by Ms. K.D. Sharon Final Year MSC (N) Obstetrics and Gynaecology Nursingkalla sharonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Embryology 1Document72 pagesIntroduction To Embryology 1Sam MumoNo ratings yet
- Contemporary WorldDocument3 pagesContemporary WorldAlyssa BihagNo ratings yet
- Final Doula Brochure For EmailDocument2 pagesFinal Doula Brochure For Emailapi-279027417No ratings yet
- Brochure SPC2023Document3 pagesBrochure SPC2023Edwin KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Picture To Be Added Here: Pregnancy Health and Antenatal TestingDocument2 pagesPicture To Be Added Here: Pregnancy Health and Antenatal TestingYanni YangNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Publikasi Skripsi - Copy-3Document12 pagesJurnal Publikasi Skripsi - Copy-3Wahyu El RoyyanNo ratings yet
- In Defense of AbortionDocument4 pagesIn Defense of Abortiondaniel maingiNo ratings yet
- Midwifery CpdprogramDocument7 pagesMidwifery CpdprogramPRC BoardNo ratings yet
- Episiotomy: Dr. Fekadu R (MD) November, 2012/19Document11 pagesEpisiotomy: Dr. Fekadu R (MD) November, 2012/19tareNo ratings yet
- Role Play: NCM 107 RleDocument4 pagesRole Play: NCM 107 RlekeightNo ratings yet
- Assessing The State of Professional Practice of Midwifery in The PhilippinesDocument11 pagesAssessing The State of Professional Practice of Midwifery in The PhilippinesJhue hanNo ratings yet
- Gonadal HormonesDocument3 pagesGonadal Hormonesabayaivyliana25No ratings yet
- Relationship Between Maternal Characteristics and Postpartum Hemorrhage: A Meta-Analysis StudyDocument11 pagesRelationship Between Maternal Characteristics and Postpartum Hemorrhage: A Meta-Analysis Study16.11Hz MusicNo ratings yet
- NCM107 (Lec) - ReviewerDocument9 pagesNCM107 (Lec) - ReviewerAlthea ManarpiisNo ratings yet
- Labor and DeliveryDocument70 pagesLabor and DeliveryャチNo ratings yet
- Retained Placenta CPDocument18 pagesRetained Placenta CPjayashreeselvaraj75% (12)
- OBGYN Vaginal Delivery DikaDocument10 pagesOBGYN Vaginal Delivery DikaOnyedika EgbujoNo ratings yet
- Pengalaman Ibu Yang Mengalami Baby Blues: Literature Review Annisa Pir Laily Pazriani, Murtilita, Uray Fretty HayatiDocument12 pagesPengalaman Ibu Yang Mengalami Baby Blues: Literature Review Annisa Pir Laily Pazriani, Murtilita, Uray Fretty HayatiLalaNo ratings yet