Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Surface Water Collection: Units
Uploaded by
Labib AbdallahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Surface Water Collection: Units
Uploaded by
Labib AbdallahCopyright:
Available Formats
EWC 331
Water Supply Engineering
Lecture -1
Surface Water Supply Scheme
Topics References
• Surface water collection 1. A Text Book of Water Supply
units Engineering
Authors: M. A. Aziz
1st ed., Hafiz Book Center
• Water treatment units
3. Water Supply and Sanitation
Authors: M. Feroz Ahmed, Md.
Mujibur Rahman
1st ed., ITN-BUET
3. Water and Environmental
Engineering
Authors: M. Habibur Rahman,
Abdullah Al-Muyeed
1st ed., ITN-BUET
Public Water Supply
• Public water supply refers to water withdrawn by
public and private water suppliers and delivered to
users.
• Public water suppliers provide water to domestic,
commercial and industrial users.
• Provides water to at least 25 people or has a
minimum of 15 service connections.
Objectives of Public Water Supply
Maj Dr. Kazi Shamima Akter
EWC 331
Water Supply Engineering
Elements of Public Water Supply
1. Source of supply 2. Collection system
3. Treatment or purification plant 4. Distribution system
Surface Water Collection System
Surface Water Collection System Units
1. Intake
• An intake is a device or a structure placed in a surface
water source to permit the withdrawal of water from
the source and its discharge into an intake conduit or
pipe (intake main).
• From the intake main the water will then flow into the
water-works system.
• Intakes are generally consist of opening protected by a
strainer or grating through which the water enters the
intake main.
Maj Dr. Kazi Shamima Akter
EWC 331
Water Supply Engineering
Hoover Dam Intake Towers,
Arizona, USA
Maj Dr. Kazi Shamima Akter
EWC 331
Water Supply Engineering
Movable weir with intake screen, Japan
Consideration for designing and locating the intake structures –
Maj Dr. Kazi Shamima Akter
EWC 331
Water Supply Engineering
Type of Intakes for Water Collection
Trash Rack/ Screen
Maj Dr. Kazi Shamima Akter
EWC 331
Water Supply Engineering
River Intakes
Maj Dr. Kazi Shamima Akter
EWC 331
Water Supply Engineering
Sharulia Intake Station, SWTP, DWASA, Dhaka
Bar Screens on the outside
Additional screens before pumping
River training works to protect
the banks besides the intake
Maj Dr. Kazi Shamima Akter
EWC 331
Water Supply Engineering
Inside the pump station
Reservoir Intake
• It is constructed when the flow in the river is not
guaranteed throughout the year.
• A dam is constructed across the river to store the
water in the reservoir so formed.
• Sited with due reference to sources of pollution,
prevailing winds and surface currents.
• Reservoir intakes lie closer to bank in the deepest
part of the reservoir.
Maj Dr. Kazi Shamima Akter
EWC 331
Water Supply Engineering
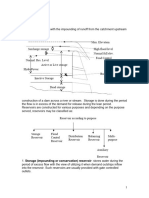
• Reservoir Intakes essentially consist of an Intake
tower constructed on the slope of Dam.
• The location of the intake tower should be such that
the Intake can draw water in sufficient quantity even
in the driest period.
• Intake pipes are fixed at different levels, so as to
draw water near the surface in all variations of water
levels.
• In gravity dam, intake tower is constructed inside the
dam itself.
Fig: Intake well / Valve tower for concrete gravity or masonry dams
Maj Dr. Kazi Shamima Akter
EWC 331
Water Supply Engineering
• Lake Intakes are mostly submerged intake.
• These Intakes are constructed in the bed of lake
below the low water level so as to draw water even
in dry season.
• It mainly consist of a pipe laid in the bed of the lake.
• One end of the pipe which is in middle of the lake is
fitted with bell mouth opening covered with a mesh
and protected timber or concrete crib.
Maj Dr. Kazi Shamima Akter
EWC 331
Water Supply Engineering
• The water enters in the pipe through the bell mouth
opening and flows under gravity to the bank where it
is collected in a sump well and then pumped to the
treatment plant for necessary treatment.
Bell Mouth Entrance
Canal Intake
• For small town a nearby irrigation canal can be
used as the source of water.
• The intake well is generally located in the bank
of the canal.
• Canal should lie on upstream and downstream
side of the intake to prevent erosion of sides and
bed of canal.
Maj Dr. Kazi Shamima Akter
EWC 331
Water Supply Engineering
Maj Dr. Kazi Shamima Akter
EWC 331
Water Supply Engineering
Intake Design Consideration
Intake Velocity:
- velocity below 0.3 fps allows fish to escape, reduces
ice problems and reduce entrainment of suspended
matter
Intake Port Location:
- multiple intake ports at several elevations are
preferable
- location of ports determined by testing water quality
- topmost port not less than 2m below water surface
- bottom port at least 1 m above bottom
Gates:
- Sluice gates typically used to control flow of water
from source to the water conveyance system
Control of Ice: (for colder regions)
- keep intake ports sufficiently below water level
- steam piping, compressed air, space heaters
Maj Dr. Kazi Shamima Akter
EWC 331
Water Supply Engineering
Intake Design Consideration - Screening
Coarse Screen:
- bar racks with 2- 3՛՛ clear spacing
- should be installed in the outside
- provision for cleaning
Fine Screen:
- to remove smaller objects that might damage pumps
- heavy wire mesh having 0.25 ՛՛ square openings
- design velocity 0.4 - 0.8 m/s
- requires frequent cleaning (travelling screens used
often)
Microstrainer:
- to remove plankton and algae
(to improve sedimentation and chlorination
performance)
- fine wire mesh
- slime build up
- will not handle sand, silt and abrasive material
Maj Dr. Kazi Shamima Akter
EWC 331
Water Supply Engineering
Maj Dr. Kazi Shamima Akter
EWC 331
Water Supply Engineering
Intake Main & Transmission Main
• A pipe line must be used to deliver water from the
source to the treatment plant.
• Intakes located at long distances from the pumps
usually deliver their water to the pump well at the
shore end by gravity.
• Conveyance of water from intake will require a
large pipe or conduit so that the velocity would be
low.
• But velocity should not be low enough to allow
sedimentation.
• The conduit may be a submerged pipe or tunnel.
• A submerged pipe should be protected -
By burying it in a trench
By surrounding it with rock or holding it in place
with piling
Maj Dr. Kazi Shamima Akter
EWC 331
Water Supply Engineering
• The kind of pipe to be used – cast iron, steel,
concrete, asbestos cement or even wood, will
depend to some extent on local conditions and
local economy, determined on an engineering
basis.
• The size of the pipe/ conduit is determined by the
volume of water to be delivered and the pressure or
head of water.
Surface Water Collection – Pumping Station
• A pumping station is essential for pumping water from
the source through the intake to allow water to flow by
gravity through the transmission main to the
treatment plant.
Pumping station with transmission pipe
[Source: ATC Williams Consultancy, Australia]
Maj Dr. Kazi Shamima Akter
EWC 331
Water Supply Engineering
Surface Water Treatment – Treatment Units
• In case of surface water, the treatment procedure
may involve the removal of –
turbidity
color
taste
odor
microorganisms (bacteria)
• Ground water from wells may be treated to reduce –
hardness
iron
corrosive qualities (alkalinity)
• Disinfection means destruction of pathogenic
organisms to make the water safe.
• Commonly used water treatment methods include –
screening
sedimentation
chemical treatment
sand filtration
disinfection
Maj Dr. Kazi Shamima Akter
EWC 331
Water Supply Engineering
• Some of the treatment processes/unit operations for
removal of specific impurities are –
Aeration
Water softening
Arsenic removal
Iron removal
Activated carbon application
Fluoridation and de-fluoridation
Demineralization
Desalination
Maj Dr. Kazi Shamima Akter
You might also like
- Surface water collection and transmissionDocument31 pagesSurface water collection and transmissionLabib AbdallahNo ratings yet
- 02 - 3 Design of Intakes - V2Document53 pages02 - 3 Design of Intakes - V2Mohammed JemalNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Structures II Lecture NoteDocument197 pagesHydraulic Structures II Lecture NoteAbebaw100% (1)
- Intake StructuresDocument32 pagesIntake StructuresSai Geotechnical LabNo ratings yet
- AK - Design of Diversion Weir and Intake Works Jan 2020Document50 pagesAK - Design of Diversion Weir and Intake Works Jan 2020Manoj100% (1)
- Lec 8 (Add) Source DevelopmentDocument26 pagesLec 8 (Add) Source DevelopmentShahzaib AhmadNo ratings yet
- Intake Structure For Water Supply: Mathanakeerthi S Assistant Professor Civil Engineering Sns College of EngineeringDocument17 pagesIntake Structure For Water Supply: Mathanakeerthi S Assistant Professor Civil Engineering Sns College of EngineeringArpan SahaNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Raj Kumar Bairwa 13512026 M.Tech Ist Year A.H.E.S, Iit RoorkeeDocument22 pagesPresented By: Raj Kumar Bairwa 13512026 M.Tech Ist Year A.H.E.S, Iit RoorkeeMamuye Busier YesufNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3Document18 pagesUnit - 3Varun Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- IWRM and Water Resource ManagementDocument35 pagesIWRM and Water Resource ManagementprideNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Design of Hydropower PlantsDocument32 pagesChapter 4 Design of Hydropower Plantsbiggestbro0No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 WcuDocument29 pagesChapter 4 WcuKuba100% (3)
- Irrigation Lect 7Document20 pagesIrrigation Lect 7Hamad RazaNo ratings yet
- Well Come To Academic Year: 2013 Hydraulic Structure-IDocument32 pagesWell Come To Academic Year: 2013 Hydraulic Structure-IHenok MandefroNo ratings yet
- Types of DamDocument18 pagesTypes of DamErwin Bolamino BlasNo ratings yet
- Intake StructuresDocument75 pagesIntake StructuresLakshmi Keshav K100% (1)
- Chapter Three Intake Structures1Document19 pagesChapter Three Intake Structures1Gech SolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 WSUD 2016Document65 pagesChapter 3 WSUD 2016eyuleme146No ratings yet
- Open CanalDocument19 pagesOpen Canaleslam2030mohamedNo ratings yet
- 3 - Spring Water TappingDocument39 pages3 - Spring Water Tappingمهندس ابينNo ratings yet
- Open CanalDocument19 pagesOpen Canaleslam2030mohamedNo ratings yet
- WT2 - Preliminary TreatmentDocument46 pagesWT2 - Preliminary TreatmentBelete DestawNo ratings yet
- Intake StructuresDocument232 pagesIntake StructuresPRATHAP MANTHIRA GIRINo ratings yet
- Design of Hydraulic Structures: B.Tech Civil Credit Hours: 03Document12 pagesDesign of Hydraulic Structures: B.Tech Civil Credit Hours: 03Suleman Faisal100% (1)
- Presentation100completed 160315213306Document123 pagesPresentation100completed 160315213306msea100% (1)
- Saidi Issa B-10-022. Civil Engineering: Zonal Irrigation & Technical Services Unit TaboraDocument31 pagesSaidi Issa B-10-022. Civil Engineering: Zonal Irrigation & Technical Services Unit TaborachingtonyNo ratings yet
- Hs-Ii, Lecture On CH-1Document41 pagesHs-Ii, Lecture On CH-1natiz addisNo ratings yet
- Ground & Sub-Surface Water Sources GuideDocument32 pagesGround & Sub-Surface Water Sources GuideKim JunmyeonNo ratings yet
- Summer I ZingDocument64 pagesSummer I ZingShivam Gupta0% (1)
- 6 - IntakeDocument43 pages6 - IntakeSheeraz AhmedNo ratings yet
- IntakeDocument20 pagesIntakePratik RaoNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument44 pagesPhysicsvamaNo ratings yet
- WelcomeDocument50 pagesWelcomeBalakrishna SNo ratings yet
- Dam Construction Surveying GuideDocument61 pagesDam Construction Surveying GuideShashank ZutshiNo ratings yet
- Layout of Reservoir, Diversion Structures and Other StructuresDocument36 pagesLayout of Reservoir, Diversion Structures and Other StructuresSuman RegmiNo ratings yet
- RECAPPING AbsDocument36 pagesRECAPPING AbsVaishnavi KambleNo ratings yet
- Utils Q1 ReviewerDocument6 pagesUtils Q1 ReviewerBognot, Charles Dave Q.No ratings yet
- Plumbing Services Overview for Hospital BuildingDocument38 pagesPlumbing Services Overview for Hospital BuildingShefali GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering Notes PDFDocument45 pagesEnvironmental Engineering Notes PDFVamshi ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Canal Maintenance & OperationDocument31 pagesCanal Maintenance & OperationSaiba AteeqNo ratings yet
- Unit3diversionheadwork 140927114314 Phpapp01Document29 pagesUnit3diversionheadwork 140927114314 Phpapp01vivekNo ratings yet
- EE - Sewer AppurtenancesDocument20 pagesEE - Sewer AppurtenancesMadhuNo ratings yet
- Collection and Distribution of Waters: IntakesDocument35 pagesCollection and Distribution of Waters: IntakesMamuye Busier Yesuf100% (1)
- BS NotesDocument34 pagesBS NotesShreyas SuryavanshiNo ratings yet
- Elements of Dam EngineeringDocument72 pagesElements of Dam Engineeringhaile gideyNo ratings yet
- Hydroelectric Power Plant Components and WorkingDocument20 pagesHydroelectric Power Plant Components and WorkingAd Man GeTigNo ratings yet
- IntakesDocument30 pagesIntakesRNo ratings yet
- 1..diversion Head WorksDocument45 pages1..diversion Head WorksBaba Maisam ShabirNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 DamDocument185 pagesUnit 8 DamBittu RajkumarNo ratings yet
- 6 - IntakeDocument36 pages6 - IntakeSyed Talha AhmedNo ratings yet
- Collection and Conveyance of Raw Water From Source: Intake StructuresDocument3 pagesCollection and Conveyance of Raw Water From Source: Intake StructuresAllana Grace RevecheNo ratings yet
- Quality and Quantity of WaterDocument35 pagesQuality and Quantity of WaterAkshaykumar UNo ratings yet
- Embankment Dam LectureDocument43 pagesEmbankment Dam Lectureteme beyaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power Generation EE 204 ADocument24 pagesElectrical Power Generation EE 204 Adp05No ratings yet
- SOMALI REGIONAL PRESENTATION ON INTRODUCTION TO HOW TO CONSTRUCT WOREDA LEVEL SMALL MICRO EARTH FILL DAMSDocument54 pagesSOMALI REGIONAL PRESENTATION ON INTRODUCTION TO HOW TO CONSTRUCT WOREDA LEVEL SMALL MICRO EARTH FILL DAMSSaddam H. MussieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 ModDocument27 pagesChapter 5 Modsemerekahsu8No ratings yet
- CHapter - 1 HYDRAULIC STRUCTURE IIDocument63 pagesCHapter - 1 HYDRAULIC STRUCTURE IIAmanuelNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsFrom EverandIrrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsNo ratings yet
- Water Supply Network Dead-End Method Equivalent Pipe: AnalysisDocument21 pagesWater Supply Network Dead-End Method Equivalent Pipe: AnalysisLabib AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Lecture Outline: - Design of WaterDocument22 pagesLecture Outline: - Design of WaterLabib AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures Course SyllabusDocument36 pagesDesign of Reinforced Concrete Structures Course SyllabusLabib AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures Course SyllabusDocument36 pagesDesign of Reinforced Concrete Structures Course SyllabusLabib AbdallahNo ratings yet
- EWC-301 Lec-35 & 36 PERT CL 30 Dec 21Document26 pagesEWC-301 Lec-35 & 36 PERT CL 30 Dec 21Labib AbdallahNo ratings yet
- EWC-301 Lec-29 & 30 Linear ProgClassDocument68 pagesEWC-301 Lec-29 & 30 Linear ProgClassLabib AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Gso 149 Unbottled Drinking WaterDocument12 pagesGso 149 Unbottled Drinking Waternizar.e keloth kandi100% (3)
- Books of Extended Abstracts - ICOLD Austria2018Document514 pagesBooks of Extended Abstracts - ICOLD Austria2018Brayan Torres ZagastizabalNo ratings yet
- DidesaDocument16 pagesDidesadawit itanaNo ratings yet
- SlopeDocument11 pagesSlopeValentyna CamposNo ratings yet
- NWC Water Treatment Field Trip ReportDocument5 pagesNWC Water Treatment Field Trip ReportericroyalNo ratings yet
- 2881 Flood - Englishfinal19022007Document40 pages2881 Flood - Englishfinal19022007C E R E B R ONo ratings yet
- Management of Lakes in India 10mar04Document20 pagesManagement of Lakes in India 10mar04Chinglen KhunNo ratings yet
- Case Study SpecsDocument47 pagesCase Study Specsallana marie servanoNo ratings yet
- Vietnam National Commission On Large Dams Foundation TreatmentsDocument23 pagesVietnam National Commission On Large Dams Foundation TreatmentsShirley MunozNo ratings yet
- Foundation TratmentDocument9 pagesFoundation TratmentC_C_8717No ratings yet
- De 7Document8 pagesDe 7Khiêm Trần ThịNo ratings yet
- Kafalkada Pipe Design Scheme 2Document16 pagesKafalkada Pipe Design Scheme 2Civil EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Socio-Economic Status and Environmental Issues of Kaptai, Rangamati. by Abu Khairul BasharDocument58 pagesSocio-Economic Status and Environmental Issues of Kaptai, Rangamati. by Abu Khairul BasharAbu Khairul BasharNo ratings yet
- Smart Irrigation System A Water Management Procedu PDFDocument7 pagesSmart Irrigation System A Water Management Procedu PDFankush dhyalNo ratings yet
- Water Storage Needs AssessmentDocument6 pagesWater Storage Needs AssessmentNouri Ben YahiaNo ratings yet
- 1 Fe 0668Document784 pages1 Fe 0668gaurav dahalNo ratings yet
- Complete Sanctioned GAC (UWSS Rajasthan)Document31 pagesComplete Sanctioned GAC (UWSS Rajasthan)Rajesh GangwalNo ratings yet
- Recent Research at The Buddhist Monaster PDFDocument8 pagesRecent Research at The Buddhist Monaster PDFအသွ်င္ ေကသရNo ratings yet
- RESERVOIRSDocument26 pagesRESERVOIRSFelix HabarugiraNo ratings yet
- Immediate Flood Report Final Hurricane Harvey 2017Document32 pagesImmediate Flood Report Final Hurricane Harvey 2017KHOU100% (1)
- Lesson 1 HydrologyDocument4 pagesLesson 1 Hydrologysenior highNo ratings yet
- Hydroelectric Powerplant: ContentsDocument36 pagesHydroelectric Powerplant: ContentsSecret SecretNo ratings yet
- Piano Key Spillway For DamsDocument21 pagesPiano Key Spillway For DamsMahaManthra0% (1)
- Summer TrainingDocument41 pagesSummer Trainingapi-382513988% (8)
- Hydroelectric Power Plant: G2 (From 6 Feb - 17 Feb) - Day 1 Supervised By: Eng - Amro SabryDocument8 pagesHydroelectric Power Plant: G2 (From 6 Feb - 17 Feb) - Day 1 Supervised By: Eng - Amro SabryAhmed Abd El MoatiNo ratings yet
- Environmental Hazards of Dams and Reservoirs PDFDocument11 pagesEnvironmental Hazards of Dams and Reservoirs PDFmeth nawogNo ratings yet
- Eee4 PDFDocument46 pagesEee4 PDFوسام العزاويNo ratings yet
- RiskSafet FaberDocument330 pagesRiskSafet FaberAdenilson SwokowskiNo ratings yet
- Design of Continuous Flushing Settling Basin and PowerhouseDocument223 pagesDesign of Continuous Flushing Settling Basin and PowerhouseRAJ KC100% (5)
- Complaint Letter Submitted To The Secretary of Co-Operation Department On Wednesday, 19 June 2013Document20 pagesComplaint Letter Submitted To The Secretary of Co-Operation Department On Wednesday, 19 June 2013স্বরূপ মোদকNo ratings yet