Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Definition Diary (CD)
Uploaded by
NURAIN0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views15 pagesThe document defines key terms related to child development and human anatomy. It discusses the stages of prenatal development from fertilization through implantation. Key events include formation of the zygote, blastocyst, and amniotic sac. The three germ layers (ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm) develop and various internal and external organs and structures are formed in the embryo.
Original Description:
Original Title
DEFINITION DIARY (CD)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines key terms related to child development and human anatomy. It discusses the stages of prenatal development from fertilization through implantation. Key events include formation of the zygote, blastocyst, and amniotic sac. The three germ layers (ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm) develop and various internal and external organs and structures are formed in the embryo.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views15 pagesDefinition Diary (CD)
Uploaded by
NURAINThe document defines key terms related to child development and human anatomy. It discusses the stages of prenatal development from fertilization through implantation. Key events include formation of the zygote, blastocyst, and amniotic sac. The three germ layers (ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm) develop and various internal and external organs and structures are formed in the embryo.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
DEFINITION DIARY (CD)
Submitted to Dr Swati Partani
By Nurain Shaikh
Roll no : 71
BLOCK 1 - Introduction
1. Child development - A specialized area of study which concerns itself with
growth and development of a child right from conception to adolescence.
2. Growth - Growth signify the changes that are quantitative that is increase in the
height of the child, size of the body etc.
3. Development - A series of progressive changes that occur as a result of maturation
and learning is called development. The changes are qualitative. Changes
in development are qualitative and quantitative.
4. Developmental phases - Development is divided into various domains. The main
domains are Physical, Motor, Cognitive, Social, Emotional and Moral
Development
5. Developmental Stages - Prenatal period, Infancy, Toddlerhood, Early Childhood,
Late Childhood, Adolescence, Young Adulthood, Middle Adulthood and Late
Adulthood.
6. Developmental Domains – The development is divided into different domains.
The main domains are physical, cognitive, motor, language, emotional, social and
moral development.
7. Heredity - The sum of all biological mechanisms by which certain features are
passed down from parents to their offspring is known as heredity.
8. Environment - Environment plays an important role in the child’s development,
the caregivers, teachers, peers are the example of the environment of a growing
child.
9. Prenatal -Prenatal development begins with fertilisation, during the germinal
stage of embryonic development, and continues until birth in the fetal stage.
10. Postnatal - The first six weeks after birth. It is critical to the health and survival
of a mother and the new-born.
11. Infancy - The state or period of toddlerhood. Infancy is sub-divided into neonatal
period and toddlerhood.
12. Neonatal - The state or period of babyhood or early childhood.
13. Toddlerhood - A toddler is a child who is between the ages of 12 and 36 months.
Toddlerhood is a period of rapid cognitive, emotional, and social development.
14. Childhood - This stage is also known as emotional outburst stage. It includes two
sub stages that is early childhood and school going.
15. Preschool/Early Childhood - Early childhood, defined as the years between birth
and the age of eight, is a period of remarkable growth, with brain development at
its peak. Early childhood is often called as the ‘Toy age’.
16. School going – This stage is also termed as gang age. Children learn the
foundations of their social behaviour in their peer group. It helps them to develop a
highly organized social life.
17. Adolescence – Adolescence is the phase of life between childhood and
adulthood, from ages 10 to 18. It is also defined as stress and storm stage.
18. Early Adolescence - Early adolescence occurs between the ages of 10 and 14.
Adolescents go through the early stages of puberty during this developmental
stage.
19. Middle Adolescence - As they strive for greater independence, many middle
adolescents have more arguments with their parents. There are many emotional
changes.
20. Late Adolescence - Late adolescents have typically completed physical
development and reached full adult height. They usually have better impulse
control by this point and may be able to accurately assess risks and rewards. They
have matured in their behaviour.
21. Cephalocaudal – From head to tail, as in the long axis of the body. The term
refers to the maturation of an embryo or infant, wherein the greatest development
takes place at the top of the body (i.e., the head) before the lower parts (i.e., the
arms, trunk, legs).
22. Proximodistal - From the centre to the outskirts. In the context of maturation, the
term typically refers to the tendency of children to learn motor skills from the
centre outward, such as when they learn to move their heads, trunks, arms, and
legs before learning to move their hands and feet.
23. Learning – The acquisition of new information, behaviors, or abilities as a result
of practice, observation, or other experiences, as demonstrated by a change in
behavior, knowledge, or brain function.
24. Maturation - The biological processes that lead to the organs of an organism's
functional or full development.
25. Equilibrium - A state of physical or mental balance or stability (e.g., in posture,
physiological processes, psychological adjustment).
26. Disequilibrium – A state of cognitive imbalance. We experience such a state of
imbalance when encountering information that requires us to develop new schema
or modify existing schema.
BLOCK 2 – Prenatal Development
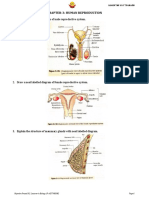
27. Testicles – Testicles is found in the scrotum. Produces sperm as well as male
hormone. There are a number of tubes inside the testes called seminiferous tubules
that produce sperm.
28. Epididymis – Each testicle has a long coiled tube that sits on the backside it is
called as the epididymis. It aids in the transport and preservation of the sperm cell
produced by the testicles, as well as the maturation of the sperm, with an average
length of 20 feet.
29. Vas deferens –The ejaculatory duct joins the duct of the seminal vesicle to form
the urethral duct, which transports spermatozoa from the epididymis. Also known
as the ductus deferens, the seminal duct, and the spermatic duct.
30. Scrotum – The bag of skin that contains the two roundish male sex organs
(testicles).
31. Lobules - A small part of a lobe in the breast. A breast lobule is a gland that makes
milk. The nipple and areola are shown on the outside of the breast. The lymph
nodes, lobes, lobules, ducts, and other parts of the inside of the breast are also
shown.
32. Semen – Ejaculate fluid is the liquid that is released during ejaculation. It contains
sperm, prostate gland secretions, bulbourethral gland secretions, and seminal
vesicles. Seminal fluid is another name for it.
33. Prostate gland – A small organ in a man’s body near the bladder that produces a
liquid in which sperm is carried.
34. Penis –The male organ used for urinating and intromission, when it enters the
female’s vaginal canal to deliver sperm. The urethra passes via the penis, which is
mostly made up of erectile tissue and has a mushroom-shaped cap (see corpus
cavernosum; corpus spongiosum) (glans penis).
35. Seminal vesicles –In human males, one of two membrane pouches found between
the bladder and the rectum, measuring roughly 8 cm (3 in) in length. Seminal
vesicles produce and store a fluid that combines with prostate gland secretions to
form the bulk of the semen.
36. Urethra – A duct with a membrane lining that transports urine from the urinary
bladder to the outside. It travels through the corpus spongiosum of the penis in
males and also serves as a conduit for ejaculation semen. The urethra in females is
less than 4 cm long and opens anterior to the vaginal entrance.
37. Seminiferous Tubules – Any of the countless minute, convoluted tubules seen in
the testis lobules. The germ cells that give rise to spermatozoa line the
seminiferous tubules (see spermatogenesis). Sertoli cells are also present. A testis
lobule can have one to multiple seminiferous tubules, and a single testis can have
up to 400 lobules.
38. Ovary – One of the two parts of the female body that produce eggs.
39. Fallopian Tube – One of the slender fleshy tubes that transport ova (egg cells)
from each ovary to the uterus, where fertilisation can take place.
40. Uterus – The part of a woman or where a baby develops before it is born.
41. Vagina – The passage in the body of a woman that connects the outer sex organs
to the part where a baby grows (womb).
42. Fertilization – A zygote is formed by the union of a sperm and an egg cell. In fish
and amphibians, external fertilisation happens outside the female's body.
Fertilization takes place in the fallopian tube in humans.
43. Ultrasonography – Ultrasonography is an imaging technology that uses sound at
a frequency that beyond the human audibility range to measure and record
structures and structural change within the body (or sonography). Echoes from
ultrasound waves reflected off tissue surfaces are recorded to create structural
images for diagnostic reasons, such as examining a growing foetus during
pregnancy.
44. Embryo - Between the cleavage of the fertilised egg and birth in the phases of
development. During the first eight weeks of pregnancy, the embryo is made up of
the products of conception; beyond that, it is called a foetus.
45. Zygote – The egg formed free the fertilization of the male gamete and female
gamete is called the zygote.
46. Implantation – The attachment of the fertilized egg or blastocyst to the wall of
the uterus at the start of pregnancy.
47. Blastocyst - By the fifth or sixth day, the fertilized egg is known as a blastocyst, a
rapidly dividing ball of cells
48. Endometrium – The mucous membrane lining the uterus, which thickens during
the menstrual cycle in preparation for possible implantation of an embryo.
49. Ectoderm – The outermost layer of cells or tissue of an embryo in early
development, or the parts derived from this, which include the epidermis and nerve
tissue
50. Endoderm –The innermost layer of cells or tissue of an embryo in early
development, or the parts derived from this, which include the lining of the gut and
associated structures.
51. Mesoderm –The middle layer of cells or tissues of an embryo, or the parts
derived from this (e.g. cartilage, muscles, and bone).
52. Amniotic sac –The fluid-filled sac that contains and protects a fetus in the womb.
53. Placenta –The placenta is an organ that develops in your uterus during pregnancy.
This structure provides oxygen and nutrients to your growing baby and removes
waste products from your baby’s blood. The placenta attaches to the wall of your
uterus, and your baby’s umbilical cord arises from it.
54. Umbilical cord – The tube that connects a baby to its mother before it is born.
55. Lanugo – Fine, soft hair, especially that which covers the body and limbs of a
human fetus.
56. Vernix - A greasy deposit covering the skin of a baby at birth.
57. Amnion – The innermost membrane that encloses the embryo of a mammal, bird,
or reptile.
58. Chorion - The outermost membrane surrounding an embryo.
59. Depression- A group of conditions associated with the elevation or lowering of a
person’s mood, such as depression or bipolar disorder.
60. Pollutants – A substance that pollutes air, rivers, etc.
61. Fetal Alcohol Syndrome - A group of adverse fetal and infant health effects
associated with heavy maternal alcohol intake during pregnancy
62. Rubella virus – The elements, molecules, and particles involved in pollution –
life can be harmed when exposed to these materials.
63. C-section - A surgical procedure that involves making incisions through a
woman's abdomen and uterine walls to deliver a baby when vaginal birth is not
possible
64. Vacuum extraction - Vacuum extraction, is a method to assist delivery of a baby
using a vacuum device. It is used in the second stage of labour if it has not
progressed adequately.
65. Forcep delivery – A forceps birth is a type of vaginal delivery that requires
assistance. It’s sometimes required during vaginal childbirth. A health care worker
applies forceps to the baby’s head, an equipment shaped like a pair of giant spoons
or salad tongs, to help guide the infant out of the birth canal.
66. Transverse birth – This kid is in a transverse lay, which means he or she is lying
horizontally rather than vertically across the uterus. The baby’s back may be
positioned in a transverse lay as follows: The back should be facing the birth canal.
One shoulder is oriented in the direction of the birth canal. Face the delivery canal
with your hands and feet up.
67. Breech birth - A breech birth is when a baby is born bottom first instead of head
first, as is normal. Around 3–5% of pregnant women at term (37–40 weeks
pregnant) have a breech baby
68. Preterm - Preterm birth is when a baby is born too early, before 37 weeks of
pregnancy have been completed.
69. Small for Date infants - A baby that is little for gestational age is one that is
smaller than the average for the number of weeks of pregnancy. Birthweights for
SGA newborns are often below the 10th percentile for babies of the same
gestational age.
70. Rhesus factor - Rhesus (Rh) factor is an inherited protein found on the surface of
red blood cells. If your blood has the protein, you're Rh positive. If your blood
lacks the protein, you're Rh negative. Rh positive is the most common blood type
BLOCK 3 – Neo-Natal Development
71. Colostrum - The mother's pale-yellow first milk, which carries antibodies and has
several antibacterial abilities, and thus offers not only nutrition but also the
foundation for the neonate's immune system.
72. Meconium - A new born's first poop is meconium, which is excreted within 24
hours of birth. Amniotic fluid is present in this sticky, thick, dark green stool.
73. Abdominal breathing - The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle that connects
our chest to our abdomen. When we breathe in, the diaphragm contracts, flattens,
and moves downward, sucking air into the lungs. As the diaphragm descends, the
abdominal contents descend, forcing the abdominal wall out.
74. Reflexes - Any of a number of automatic, unlearned, relatively fixed responses to
stimuli that do not require conscious effort.
75. Palmar grasp – When any object is gently placed in the neonate’s palm, it
immediately curls its fingers around it and tightly hold’s the object majorly using
it’s palm. This reflex prepares the neonate for voluntary grasping and disappears at
3 to 4 months.
76. Babinski - When the sole of the foot is gently stimulated, the big toe extends
upward and the other toes fan out in a healthy infant, is Babinski reflex.
77. Pincer grasp - The manner of grasping an object between the thumb and
forefinger.
78. Tonic neck - When a baby's head is shifted to one side, the opposite arm reaches
out and bends up at the elbow. This is also termed as the fencing position. This
reflex enables the neonates to reach out towards objects and last until 4 to 6
months.
79. Eye blink – The involuntary movements of eyes in neonates in the presence of
extreme light.
80. Rooting reflex - When the cheek or lip is touched, normal new born reflexively
move their faces toward the stimulation and produce sucking (rooting) actions with
their mouths. This is called the rooting reflex.
81. Sucking reflex - a basic reflex in which the young of many mammals (including
human infants) grasp a nipple with their lips and draw milk into their mouths by
suction.
82. Swimming reflex - When a baby is placed in water on their stomach, their arms
and legs start to move in a swimming motion. This reflex lasts for 4 to 6 months.
83. Moro reflex - A Moro reflex may involve the infant suddenly splaying their arms
and moving their legs before bringing their arms in front of their body.
84. Stepping reflex - Because a baby appears to take steps or dance when held
upright with his or her feet touching a solid surface, this reaction is also known as
the walking or dance reflex.
BLOCK 4 - Physical Development
85. Physical development - Physical development (PD) is the growth and
development of both the brain and body in infancy and early childhood.
86. Growth Cycle - Physical changes in the brain cause changes in thinking and
learning. The recurring patterns of these changes point to common growth cycles
in behaviour and the brain—a cyclical property that explains the extraordinary
human capacity for plasticity.
87. Homeostasis - Homeostasis is a term that refers to psychological and
physiological balance achieved when one's needs and desires have been met. In a
physiological context, homeostasis is disrupted by what is referred to as a need
state, which is an innate need, like hunger.
88. Maturation - Maturation is the process of learning to cope and respond
emotionally appropriate. It does not necessarily occur in alongside with ageing or
physical development, but it is a part of growth and development.
89. Endocrine Functioning - Endocrine glands release hormones into the
bloodstream. This lets the hormones travel to cells in other parts of the body. The
endocrine hormones help control mood, growth and development, the way our
organs work, metabolism, and reproduction. The endocrine system regulates how
much of each hormone is released.
90. Endo-morphic - Fat body shape
91. Ecto-morphic - Thin body shape
92. Mesomorphic - Muscular body shape
93. Epiphysis - Expanded end of the long bones in animals, which ossifies separately
from the bone shaft but becomes fixed to the shaft when full growth is attained.
94. Diaphysis - The diaphysis is the main or midsection (shaft) of a long bone. It is
made up of cortical bone and usually contains bone marrow and adipose tissue
(fat).
95. Ossification - Hardening of bones as a result of the deposition of the Minerals,
Calcium and Phosphorus
96. Adipose Tissue - Body fat is a term used to describe adipose tissue. It can be
found in every part of the body. It's found beneath the skin (subcutaneous fat),
surrounding internal organs (visceral fat), between muscles, in bone marrow, and
in breast tissue.
97. Puberty - In common law, the age at which a person becomes capable of sexual
reproduction of progeny is presumed to be 14 years for males and 12 years for
females.
98. Malocclusion - An abnormal occlusion in which teeth are not in a normal position
in relation to adjacent teeth in the same jaw and/or the opposing teeth when the
jaws are closed.
BLOCK 5 - Motor Development
99. Motor Development –From infants’ first spontaneous waving and kicking
movements to the adaptive control of reaching, locomotion, and complicated
movements, motor development refers to improvements in children’s ability to
control their bodies’ movements.
100. Hand Skills –It is a set of activities or talents that need fine motor skills,
sometimes known as fine motor skills, tiny muscle coordination to regulate small
precise actions Especially in the hands and on the face. Handwriting, drawing, and
other forms of expression are examples. chopping, slicing, and handling little
items
101. Leg Skills – A set of talents that allow us to perform tasks that require huge
muscles in our legs and whole-body movements, often known as gross motor
skills. Gross motor skills are used in a variety of physical activities, including
running.to the ranking of leaves.
102. Handedness – When executing specific tasks, one hand is consistently used
rather than the other. The preference is frequently linked to a motor cortex
dominance effect on the opposite side of the body. Also known as hand
dominance.
103. Auxiliary – The non-dominant hand is linked to your brain's non-dominant
hemisphere, which is the one that isn't used as much. Both hemispheres are
stimulated when you use your nondominant hand, which might lead to you
thinking differently and being more creative.
104. Ambidextrous – Ambidextrous refers to the ability to use both the left and
right hands equally well. This is based on the Latin terms “ambi” and “both sides,”
which mean “both sides” and “both sides” respectively. “Dexter” is a Latin word
that means “right” or “favourable.” As a result, it is the ability to Make good use of
both hands.
105. Motor skills – Ability to move our bodies and manipulate objects. The two
basic forms of skills are Gross motor and Fine motor.
106. Gross skills - Gross motor skills focus on large muscle groups of the body
example legs and arms. They involve larger movements such as balancing, running
and jumping.
107. Fine skills - Describes activities or skills that require small muscle
coordination to control small, precise movements, particularly in the hands and
face. Handwriting, drawing, cutting, and manipulating small objects are examples
of fine motor skills.
BLOCK 6 - Cognitive Development
108. Cognitive development - Cognitive development refers to how children think,
explore, and solve problems. It is the acquisition of knowledge, skills, problem-
solving abilities, and behavioral patterns that allow children to think about and
fully understand their surrounding.
109. Schemes - Cognitive structures or patterns that helps the child to organize the
knowledge he gained from his experiences to understand the world. They are the
smallest units in cognitive theory of development.
110. Jean Piaget – A psychologist who developed a theory of cognitive
development in children from infancy to adolescence.
111. Cognition – Cognition is the process of acquiring knowledge and
understanding through the senses, thoughts and experience. It involves mental
process and actions.
112. Egocentrism – It is the inability of the child to pay attention to other’s point of
view’s other than its own. They consider themselves as the focal focal point.
113. Centration – It is the tendency that allows only to focus on any one aspect of
the thing or situation, neglecting the other aspects.
114. Hierarchical Classification – The organisation of objects into groups and sub-
groups on the basis of similarities and differences.
115. Reversibility – It is the ability which allows the child to go back and forth,
analyse the whole thing and come up with a result. The child repeats the action to
know the surrounding.
116. Irreversibility - The child cannot mentally reverse a set of steps.
117. Adaptation – It involves building schemes through direct interaction with the
environment and is the result of assimilation and accommodation. (AS + AC =
AD)
118. Assimilation - The process of interpreting and comprehending the external
world using current schemes.
119. Accommodation – The process of using the existing schema or revising the
existing schema in order to understand the things environment.
120. Sensorimotor Stage - This stage, according to Piaget, lasts from birth to two
years, during which the child uses its developing sensory and motor skills to
comprehend the environment and develop new experiences.
121. Circular Reaction – Repetition of sensorimotor responses which arise from
new experiences and motor activity leading to the formation of the infant’s first
schemes.
122. Mental Representation – Internal depictions of information, both images and
concepts that the mind can manipulate.
123. Imitation - The act of purposefully or inadvertently replicating the behaviour
of another person, group, or object.
124. Coordination - The organisation of the various elements of a complex body or
activity so that the child can work effectively together.
125. Problem-solving - Problem-solving is a mental process which includes
identifying, analysing, and resolving issues. The ultimate goal of problem solving
is to overcome problems and seek the best solution to the problem.
126. Object permanence - The understanding that objects continue to exist even
when out of sight.
127. Deferred imitation – The ability to remember and copy the behaviors of
models who are not present.
128. Mental images - A mental image, sometimes known as a mental picture, is an
experience that, in most cases, resembles the experience of visually experiencing
some object, event, or scene, but occurs while the related object, event, or scene is
not present physically.
129. Goal-oriented - Individuals' different perspectives and responses to
achievement situations are explained by goal orientations, which refer to the
reasons or motives for engaging in learning activities.
130. Exploration - Exploration incorporates using observation, conversation, and
directed thought to gather new information in order to solve an issue.
131. Mental representation - Internal representations of information, including
images and concepts that the mind can manipulate.
132. Preoperational Stage - The stage described by piaget as lasting from 2 to 7
years of age and is divided into preconceptual (2 to 4 years) and intuitive (4 to 7
years) stages.
133. Recognition - A form of remembering characterized by a feeling of familiarity
when something previously experienced is again encountered.
134. Symbolic Play - Children's ability to represent other things, activities, or ideas
in play by using objects, actions, or ideas. Social skills, intellectual ability, early
literacy concepts, and behavioural self-regulation are all enhanced by symbolic
play.
135. Symbolic Thinking - The ability to think about objects and events beyond
one's immediate surroundings. Language, numeracy, and creative or ritual
expression all exhibit the use of signs, symbols, concepts, and abstract
interconnections.
136. Perspective - A point of view or a certain way to look at something is
described to as a perspective.
137. Concrete operational stage – The stage as stated by Piaget that lasts from
ages 7 to 11 and is marked by important milestones.
138. Formal operational stage - The ability to solve an issue in a logical and
methodical form occurs at the formal operational stage. Children at the formal
operational stage of cognitive development are usually able to prepare a problem-
solving strategy fast and efficiently.
139. Fact-finding - Finding or verifying facts or reliable information, especially by
a neutral person in attempt to settle a conflict or controversy.
140. Pendulum Problem - The ability to analyse variables (length, weight, force of
drop, and height of drop) in a structured manner usually comes in early
adolescence and is evidence of theoretically -deductive reasoning, which defines
the formal operational stage of development.
BLOCK 7 - Language Development
141. Language development - Language development is the process by which
children learn to understand and communicate language in order to express their
wants and needs during their early childhood.
142. Gestures - The earliest type of communication in which the body's limbs are
used to supplement speech. It serves the purpose as a substitute. Gestures can be
meaningful if only used with speech.
143. Communication - The transmission of information, whether verbal or
nonverbal, in order to communicate, relate and exchange ideas, knowledge,
feelings, and experiences, and for a variety of other interpersonal and social
purposes.
144. Symbols – Symbols are pre-speech form of communication
145. Self-evaluation - To evaluate oneself or one's actions, performance, language.
146. Academic achievement - In a general sense, academic achievement is the
current level of a student's learning. Students who do well in school are better
able to make the transition into adulthood and to achieve occupational and
economic success.
147. Influence – The capacity to have an effect on the character, development, or
behaviour of someone or something, or the effect itself.
148. Forms of pre-speech – Substitute forms of communication used by infants
before they say their first word.
149. Crying – Crying is the first form of communication in neonates. It is used to
express any kind of bodily discomfort, the need for someone to relieve their pain,
hunger, fatigue etc.
150. Cooing - Cooing is a pre-speech form of communication that involves
explosive sounds such as gurgling, grunts, and sighs caused by chance movements
of the vocal mechanisms.
151. Babbling – The pre-speech form of communication that involves definite,
practiced, voluntary and repetitive sounds produced by a baby that don’t have any
meaning or association is known as babbling.
152. Emotional expressions – Facial and bodily changes happening in order to
express the emotions is called emotional expressions. For example relaxing the
body, waving of the arms and legs and also smiling represents pleasant emotion
153. Voluntary – Voluntary action means proceeding from the will or from one's
own choice or consent without being in force of others.
154. Involuntary – Actions that describe activity, movement, behavior, or other
processes (e.g., reflexes) that occur without intention.
155. Caregiver - A person who attends to the needs of and provides assistance to
someone else who is not fully independent, such as an infant.
156. Parents - Parents are among the most influential people in their children's life.
Mothers and fathers, as well as other caregivers who function as parents, are all
considered parents. Children rely on their parents to give them with care,
encouragement, support, and access to activities that enable them to master
essential developmental skills from the moment they are born.
157. Practice - Repetition of an act, behaviour, or series of activities, typically to
improve performance or learn a skill. For example, in the babbling stage with
practice the baby is able to control the vocals and makes it possible to repeat
sounds by joining the words together like ‘ma-ma’
158. Infant stimulation - Infant Stimulation includes activities that arouse or
stimulate baby’s senses of sight, sound, touch, taste and smell.
159. Desire to interact - It is the child's motivation to learn to talk and to spend
more time with others willingly as an effort needed for the learning.
160. Ordinal position - Ordinal position refers to the actual order in which the
child was born. The first born speech is superior to that of later-born in the same
family. This is because parents can devote more time to teaching and encouraging
their children to speak than they can to later-born children.
161. Authoritarian parenting - This parenting style emphasises the importance of
seeing but not hearing children. This parenting style is an impediment to learning.
162. Multiple births – Multiple births means more than one child. It has been
discovered that the incidence of language delay in multiple births is significantly
higher than in single birth children.
163. Gender differences - Gender differences in language use emerge early, with
girls more likely to use language in the context of emotional relationships with
others, while boys are more likely to use language to describe objects and events.
164. Personality - Personality is commonly regarded as a complex, totality shaped
by a range of factors, including hereditary and legal tendencies; physical
maturation; early training; identification with significant individuals and groups;
culturally conditioned values and roles; and critical experiences and relationships.
165. Pronunciation - Learning to pronounce words is the first step in learning to
speak. It is acquired by imitation. The manner a word or a language is spoken is
referred to as pronunciation.
166. General vocabulary – The initial vocabulary that the child acquires which
incudes the words that can be used in a variety of different situations.
167. Sentence formation – It is the third stage of language development where a
child starts to combine different words, to form a grammatically correct sentence
in order make others understand what they want to say. It is also more likely to
contain errors.
168. Logical thinking - Thinking that is consistent with formal principles of logic.
BLOCK 8 - Social Development
169. Social development - Social development means acquisition of the ability to
behave in accordance with social expectation.
170. Social self – The parts of one’s identity that are built up by being impacted by
others, interpersonal ties, and shared experiences, also the abilities that can
influence others
171. Social expectations – The expectations of society are unspoken norms, that
will reflect the behavior and reaction of an individual that is socially acceptable.
Expectations of the society are influenced by a variety of factors, including the
individual's culture, religion, age group, social class, and geographic area.
172. Antisocial – People who are antisocial, despite knowing the socially accepted
norms or what that particular group expects, they purposefully disobey the norms
to go against the group because of their antagonist attitude toward people.
173. Non-social – Non-social people have behaviour that does not exhibit
achievement in any of the three stages that define a social person.
174. Asocial – A person with asocial behavior is someone who is either unmotivated
by social engagement or has a strong preference for solitary pursuits.
175. Socially approved - The accepted behaviour that an individual is required to
comply to in a certain group, community, or culture is referred to as being socially
approved. It also serves as a foundation for other actions.
176. Quick learner - A quick learner is someone who can learn, understand, and
apply new information quickly than their peers. Quick learners demonstrate good
communication, listening, and analytical abilities, as well as the ability to
assimilate information and apply it effectively.
177. Socially active – Relationships with people in the surrounding helps to
understand the social settings and enhances the socialising skills of the child
178. Parental attitude - Parental attitudes are the primary social influences that a
child encounters during his early years. It is also critical for children to form
healthy–unhealthy relationships with their surroundings. The child's behaviour is
heavily influenced by the attitude he receives from his parents.
BLOCK 9 – Emotional Development
179. Emotional development – A steady improvement in the ability to experience,
express, and comprehend the whole spectrum of emotions, as well as the ability to
cope with them effectively.
180. Emotion - An individual's attempt to deal with a personally meaningful
problem or event through a complicated reaction pattern involving experiential,
behavioural, and physiological factors.
181. Pleasant emotion – Emotions that make us feel good, which are helpful and
important for our development are called pleasant emotion.
182. Unpleasant emotion - When something is unpleasant, it makes us feel awful,
sad or uncomfortable and also are harmful for our development are termed as
unpleasant emotion.
183. Curiosity / Inquisitiveness - The drive to examine, observe, or collect
knowledge, especially when the subject matter is new or interesting. This desire is
found in young toddlers that employ sensory exploration and motor manipulation
to explore, bite, handle, taste, or smell almost everything in their immediate
environment.
184. Joy / happiness - Happiness is often defined as a pleasant emotional state that
is characterized by feelings of contentment, joy, gratification, satisfaction, and
well-being.
185. Fear - Fear is a subjective response that occurs in association with bodily
arousal when a person is presented with a potentially dangerous situation. All of a
child's fears emerge from his or her past memories and experiences. Some fears are
learned by imitation, while others are based on first hand experiences.
186. Anger - Anger is one of the most fundamental negative emotions, and it
typically has a reason. Anger is something that everyone goes through. Aggression
and temper tantrums are the most common forms of anger in pre-schoolers. It is
challenging to deal with for both adults and children.
187. Jealousy - It's a reaction to the loss of affection, whether real, imagined, or
threatened. It's a dread associated with the desire to keep a certain item. It is an
outgrowth of rage that leads to a resentful attitude toward directed persons.
188. Stimuli – Stimulus is something that causes another thing to occur, develop, or
become more active. It also give rise to sensory, behavioral and emotional
response.
189. Response - A remark made in response to someone or something or a stimuli
is termed as a response.
190. Transitory emotions – These types of emotions are not permanent they are
temporary. It is more likely to be seen in children. The switching up of emotions
happens quickly, but as moving to adulthood the emotions becomes more
permanent.
191. Temper tantrums - A violent outburst of anger that typically occurs between
the ages of 2 and 4 and includes behaviours such as screaming, kicking, biting,
hitting, and head banging The incidents are frequently out of proportion to the
direct offence and are sometimes viewed as an expression of accumulated tensions
and frustrations.
192. Emotional catharsis - A catharsis is an emotional release. According to
psychoanalytic theory, this emotional release is linked to a need to relieve
unconscious conflicts. For example, experiencing stress over a work-related
situation may cause feelings of frustration and tension.
193. Emotional quotient - The ability to understand, control, and manage our own
emotions in positive ways to relieve stress, communicate effectively, empathise
with others, overcome challenges, and defuse conflict is referred to as emotional
quotient (EQ).
194. Social quotient - The proportion of chronological age to social age A social
quotient is similar to an IQ score in that a score of 100 shows average age
performance and a score of less than 100 indicates below average functioning. The
social intelligence quotient is a term that is becoming more popular. Social
intelligence is crucial in many parts of a person's life since it aids in the
development of connections.
195. Parental favouritism - When one or both parents show constant bias toward
one child over the other, this is known as parental favouritism. More time spent
together, less discipline, and more privileges are all possible outcomes.
196. Mockery - Mockery is the act of making fun of someone or something, simply
by teasing them, but more commonly by creating a parody, apparently imitating
them in a way that reveals their flaws. Early on, mockery is not a common thing,
but it gets more common as the latency child enters the social arena of sibling
rivalry, competition, and social engagement.
197. Covert expressions- Any emotion that can’t be seen facially that is hidden or
not directly visible, open to view, or publicly known, whether by accident or
deliberately is known as covert expressions. For example in adults to express grief
it is an covert expressions which includes loss appetite, sleeplessness etc.
198. Overt - Referring to any emotion that is not hidden or is directly visible, open
to view, or publicly known and expressed openly. This is seen mainly in children
their form of expressing grief is crying.
199. Hormonal turmoil -
BLOCK 10 – Moral Development
200. Moral development - It involves the formation of a set of culturally defined
rules in the child to govern behaviour. The rules differ from one culture to the
next. The word moral is derived from the Latin word ‘mores’ which means
manners or customs.
201. Moral behavior - Moral behaviour is defined as behavior that belongs to the
social group's moral code. The action is the result of the thoughts that have been
shaped in us. The expected behavior patterns of all group members are determined
by the rules of behavior to which members of a culture have become accustomed.
202. Moral feeling - Moral feeling is the ability to experience pleasure or
unhappiness just by being aware that our activities are in accordance with or in
violation of the law of duty. It means how does a person feel during that particular
situation.
203. Moral judgement - The study of how people think about good and wrong, as
well as how they acquire and apply moral norms, is known as moral judgement.
For example, if someone follows a given rule, they ask oneself, why are they
obeying that rule.
204. Cultural practices - Cultural practises are common ideas of how people in a
culture behave on a regular basis, while cultural values are shared cultural ideals.
205. Rationalizing - Moral rationalisation refers to a person's ability to portray
immoral behaviour as moral behaviour. It stems from a dispute of motivations and
a desire to portray oneself as virtuous.
206. Immoral behavior - Immoral behaviour is defined as behaviour that deviates
from social norms. This is not due to ignorance, but rather to a deliberate refusal to
follow the norm or a lack of a sense of need to obey.
207. Non – moral behavior - Nonmoral behavior is the result of a lack of
understanding of what the social group expects, rather than a deliberate rejection
of the group's standards. Some of the behavior of the children are unmoral rather
an immoral,
208. Impulsive aspect – The impulsive aspect is termed as a natural tendency to
behave recklessly and without proper consideration of the consequences.
209. Intellect aspect - The intellectual part is that children must be taught to think
about what is right and wrong by providing them with answers as to why this is
correct and why this is incorrect.
210. Serving guidance – Helps to create guidelines which will help the child to
behave and conform to the social expectations in order to maintain the social
system.
211. Developing internal control – Developing internal controls means to ensure
that they are willing to act in a socially desirable manner rather than being forced
to do so. This allows the child to act independently without the assistance of an
adult.
212. Correct ethic - The morally righteous principles accepted by a person or a
group or considered acceptable to a specific field.
213. Self – criticism – Self criticism enables the person to analyse its moral values,
and allows to work and rework in order to get the right values.
214. Acceptance by peers - The degree to which a kid or adolescent is socially
accepted by peers is known as peer acceptance. It encompasses a child's or
adolescent's peer popularity as well as the ease with which he or she may establish
and manage satisfying peer relationships.
215. Guilt - When an individual's behavior does not meet the standards set by their
conscience, feelings of guilt develop. It is a type of negative self-evaluation that
occurs when an individual recognises that his behavior is inconsistent with a given
moral value to which he feels obligated to conform.
216. Moral conscience - Moral conscience is an element of the mind's cognitive
process that determines whether or not an action is morally correct. To put it
another way, it is the awareness of moral ideals and whether or not one's actions
are consistent with these beliefs. It's a tool for self-discipline, correction, and
regulation.
You might also like
- Pregnancy Week by WeekDocument25 pagesPregnancy Week by WeekNicoleta Adriana Petre100% (1)
- MISOSA S51Quarter 2, Modules 1-3Document27 pagesMISOSA S51Quarter 2, Modules 1-3Di VianNo ratings yet
- R Gupta Popular Master Guide For CUET-UG Biology 2022Document101 pagesR Gupta Popular Master Guide For CUET-UG Biology 2022Somya KulshresthaNo ratings yet
- The Cell Biology of Stem Cell PDFDocument246 pagesThe Cell Biology of Stem Cell PDFgillNo ratings yet
- Notes On The Human Female Reproductive SystemDocument10 pagesNotes On The Human Female Reproductive Systemfichte121No ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument24 pagesHuman Reproductionprayaasplb100% (1)
- Science 5 DLP 1 - Human Reproductive SystemDocument12 pagesScience 5 DLP 1 - Human Reproductive SystemMark Cua89% (35)
- Oral Histology Questions Part 1Document8 pagesOral Histology Questions Part 1hamzkk100% (3)
- Miscarriages and NutritionDocument70 pagesMiscarriages and NutritionErwin Ginting100% (2)
- Module 11. Pre-Natal DevelopmentDocument5 pagesModule 11. Pre-Natal DevelopmentRachel Joy SaldoNo ratings yet
- MarsiiDocument35 pagesMarsiiMariel Magtalas100% (1)
- n213 Unit 2 BDocument390 pagesn213 Unit 2 BJeonghwa Park100% (1)
- Reproductive - Systems - in - Vertebrates ss2Document12 pagesReproductive - Systems - in - Vertebrates ss2Ezeh PrincessNo ratings yet
- Embryology Notes emDocument25 pagesEmbryology Notes emAnonymous IwWT90VyNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument30 pagesBiology Investigatory ProjectSANDIPAN BISWAS80% (5)
- Complex Exam Stomat (2 Course) 04.12.20Document116 pagesComplex Exam Stomat (2 Course) 04.12.20محمد الصبارNo ratings yet
- Reproduction and Development ReviewerDocument5 pagesReproduction and Development ReviewerDieterici MansuetoNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Science in Nursing: Care of Mother, Child and ADOLESCENT (Well Clients)Document9 pagesBachelor of Science in Nursing: Care of Mother, Child and ADOLESCENT (Well Clients)Jerica Mae VenoyaNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument42 pagesGen BioJoyce Anne Mae AdorioNo ratings yet
- Reproduction and EmbryologyDocument20 pagesReproduction and EmbryologyDaaeennggNo ratings yet
- Science 10 ReviewerDocument14 pagesScience 10 ReviewerMonique FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 by SuryaDocument29 pagesUnit 2 by SuryayashiranjNo ratings yet
- Ullang - NCM 107a Module1-2Document16 pagesUllang - NCM 107a Module1-2Rahima UllangNo ratings yet
- The Human Reproductive System FinalDocument16 pagesThe Human Reproductive System FinalIlac Tristan BernardoNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive System Yr 11 Biology 114629Document7 pagesHuman Reproductive System Yr 11 Biology 114629Zach ZaneNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive System - Wikipedia PDFDocument4 pagesHuman Reproductive System - Wikipedia PDFAubrey EuropeNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Human ReproductionDocument3 pagesChapter - 3 Human ReproductionMr.Prashant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy ReportDocument17 pagesAnatomy ReportMabeth PagatpatNo ratings yet
- Document (17) XXDocument45 pagesDocument (17) XXShafiq SaweraNo ratings yet
- Reparoductive SystemDocument4 pagesReparoductive SystemAhmed Mohammed omarNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemJoseph CristianNo ratings yet
- Eproduction Is The Process of Giving Birth To Their Young Ones Which Are Identical To Their ParentsDocument3 pagesEproduction Is The Process of Giving Birth To Their Young Ones Which Are Identical To Their Parents꧁༒૮αll ʍ૯ ૨αj༒꧂No ratings yet
- Human Reproduction - II Puc - Regular NotesDocument23 pagesHuman Reproduction - II Puc - Regular NotesVasudevNo ratings yet
- LAP 14 Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesLAP 14 Male and Female Reproductive SystemWarren Grace NavarroNo ratings yet
- Vertebrates: Reproductive System AnimalsDocument2 pagesVertebrates: Reproductive System AnimalsKathleen Castañeda FernandezNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument18 pagesThe Reproductive Systemcmillica1176No ratings yet
- Notes ReproductionDocument12 pagesNotes Reproductionkeshavkhaneja7No ratings yet
- Pregnancy and Fetal Development: Shumaila Rani Nursing Instructor (SNC)Document95 pagesPregnancy and Fetal Development: Shumaila Rani Nursing Instructor (SNC)sadia ahmadNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive Systems: Rivka H. Borger, Pa Touro College Biology 102 SPRING 2020Document38 pagesThe Reproductive Systems: Rivka H. Borger, Pa Touro College Biology 102 SPRING 2020Stuart DitchekNo ratings yet
- Week 6Document3 pagesWeek 6John JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Hr-Module 1-Lesson 1Document35 pagesHr-Module 1-Lesson 1Sevilla, Marpolo Joaquin Z.No ratings yet
- The Human Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesThe Human Reproductive SystemEhr WinNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Gender Society 1Document32 pagesModule 2 Gender Society 1John Syvel QuintroNo ratings yet
- Developmental PsychologyDocument2 pagesDevelopmental PsychologypsychcookieNo ratings yet
- Biology (Human Reproductive Anatomy) Lecture Notes or Book NotesDocument6 pagesBiology (Human Reproductive Anatomy) Lecture Notes or Book NotesCharline Lucille BanoNo ratings yet
- Development of The Learners at Various Stage: Submitted byDocument22 pagesDevelopment of The Learners at Various Stage: Submitted byArly Boy TadumanNo ratings yet
- Process of FertilisationDocument5 pagesProcess of FertilisationGeorgia SloanNo ratings yet
- Please Discuss Your Answer BrieflyDocument4 pagesPlease Discuss Your Answer BrieflyAlexis John Hisula VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction Module 1 - Development and Function of Reproductive SystemDocument55 pagesHuman Reproduction Module 1 - Development and Function of Reproductive SystemAdc ClamorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 - ReproductiveDocument18 pagesChapter 19 - Reproductiveapi-220531452No ratings yet
- Cad Module 11 23 Unit1 Unit5 ReviewerDocument47 pagesCad Module 11 23 Unit1 Unit5 ReviewerJelmar CastuloNo ratings yet
- Additional Notes Handout 2Document5 pagesAdditional Notes Handout 2Rovina Narayan DiasNo ratings yet
- GENSOC M2 Lesson 4Document7 pagesGENSOC M2 Lesson 4cassy margaNo ratings yet
- EmbryologyDocument9 pagesEmbryologyRuhul Qudus NaimNo ratings yet
- GEC SELF Lesson 5-Activity 5Document9 pagesGEC SELF Lesson 5-Activity 5Hannah Lee LumosbogNo ratings yet
- Reproductive HealthDocument21 pagesReproductive HealthRosalie Valdez EspirituNo ratings yet
- MenstruationDocument4 pagesMenstruationMelgeri Aubrey E. UngosNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument11 pagesThe Reproductive Systemdevgod729No ratings yet
- Module 2 Gender SocietyDocument28 pagesModule 2 Gender SocietyMariza GiraoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System HandoutDocument21 pagesReproductive System HandoutJei SanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3: Human Reproduction: 1. Draw A Neat Labelled Diagram of Male Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesChapter-3: Human Reproduction: 1. Draw A Neat Labelled Diagram of Male Reproductive SystemSanaullah M SultanpurNo ratings yet
- Foetal DevelopmentDocument50 pagesFoetal Developmentdipendrakumarkushawaha44No ratings yet
- Sex Education Is An International Refereed Journal Concerned Both With The Practice ofDocument11 pagesSex Education Is An International Refereed Journal Concerned Both With The Practice ofJacylyn Alo TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System LessonDocument3 pagesReproductive System LessonmargemunozNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument3 pagesHuman ReproductionsamyukthaNo ratings yet
- Science 10 3rd Grading Module 1 REPRODUCTIVESYSTEMDocument32 pagesScience 10 3rd Grading Module 1 REPRODUCTIVESYSTEMvinesse100% (1)
- Human Reproduction UPDATEDDocument16 pagesHuman Reproduction UPDATEDCandy OpsadNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology GCSDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology GCSSherry Ann FayeNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Development: Lesson 2Document10 pagesPlant and Animal Development: Lesson 2hellohelloworldNo ratings yet
- Biology of Stem Cells: An Overview: Pedro C. Chagastelles and Nance B. NardiDocument5 pagesBiology of Stem Cells: An Overview: Pedro C. Chagastelles and Nance B. NardiMayuri DuttaNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Development of The Learners at Various StagesDocument25 pagesModule 6 - Development of The Learners at Various StagesRachelle DalingNo ratings yet
- The Istanbul Consensus Workshop On Embryo Assessment: Proceedings of An Expert MeetingDocument13 pagesThe Istanbul Consensus Workshop On Embryo Assessment: Proceedings of An Expert MeetingchristopherNo ratings yet
- LIFS 1902 - General Biology II: Video 4 - Human DevelopmentDocument20 pagesLIFS 1902 - General Biology II: Video 4 - Human DevelopmentGary TsangNo ratings yet
- Biological Science NotesDocument35 pagesBiological Science NotesPianomanSuperman100% (2)
- Maternal Child Nursing Care 2nd Edition Ward Test BankDocument28 pagesMaternal Child Nursing Care 2nd Edition Ward Test Bankalicenhan5bzm2z100% (34)
- Stages of Prenatal DevelopmentDocument15 pagesStages of Prenatal DevelopmentsoraruNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysioDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiofrances_ortezaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Module 11: Pre-Natal PeriodDocument42 pagesUNIT 1 Module 11: Pre-Natal PeriodJenno Lloyd Samaniego DariaNo ratings yet
- Fertilization & ImplantationDocument54 pagesFertilization & ImplantationMarvelousNo ratings yet
- EmekaDocument17 pagesEmekamutiyasNo ratings yet
- Hysteroscopy Newsletter Vol 5 Issue 3 EnglishDocument19 pagesHysteroscopy Newsletter Vol 5 Issue 3 EnglishHisteroscopia.esNo ratings yet
- Genes 14 Article Reproduction AnimalDocument12 pagesGenes 14 Article Reproduction AnimalCarol RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Implantation & Second WeekDocument18 pagesImplantation & Second WeekCabdiladif Ahmed McrfNo ratings yet
- General Embryology 2022Document130 pagesGeneral Embryology 2022KAMAL ALSOFIANYNo ratings yet
- moduleLESSON Genes and BehaviorDocument11 pagesmoduleLESSON Genes and BehaviorRecxs Baludio AtchaNo ratings yet
- Placentation: Structure, Type and Physiology of Placenta: Nimita KantDocument24 pagesPlacentation: Structure, Type and Physiology of Placenta: Nimita KantNikkNo ratings yet
- C9 Fertilization and Foetal DevelopmentDocument39 pagesC9 Fertilization and Foetal Developmenteryna sofeaNo ratings yet
- Bovine and Buffalo in Vitro Embryo Production Using Oocytes (2002)Document8 pagesBovine and Buffalo in Vitro Embryo Production Using Oocytes (2002)Anamaria Blaga PetreanNo ratings yet
- Prenetal - HGDDocument11 pagesPrenetal - HGDJananee RajagopalanNo ratings yet