Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Internet Sources A. Reviewing Previous Lesson or Presenting The New Lesson (Elicit)
Uploaded by
arlene aliporoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Internet Sources A. Reviewing Previous Lesson or Presenting The New Lesson (Elicit)
Uploaded by
arlene aliporoCopyright:
Available Formats
Grade
School DASNHS Level 8
Learning
Teacher ARLENE M. ALIPORO Area SCIENCE
Teaching APRIL 5-8, 2020
DAILY Dates and (Burgos, Del Pilar,
LESSON Quarter THIRD
Time Agoncillo, Dagohoy,
LOG Luna)
I. OBJECTIVES
The learners demonstrate understanding of the particle nature of matter as basis for
A. Content Standard
explaining properties, physical changes, and structure of substances and mixtures
The learners shall be able to present how water behaves in its different states within the
B. Performance Standard
water cycle
Explain physical changes in terms of the arrangement and motion of atoms and
C. Learning Competency molecules.
S8MT-IIIc-d-9
1. Differentiate physical from chemical change.
2. Enumerate and discuss the different physical/phase changes in matter (evaporation,
D. Specific Learning condensation, sublimation, deposition, freezing, melting)
Objectives 3, Show how phase changes in matter are affected by change in temperature at molecular
level.
4. Present how water behaves in different states in a water cycle.
Physical Changes in terms of the Arrangement and Motion of Atoms and
II. CONTENT
Molecules.
III. LEARNING
RESOURCES
A. References
1. Teacher’s Guide
pages
2. Learner’s Materials Self-Learning Modules of students Week 3
pages
3. Textbook pages Science And Technology For Lifelong Learning pp. 225-227, 228-230
4. Additional Materials
from Learning
Resource (LR) portal
B. Other Learning Internet Sources
Resource
IV. PROCEDURES
A. Reviewing Look Into Me: Physical or Chemical Change
previous lesson or Student will be look and watch two short video clip and will answer questions provided.
presenting the new
lesson Video Clip #1: Tearing of Paper
(ELICIT) Q1: What happen to the paper?
Q2: Did a new thing (material) form after tearing the paper into pieces?
Video Clip #2: Cooking of an Egg
Q1: What happen to the egg after it was put into the frying pan?
Q2: Did a new thing (material) form after frying the egg?
*Which of the two samples undergoes physical change? Chemical
change?
B. Establishing a Difference between Physical & Chemical Change
purpose for the Physical change – occurs when the composition of the substance is not altered (change)
lesson in the process. Example: torn paper (into pieces); broken glass
(ENGAGE)
C. Presenting Chemical change (chemical reaction) – occurs when the composition of a substance
examples/Instances having physical and chemical properties completely different from the original. Example:
of the new lesson fried egg; lit candle
(ENGAGE)
D. Discussing new Let Me Think!
concepts and Label each video whether it shows deposition, boiling, evaporation, melting, freezing,
practicing new skills sublimation, or condensation.
#1 Video #1: Freezing of Ice
(EXPLORE) Video #2: Boiling of Water
Video #3: Evaporating of Ice
Video #4: Melting of Ice
E. Discussing new Video #5: Deposition of Iodine
concepts and Video #6: sublimation of Dry Ice
practicing new skills Video #7: Condensation of Water Vapor
#2
F. (EXPLORE) *Phase Change – matter changes from one
state (solid, liquid, gas) to another.
A. Physical Changes in terms of Arrangement & Motion of Atoms and
Molecules (Through Simulation)
Name Phase Change Arrangement Motion Intermolecular Kinetic
(atoms & (atoms & Forces Energy
molecules) molecules)
Melting Solid – Liquid Apart from Move very Decrease Increase
each other fast
Freezing Liquid – Solid Very close Vibrate Increase Decrease
to each
other
Evapora Liquid – Gas Apart from Move very Decrease Increase
tion each other fast
Conden Gas – Liquid Quite far Move Increase Decrease
sation from each slowly
other
Sublima Solid – Gas Apart from Move very Decrease Increase
tion each other fast
Depositi Gas – Solid Close to Vibrate Increase Decrease
on each other
* Intermolecular forces – forces of attraction
* Kinetic Energy – energy of motion
B. Physical Changes in terms Exothermic & Endothermic Reactions
Phase Change Name Exothermic or
Endothermic
Solid – Liquid Melting Endothermic
Liquid – Gas Evaporation Endothermic
Gas – Solid Deposition Exothermic
Solid – Gas Sublimation Endothermic
G. Developing mastery Gas – Liquid Condensation Exothermic
(EXPLAIN) Liquid – Solid Freezing Exothermic
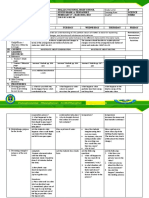
H. Finding practical Genius Challenge!
application of Label the water cycle diagram.
concepts and skills
in daily living Precipitation Condensation
(ELABORATE) Evaporation Transpiration
Percolation
I. Making
generalizations and *Water Cycle – is the path that all water follows as it moves around Earth in different
abstractions about states.
the lesson *Liquid Water – is found in oceans, rivers, lakes – and even underground.
*Solid Ice – is found in glaciers, snow, and at the North & South Poles.
*Water Vapor – a gas – is found in Earth’s atmosphere.
Why is Water Cycle Important?
- Water is necessary for all living things.
Let’s Analyze
Answer the following questions briefly.
1. Which among the phases changes involves absorption of energy?
2. What happen to the molecules whenever heat is released in during a phase change?
3. Why is phase change considered a physical change?
Let’s Try (Evaluation)
Read the following. Write the letter of your answer before the number.
1. Which of the following is an example of physical change?
A. Mixing baking soda and vinegar together, and this causes bubbles and foam.
B. A glass cup falls from the counter and shatters on the ground.
C. Lighting a piece of paper on fire and the paper burns up and leaves ashes.
D. Baking a birthday cake for your mother.
2. Which change can be easily be reversed?
A. Chemical Change C. Both a physical and a chemical change
B. Physical Change D. Neither a physical nor a chemical change
3. Which of the following takes place if the chemical properties of a substance remain
unchanged and the appearance or shape of a substance changes?
A. Chemical Change C. Both a physical and a chemical change
B. Physical Change D. Neither a physical nor a chemical change
J. Evaluating learning 4. Which is an example of a physical change?
(EVALUATE) A. Metal rusting C. Water boiling
B. Silver tarnishing D. Paper burning
5. What characteristic best describes what happen during a physical change?
A. Composition changes C. Forms stays the same.
B. Composition stays the same D. Mass is lost
6. The phase change in which a substance changes from a solid to a gas or vapor without
changing to a liquid first is
A. vaporization. B. sublimation. C. deposition. D. melting
7. The change of a substance from a solid directly to a gas is called
A. sublimation. B. melting. C. evaporation. D. condensation
8. The phase change that is the reverse of melting is
A. condensation B. sublimation. C. vaporization. D. freezing
9. All changes of the state of matter require
A. sublimation. B. energy C. vibration. D. water
10. What type of change occurs when water changes from a solid to a liquid?
A. a physical change C. an irreversible change
B. a phase change D. both a and b
K. Additional activities Let’s Create
for application or Make a poster showing a phase change happening in the environment. It should contain
remediation
a title and it should have a short description of the phase change. (see rubrics)
(EXTEND)
V. REMARKS
VI. REFLECTION
No. of learners who earned 80% in the evaluation
A. No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation who scored below 80%
B. Did the remedial lessons work? No. of learners who have caught up with the lesson
C. No. of learners who continue to require remediation
D. Which of my teaching strategies worked well? Why did these works?
E. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor can help me solve?
F. What innovation or localized materials did I use/discover which I wish to share with other teachers?
Prepared by: ARLENE M. ALIPORO Checked by: MELVINA C. BELANGO
Science Teacher Head Teacher, Science Department
You might also like
- Science Grade 3 1st Quarter TestDocument4 pagesScience Grade 3 1st Quarter TestKristine Barredo89% (64)
- Quantum Faith - CappsDocument42 pagesQuantum Faith - CappsLovis NK97% (31)
- Science Curriculum Framework 0893 - tcm143-595685Document31 pagesScience Curriculum Framework 0893 - tcm143-595685shalini rajeeshwar80% (5)
- Ionic and Covalent Bonding Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesIonic and Covalent Bonding Lesson Planrosally alcoser100% (5)
- DLL in Melting (Solid-Liquid) Science 8Document2 pagesDLL in Melting (Solid-Liquid) Science 8RosalvaDiñoKatimbang85% (26)
- WM Angelic Kingdom+ NotesDocument35 pagesWM Angelic Kingdom+ Notesbuzypet100% (1)
- Universal Law and Harmonics - The Mind MatrixDocument1 pageUniversal Law and Harmonics - The Mind MatrixTala Wraith100% (1)
- Quinta Essentia - Part 2Document329 pagesQuinta Essentia - Part 2dgE100% (5)
- Dolar - Tyche, Clinamen, DenDocument17 pagesDolar - Tyche, Clinamen, Dendivinisss100% (1)
- Valenzuela COT-DLL-Reliability Demo 2Document3 pagesValenzuela COT-DLL-Reliability Demo 2Ronald ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- A Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 8 Changes in MatterDocument4 pagesA Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 8 Changes in MatterbayangatkizzyNo ratings yet
- DLL Week 4Document5 pagesDLL Week 4Sarahlyn M. RoderosNo ratings yet
- Weekly Learning Plan 3 Grade 8 3-4 ScienceDocument11 pagesWeekly Learning Plan 3 Grade 8 3-4 ScienceBing Sepe CulajaoNo ratings yet
- Q3 Science 8 Module 4Document21 pagesQ3 Science 8 Module 4Aiza Dagandan BangaNo ratings yet
- GRADE 8, LESSON PLAN 4 - Phases of MatterDocument6 pagesGRADE 8, LESSON PLAN 4 - Phases of MatterAngelli AdlaoNo ratings yet
- Science 8 DLPDocument2 pagesScience 8 DLPmaricel fernandezNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 5 - Q1 - W3Document6 pagesDLL - Science 5 - Q1 - W3Jaypee SembilloNo ratings yet
- LP Phase Changes MendozaDocument9 pagesLP Phase Changes MendozaRommelyn RosasNo ratings yet
- Delp-Science 3-Q1-W5Document3 pagesDelp-Science 3-Q1-W5Gom BearNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 5 - Q1 - W3Document6 pagesDLL - Science 5 - Q1 - W3Reinfredo Petronio CanlasNo ratings yet
- G8 Week 3Document6 pagesG8 Week 3PRIMELYN WAGASNo ratings yet
- Multigradelessonplanwps OfficeDocument4 pagesMultigradelessonplanwps OfficeRea Mae BarriosNo ratings yet
- DLL Science-5 Q1 W4Document7 pagesDLL Science-5 Q1 W4Joyce San PascualNo ratings yet
- COT 1 - Science 8 (Matter)Document4 pagesCOT 1 - Science 8 (Matter)joan marie Pelias100% (1)
- Module 3 - Eed SC 1Document11 pagesModule 3 - Eed SC 1Florelyn Joy In-uyayNo ratings yet
- What's The Matter, Mickey?Document33 pagesWhat's The Matter, Mickey?Leah agwayasNo ratings yet
- Lesson ExemplarDocument3 pagesLesson ExemplarMark Hernand Galapate0% (1)
- Lesson ExemplarDocument3 pagesLesson ExemplarMark Hernand GalapateNo ratings yet
- Dapa National High School Dapa, Surigao Del Norte Joan Marie C. Pelias Science 8 Grade 8 3 Quarter March 18, 2021 30 Mins I. ObjectivesDocument4 pagesDapa National High School Dapa, Surigao Del Norte Joan Marie C. Pelias Science 8 Grade 8 3 Quarter March 18, 2021 30 Mins I. Objectivesjoan marie PeliasNo ratings yet
- CDocument2 pagesCR-Yel Labrador BaguioNo ratings yet
- Q1, W3 Edit ApDocument22 pagesQ1, W3 Edit ApJe-Ann Descalsota RelotaNo ratings yet
- Melc Based DLL g5 q1 Week 3Document25 pagesMelc Based DLL g5 q1 Week 3Severino OliverosNo ratings yet
- Science 1Document2 pagesScience 1Abello BadayosNo ratings yet
- Q3 DLL Sci 8 W3Document6 pagesQ3 DLL Sci 8 W3Justin Abad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2 Module 1 AnswersDocument6 pagesGen Chem 2 Module 1 AnswersSharmaine Joyce RegioNo ratings yet
- Novaliches High SchoolDocument7 pagesNovaliches High SchoolRonald ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- LeaP-Science-G8-Week 4-Q3Document4 pagesLeaP-Science-G8-Week 4-Q3Richard ViseyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.matter and Its Properties.1Document48 pagesLesson 1.matter and Its Properties.1gjhesraelNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 8 - Q3Document18 pagesDLL - Science 8 - Q3Nazer M. LacaboNo ratings yet
- Week 2 DLL Physical-ScienceDocument4 pagesWeek 2 DLL Physical-ScienceLoren Marie LemanaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1: Physical PropertiesDocument3 pagesChemistry 1: Physical Propertieskeith herreraNo ratings yet
- (FIRST QUARTER) Describe Changes in The Materials When Cooled.Document4 pages(FIRST QUARTER) Describe Changes in The Materials When Cooled.ropNo ratings yet
- Anna Sheryl F. Dimacali-Le-Science-5-Q1-Wk-3-5Document6 pagesAnna Sheryl F. Dimacali-Le-Science-5-Q1-Wk-3-5Anna Sheryl DimacaliNo ratings yet
- Dalton Particle Nature of Matter Group 1Document8 pagesDalton Particle Nature of Matter Group 1Mary Angelie Lobiano GreciaNo ratings yet
- Unit Overview Content Area: Science Grade Level: 1 GradeDocument6 pagesUnit Overview Content Area: Science Grade Level: 1 Gradeapi-531300559No ratings yet
- Abby 7asDocument4 pagesAbby 7asAbegail CalijanNo ratings yet
- L.P For ApplicationDocument12 pagesL.P For ApplicationRommelyn RosasNo ratings yet
- Changing & Separating Materials: Scheme of Work For Science TopicDocument8 pagesChanging & Separating Materials: Scheme of Work For Science Topiccarrie929ukNo ratings yet
- Sample Lesson Plan in Science V Using Explicit InstructionDocument6 pagesSample Lesson Plan in Science V Using Explicit InstructionKrimson Mike DolorzoNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 5 - Q1 - W4Document6 pagesDLL - Science 5 - Q1 - W4MELDRID OLISNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 5 - Q1 - W4Document7 pagesDLL - Science 5 - Q1 - W4Dexter DollagaNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 8 Chemistry SyllabusDocument11 pagesICSE Class 8 Chemistry Syllabusjayasribag2No ratings yet
- Chemistry 10 - 12Document333 pagesChemistry 10 - 12Théé Néw SåmûNo ratings yet
- DLL g5 q1 Wk2 Sept 5-9Document28 pagesDLL g5 q1 Wk2 Sept 5-9dyanarra torresNo ratings yet
- Gen - Chem 1-Week 1 and 2Document13 pagesGen - Chem 1-Week 1 and 2Mishal NoroñaNo ratings yet
- Science 5 Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesScience 5 Lesson PlanHanna Rezqah P. YusophNo ratings yet
- DLP Physical ChangeDocument3 pagesDLP Physical ChangeArlene c.buisanNo ratings yet
- Science 5-Q4-SLM2Document14 pagesScience 5-Q4-SLM2Rosario FuertezNo ratings yet
- Properties of MatterDocument26 pagesProperties of MatterYanah Maristela PollescasNo ratings yet
- DLL Science-5 Q1 Sept-18-22Document6 pagesDLL Science-5 Q1 Sept-18-22Joyce San PascualNo ratings yet
- DLL Week 4 ScienceDocument9 pagesDLL Week 4 ScienceGladish AnsubanNo ratings yet
- Class Ix - ScienceDocument18 pagesClass Ix - SciencedusanepankajNo ratings yet
- 1GP - Chemistry NotesDocument12 pages1GP - Chemistry NoteseriannenabazengNo ratings yet
- (Taken From The) : Curriculum GuideDocument14 pages(Taken From The) : Curriculum GuideMERCEDITA S. TOJINONo ratings yet
- WLP - Q1 - W3 ScienceDocument9 pagesWLP - Q1 - W3 ScienceCiv Eiram RoqueNo ratings yet
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Lac Session Ibona and LongakitDocument1 pageLac Session Ibona and Longakitarlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Dll-Jan.30-Feb 3Document2 pagesDll-Jan.30-Feb 3arlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- What's in The BucketDocument21 pagesWhat's in The Bucketarlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Flores - WHLP - Aug 29-Sept 2Document2 pagesFlores - WHLP - Aug 29-Sept 2arlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Pretest2023 24Document4 pagesPretest2023 24arlene aliporo100% (1)
- 3rd PTC - Minutes of The Meeting - 8 BURGOSDocument2 pages3rd PTC - Minutes of The Meeting - 8 BURGOSarlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Flores - WHLP - Jan.30 - Feb 3Document1 pageFlores - WHLP - Jan.30 - Feb 3arlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- DLL Jan.23 27Document2 pagesDLL Jan.23 27arlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- 4th PTC MINUTES DEL PILARDocument2 pages4th PTC MINUTES DEL PILARarlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Unit3matter 171128220356Document56 pagesUnit3matter 171128220356arlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- DLL 1 Nov 2 4Document4 pagesDLL 1 Nov 2 4arlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Q3W1 Properties of MatterDocument13 pagesQ3W1 Properties of Matterarlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Flores WHLP Jan.23-27Document1 pageFlores WHLP Jan.23-27arlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- DLL Q3W1Document2 pagesDLL Q3W1arlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document1 pageActivity 1arlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- FLORES COT1 T I III For SY 2021 2022 FEBRUARY 17 2022Document2 pagesFLORES COT1 T I III For SY 2021 2022 FEBRUARY 17 2022arlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Pandemic in The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesCOVID-19 Pandemic in The Philippinesarlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- An Assessment of The Distance Education in Taguig CityDocument4 pagesAn Assessment of The Distance Education in Taguig Cityarlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Region Division School Name School Id: 8 Lapu-Lapu 2021 - 2022 AP8 Mr. E. OlinoDocument1 pageRegion Division School Name School Id: 8 Lapu-Lapu 2021 - 2022 AP8 Mr. E. Olinoarlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Smashed Phils. Narrative ReportDocument3 pagesSmashed Phils. Narrative Reportarlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Other Members of The Solar SystemDocument4 pagesOther Members of The Solar Systemarlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- q3 w1 LessonDocument29 pagesq3 w1 Lessonarlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- (S8Mt-Iiia-B-8) : A. Reviewing Previous Lesson or Presenting The New Lesson (Elicit)Document4 pages(S8Mt-Iiia-B-8) : A. Reviewing Previous Lesson or Presenting The New Lesson (Elicit)arlene aliporoNo ratings yet
- Shadow People - or Opening Up A Can of WormsDocument11 pagesShadow People - or Opening Up A Can of WormsMarija KomatiasmeniNo ratings yet
- Mechanics: Introduction ToDocument11 pagesMechanics: Introduction ToBC EimorNo ratings yet
- The Sacred Depths of Nature How Life Has Emerged and Evolved Second Edition Ursula Goodenough Full ChapterDocument67 pagesThe Sacred Depths of Nature How Life Has Emerged and Evolved Second Edition Ursula Goodenough Full Chaptermarta.scordato502100% (5)
- The Seven Stages of ConsciousnessDocument10 pagesThe Seven Stages of ConsciousnessSon of Rizq100% (1)
- Class 9 ChemistrhDocument22 pagesClass 9 ChemistrhVasu BararaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 Notes Physics PDFDocument5 pagesChapter 01 Notes Physics PDFOmer FarooqNo ratings yet
- Pär Lindahl - Energy Calibration of Neutrino Telescopes Using Ultra High Energy Tau NeutrinosDocument81 pagesPär Lindahl - Energy Calibration of Neutrino Telescopes Using Ultra High Energy Tau NeutrinosMremefNo ratings yet
- Cheops SPOKE Pt. 2 - Mission GuideDocument412 pagesCheops SPOKE Pt. 2 - Mission Guidetriple7incNo ratings yet
- RPT Chemistry F4 2020 - Updated 2Document26 pagesRPT Chemistry F4 2020 - Updated 2Zamri AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Specific Heat of MetalsDocument8 pagesSpecific Heat of MetalsRobert MarcoliniNo ratings yet
- Logical Connectors - LecturaDocument5 pagesLogical Connectors - LecturaAnonymous 8nzbjZNo ratings yet
- MechanicsDocument523 pagesMechanicsJuiced-IN it80% (10)
- Chemistry Contexts PreliminaryDocument377 pagesChemistry Contexts PreliminaryEshayz111100% (3)
- Reflections of The Trinity in NatureDocument8 pagesReflections of The Trinity in NatureEFGNo ratings yet
- 23 Feynman DiagramsDocument6 pages23 Feynman DiagramsSidharth VashishtNo ratings yet
- String TheoryDocument39 pagesString Theoryantarikshsaxena100% (2)
- Samar State University Midterm Exams in PhysicsDocument3 pagesSamar State University Midterm Exams in PhysicsDennis CosmodNo ratings yet
- 11 PhysicsDocument22 pages11 PhysicsRahul NaryaniNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry Gases NotesDocument4 pagesPhysical Chemistry Gases NotesMartin AlvinNo ratings yet
- AntimatterDocument79 pagesAntimattersunny meenuNo ratings yet
- If I Have A Frozen Water Bottle That Weighs 500 MG, How Much Will It Weigh If The Water Melts?Document7 pagesIf I Have A Frozen Water Bottle That Weighs 500 MG, How Much Will It Weigh If The Water Melts?Sonny MagdadaroNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure PDFDocument6 pagesAtomic Structure PDFMiaMiaNo ratings yet
- The Hidden Science of Sex  " Spiritual Transmutation of Vital ForceDocument163 pagesThe Hidden Science of Sex  " Spiritual Transmutation of Vital Forcearvindaditya1No ratings yet