Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ORAL REVALIDA - Placenta Abruptio
Uploaded by
Mary Loise VillegasOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ORAL REVALIDA - Placenta Abruptio
Uploaded by
Mary Loise VillegasCopyright:
Available Formats
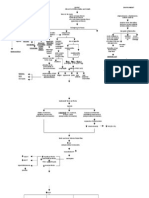
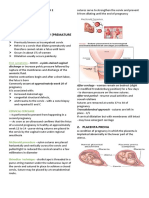
DEFINITION
ABRUPTIO PLACENTA the premature separation of the placenta from the
uterus, usually after 20 weeks gestation
PREDISPOSING FACTORS PRECIPITATING FACTORS
Age Thrombotic Hypertension Abdominal History of Premature
·Placental abruption occurs when there is a compromise
Disorders Trauma abruptio Tobacco use rupture of of the vascular structures supporting the placenta. In
placenta membranes other words, the vascular networks connecting the
Any pregnant can affect the uterine lining and the maternal side of the placenta are
woman larger clots development In such
collisions, the
torn away.
having a baby can lead to of the The risk of main effect of Pregnancies
over 35 complications placenta maternal body nicotine on
recurrence complicated
may also fold gestational TYPES
of abruptio by preterm
over the parameters is premature
causing the abdomen placentae is vasoconstriction
causing
nutrient and adding to the reportedly
rupture of partial - placenta does not completely detach from the
chronic of membranes
oxygen uterine wall.
Susceptible reduction in intra-abdominal 4-12%, uteroplacental
supply to the that are
for uteroplacental pressure rising to blood vessels,
baby to be managed
physiologic blood flow 25% in 2 expectantly
limited
complications consecutive are at
Together, leading to
these forces pregnancies areduced significant risk Total = completely removed from the uterine wall
generate blood flow to for abruptio
enough shear the placenta placentae
stress
between the ANATOMY
therefore decidual
placenta and subsequent neutrophil
uterusto reduction in
the delivery of infiltration
cause a female reproductive system
placental oxygen and
abruption nutrients to
fetus
uterus - where a fetus (unborn baby) develops and
grows
cervix - acts as the door to the uterus
vagina - provides a passageway for childbirth
Common Presenting Symptom:
vaginal bleeding, contractions,
abdominal tenderness, and decreased SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
fetal movement
Extended Disseminated Sharp
Fundal Fetal intravascular Hemorrhagic vaginal
distress shock stabbing
coagulation pain bleeding
Height
size of the Placental the tissue If the placenta pain on the happens
uterus may abruption factor begins to upper uterine after the
Diagnosis: be
disproportionate
occurs when
the placenta
thromboplastin
flows from a
detach during
pregnancy,
fundus as
initial
separation of
the placenta
PLACENTAL to the
gestational
partly or
completely
retroplacental
hematoma
there is
bleeding from
separation
occurs
separates these vessels
ABRUPTION age
from the inner
External
bleeding will
wall of the cause a bunch
The larger the
only occur if
resulting in a uterus before of clot in the
body area that the placenta
delivery.
higher fundal detaches, the separates
height greater the first from the
compared to This amount of edges
the candecrease bleeding
LABORATORY TEST DIAGNOSTIC TESTS gestational or block the
age baby's supply Internal
of oxygen and more difficult bleeding will
nutrients to control the occur if
bleeding placenta
pelvic Ultrasound fetal monitoring separates
Hemoglobin Fibrinogen
Kleihauer-Betke ultrasonography from the
Test Level Test
center
identify possible because
instruments are
evaluates a protein in to assess sources of blood would
produces used to
fetal blood in your red how wellthe vaginal bleeding
images that continuously pool under it.
the maternal blood cells protein called are used to record the
circulation that carries fibrinogen ? assess heartbeat of the
oxygen to also called organs and high-frequency fetus and the
your body's coagulation structures sound waves contractions of
organs and factor I ? within the create an image the woman's
tissues performs in female pelvis of your uterus uterus during
the blood and on a monito labor
to measure its
transports levels in your quick
carbon blood visualization
dioxide from
of the female
your organs
pelvic organs
and tissues
and structures
back to your
including the
lungs
uterus, cervix,
These tests are vagina,
performed to rule fallopian
A hemoglobin
out disseminated tubes and
testmeasures
intravascular ovaries
the amount of
hemoglobin in coagulation.
your blood sonographic
signs of
placental
A hemoglobin abruption
testmeasures include:
the amount of retroplacental
hemoglobin in hematoma,
your blood intraplacental
anechoic
areas,
separation
and rounding
of the
placental
edge
IF TREATED IF UNTREATED
Medical Management:
Nursing Management
endangers both the mother
and the baby
Medication Surgical
Independent Collaborative
OXYTOCIC Cesarean
HORMONES Section Radiologist
- Oxytocin a surgical procedure Administer fetal lung trained to interpret postpartum
used to deliver a maturation medication X-rays and other imaging hemorrhage Fetal Distress
CORTICOSTEROIDS baby through exams ? analyzes the
- betamethasone incisions in the images, looking for clues
- dexamethasone abdomen and uterus
S/S: S/S:
that may suggest if heart
Place the woman in a failure, fluid around the
when the
INTRAVENOUS severe baby isn't
Vaginal Delivery lateral position heart, pneumonia or Vaginal
Decreased
Uncontrolled Different fetal meconium
FLUID AND BLOOD vaginal receiving
application of forceps Swelling Anemia tachycardia blood Bradycardia
another condition bleeding bleeding after enough movement stain
PRODUCTS or a vacuum extractor pressure childbirth oxygen
to the fetal head to InO Monitoring through the
assist during the 2nd Obstetricians placenta
stage of labor performs the cesearan blood Postpartum
due to huge due to After the occurs when
section and vaginal pressure is hemorrhage
increase in excessive placenta is Placental a newborn
particularly isheavy Without this
delivery blood flow bleeding delivered, cause the abruption breathes a
low bleeding mother's vital support, there is
and fluid resultswhen contractions occurs mixture of
after the birth help blood the baby separates the problem with
loss of red meconium
Phsyician compress the pressure to cannot grow inner wall of the pattern of
blood cells the heart may and thrive and amniotic
diagnose the patient and exceeds bleeding drop the uterus fetal
fluid into the
struggle to vessels in the dangerously before movement
Good decide for the production of Losing lots of lungs around
deliver area where delivery
Prognosis appropriate medication new red blood enough blood quickly the time of
cells the placenta
or procedure oxygen-rich can cause a was attached
delivery.
blood to the severe can lead to
low birth This can
organs dropping
can lead to weight, decrease
your blood hemorrhagic orblock the typically
premature
pressure If the uterus shock baby's supply occurs when
In response, birth, and
does not of oxygen the fetus is
the body birth defects
contract stressed
might strongly
increase the
during labor
enough, these This can
heart rate to blood vessels
push more decrease
bleed freely orblock the
oxygenated and
blood to the baby's supply
hemorrhage of oxygen
organs occurs
Death
Poor
Prognosis
You might also like
- TAHBSO PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesTAHBSO Pathophysiologybregette50% (2)
- Abruptio PlacentaeDocument4 pagesAbruptio Placentaeeugeniamaranan.06No ratings yet
- PT LaborDocument32 pagesPT LaborAlthea MandalNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug BookDocument36 pagesName of Drug Bookh4bvyqg4npNo ratings yet
- Placenta Increta Concept MapDocument1 pagePlacenta Increta Concept MapEkay OrsolinoNo ratings yet
- Proplased Umbilical CordDocument2 pagesProplased Umbilical Cordkurlstein94% (17)
- Pathophysiology-Threatened MiscarriageDocument1 pagePathophysiology-Threatened MiscarriageMoses Gabriel ValledorNo ratings yet
- Prelim NCM 109 Lecture HandoutsDocument21 pagesPrelim NCM 109 Lecture HandoutsLillabin71% (7)
- Anomalies of The Placenta and CordDocument2 pagesAnomalies of The Placenta and CordLuiciaNo ratings yet
- Perlman 2019Document8 pagesPerlman 2019Huy Nguyễn QuốcNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaeDocument4 pagesAbruptio Placentaeeugeniamaranan.06No ratings yet
- Ijwh 218933 Retained Placenta After Vaginal Delivery Risk Factors and M 2Document8 pagesIjwh 218933 Retained Placenta After Vaginal Delivery Risk Factors and M 2terry mutiaNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics - Antepartum HemorrhageDocument4 pagesObstetrics - Antepartum HemorrhageJonathanNo ratings yet
- Ferlilisation, Implantation and Changes in PregnancyDocument7 pagesFerlilisation, Implantation and Changes in PregnancyLuke MatupiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Format 1Document3 pagesDrug Study Format 1Janeenne Fe Nicole SilvanoNo ratings yet
- Cayabyab, Natasha Alaine E. BSN Iv-E2Document5 pagesCayabyab, Natasha Alaine E. BSN Iv-E2Natasha Alaine E. CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Ruptura Prematura de Membranas: ObstetriciaDocument5 pagesRuptura Prematura de Membranas: ObstetriciaJimmy15No ratings yet
- Complications of Pregnancy 2Document4 pagesComplications of Pregnancy 2MENDIETA, JACQUELINE V.No ratings yet
- Circumvallate PlacentaDocument7 pagesCircumvallate PlacentaJonielyn LagunaNo ratings yet
- OB1 3.1 Normal Labor and Delivery IDocument6 pagesOB1 3.1 Normal Labor and Delivery IManjulaNo ratings yet
- 1st Trimester BleedingDocument67 pages1st Trimester BleedingRaiden VizcondeNo ratings yet
- Translate 2Document5 pagesTranslate 2nama singkatNo ratings yet
- Midwifery Pharmacologic Notes: Generic Name: OxytocinDocument1 pageMidwifery Pharmacologic Notes: Generic Name: OxytocinYsabelle De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Phatophysiology TentativeDocument3 pagesEctopic Phatophysiology TentativeAlexe Nicole BiscanteNo ratings yet
- DR Ward ClassDocument36 pagesDR Ward ClassChristy Mutia AlumbroNo ratings yet
- BreechDocument1 pageBreechZiyadNo ratings yet
- PATHODocument1 pagePATHOsteffiNo ratings yet
- Common Side Effects of Oxytocin Include:: CNS: Maternal: COMADocument3 pagesCommon Side Effects of Oxytocin Include:: CNS: Maternal: COMAann camposNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa: DefinitionDocument4 pagesPlacenta Previa: DefinitionCT Johara MusorNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Format OxytocinDocument1 pageDrug Study Format OxytocinKimberly GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Dug Study NCPDocument4 pagesDug Study NCPYamete KudasaiNo ratings yet
- MCHN Midterm ReviewerDocument24 pagesMCHN Midterm Reviewerpat delapenaNo ratings yet
- A Reflective JournalDocument4 pagesA Reflective JournallalaineNo ratings yet
- Types of Spontaneous AbortionDocument5 pagesTypes of Spontaneous AbortionAnnalisa TellesNo ratings yet
- Acog Committee Opinion: Medically Indicated Late-Preterm and Early-Term DeliveriesDocument5 pagesAcog Committee Opinion: Medically Indicated Late-Preterm and Early-Term DeliveriesBianca CaterinalisendraNo ratings yet
- Examination of The Placenta - AAFPDocument22 pagesExamination of The Placenta - AAFPEi Ei MyoNo ratings yet
- Uterotonic (Ecbolic) : Uterine Actions Other Actions IndicationsDocument5 pagesUterotonic (Ecbolic) : Uterine Actions Other Actions IndicationsShienna Marie SalvioNo ratings yet
- Conditions Associated With Third Trimester BleedingDocument2 pagesConditions Associated With Third Trimester BleedingBlaise Anne InocNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1751721419302301 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S1751721419302301 MainLilik AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Problems With Power DraftDocument3 pagesNCM 109 Problems With Power DraftJP Porras AliNo ratings yet
- Multiple Gestation: Complications of Labor and Birth Problems With The PassengerDocument4 pagesMultiple Gestation: Complications of Labor and Birth Problems With The PassengerAmethystNo ratings yet
- MalpresentationDocument21 pagesMalpresentationFrench Pastolero-ManaloNo ratings yet
- Post-Partum Hge - @medicine - Way2Document6 pagesPost-Partum Hge - @medicine - Way2saeed hasan saeedNo ratings yet
- Beronio, Gracel Caye M. CMC Module 5 Definition of TermsDocument2 pagesBeronio, Gracel Caye M. CMC Module 5 Definition of TermsGracel Caye Maon BeronioNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Phatophysiology Tentative 2Document3 pagesEctopic Phatophysiology Tentative 2Alexe Nicole BiscanteNo ratings yet
- Prom Umbolical Hernia PathoDocument3 pagesProm Umbolical Hernia PathoJane Ann AlolodNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DinoprostoneDocument2 pagesDrug Study DinoprostoneMva AgueroNo ratings yet
- Incompetent CervixDocument1 pageIncompetent CervixGabbi KimNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa Et Percreta A Potentially Life-Threatening ConditionDocument2 pagesPlacenta Previa Et Percreta A Potentially Life-Threatening ConditionAhsan AuliyaNo ratings yet
- University of Saint Louis: Tuguegarao City, Cagayan 3500Document4 pagesUniversity of Saint Louis: Tuguegarao City, Cagayan 3500JM RomiasNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy DisordersDocument3 pagesPregnancy DisordersroseonabreezeNo ratings yet
- Incompetent NCPDocument1 pageIncompetent NCPMina RacadioNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Parturition PDFDocument17 pagesPhysiology of Parturition PDFNestley TiongsonNo ratings yet
- Placental AbnormalitiesDocument5 pagesPlacental AbnormalitiesNica Lopez FernandezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument20 pagesDrug StudyBella SingcoNo ratings yet
- Observations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itFrom EverandObservations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itNo ratings yet
- Observations on Abortion: An account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes, and the method of preventing itFrom EverandObservations on Abortion: An account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes, and the method of preventing itNo ratings yet
- Methods of CalculationDocument14 pagesMethods of CalculationMary Loise VillegasNo ratings yet
- KineticsDocument35 pagesKineticsMary Loise VillegasNo ratings yet
- Drug Standards and LegislationsDocument22 pagesDrug Standards and LegislationsMary Loise VillegasNo ratings yet
- ORAL REVALIDA - HyperbilirubinemiaDocument1 pageORAL REVALIDA - HyperbilirubinemiaMary Loise VillegasNo ratings yet
- Oral Revalida - H-MoleDocument1 pageOral Revalida - H-MoleMary Loise Villegas0% (1)
- Oral Revalida - GDMDocument1 pageOral Revalida - GDMMary Loise VillegasNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Assessment ProcedureDocument3 pagesAntenatal Assessment ProcedureSANCHAYEETANo ratings yet
- Spina Bifida: By: Eloisa Anne N. Recto & Ane Kyla M. WaminalDocument23 pagesSpina Bifida: By: Eloisa Anne N. Recto & Ane Kyla M. WaminalKrizia Ane SulongNo ratings yet
- EMBRYOLOGYDocument4 pagesEMBRYOLOGYbhagavan prasadNo ratings yet
- Post-Term PregnancyDocument21 pagesPost-Term PregnancyPoonam RanaNo ratings yet
- OBG Curriculum Part-IIDocument46 pagesOBG Curriculum Part-IIUsman MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding: BY: Dinabandhu Barad MSC Tutor Dept. of Child Health Nursing SNC, Soa, DtuDocument57 pagesBreastfeeding: BY: Dinabandhu Barad MSC Tutor Dept. of Child Health Nursing SNC, Soa, DtuAbdul Azis G. CamidNo ratings yet
- Liceo de Cagayan University: College of NursingDocument18 pagesLiceo de Cagayan University: College of NursingJulie Ann Obenza GaiteraNo ratings yet
- Infant Mortality Rate and Medical Care in Kaliro District, UgandaDocument9 pagesInfant Mortality Rate and Medical Care in Kaliro District, UgandaKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- Episiotomy: Dr. Fekadu R (MD) November, 2012/19Document11 pagesEpisiotomy: Dr. Fekadu R (MD) November, 2012/19tareNo ratings yet
- Neet Ug Absolute Biology Vol 2Document22 pagesNeet Ug Absolute Biology Vol 2Rakesh Agarwal0% (1)
- Placenta Previa: View Media GalleryDocument7 pagesPlacenta Previa: View Media GalleryMargaret AssilasNo ratings yet
- Fernandez Fetal Malposition 3Document2 pagesFernandez Fetal Malposition 3Mark FernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Human Sexual Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesChapter 16 - Human Sexual Reproductive SystemChaw Wei HengNo ratings yet
- TOLACDocument10 pagesTOLACmariaNo ratings yet
- Breast Changes During Pregnancy: Areola Enlarged, Nipple More SensitiveDocument2 pagesBreast Changes During Pregnancy: Areola Enlarged, Nipple More Sensitivenina nikmahNo ratings yet
- Final Doula Brochure For EmailDocument2 pagesFinal Doula Brochure For Emailapi-279027417No ratings yet
- Nursing Intervention FixDocument12 pagesNursing Intervention FixPutri AzizahNo ratings yet
- Research PDFDocument4 pagesResearch PDFPheony LaniogNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument12 pagesNotesRosemarie R. ReyesNo ratings yet
- Threatened AbortionDocument1 pageThreatened AbortionKEn PilapilNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Health Questions With AnswersDocument3 pagesReproductive Health Questions With AnswersPrajwal d100% (1)
- Clomifene Citrate (Ikaclomin)Document9 pagesClomifene Citrate (Ikaclomin)asdwasdNo ratings yet
- Tazneen Hossain Tani - Applied Ethics - Quiz 2Document3 pagesTazneen Hossain Tani - Applied Ethics - Quiz 2Tazneen Hossain TaniNo ratings yet
- DC 2019-0436 Moratorium For The Implementation of Selected Sections of AO 2019-0026 - National Policy in The Provision of Birthing Assistance To Primigravid and Grand Multigravid Women PDFDocument2 pagesDC 2019-0436 Moratorium For The Implementation of Selected Sections of AO 2019-0026 - National Policy in The Provision of Birthing Assistance To Primigravid and Grand Multigravid Women PDFJess Maglunob100% (1)
- Vaginal Birth After Caesarean Section: What Are The Benefits and Risks of VBAC?Document2 pagesVaginal Birth After Caesarean Section: What Are The Benefits and Risks of VBAC?Riska PermatasariNo ratings yet
- Employees' State Insurance Corporation: Strike Out If Not ApplicableDocument1 pageEmployees' State Insurance Corporation: Strike Out If Not Applicablenasir ahmedNo ratings yet
- Leave Policy-2022Document9 pagesLeave Policy-2022shivaNo ratings yet
- Contemporary WorldDocument3 pagesContemporary WorldAlyssa BihagNo ratings yet
- Pedia Case File PDFDocument25 pagesPedia Case File PDFSanskriti SinghNo ratings yet
- T.A of Family Medicine: Contraception by Dr. Fatma OsamaDocument15 pagesT.A of Family Medicine: Contraception by Dr. Fatma OsamaAbdulla1999 AshrafNo ratings yet