Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TUTORIAL CELLULAR RESPIRATION BIO150
Uploaded by
iffahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TUTORIAL CELLULAR RESPIRATION BIO150
Uploaded by
iffahCopyright:
Available Formats
TUTORIAL CELLULAR RESPIRATION BIO150
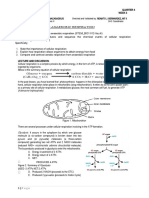
1. Which of the following stages in glycolysis yields a molecule ATP from ADP?
→
A. Glucose Glucose phosphate
→
B. Glucose phosphate Fructose phosphate
→
C. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate Glycerate 1,3-biphosphate
→
0
D. Glycerate 1,3-biphosphate Glycerate 3-phosphate
2. All the following describe the anaerobic respiration EXCEPT
A. Anaerobic respiration occurs in the absent of oxygen.
:
B. Anaerobic respiration takes place in the cytosol and mitochondria.
C. The total energy released is restricted to the two ATPs formed directly.
D. Only glycolysis occurs during anaerobiosis.
3. Which of the following statements is false?
A. Glycolysis can occur with or without oxygen.
B. Glycolysis occurs in the mitochondria.
C. Glycolysis is the first step in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
D. Glycolysis produces 2 ATP, 2 NADH and 2 pyruvates.
4. This process uses NADH and FADH2 to produce ATP.
a
A. Oxidative phosphorylation B. Fermentation
C. Glycolysis D. Krebs cycle
5. Which metabolic pathway is a common pathway to both anaerobic and aerobic metabolism?
A. The electron transport chain B. The Krebs cycle
C. The oxidation of pyruvic acid •
D. Glycolysis
6. Cyanide blocks the respiratory electron transport chain. As a result
-
A. The Krebs cycle speeds up.
0
B. Electrons and hydrogens cannot flow from NADH to oxygen.
C. Three ATPs are produced for every pair of electrons.
D. Production of water increases.
UiTM Cawangan Perlis
7. Why is ATP an important molecule in metabolism?
A. It is extremely stable.
0
C. Its phosphate bonds are easily formed and broken.
D. Its hydrolysis is undergoing.
8. During glycolysis, glucose is split into
:
A. 2 pyruvic acid molecules.
B. 4 pyruvic acid molecules.
C. 1 lactic acid plus 2 ethanol molecules.
D. 2 lactic acid plus 2 ethanol molecules.
9. How many carbon atoms are in an oxaloacetic acid molecule, which joins with an acetyl group
during Krebs cycle?
A. 3 B. 3 C. 2 D. 1
10. Which metabolic pathway is common to both fermentation and cellular respiration?
A. The Krebs cycle B. The electron transport chain
0
C. glycolysis D. synthesis of acetyl-CoA from pyruvate
11. Respiration ______________ and cellular respiration ________________.
A. produces glucose; is gas exchange 0B. is gas exchange; produces ATP
C. uses glucose; produces glucose D. produces ATP; is gas exchange
12. What term is used to describe a situation in which the energy released from one reaction
provides the energy required for another reaction?
:
A. Electron transport chain B. Energy coupling
C. Cellular respiration D. Energy conservation
13. During cellular respiration, the energy in glucose is
A. Carried by electrons.
B. Used to manufacture glucose by exergonic reactions.
C. Released all at once.
D. Transferred to starch.
UiTM Cawangan Perlis
14. Aerobic respiration produces more ATP for every unit of glucose when compared with
fermentation because
A. Fermentation produces lactic acid that poisons the cells.
B. Enzymes that are involves in aerobic respiration are more effective.
C. Aerobic respiration combines the energy from oxygen with the energy from
carbohydrates.
15.
0D. All the carbon can be oxidized to carbon dioxide during aerobic respiration.
The process that changes pyruvic acid to lactic acid during anaerobic respiration in the muscle
cell is
0A. reduction. B. oxidation.
C. phosphorylation. D. decarboxylation
16. During aerobic respiration, the last step that takes places in the electron transport chain is
①
A. reduction of O2 to produce water. B. carbon dioxide formation.
onomiosmoors
C. lactic acid production. D. ADP phosphorylation.
17. Among the following processes, which one does not happen during glycolysis?
A. Formation of NADH B. Formation of pyruvate
C. Building of ATP molecule O
D. Formation of acetyl-CoA
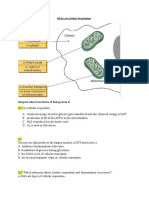
18. Where in the cell does the chemical process of glycolysis occur?
A. Ribosome
OB. Cytoplasm
C. Cell wall D. Chloroplast
19. In aerobic respiration, the final electron acceptor in the electron transport system is
-
A. NAD B. FAD
C. cytochrome
o
D. oxygen
20. Which process describes the formation of ATP using energy released by the electron transport
chain in respiration?
A. cyclic photophosphorylation B. non-cyclic photophosphorylation
0
C. oxidative phosphorylation D. substrate-level phosphorylation
21. Metabolism is best described as
A. making substances in cells.
B. the way in which a cell uses energy.
UiTM Cawangan Perlis
C. the way in which a cell obtains energy.
÷
D. all the chemical reactions taking place in cells.
22. Aerobic respiration produces more ATP compared to anaerobic respiration because
A. The enzymes involved in aerobic respiration are more efficient.
B. Lactic acid produced in animal cell or ethanol produced in plant cell reduces the enzyme
efficiency.
C. All the carbons in glucose are oxidized to carbon dioxide in aerobic respiration.
D. Aerobic respiration obtains energy from the mitochondria.
23. Which of the following statements about the electron transport chain are true?
I. ATP is synthesized by ATP synthase on the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.
II. FADH2 transfers its hydrogen atoms to the flavor-protein complex.
III. Cytochrome oxidize contains copper as its prosthetic group.
IV. Production of ATP in the electron transport chain is called oxidative phosphorylation.
A. I, II and III B. I, II and IV
C. I, III and IV D. II, III and IV
24. The energy given up by electrons as they move through the electron transport chain is used to
:
A. break down glucose. B. make NADH and FADH2.
C. pump H+ through the membrane. D. manufacture glucose.
25. NADH and FADH2 are the products of
A. decarboxylation reactions. B. reduction reactions.
C. glycolysis. D. formation of acetyl-CoA.
26. During chemiosmosis, ___________ are transferred from NADH and FADH2 to an acceptor-
molecules and the energy released is used to create a (an) ___________ gradient across the
-
inner mitochondrial membrane.
A. protons; electron o
B. electrons; proton
C. water molecules; oxygen D. ADP molecules; ATP molecule
27. Which of the following statements are the limitations of anaerobic respiration?
I. The constant accumulation of pyruvate can cause toxicity in the body.
II. ATP produced is not enough.
UiTM Cawangan Perlis
III. Oxygen supply is not sufficient.
IV. The conversion of pyruvate into ATP takes a long time.
:
A. I and II B. I and IV
C. II and III D. I, II and III
28. Which of the following statements differentiates between fermentation and cellular
respiration?
A. NADH is oxidized by the electron transport chain only in respiration.
B. Substrate-level phosphorylation is unique to fermentation.
C. Only respiration oxidizes glucose.
D. Only fermentation a catabolic pathway.
29. As a result of glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation and the citric acid cycle, only a small portion of the
energy of glucose has been converted to ATP. At this point, most of the usable energy is
contained in
:
A. reduced electron carriers NADH and FADH2.
B. acetyl coenzyme A.
C. pyruvate.
D. carbon dioxide.
30. During glycolysis, one glucose molecule is split into
A. two pyruvate molecules. B. two lactic acid molecules.
C. one lactic acid + one ethanol. D. two coenzyme A molecule
UiTM Cawangan Perlis
You might also like
- The Chlamydomonas Sourcebook: Organellar and Metabolic Processes: Volume 2From EverandThe Chlamydomonas Sourcebook: Organellar and Metabolic Processes: Volume 2No ratings yet
- 2 Semester Final Exam (2009A.Y.) Grade 11 Subject: Biology Time: 1:10 Mark: 40%Document5 pages2 Semester Final Exam (2009A.Y.) Grade 11 Subject: Biology Time: 1:10 Mark: 40%Nahom GarefoNo ratings yet
- Mana Barumsaa Bultii Addaa Waldaa Misooma OromiyaaDocument8 pagesMana Barumsaa Bultii Addaa Waldaa Misooma OromiyaaNafiyaf BerhanuNo ratings yet
- Proteins Cross Mitochondrial Membranes in Unfolded Form with Hsp70 ChaperonesDocument5 pagesProteins Cross Mitochondrial Membranes in Unfolded Form with Hsp70 ChaperonesAnandVatsNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Photosynthesis & Respiration Multiple ChoiceDocument11 pagesAP Bio Photosynthesis & Respiration Multiple ChoiceSamuel SiyumNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Review WorksheetDocument6 pagesCellular Respiration Review WorksheetTaniaBarrios-ChongNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 5 Review QuestionsDocument9 pagesBiology Unit 5 Review QuestionsMoa ArmyNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration Practice Quiz QuestionsDocument7 pagesAerobic Respiration Practice Quiz QuestionsNurhan Ulukan0% (1)
- Worksheet No.10 MargalloDocument11 pagesWorksheet No.10 Margalloaljon disabelleNo ratings yet
- SHS Biology Quarterly Assessment AnswersDocument6 pagesSHS Biology Quarterly Assessment AnswersDiane GuilaranNo ratings yet
- Biota Quiz Bee Mock Test Part 2Document2 pagesBiota Quiz Bee Mock Test Part 2Ken Juliana Fe IsaacNo ratings yet
- Biology 10Document8 pagesBiology 10BehruzNo ratings yet
- SUMMATIVE TEST-SCIENCE 9 (Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration)Document3 pagesSUMMATIVE TEST-SCIENCE 9 (Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration)lavenia acdal100% (1)
- Chapter 8 & 9 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Test: Multiple ChoiceDocument4 pagesChapter 8 & 9 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Test: Multiple ChoiceAmberlie MaiNo ratings yet
- AP M10 Ch9 Respiration Worksheet2Document5 pagesAP M10 Ch9 Respiration Worksheet2Jakie Ubina0% (1)
- EncencodedeYoCyzmXzEHxIy3txlZKh8LHIuBRdGyhmLH8 Ter1yuhmUdOrLZL39b VioDocument9 pagesEncencodedeYoCyzmXzEHxIy3txlZKh8LHIuBRdGyhmLH8 Ter1yuhmUdOrLZL39b VioLady Jane BenignoNo ratings yet
- A. Fill The Blank Bracket With The Right Answer. No 1 Is An ExampleDocument5 pagesA. Fill The Blank Bracket With The Right Answer. No 1 Is An ExampleKrizthya Diaz HermawanNo ratings yet
- Essentials of The Living World 4th Edition Johnson Test Bank DownloadDocument17 pagesEssentials of The Living World 4th Edition Johnson Test Bank DownloadKathleen Salinas100% (21)
- Biology Practice PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesBiology Practice Photosynthesisbrowhocares121212No ratings yet
- Fermentation vs Aerobic RespirationDocument9 pagesFermentation vs Aerobic RespirationJoshua Ng BundokNo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument6 pagesGeneral BiologyErwin AllijohNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Review KEY GuideDocument3 pagesCellular Respiration Review KEY GuideerikabeltranNo ratings yet
- Nejib Bio Item gr-11 ch-5 Sec. B, C,& I AssignmentDocument8 pagesNejib Bio Item gr-11 ch-5 Sec. B, C,& I AssignmentDaniel GtsadkanNo ratings yet
- Biology The Unity and Diversity of Life 15Th Edition Starr Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument35 pagesBiology The Unity and Diversity of Life 15Th Edition Starr Test Bank Full Chapter PDFBeckySmithnxro100% (9)
- Biology How Life Works 2nd Edition Morris Test BankDocument51 pagesBiology How Life Works 2nd Edition Morris Test BankRichard RunnelsNo ratings yet
- Biology The Unity and Diversity of Life 15th Edition Starr Test BankDocument38 pagesBiology The Unity and Diversity of Life 15th Edition Starr Test Bankapodaawlwortn3ae100% (7)
- Worksheet Respiration in PlantsDocument1 pageWorksheet Respiration in PlantsAakif RazaNo ratings yet
- MDCAT 2022 Biology Bioenergetics MCQsDocument36 pagesMDCAT 2022 Biology Bioenergetics MCQsSalman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration (Quizziz)Document5 pagesCellular Respiration (Quizziz)mariaNo ratings yet
- 1.0.0.a - Pre-Test - Breathing On Mars - SWebsterDocument6 pages1.0.0.a - Pre-Test - Breathing On Mars - SWebsterJessa Lynn E. AcalaNo ratings yet
- CRespiration and Photosynthesis Review KeyDocument5 pagesCRespiration and Photosynthesis Review Keyvictoire BadoNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism ActivityDocument2 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism ActivityIbuki TechNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Gen BioDocument50 pagesReviewer Gen Biorcmc ubasanNo ratings yet
- Phospholipid SynthesisDocument74 pagesPhospholipid Synthesischemistry tutorialNo ratings yet
- CBTA FOCUS AREA REVISION QUESTIONS ON RESPIRATIONDocument3 pagesCBTA FOCUS AREA REVISION QUESTIONS ON RESPIRATIONMolly KuttyNo ratings yet
- Summative Test #2 Gen BioDocument2 pagesSummative Test #2 Gen BioKennedy Fieldad Vagay100% (1)
- Glycolysis Krebscycle Practice Questions SCDocument2 pagesGlycolysis Krebscycle Practice Questions SCapi-323720899No ratings yet
- Abune Gorgorios Schools: 2012ec Second Semester Worksheet - 3 For Grade 11Document3 pagesAbune Gorgorios Schools: 2012ec Second Semester Worksheet - 3 For Grade 11Nardos AlemayewNo ratings yet
- MCQ S On Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesMCQ S On Cellular RespirationSAVORY SITHNo ratings yet
- Problem Set BS20001 PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesProblem Set BS20001 PhotosynthesisAbhinaba SahaNo ratings yet
- Biology G 12 Unit 3 100 Questions and Answers For Entrance PreparationDocument9 pagesBiology G 12 Unit 3 100 Questions and Answers For Entrance PreparationSkat KatNo ratings yet
- Biology Olympiad Activity Book: Cellular RespirationDocument2 pagesBiology Olympiad Activity Book: Cellular RespirationMeirbekNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - 2nd Summative Test (Grade 9)Document5 pagesQuarter 1 - 2nd Summative Test (Grade 9)BryanJAbuloc100% (4)
- Bioenergetics McqsDocument15 pagesBioenergetics McqsRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Sample Test Questions 1Document16 pagesSample Test Questions 1api-242405009No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration GuideDocument8 pagesCellular Respiration GuideArmanai KhamzinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Study GuideDocument8 pagesChapter 8 Study Guideamyjordan1No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Multiple Choice Practice: CO H O O PDocument7 pagesChapter 10 Multiple Choice Practice: CO H O O PShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet
- (Respiration in Plants - II Best Revision NotesDocument80 pages(Respiration in Plants - II Best Revision Notesarchitmandloi30No ratings yet
- Biology Life On Earth With Physiology 11th Edition Audesirk Test BankDocument19 pagesBiology Life On Earth With Physiology 11th Edition Audesirk Test Bankloganwalkertcaenpjsid100% (30)
- AP Biology Outline - Chapter 7Document4 pagesAP Biology Outline - Chapter 7Omar LopezNo ratings yet
- Summative Test #4 Gen BioDocument1 pageSummative Test #4 Gen BioKennedy Fieldad VagayNo ratings yet
- Biology Life On Earth With Physiology 11Th Edition Audesirk Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument40 pagesBiology Life On Earth With Physiology 11Th Edition Audesirk Test Bank Full Chapter PDFodetteisoldedfe100% (12)
- Kedah Matriculation Biology Cell Respiration WorkshopDocument4 pagesKedah Matriculation Biology Cell Respiration WorkshopShuPingLockNo ratings yet
- Ch09 Test File-Pathways That Harvest Chemical EnergyDocument39 pagesCh09 Test File-Pathways That Harvest Chemical EnergyDollar'sCornerNo ratings yet
- Biology Life On Earth 11th Edition Audesirk Test BankDocument19 pagesBiology Life On Earth 11th Edition Audesirk Test Bankaureliacharmaine7pxw9100% (32)
- Biology Life On Earth 11Th Edition Audesirk Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument40 pagesBiology Life On Earth 11Th Edition Audesirk Test Bank Full Chapter PDFodetteisoldedfe100% (12)
- Bio Tutorial 7Document4 pagesBio Tutorial 7Viyasinei KumaramoneyNo ratings yet
- True or False: Figure 8-4Document3 pagesTrue or False: Figure 8-4crqin qinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Respiration: I. An Overview of Glucose OxidationDocument5 pagesChapter 6 - Respiration: I. An Overview of Glucose OxidationMaiQuyenNguyenNo ratings yet
- Neurochemical Cascade of ConcussionDocument16 pagesNeurochemical Cascade of ConcussionJoan Choi100% (1)
- Exam Experiences 5Document17 pagesExam Experiences 5rvlucianoNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate, Protein and Lipid InterrelationshipDocument13 pagesCarbohydrate, Protein and Lipid InterrelationshipJhet Ardian CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Train With PowerDocument29 pagesTrain With PowerFlorin JichiNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument19 pagesCellular RespirationJerome CarpioNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Exam 1 ReviewDocument37 pagesBiochemistry Exam 1 ReviewThomas B.100% (1)
- Solution Brahmastra-19-02-2023Document38 pagesSolution Brahmastra-19-02-2023Vaibhav Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Grade 11: General Biology IDocument38 pagesGrade 11: General Biology ITEOFILO GATDULANo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry ExamDocument8 pagesClinical Chemistry Examridwaan tukaleNo ratings yet
- Respiration 5.2.1Document11 pagesRespiration 5.2.1bexNo ratings yet
- Life Processes: Nutrition, Respiration, and MoreDocument20 pagesLife Processes: Nutrition, Respiration, and MoreAARTI1012100% (1)
- Biology of The Cell Assignment - Answer KeyDocument2 pagesBiology of The Cell Assignment - Answer KeyBen-ZionWeltschNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: An Overview and the ProcessDocument28 pagesCellular Respiration: An Overview and the ProcessEvans Junior T. MuvutiNo ratings yet
- Role of OxygenDocument14 pagesRole of OxygenrainrulletNo ratings yet
- Yeast On The Rise: Investigative Study of Fermentation in The Introductory Biology CurriculumDocument17 pagesYeast On The Rise: Investigative Study of Fermentation in The Introductory Biology CurriculumMohideen JasminNo ratings yet
- Production and Characterization of Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) From Burkholderia Cepacia ATCC 17759 Grown On Renewable Feed StocksDocument154 pagesProduction and Characterization of Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) From Burkholderia Cepacia ATCC 17759 Grown On Renewable Feed StocksIftikhar AliNo ratings yet
- 14.respiration New BioHackDocument8 pages14.respiration New BioHackAnush KhillareNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Respiration and FermentationDocument18 pagesAnaerobic Respiration and FermentationSean Nixter BallestraNo ratings yet
- Atp Synthesis by Cellular Respiration AT P: Caroline SueperDocument9 pagesAtp Synthesis by Cellular Respiration AT P: Caroline SueperCaroline SueperNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 7 Respiration in PlantsDocument6 pagesChapter - 7 Respiration in Plantsben martinNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Lab ResultsDocument13 pagesCellular Respiration Lab ResultsAlyona Booth100% (1)
- Health Optimizing PEDocument3 pagesHealth Optimizing PEJuan Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 14 Respiration in Plants-NotesDocument4 pages14 Respiration in Plants-NotesAnanth DharanidharanNo ratings yet
- Wardlaws Perspectives in Nutrition A Functional Approach 1st Edition Byrd Bredbenner Test BankDocument38 pagesWardlaws Perspectives in Nutrition A Functional Approach 1st Edition Byrd Bredbenner Test Bankedricduyenuc1uw100% (24)
- Genomic Inference of The Metabolism and Evolution of The Archaeal Phylum AigarchaeotaDocument11 pagesGenomic Inference of The Metabolism and Evolution of The Archaeal Phylum Aigarchaeotamaria pamelaNo ratings yet
- Your Body's Metabolism ExplainedDocument36 pagesYour Body's Metabolism ExplainedJerilee SoCute Watts100% (1)
- RESPIRATION: THE BREAKDOWN OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS FOR ENERGYDocument4 pagesRESPIRATION: THE BREAKDOWN OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS FOR ENERGYAlfiya ShereefNo ratings yet
- Yumpu PDF DownloaderDocument14 pagesYumpu PDF DownloaderPoc Vezem0% (1)
- DLL Science 9 JulyDocument10 pagesDLL Science 9 JulyMark Kiven MartinezNo ratings yet
- Experiment #4 - Enzymatic Reduction of Methyl AcetoacetateDocument5 pagesExperiment #4 - Enzymatic Reduction of Methyl AcetoacetateJasmin CeciliaNo ratings yet