Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Jeremiah MoussaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Jeremiah MoussaCopyright:
Available Formats
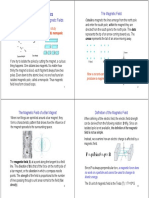
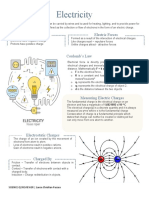
Lorentz Force F=qvB
m1 m2 F=ILB
Fg=G
r2 Cathode ray tube A
Recognition that there is a vacuum tube in which a
linear relationship between hot cathode emits a beam
field strength and inverse of electrons that pass
square of distance (i.e. through a high voltage
anode and are focused or
deflected before hitting a
) fluorescent screen.
The Inverse square law. The
Implication is that as r Solenoid A coil of wire
increases Fg will decrease that acts as an
dramatically. electromagnet when
electric current is passed
Earth mass=5.98 ×1024 through it due to the
Earth R=6.37 ×10 6 magnetic field that is set
up by the current passing
V through it. Solenoids are
F=qE W =qV V =Ed∨E=
d often used to control the
motion of metal objects,
W¿ qEd after Finding E which isV m−1 such as the switch of a
relay.
ma=qE
Magnetic field A
q1q2 magnetic field is a region
F=k 2
k =9.0 ×10 9 N m2 C−2 influenced by a magnet or
r something with the
properties of a magnet.
Magnetic Fields will
experience a force when
it’s perpendicular.
For Electrons It must be
Potenial Eg=mg ∆ h parallel for work to be
1 2 done.
Kinetic Energy , E K = mv
2
Gravitational fields are
Gravitational field the region around an
object where other objects will experience a
monopoles, attractive and
gravitational force. extends to an infinite
Electric field A region of space where
charged objects experience a force due to the
distance.
field created by another charged object. Electrical Fields are
monopoles and dipoles are
Geostationary satellite. attractive and repulsive
Satellite that remains in orbit and can be constrained to
above the same place on the a fixed distance.
Earth’s surface. It has the Magnetic Fields are
same period as the Earth’s dipoles, are attractive and
rotation, i.e. 24 hours. Only repulsive and can be
occurs at an altitude of 36 000 constrained to a fix
km above the Earth. distance.
A Satellite is an object in
Kelpler’s laws. 1. The plants a stable orbit around
move in elliptical orbits with another object.
the sun at one focus.
Fn=Fnet −Fg
2. The line connecting a Apparent weight. The
planet to the sun sweeps out weight felt by a person
equal areas in equal intervals when their body is
of time. stationary or in motion.
r3 Sometimes it is higher or
3. 2 lower than their usual
T weight. Equivalent to the
size of the normal reaction
distance 2 πr force acting on the person.
v= =
time T
2 2
Recognition that the
v 4 π r GM gradient of the line is a
a= = 2 = 2 =g
r T r function of the object
mass which is multiplied
Centripetal acceleration by the universal
Acceleration directed towards gravitational constant.
the centre of a circle when an Gradient=Gm
object moves with constant
speed in a circular path. Explain why the
magnitude of the
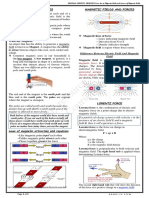
τ =r ⊥ F F=nILB magnetic field at point p?
At P the magnetic field
1 mv from the top magnet will
m v 2=qV r=
2 qB be to the left and the
magnetic field from the
Particle accelerator A bottom magnet will be to
machine that can accelerate a the right. They will be
charged particle (proton,
Explain why it must be in an orbit above the equal in magnitude, as P
electron) or an atomic nucleus
equator? Satellite orbits must lie in planes is equidistant from both
to very high speeds, including
speeds that approach the speed passing through Earth’s centre. If not above the magnets, but because
of light. equator, its orbit must alternate from N to S they are opposite in
hemispheres. direction, they will cancel
If The electrons emerge with each other out.
2 qV The purpose of the commutator is to reverse
no deflection. v=√ to What would be the length
m the current in the rotating coil every half
find speed. of a year if the earth and
rotation. This ensures that the torque (twisting
the sun is doubled?
the effect of the magnetic force) on the rotating
V V
qvB=q d=q coil is always in the same direction so that it
d d r3
keeps in the same direction. 2
=constant =¿ ¿
t
The mass of the electron is
−31
9.1 ×10 Kg
A space shuttle of mass 200 t
is in circular orbit around the Faraday’s Law states that
earth at a height of 200km.
Find the kinetic energy of the N so the EMF is
space shuttle the orbit. opposite in sign to the
GMm change in the magnetic
Formula Ek= flux.
2r
Between t = 2 s and t = 5 s
An induced emf , is produced the loop is entering the
by changing magnetic flux in magnetic field and the
process called electromagnetic flux through the loop is
induction. increasing so the change
in flux is positive and
Magnetic Flux is defined as hence the EMF will be
the product of the strength of negative. Between t = 7 s
the magnetic field, B, and the and t = 10 s the loop is
area of the field perpendicular leaving the magnetic field
to the field lines. and the flux through the
Φ=B⊥ A magnetic flux unit loop is decreasing so the
An AC alternator has slip rings that transfer the change in flux is negative
Wb weber or T m-2
alternating nature of the current in the coil to and hence the EMF will
the output. A DC generator has a split ring be positive.
The induced emf in straight
commutator to reverse the current direction
conductor moving in a
magnetic field B is given by every half turn so that the output current is DC motors have split
ϵ=lvB always in the same direction. rings. AC have slip rings.
The emf induced in Transformers will not
conducting loop in which work with DC voltage
there is a changing magnetic since it has a constant,
flux is proportional to the unchanging current that
negative rate of change in creates no change in
flux. magnetic flux.
△Φ B
ϵ=−N
△t
Lenz’s law states that an
induced emf always gives rise
to a current whose magnetic
field will oppose the original
change in flux.
There are 3 distinct steps to
determine the induced current
direction according to Lenz’s
law.
1. What is the change that is
happening?
2. What will oppose the
change and/or restore the
original conditions?
3. What must be the current
direction to match this
opposition?
A coil rotated in a magnetic
field will produce an
alternating induced current in
the coil. How that current is
harnessed will determine
Newton’s first law states
that every object continues
to be at rest, or continues
with constant velocity,
unless it experiences an
unbalanced force. This is
also called the law of
inertia.
Newton’s second law states
that the acceleration of a
body experiencing an
unbalanced force is directly
proportional to the net force
and inversely proportional
to the mass of the body:
Fnet = ma.
Newton’s third law states
that when one body exerts a
force on another body (an
action force), the second
body exerts an equal force
in the opposite direction on
the first (the reaction force):
A normal reaction force,
FN , acts between an object
and a surface, at right
angles to the surface.
On a horizontal surface, FN
= Fg and the object is
stationary.
On an inclined surface, FN
is equal and opposite to the
component of the weight
force acting perpendicular
to the plane:
FN = Fg cos θ. • The net
force acting on an object on
a plane inclined at an angle
θ is: Fnet = Fg sin θ when
friction is negligible.
You might also like
- Chapter 16 Magnetic Fields: Electricity and MagnetismDocument11 pagesChapter 16 Magnetic Fields: Electricity and MagnetismeltytanNo ratings yet
- ESD TR53 01 15 FinalDocument4 pagesESD TR53 01 15 FinalTrantan CdtNo ratings yet
- AKAsh GravitationDocument36 pagesAKAsh GravitationDaitya PurushNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Forces and Fields: (Chapter 12)Document48 pagesMagnetic Forces and Fields: (Chapter 12)Allan Gabriel LariosaNo ratings yet
- Course of Multiphase FlowDocument185 pagesCourse of Multiphase FlowArindam DeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 19 Moving Charges and MagnetismDocument31 pagesChapter - 19 Moving Charges and MagnetismNafees FarheenNo ratings yet
- Alt F4Document4 pagesAlt F4John Rhey ChavezNo ratings yet
- Magnetostatics and Magnetic Fields ExplainedDocument5 pagesMagnetostatics and Magnetic Fields ExplainedAwais YousafNo ratings yet
- DC Machines FundamentalsDocument4 pagesDC Machines FundamentalsBelly MenesesNo ratings yet
- Phy 107 Fall 06 Lect 14Document5 pagesPhy 107 Fall 06 Lect 14FerariNo ratings yet
- Magnetism: Magnetic Fingerprinting Allows Fingerprints To Be Seen On SurfacesDocument52 pagesMagnetism: Magnetic Fingerprinting Allows Fingerprints To Be Seen On SurfacesPRADITYO PUTRA PURNOMO ,No ratings yet
- BKM Classes - EMIDocument25 pagesBKM Classes - EMIdny001No ratings yet
- Fields: Gravitational & ElectricDocument32 pagesFields: Gravitational & Electricsaeed akhtarNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Magnetic ExplorationDocument17 pagesIntroduction to Magnetic ExplorationmaheshNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-1 SummaryDocument8 pagesCHAPTER-1 SummaryRaven John Yecyec RufinoNo ratings yet
- (Week 5) Magnetic CircuitsDocument54 pages(Week 5) Magnetic Circuitsfarhatul qistinaNo ratings yet
- Dc-Ac-Module-1-Reduced ReviewerDocument6 pagesDc-Ac-Module-1-Reduced ReviewerMR RecañaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Forces and Magnetic FieldsDocument12 pagesMagnetic Forces and Magnetic FieldsKristine Caye DyNo ratings yet
- Hall EffectDocument1 pageHall EffectCristian AlexisNo ratings yet
- Phys1006 HW9Document1 pagePhys1006 HW9DanNo ratings yet
- Moving Charges and MagnetismDocument27 pagesMoving Charges and MagnetismAkashNo ratings yet
- Electro Magnetism GuideDocument7 pagesElectro Magnetism GuideedugenetNo ratings yet
- 4TH GP (PERFORMANCE TASK #1) Summary of TopicDocument11 pages4TH GP (PERFORMANCE TASK #1) Summary of TopicMARY GLORY IGNACIONo ratings yet
- General Physics2 Lesson 3 PDFDocument2 pagesGeneral Physics2 Lesson 3 PDFJohn Renzo MolinarNo ratings yet
- Lecture11 SSP 2007Document5 pagesLecture11 SSP 2007Raza Ali RazaNo ratings yet
- Steady Magnetic FieldDocument166 pagesSteady Magnetic Fieldhamza alqadasiNo ratings yet
- Bab 6 Magnetic Fields in MatterDocument19 pagesBab 6 Magnetic Fields in MatterAfdal Wiranu PutraNo ratings yet
- Charged Particle Motion in Magnetic FieldsDocument10 pagesCharged Particle Motion in Magnetic FieldsRahul Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- Note 2002 Chapter21Document41 pagesNote 2002 Chapter21azureusNo ratings yet
- 9 - Electromagnetic Wave - Theory & Solved Exam.Document10 pages9 - Electromagnetic Wave - Theory & Solved Exam.Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Charges Interaction 4 Electric Charge 1 Conductors and Insulators 3Document84 pagesCharges Interaction 4 Electric Charge 1 Conductors and Insulators 3ani 9No ratings yet
- Magnetic Fields and Magnetic Forces: Properties of MagnetDocument54 pagesMagnetic Fields and Magnetic Forces: Properties of Magnetمارتن بولسNo ratings yet
- Ders 04 Mag Circuit PDFDocument10 pagesDers 04 Mag Circuit PDFBUĞRA UYĞURNo ratings yet
- Electric ChargeDocument3 pagesElectric ChargeAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- CH5 Magnetism and MatterDocument5 pagesCH5 Magnetism and MatterBabu JenaNo ratings yet
- Physics MainsDocument57 pagesPhysics MainsAdit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Mag & MatterDocument10 pagesMag & MatterRishabh DakshNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document60 pagesLecture 1Fakhry Al-DokomNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Fields and ForcesDocument23 pagesMagnetic Fields and ForcesqpncsorianoNo ratings yet
- Forces On Moving ChargesDocument14 pagesForces On Moving ChargesSimonNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL PRINCIPLES OF MAGNETISMDocument16 pagesELECTRICAL PRINCIPLES OF MAGNETISMIsrael MuliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Electromagnetic InductionDocument15 pagesChapter 17 Electromagnetic InductionKELLY NGU SHU YI MoeNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Forces, Materials, and DevicesDocument18 pagesMagnetic Forces, Materials, and DevicesJefry Pasaribu GoratNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Fields, Hall Effect and Electromagnetic InductionDocument12 pagesMagnetic Fields, Hall Effect and Electromagnetic Inductionwina ariffNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 2 - CH 19 Magnetic Fields and ForcesDocument21 pagesAP Physics 2 - CH 19 Magnetic Fields and ForcesBhagyaNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-+2 Physics FOCUS AREA Notes by NSSDocument29 pagesHsslive-+2 Physics FOCUS AREA Notes by NSSaryan.chithra2020No ratings yet
- EMI & AC 12thDocument5 pagesEMI & AC 12thTootsy DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction: Theory and Exercise BookletDocument62 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: Theory and Exercise Bookletabc9999999999No ratings yet
- 30035Document33 pages30035nandhakishore412No ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument12 pagesScience ReviewerLance Christian PascuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document7 pagesChapter 8Taylor JammiesonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Magnetism and Matter - WatermarkDocument23 pagesChapter 5 - Magnetism and Matter - WatermarkKABIR KALWANINo ratings yet
- Magnetism & Matter CH5Document24 pagesMagnetism & Matter CH5Rishab SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21Document30 pagesChapter 21tonyformedNo ratings yet
- 4 MagnetsDocument33 pages4 Magnetsdogclutch0% (1)
- Electromagnetic Force: F EubDocument18 pagesElectromagnetic Force: F Eubpoonam guptaNo ratings yet
- Mri 6Document39 pagesMri 6sarithaNo ratings yet
- EE340 Week1 Ch1 AhmedDocument62 pagesEE340 Week1 Ch1 AhmedMuhannad BedaiwiNo ratings yet
- Moving Charges MagnetismDocument5 pagesMoving Charges MagnetismPranshu PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 21 Electromagnetic InductionDocument21 pagesChapter - 21 Electromagnetic InductionNafees FarheenNo ratings yet
- All Units 2marks Em WavesDocument22 pagesAll Units 2marks Em Waves210801059No ratings yet
- Geophysical Field Theory and Method, Part B: Electromagnetic Fields IFrom EverandGeophysical Field Theory and Method, Part B: Electromagnetic Fields INo ratings yet
- InfiniSolar 10KW ManualDocument53 pagesInfiniSolar 10KW ManualZeeshan AhmadNo ratings yet
- NEO - NEET - 12 - P1 - PHY - E - Current Electricity - 09 - 211Document92 pagesNEO - NEET - 12 - P1 - PHY - E - Current Electricity - 09 - 211thenmozhishri13007No ratings yet
- QualifyingExamProblemSolutionsUnivOfILLionisNotesStatisticalMechanics PDFDocument216 pagesQualifyingExamProblemSolutionsUnivOfILLionisNotesStatisticalMechanics PDFHarikrishnan GurusamyNo ratings yet
- Building Form and Orientation For Sun and WindDocument3 pagesBuilding Form and Orientation For Sun and Windsusmita sethi0% (1)
- Study Guide for SLK POM/PCE TestDocument20 pagesStudy Guide for SLK POM/PCE TestAlex Trujillo GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Next Generation High Performance Walls: Construction GuideDocument52 pagesNext Generation High Performance Walls: Construction GuideРостислав ГатевNo ratings yet
- Harmonised Amateur Radio Exam GuideDocument40 pagesHarmonised Amateur Radio Exam GuideserepezNo ratings yet
- Soot Blower Wall Blower FormatDocument4 pagesSoot Blower Wall Blower FormatMoorthy NaveenNo ratings yet
- Invoice 1553736Document1 pageInvoice 1553736yashuNo ratings yet
- Function: Electrical, Electronics and Control Engineering at Operational LevelDocument3 pagesFunction: Electrical, Electronics and Control Engineering at Operational LevelRamesh BalasubramaniNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine ElementsDocument4 pagesDesign of Machine ElementsniteshNo ratings yet
- Copper CapabilitiesDocument9 pagesCopper CapabilitiesAliya SerikbolNo ratings yet
- FDN For Stationary Equipment-2013!11!07-KOINDocument1 pageFDN For Stationary Equipment-2013!11!07-KOINsinambeladavidNo ratings yet
- Buy Emerson 0.65-168 (KVA-VAH) Interactive UPS Online - GeMDocument4 pagesBuy Emerson 0.65-168 (KVA-VAH) Interactive UPS Online - GeMArun Chand C VNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Bioelectricity-1Document49 pagesLecture 1 - Bioelectricity-1bnvjNo ratings yet
- Switchgear & Protection: - in An Electric Power System, Switchgear Is The Combination of Electrical SwitchesDocument5 pagesSwitchgear & Protection: - in An Electric Power System, Switchgear Is The Combination of Electrical SwitchesSalim ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Checkpoints: Checkpoint 1 Checkpoint 2 Checkpoint 3 Checkpoint 4 Checkpoint 5 Checkpoint 6Document56 pagesCheckpoints: Checkpoint 1 Checkpoint 2 Checkpoint 3 Checkpoint 4 Checkpoint 5 Checkpoint 6CynthiaNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 NotesDocument68 pagesPhysics 1 NotesMikhael Glen Lataza100% (1)
- B10702Document7 pagesB10702mouad naciriNo ratings yet
- PHY3512 Tut7 SolutionsDocument4 pagesPHY3512 Tut7 SolutionsFeel-more HekandjoNo ratings yet
- FM Consultancy Utility Distribution SpecificationsDocument3 pagesFM Consultancy Utility Distribution SpecificationssppatilNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document4 pagesAssignment 3Lala's gamingNo ratings yet
- TM_Midea_V8 IDU_Wall Mounted_20230512_V4Document18 pagesTM_Midea_V8 IDU_Wall Mounted_20230512_V4rodrigobenitez754No ratings yet
- 1138029963Document350 pages1138029963huynh dungNo ratings yet
- DINAMIKA POPULASI BAKTERI DALAM PRODUKSI BIOMETANADocument7 pagesDINAMIKA POPULASI BAKTERI DALAM PRODUKSI BIOMETANAAkasha ChironNo ratings yet
- Wima MKS 4-4147Document13 pagesWima MKS 4-4147Anonymous vKD3FG6RkNo ratings yet
- 555 IC timer operation guideDocument5 pages555 IC timer operation guideGeet SehgalNo ratings yet
- Method of Statement For Hydrostatic Test: DocumentDocument3 pagesMethod of Statement For Hydrostatic Test: DocumentIlyas RunNo ratings yet