Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.3 Fertilisation and Seed Formation
Uploaded by
ELLEN KOH YEAN YE0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views9 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views9 pages2.3 Fertilisation and Seed Formation
Uploaded by
ELLEN KOH YEAN YECopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
At the end of this topic,
Students Will Be Able To
What are
fruits?
How are
seeds formed?
What happens
after pollination?
Describe the processes of
fertilisation and seed formation.
© 2020 Marshall Cavendish Education Pte Ltd
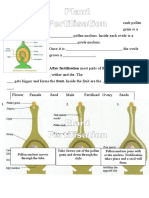
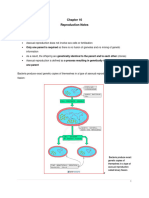
After Pollination,
1 The pollen grain contains
two cells – a tube cell and
a generative cell.
2 The tube cell starts
growing downwards to
form the pollen tube.
© 2020 Marshall Cavendish Education Pte Ltd
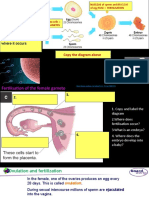
After Pollination, (cont’d)
3 The generative cell
divides to form two sperm
nuclei.
They travel through the
pollen tube to reach the
ovule.
© 2020 Marshall Cavendish Education Pte Ltd
After Pollination, (cont’d)
4 One of the sperm nuclei
fuses with the egg (ovum)
nucleus in the ovule to
form a zygote (fertilised
egg).
5 The other sperm nucleus
fuses with the central
nucleus, which will form
the endosperm (food
store for the seed).
© 2020 Marshall Cavendish Education Pte Ltd
Fertilisation
The fusion of a sperm with an egg to form
a zygote or fertilised egg is called
fertilisation.
• The nuclei of cells contain information
that is transferred from the parents to
their young during fertilisation.
• This is why young organisms share
many similar characteristics with their
parents.
© 2020 Marshall Cavendish Education Pte Ltd
Seed Formation
After fertilisation, the petals and other parts that help in pollination
wither and drop off. Seed formation begins.
The zygote develops into an
embryo. This embryo will eventually
develop into a young plant.
The endosperm starts to form.
It stores and provides food for the
developing embryo. Each ovule develops into a
seed, which carries the embryo
and the endosperm.
Seed
© 2020 Marshall Cavendish Education Pte Ltd
Fruits
The ovary develops into a fruit, which carries and protects the seeds.
The seeds are released when the fruit is ripe.
How a guava fruit develops
© 2020 Marshall Cavendish Education Pte Ltd
Fruits
• Fruits develop from the ovaries of flowers after fertilisation.
• They carry seeds inside them.
• They may or may not be edible, sweet or juicy.
Examples of fruits
Papaya Vanilla orchid Green bean
Oak Wheat Mango
© 2020 Marshall Cavendish Education Pte Ltd
© 2020 Marshall Cavendish Education Pte Ltd
You might also like
- Gardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3From EverandGardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3No ratings yet
- 6.3 Pollination and Fertilisation, 6.4 Development of Seeds and Fruits and 6.5 Importance of Seeds For SurvivalDocument56 pages6.3 Pollination and Fertilisation, 6.4 Development of Seeds and Fruits and 6.5 Importance of Seeds For Survivalwickedbiology101No ratings yet
- Why Some Seeds Don't Grow: 10 Principles for Educating Mentoring and Parenting Urban YouthFrom EverandWhy Some Seeds Don't Grow: 10 Principles for Educating Mentoring and Parenting Urban YouthNo ratings yet
- Nota & Latihan Biology KSSM Form 5 Bab 6.2 - WeAcademia (2021)Document1 pageNota & Latihan Biology KSSM Form 5 Bab 6.2 - WeAcademia (2021)Xinyee BongNo ratings yet
- Salak TerbangDocument12 pagesSalak TerbangChelsica ChelsicaNo ratings yet
- The Structure of FlowerDocument2 pagesThe Structure of Flowertaren17470No ratings yet
- Seed Germination Processes and RequirementsDocument7 pagesSeed Germination Processes and RequirementsKaye bagasinNo ratings yet
- Reproduction 3 - Flowering and Non-FloweringDocument27 pagesReproduction 3 - Flowering and Non-Floweringrenato.minaNo ratings yet
- Bio CH6 F5 StudywithadminDocument7 pagesBio CH6 F5 StudywithadminRathi MalarNo ratings yet
- Term II - Reproductive InvertebrateDocument2 pagesTerm II - Reproductive InvertebrateRolled SibuyiNo ratings yet
- Reproduction & Growth: 4.5 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument25 pagesReproduction & Growth: 4.5 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsZainurain Zainal AbidinNo ratings yet
- Salak TerbangDocument12 pagesSalak TerbangChelsica ChelsicaNo ratings yet
- S W B A T: at The End of This Topic, Tudents Ill e Ble oDocument8 pagesS W B A T: at The End of This Topic, Tudents Ill e Ble oELLEN KOH YEAN YENo ratings yet
- Science Lesson: With Teacher Aninda/Feny/Amal /lidaDocument9 pagesScience Lesson: With Teacher Aninda/Feny/Amal /lidaGIS Grade 5ANo ratings yet
- HOW ORGANISMS REPRODUCEDocument35 pagesHOW ORGANISMS REPRODUCECool VighneshNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantDocument10 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantdebbycleyNo ratings yet
- Biology Lesson 6 For Grade 7 Students TataDocument3 pagesBiology Lesson 6 For Grade 7 Students TataBirutawit YitbarekNo ratings yet
- Reproduction & Growth: 4.5 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument25 pagesReproduction & Growth: 4.5 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsSanthiya MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Q2 - ReproductionDocument79 pagesQ2 - ReproductionInkie VenturinaNo ratings yet
- To Know How Gametes Are Specialised Cells Adapted For A Particular Function To Know What Fertilisation Is and Where It OccursDocument10 pagesTo Know How Gametes Are Specialised Cells Adapted For A Particular Function To Know What Fertilisation Is and Where It OccursPedroDavid JoaquinFernandoNo ratings yet
- TOP Science Grade 5 Worksheets Chapter 1Document11 pagesTOP Science Grade 5 Worksheets Chapter 1agustina simorangkirNo ratings yet
- DICOT SEED EMBRYO DEVELOPMENTDocument3 pagesDICOT SEED EMBRYO DEVELOPMENTSamantha Jesi Shania EstradaNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction 2015Document46 pagesPlant Reproduction 2015Jodd Ardee TorresNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants FlowerDocument7 pagesChapter-2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants FlowerbpmbhamoraNo ratings yet
- 2 3 Yt How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument59 pages2 3 Yt How Do Organisms ReproduceCool VighneshNo ratings yet
- What Is Seed Propagation?Document10 pagesWhat Is Seed Propagation?Corre JaúNo ratings yet
- Complete 9A PDFDocument40 pagesComplete 9A PDFmillergra100% (1)
- Classroom Presentation Toolkit Flowering PlantsDocument16 pagesClassroom Presentation Toolkit Flowering PlantsXRKhaloodiNo ratings yet
- HSC Biology Module 5Document21 pagesHSC Biology Module 5adneeniqbal259No ratings yet
- Exp SC 04 - Chapter 09Document7 pagesExp SC 04 - Chapter 09megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Handout For Feb 19 23Document10 pagesReproduction Handout For Feb 19 23cykg4qkbtqNo ratings yet
- Ass 2022Document6 pagesAss 2022ajwfguyawNo ratings yet
- Clitoris Ovary Labia (Majora & Minora) Uterus Cervix Urethra Vagina Endometrium Fallopian Tube (Oviduct) BladderDocument5 pagesClitoris Ovary Labia (Majora & Minora) Uterus Cervix Urethra Vagina Endometrium Fallopian Tube (Oviduct) BladderQueng ElediaNo ratings yet
- Animal Cloning: Artificial Clones in Animals, and A Comparison of Reproductive and Non-Reproductive CloningDocument2 pagesAnimal Cloning: Artificial Clones in Animals, and A Comparison of Reproductive and Non-Reproductive CloningNicolas JayNo ratings yet
- Double Fertilization in PlantsDocument24 pagesDouble Fertilization in PlantsAshmit Srinjoy DuttaNo ratings yet
- Plant Fertilisation: After Fertilisation Most Parts of TheDocument2 pagesPlant Fertilisation: After Fertilisation Most Parts of TheIrram RanaNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of A Flowering PlantDocument5 pagesLife Cycle of A Flowering Plantapi-482274317No ratings yet
- 10.2 Double FertilisationDocument39 pages10.2 Double FertilisationKA YAN YAPNo ratings yet
- Pollen Germination On Stigma Through A Permanent SlideDocument1 pagePollen Germination On Stigma Through A Permanent SlideGolu YadavNo ratings yet
- Pollinators Vital for Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument29 pagesPollinators Vital for Reproduction in Flowering PlantsBHUPENDER KUMARNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction StudentDocument64 pagesPlant Reproduction StudentmrkoutsantanouNo ratings yet
- S W B A T: at The End of This Topic, Tudents Ill e Ble oDocument8 pagesS W B A T: at The End of This Topic, Tudents Ill e Ble oELLEN KOH YEAN YENo ratings yet
- Parts of The Seed: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesParts of The Seed: ObjectiveJoan Rayos PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Pollination-and-Fertilisation Task 3Document1 pagePollination-and-Fertilisation Task 3shyamalaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction and Embryonic Development in Plants and AnimalsDocument3 pagesReproduction and Embryonic Development in Plants and AnimalsJoy BoyNo ratings yet
- 117 - Fertilisation and Seed ProductionDocument4 pages117 - Fertilisation and Seed ProductionPeter TingNo ratings yet
- Fertilization and DispersalDocument23 pagesFertilization and DispersalangelsonuandaniNo ratings yet
- 16 Reproduction Notes Igcse BiologyDocument29 pages16 Reproduction Notes Igcse Biologyasmatullahmohammed2No ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System and Pregnancy ExplainedDocument2 pagesMale Reproductive System and Pregnancy ExplainedAmaya AliNo ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument1 pagePlant ReproductionManuel LopezNo ratings yet
- GR 9 CH 6 and 7 Question and AnswerDocument18 pagesGR 9 CH 6 and 7 Question and AnswerlegendarychampionthorNo ratings yet
- Activity 4Document10 pagesActivity 4Kalea Kassandra MatthewsNo ratings yet
- B10 - ReproductionDocument5 pagesB10 - Reproductionpiechloe597No ratings yet
- Class 8 Science: Reproduction in AnimalsDocument21 pagesClass 8 Science: Reproduction in AnimalsJ CNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction: Second Year ScienceDocument29 pagesPlant Reproduction: Second Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Double FertilizationDocument4 pagesDouble FertilizationHemanta JenaNo ratings yet
- Animal Reproduction and Development: Stages of Development: Instructor: Ma. Christine E. IbayDocument17 pagesAnimal Reproduction and Development: Stages of Development: Instructor: Ma. Christine E. IbayCruella MajoNo ratings yet
- Asexual Vs Sexual ReproductionDocument4 pagesAsexual Vs Sexual ReproductionKim MagtotoNo ratings yet
- Diversity in Living Organisms Notes For Class 10 Download in PDFDocument3 pagesDiversity in Living Organisms Notes For Class 10 Download in PDFgooodeNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 ReproductionDocument8 pagesCHAPTER 8 ReproductionBharat KumarNo ratings yet
- The Malaysian Education System and The Four PhilosophyDocument8 pagesThe Malaysian Education System and The Four PhilosophyELLEN KOH YEAN YENo ratings yet
- The Reforms of National Assessments in Malaysian Education SystemDocument19 pagesThe Reforms of National Assessments in Malaysian Education SystemELLEN KOH YEAN YENo ratings yet
- EJ1069288 The Actualization of The Malaysian National Education Philosophy inDocument12 pagesEJ1069288 The Actualization of The Malaysian National Education Philosophy inAbdul Ghaffar JaafarNo ratings yet
- Values Education and The Malaysia Education Blueprint: Abdul Rahman Bin MD AroffDocument15 pagesValues Education and The Malaysia Education Blueprint: Abdul Rahman Bin MD AroffNurul HudaNo ratings yet
- Fulfilling The Aspirations of Malaysian Education Blueprint 2013-2025 - Issues and ChallengesDocument5 pagesFulfilling The Aspirations of Malaysian Education Blueprint 2013-2025 - Issues and ChallengesELLEN KOH YEAN YENo ratings yet
- 140-Article Text-252-1-10-20211126Document9 pages140-Article Text-252-1-10-20211126ELLEN KOH YEAN YENo ratings yet
- Educational Development and Reformation in Malaysi PDFDocument15 pagesEducational Development and Reformation in Malaysi PDFMageeswaran ChandranNo ratings yet
- S W B A T: at The End of This Topic, Tudents Ill e Ble oDocument8 pagesS W B A T: at The End of This Topic, Tudents Ill e Ble oELLEN KOH YEAN YENo ratings yet
- 2.0 Chapter 2 TitleDocument4 pages2.0 Chapter 2 TitleELLEN KOH YEAN YENo ratings yet
- 1.3 Mineral Salts and Plant Growth - RemarksDocument3 pages1.3 Mineral Salts and Plant Growth - RemarksELLEN KOH YEAN YENo ratings yet
- StomataDocument1 pageStomataELLEN KOH YEAN YENo ratings yet
- Solar Cells Resemble PhotosynthesisDocument10 pagesSolar Cells Resemble PhotosynthesisELLEN KOH YEAN YENo ratings yet
- Science Ahead: An International Lower SecondaryDocument33 pagesScience Ahead: An International Lower SecondaryELLEN KOH YEAN YENo ratings yet
- Sexual IncompatibilityDocument3 pagesSexual IncompatibilitySanjoy NingthoujamNo ratings yet
- Flower Dictionary: Meanings and SymbolismDocument3 pagesFlower Dictionary: Meanings and SymbolismnmrasaNo ratings yet
- Test Reproduction Flowering Plants-AnswerDocument11 pagesTest Reproduction Flowering Plants-AnsweressunNo ratings yet
- Ethiopian Horticulture Producer Exporters Association (EHPEA) Member DirectoryDocument7 pagesEthiopian Horticulture Producer Exporters Association (EHPEA) Member DirectoryNahomaBek100% (1)
- Integrated Science 10-1-2 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument9 pagesIntegrated Science 10-1-2 Sexual Reproduction in Plantsfalesa matthewsNo ratings yet
- All About FlowersDocument43 pagesAll About FlowersjeffinjoffiNo ratings yet
- Archivo - Fedex - 20230317 (09 01 09)Document14 pagesArchivo - Fedex - 20230317 (09 01 09)Daniel MensiasNo ratings yet
- 2023 Wedding Engagement Decoration PricelistDocument9 pages2023 Wedding Engagement Decoration PricelistMonang Ridwan WibowoNo ratings yet
- Pollination Class 12 Biology ProjectDocument18 pagesPollination Class 12 Biology ProjectRajat Rawat0% (1)
- GR12 - Chapter 2 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument3 pagesGR12 - Chapter 2 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsNameNo ratings yet
- How flowers and pollinators coevolve to ensure reproductionDocument27 pagesHow flowers and pollinators coevolve to ensure reproductionAnny LovibNo ratings yet
- FLOWER ARRANGEMENT - Perez & PernitoDocument53 pagesFLOWER ARRANGEMENT - Perez & PernitoAlessandra Marigold Aguilar Perez100% (1)
- Insect PollinationDocument16 pagesInsect PollinationMecheri MeriemNo ratings yet
- Fenologi Pembungaan Dan Pembentukan Buah Uncaria Gambir Roxb Di Kenagarian Barung Barung Belantai Kecamatan Koto Xi Tarusan Kabupaten Pesisir SelatanDocument9 pagesFenologi Pembungaan Dan Pembentukan Buah Uncaria Gambir Roxb Di Kenagarian Barung Barung Belantai Kecamatan Koto Xi Tarusan Kabupaten Pesisir Selatanrahmi yunitaNo ratings yet
- Cross - Artificial Pollination On Hibiscus Rosa-: Sinensis LDocument9 pagesCross - Artificial Pollination On Hibiscus Rosa-: Sinensis LMariyam SorenNo ratings yet
- LA UNION CULTURAL INSTITUTE SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL FLOWER DISSECTION ACTIVITYDocument4 pagesLA UNION CULTURAL INSTITUTE SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL FLOWER DISSECTION ACTIVITYEvaMarieEsperaNo ratings yet
- RoseDocument9 pagesRoseAnujaSunnyNo ratings yet
- InflorescenceDocument2 pagesInflorescenceelcivilengNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument11 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsSahil GautamNo ratings yet
- Pollination and Fertilization: Key to Plant ReproductionDocument6 pagesPollination and Fertilization: Key to Plant Reproductionchristian capunongNo ratings yet
- Artificial Pollination and Fruit Quality in Red PitayaDocument7 pagesArtificial Pollination and Fruit Quality in Red PitayaMelvin MarinNo ratings yet
- Saint Mary's University: School of Health and Natural SciencesDocument7 pagesSaint Mary's University: School of Health and Natural SciencesEj AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- Spider Plant Reproduction MethodsDocument9 pagesSpider Plant Reproduction MethodsWorkout PrietoNo ratings yet
- GlossaryDocument3 pagesGlossaryankaa1080No ratings yet
- REVISION TEST - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - QPDocument5 pagesREVISION TEST - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - QPMohamed zidan khanNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument18 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsBħuvi ÀnthaRaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants Powerpoint SlidesDocument55 pagesReproduction in Plants Powerpoint SlidesTay Kai xin (Ahs)No ratings yet
- FLOWERING PLANTS CHAPTER 2-Converted-MergedDocument12 pagesFLOWERING PLANTS CHAPTER 2-Converted-MergedPAVITHRAN PadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jan 09, 2024Document12 pagesAdobe Scan Jan 09, 2024lthakurr124No ratings yet
- Pertemuan - 10 Rumus Dan Diagram BungaDocument7 pagesPertemuan - 10 Rumus Dan Diagram BungaHirmaa HirmaaNo ratings yet