Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Learning Outcomes:: Crust Mantle Outer Core Inner Core
Uploaded by
Klyde Elmarc F. GalantaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Learning Outcomes:: Crust Mantle Outer Core Inner Core
Uploaded by
Klyde Elmarc F. GalantaCopyright:
Available Formats
SOCIAL SCIENCES (GEOGRAPHY) GEOMORPHOLOGY
GRADE 10 TERM 2
UNIT 1: THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH - MEMO
LEARNING OUTCOMES:
• Internal Structure of the Earth
• Classification of Rocks
• The Rock Cycle
• Intrusive Igneous Activity and associated features
• Overview of landforms associated with different rocks
INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH
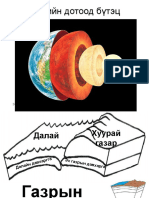
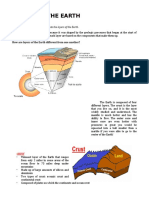
The Earth is made up of four layers.
The Crust Crust
• Outermost layer of the Earth. Mantle
• Comparatively thin layer – ranges from 8 km to Outer Core
40 km in thickness.
• Divided into two types: continental crust and Inner Core
oceanic crust.
• Boundary between the crust and the mantle
(next layer) is called the Mohorovicic
Discontinuity (Moho Discontinuity).
Continental Crust
• Consists mainly of Granite rocks. Figure 1: Layers of the Earth
• Thicker layer with low density.
• Granite rocks composed of silicon and aluminium.
• Called SIAL.
Continental Crust
• Mainly composed of basalt and is a thinner layer with a higher density.
• Rich in silicon and magnesium.
• Called SIMA.
The Mantle The Crust
• Next layer (beneath the crust). Material in the
• Thickness of about 2900 km. mantle heats up and
rises in the mantle, as
• Consists of molten rock (semi-fluid or semi-
a result of pressure.
melted material).
This material rises
• Temperatures may reach 500°C. toward the crust
where it cools and
The Core begins to heat again
• The core is in the centre of the Earth: consists of creating a convection
an outer core, that is liquid, and an inner core current within the
that is solid. mantle
• The combined radius of the core is about 3475km.
• The core’s temperature is above 2000° C. The Outer Core
• The core is made of Nickel and Iron.
© e-classroom 2015 www.e-classroom.co.za
1
SOCIAL SCIENCES (GEOGRAPHY) GEOMORPHOLOGY
GRADE 10 TERM 2
UNIT 1: THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH - MEMO
The layers can also be divided into different sections.
Namely,
Lithosphere: the rigid outer part of the Earth,
consisting of the crust and upper mantle.
Asthenosphere: the upper layer of the Earth’s mantle,
below the lithosphere, in which there is
relatively low resistance to plastic flow
http://goo.gl/IR0C5o
and convection is thought to occur.
Mesosphere: The mesosphere refers to the mantle in
the region under the lithosphere and the
asthenosphere, but above the outer core.
The upper boundary is defined as the
sharp increase in seismic wave velocities Figure 2: Layers of the Earth
and density at a depth of 660km.
ACTIVITY 1
For each of the igneous intrusions below; write a description of the intrusion and draw a sketch diagram
of what the intrusion would look like.
Intrusion Description of formation and identifying features Sketch Diagram
is a large emplacement of igneous intrusive (also Use images from the
Batholith called plutonic) rock that forms from cooled magma diagram given to learners.
deep in the Earth’s crust.
a mass of igneous rock formed from magma that did
not find its way to the surface but spread laterally into
Laccolith
a lenticular body, forcing overlying strata to bulge
upward.
a mass of igneous rock similar to a laccolith but
Lopolith
concave downward rather than upward.
a long, narrow, cross-cutting mass of igneous rock
Dyke
intruded into a fissure in older rock.
a tabular body of intrusive igneous rock, ordinarily
Sill between beds of sedimentary rocks or layers of
volcanic ejecta.
A large intrusion that often stands above the
Monolith
surrounding land as a towering wall of rock.
Pipe Central vents of volcanoes.
© e-classroom 2015 www.e-classroom.co.za
2
SOCIAL SCIENCES (GEOGRAPHY) GEOMORPHOLOGY
GRADE 10 TERM 2
UNIT 1: THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH - MEMO
SOME DEFINITIONS:
Strata Horizontal layers of sedimentary rock.
Magma Liquid rock inside the Earth.
Lava Liquid rock that flows on the Earth’s surface.
The process that breaks down large rock surfaces into smaller boulders,
Weathering
stones, pebbles and grains of sand.
The process whereby weathered material is carried away by wind, water or ice
Erosion
rubs away the surface of the Earth.
© e-classroom 2015 www.e-classroom.co.za
3
You might also like
- l3 Earth's Internal HeatDocument75 pagesl3 Earth's Internal HeatLearni J. EscoteNo ratings yet
- The Three Types of RocksDocument12 pagesThe Three Types of RocksClemencia Eduria MasibaNo ratings yet
- Layers of The Earth WorksheetDocument1 pageLayers of The Earth WorksheetCharmaine WrightNo ratings yet
- Q1 M1 PPT Layers of The EarthDocument97 pagesQ1 M1 PPT Layers of The EarthMarilyn LaquindanumNo ratings yet
- Layers of The EarthDocument42 pagesLayers of The EarthDrei BangateNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Module 1 - Plate TectonicsDocument4 pagesUnit 1 - Module 1 - Plate TectonicsJell De Veas Torregoza100% (2)
- Earths InteriorDocument64 pagesEarths InteriorBuuye ChNo ratings yet
- Slope StabilityDocument70 pagesSlope StabilitysaviodebritoNo ratings yet
- Properties of CarbonatesDocument35 pagesProperties of CarbonatesnftwoNo ratings yet
- The Layers of The EarthDocument34 pagesThe Layers of The Earthmyrrdane100% (1)
- Science Reviewer (Grade 10)Document3 pagesScience Reviewer (Grade 10)Dove Mendelieve100% (7)
- Gems&Gemology: Winter 1991Document81 pagesGems&Gemology: Winter 1991saopaulo100% (1)
- FavonaPaper2008 PDFDocument12 pagesFavonaPaper2008 PDF'Francisco GonzalezNo ratings yet
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN Earth and Life Sciences Grade 11 Week 4Document10 pagesDETAILED LESSON PLAN Earth and Life Sciences Grade 11 Week 4Austin Capal Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Geologist Cover LetterDocument2 pagesGeologist Cover LetterCosmin Ducea100% (2)
- MINING GEOLOGY Module 1 PDFDocument33 pagesMINING GEOLOGY Module 1 PDFKunal KishorNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Earth Structure Minerals and RocksDocument15 pagesLesson 1 Earth Structure Minerals and Rocksena.elznerNo ratings yet
- Geology-Notes 1PDocument43 pagesGeology-Notes 1Praul.rodriguezNo ratings yet
- G10 Geosphere - Sync DiscussionDocument206 pagesG10 Geosphere - Sync Discussionhatdog dakoNo ratings yet
- The Geosphere: Our Dynamic EarthDocument27 pagesThe Geosphere: Our Dynamic EarthShaila SegunderaNo ratings yet
- Science - q1l1 NotesDocument2 pagesScience - q1l1 NotesKine HenituseNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument12 pagesSCIENCEBellaaaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science NoteDocument4 pagesEarth Science NoteAbigail OconNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument14 pagesEarth ScienceROUENDANIELLE PLANDEZNo ratings yet
- Science 10 1st Grading Module 1Document27 pagesScience 10 1st Grading Module 1vinesseNo ratings yet
- Sci10 UNIT II Lesson 1Document26 pagesSci10 UNIT II Lesson 1Hezil Mae MancaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter1-Introductiontogeology PRTDocument72 pagesChapter1-Introductiontogeology PRTWan SyazwanNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Structure of The Earth and Its CompositionDocument20 pages1.2 Structure of The Earth and Its CompositionMa. Chatrina MalanogNo ratings yet
- Igneous Chap 1Document42 pagesIgneous Chap 1businessmira7No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Earth ScienceDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Earth ScienceHannah EstebarNo ratings yet
- Earth, Internal Structure of The Earth and Deformation of The CrustDocument59 pagesEarth, Internal Structure of The Earth and Deformation of The CrustVJ MendozaNo ratings yet
- Physical Geography 2ndDocument21 pagesPhysical Geography 2ndAwais BakshyNo ratings yet
- Chapter1-Introductiontogeology PRTDocument84 pagesChapter1-Introductiontogeology PRTSky FireNo ratings yet
- CL 7 - SST (G)Document4 pagesCL 7 - SST (G)K BhaiNo ratings yet
- Layers of The EarthDocument3 pagesLayers of The EarthVenice MedranoNo ratings yet
- Layers of The EarthDocument17 pagesLayers of The EarthSandeep Kumar K RNo ratings yet
- Geomophology PDFDocument20 pagesGeomophology PDFJoel T MbulanjeNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument44 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsNeal Lorenzo CastilloNo ratings yet
- About The MantleDocument3 pagesAbout The MantleCj QueñanoNo ratings yet
- Composition of RocksDocument27 pagesComposition of RocksmunazirNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument2 pagesGeographyMaheenRazaQureshiNo ratings yet
- Science First GradingDocument26 pagesScience First GradingCara Loriz TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Geo100 1P Module 1 Reviewer PDFDocument11 pagesGeo100 1P Module 1 Reviewer PDFRaphael Ivan FernandezNo ratings yet
- Earth'S Layers Layers Based On Chemical Composition Mantle: Seismic TomographyDocument2 pagesEarth'S Layers Layers Based On Chemical Composition Mantle: Seismic TomographyDudrey Anne SalcedaNo ratings yet
- gr10t2 Ss Geo Unit1 The Structure of The EarthDocument6 pagesgr10t2 Ss Geo Unit1 The Structure of The EarthNeveNo ratings yet
- Chapt 2 MarshakDocument13 pagesChapt 2 Marshak周牮No ratings yet
- Chapter 1&2Document38 pagesChapter 1&2Solomon DesalegnNo ratings yet
- Earth StudyDocument28 pagesEarth Studyrewardfulgueras9No ratings yet
- Internal Structure of The EarthDocument7 pagesInternal Structure of The EarthMargarette MartinNo ratings yet
- ES Chapter 18Document69 pagesES Chapter 18Mark Sherwin MangarinNo ratings yet
- Geology Chapter 1 - 4Document95 pagesGeology Chapter 1 - 4Yoni RebumaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE M1 Week1Document8 pagesSCIENCE M1 Week1Vyrox MPNo ratings yet
- Earth's Internal LayersDocument3 pagesEarth's Internal LayersJoana Marie ArinzaNo ratings yet
- Basic Review of The EarthDocument42 pagesBasic Review of The Earthjohn02cena03No ratings yet
- Geo Notes S1Document78 pagesGeo Notes S1walaa yasserNo ratings yet
- Earth's StructureDocument12 pagesEarth's StructureMelissa MoralesNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Faults2ndDocument65 pagesEarthquake Faults2ndMAYETTE CHIONGNo ratings yet
- Layers of EarthDocument31 pagesLayers of EarthPrincess Raychel Delos AngelesNo ratings yet
- EASE Module 12 Inside The Solid EarthDocument42 pagesEASE Module 12 Inside The Solid EarthArianne Alano100% (1)
- Interior of The Earth ActivityDocument3 pagesInterior of The Earth ActivityRebecca WEINo ratings yet
- Earth Structure and SubsystemsDocument61 pagesEarth Structure and SubsystemsKuudan FusionNo ratings yet
- Celine Jamaica Q SciDocument5 pagesCeline Jamaica Q SciCygresy GomezNo ratings yet
- Layers of The Earth NotesDocument2 pagesLayers of The Earth NotesGirli JoseeNo ratings yet
- Interior of The EarthDocument12 pagesInterior of The Earthunwantedaccountno1No ratings yet
- Quiz Answer KeyDocument7 pagesQuiz Answer KeyMuhammad AtharNo ratings yet
- Appendix 2: Terms of Reference For Bawgata Lower Hydropower Project Feasibility StudyDocument16 pagesAppendix 2: Terms of Reference For Bawgata Lower Hydropower Project Feasibility StudyWalterHuNo ratings yet
- 12 Lassalle - AAPG 1995 - Aquitaine Basin - Evolution and Hydrocarbons PDFDocument23 pages12 Lassalle - AAPG 1995 - Aquitaine Basin - Evolution and Hydrocarbons PDFAlexandru BadescuNo ratings yet
- Degana - Balda TungstenDocument7 pagesDegana - Balda TungstenSubham MNo ratings yet
- Sed Structures Lab Str2Document21 pagesSed Structures Lab Str2oligoket238100% (3)
- Supergene Alteration of Ore Deposits: From Nature To Humans: Harald G. DillDocument6 pagesSupergene Alteration of Ore Deposits: From Nature To Humans: Harald G. DillAnggit Tri AtmajaNo ratings yet
- Ongc GT Answer Key 2014Document4 pagesOngc GT Answer Key 2014Vikash KumarNo ratings yet
- The Science of EarthquakesDocument11 pagesThe Science of EarthquakesRoy Isaac SilladorNo ratings yet
- Sulu BasinDocument12 pagesSulu Basinluke buetaNo ratings yet
- E 07-039Document23 pagesE 07-039Pawel OlejczykNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 Q1 Mod6 The Earths MechanismDocument27 pagesSCIENCE 10 Q1 Mod6 The Earths MechanismRizzel RustiaNo ratings yet
- 5 - 18b - Mineral ResourcesDocument90 pages5 - 18b - Mineral ResourcesDa Apollyon100% (4)
- Holy Smokes-Its A VolcanoDocument36 pagesHoly Smokes-Its A VolcanoJocker Miranda ColumnaNo ratings yet
- htzdVZNX3CXyP5MOehQR PDFDocument6 pageshtzdVZNX3CXyP5MOehQR PDFHarman Singh KalsiNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Low Resistivity Pay DeepwaDocument14 pagesEvaluation of Low Resistivity Pay DeepwaAbuobida MustafaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Notes Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 2 Physical Features of IndiaDocument5 pagesCBSE Notes Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 2 Physical Features of IndiaPraneeth ReddyNo ratings yet
- DRRR ReviewerDocument74 pagesDRRR ReviewerMA. HAZEL TEOLOGONo ratings yet
- Earth Science 2Document32 pagesEarth Science 2Roejhen BalmacedaNo ratings yet
- Online Rocks and Minerals 5th Grade Science NotesDocument1 pageOnline Rocks and Minerals 5th Grade Science NotesSuvashreePradhanNo ratings yet
- Work of Sea WavesDocument4 pagesWork of Sea Wavessajal anjaliNo ratings yet
- Appendix e Geology Terrain and Soils of The Refinery and RSF 2Document49 pagesAppendix e Geology Terrain and Soils of The Refinery and RSF 2Eng Abdikarim WalhadNo ratings yet
- Midterm Sample # 1 - GEO1111Document7 pagesMidterm Sample # 1 - GEO1111mhadd071No ratings yet
- Lecture 14 - Petroleum Geology - Sokari BraideDocument101 pagesLecture 14 - Petroleum Geology - Sokari BraideGiovanni AmansureNo ratings yet
- Heat Flow Robert HallDocument4 pagesHeat Flow Robert HallhilboyzNo ratings yet