Professional Documents
Culture Documents
10 Sci Lightreflectionandrefraction Tp01
Uploaded by
abhinav kumarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
10 Sci Lightreflectionandrefraction Tp01
Uploaded by
abhinav kumarCopyright:
Available Formats
myCBSEguide
Class 10 - Science
Light Reflection and Refraction Test 01
Question No. 1 to 5 are based on the given text. Read the text carefully and answer the questions:
While dealing with the reflection of light by spherical mirror set of sign convention is followed. In this convention, the pole (P)
of the mirror is taken as the origin. The object is placed to the left of the mirror. All distance measured to the right of the origin
is taken positively. Distance to the left is measured negative. All distance parallel to the principle is measured from the pole.
1. Linear magnification produced by a concave mirror may be
a. less than 1, more than 1 or equal to 1
b. more than 1 or equal to 1
c. less than 1 or equal to 1
d. less than 1 or more than 1
2. Magnification produced by a plane mirror
a. zero
b. equal to one
c. less than one
d. greater than one
3. If the magnification of -1 is to be obtained by using a converging mirror, then the object has to be placed
a. beyond the centre of curvature
b. at infinity
c. between pole and focus
d. at the centre of curvature
4. The ratio of the height of an image to the height of an object known as
a. magnification
b. none of these
c. refractive index
d. lateral displacement
To practice more questions & prepare well for exams, download myCBSEguide App. It provides complete study
material for CBSE, NCERT, JEE (main), NEET-UG and NDA exams. Teachers can use Examin8 App to create similar
papers with their own name and logo.
5. If the magnification has a plus sign then the image is ________ and ________.
a. real, erect
b. virtual, inverted
c. virtual, erect
Copyright © myCBSEguide.com. Mass distribution in any mode is strictly prohibited.
1/5
myCBSEguide
d. real, inverted
6. The image of a bright object is brought on a screen with the help of a concave mirror. If the upper half of the concave
mirror is covered, the effect on the image will be:
a. Its size becomes half
b. The image changes position
c. The image disappears
d. Brightness will be reduced
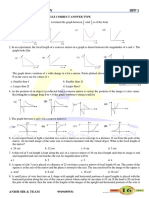
7. As light IM is incident on the surface PQ, as shown the emergent ray has to be:
a. ND
b. NC
c. NB
d. NA
8. A student obtains a blurred image of an object on a screen by using a concave mirror. In order to obtain a sharp image on
the screen, he will have to shift the mirror.
a. towards the screen
b. to a position very far away from the screen
c. depending upon the position of the object
d. away from the screen
9. Assertion (A): As light travels from one medium to another, the frequency of light does not change.
Reason (R): Because frequency is the characteristic of source.
a. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c. A is true but R is false.
d. A is false but R is true.
10. Assertion (A): A virtual image cannot be photographed.
Reason (R): Only real objects are photographed.
a. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c. A is true but R is false.
d. A is false but R is true.
11. State True or False:
i. The incident ray, the normal to the surface at the point of incidence and the reflected ray, all lie in the same plane.
a. True
b. False
ii. The absolute refractive index of a medium is simply called its refractive index.
a. True
b. False
To practice more questions & prepare well for exams, download myCBSEguide App. It provides complete study
material for CBSE, NCERT, JEE (main), NEET-UG and NDA exams. Teachers can use Examin8 App to create similar
Copyright © myCBSEguide.com. Mass distribution in any mode is strictly prohibited.
2/5
myCBSEguide
papers with their own name and logo.
12. Fill in the blanks:
a. The phenomenon of change in the path of a beam of light as it passes from one medium to another is called
________ of light.
b. The ________ of a lens is a straight line passing through its two centres of curvature.
13. A ray of light is refracted as shown in the figure. Which medium A or B is optically denser than the other?
14. What is magnification of lens ?
15. A concave lens has a focal length of 10 cm. An object 2.5 cm high is placed 30 cm from the lens. Determine the position
and size of the image.
16. i. What happens to a ray of light when it travels from one medium to another having equal refractive indices?
ii. State the cause of refraction of light.
17. At one of the blind ends of a road in a colony lot of accidents used to take place. One day Kunwar moved into a house
near the blind end. On a certain day he saw an accident take place at the blind end. He at once rushed to the spot and
helped the victims with first aid. He, then telephoned for an ambulance. Later on he met the President of the welfare
committee of the colony and requested him to install huge convex mirrors at both ends of the blind end. After the
installation of the mirrors the accident rates suddenly dropped.
i. What according to you are the values displayed by Kunwar?
ii. Why did Kunwar advise the installation of convex mirror?
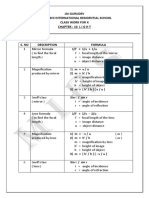
18. What are Cartesian sign conventions used in spherical mirror ? What is the mirror formula ?
Copyright © myCBSEguide.com. Mass distribution in any mode is strictly prohibited.
3/5
myCBSEguide
Class 10 - Science
Light Reflection and Refraction Test 01
Solution
1. (a) less than 1, more than 1 or equal to 1
Explanation: less than 1, more than 1 or equal to 1
2. (b) equal to one
Explanation: equal to one
3. (d) at the centre of curvature
Explanation: at the centre of curvature
4. (a) magnification
Explanation: magnification
5. (c) virtual, erect
Explanation: virtual, erect
6. (d) Brightness will be reduced
Explanation:
If the upper half of the concave mirror is covered, the amount of light that gets reflected from the mirror will be reduced.
Consequently, the brightness of the image that is formed on the screen will be reduced.
To practice more questions & prepare well for exams, download myCBSEguide App. It provides complete study
material for CBSE, NCERT, JEE (main), NEET-UG and NDA exams. Teachers can use Examin8 App to create similar
papers with their own name and logo.
7. (b) NC
Explanation: For parallel surfaces the emergent and incident rays should be parallel.
8. (a) towards the screen
Explanation: The blurred image is seen only when the separation between the screen and mirror is less than the focal
length.
9. (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
10. (c) A is true but R is false.
Explanation: An image on a plane mirror is virtual and it can be photographed.
11. State True or False:
i. (a) True
Explanation: True
ii. (a) True
Explanation: True
12. Fill in the blanks:
a. Refraction
b. Principal axis
13. During refraction of light, when a ray of light enters from denser medium to rarer medium it bends away from the
normal due to increase in its velocity. medium A is optically denser than medium B because ray of light is bending away
from the normal.
14. Magnification of a lens is to the ratio of the height of the image formed by lens to the actual height of object.
If h is the height of the object and h' the height of the image formed by lens, then magnification m =
h
Copyright © myCBSEguide.com. Mass distribution in any mode is strictly prohibited.
4/5
myCBSEguide
If u and v are the distances of object and image
′
h v
m = =
h u
15. Since the lens is concave, hence f is negative
Given: u = - 30 cm; f= - 10 cm; h = 2.5 cm; v = ?; h' = ?
The lens formula for concave lens is
1 1 1
− =
v u f
v
−
−30
1
=
1
−10
v
=
1
10
−
1
30
−3−1
1
v
=
30
v = -7.5 cm
The negative sign indicates the virtual nature of the image.
The image is at a distance of 7.5 cm from lens (in front of lens).
−7.5
The magnification m = v
u
=
30
= = +0.25
The positive sign with the magnification indicates that the image formed erect.
The size of the image is determined by h'.
′
h
= m
h' = h × m
= 2.5 × 0.25
= 0.625 m
Thus the image formed is virtual and erect. It is at a distance of 7.5 cm from lens and its size is 0.625 cm.
To practice more questions & prepare well for exams, download myCBSEguide App. It provides complete study
material for CBSE, NCERT, JEE (main), NEET-UG and NDA exams. Teachers can use Examin8 App to create similar
papers with their own name and logo.
16. i. It does not deviate from its path because both the medium have same refractive indices.
ii. Speed of light changes when it travels from one medium to another due to which it deviates from its path.
17. i. The values displayed by Kunwar are concern for others, helping nature and correct use of knowledge.
ii. A convex mirror has a wide range of view. As a result, it is capable of showing the traffic on the other side of the
blind end. Since, Kunwar was aware of this fact, therefore he advised for their installation.
18. The modern Cartesian sign conventions are :
(a) All the rays are drawn from left to right.
(b) All distances are measured from the pole of the spherical mirror.
(c) The distances measured in the direction of the incident light are taken as positive and those measured in a direction
opposite to the direction of incident light are taken as negative.
(d) The heights measured upwards and perpendicular to the principal axis of the mirror are taken as positive and vice
versa.
Since the object is always placed on the left of the mirror, u is always negative.
If u is the distance of object and v the distance of image from pole of the mirror, then
or
2 1 1 1 1 1
= + = +
R v u f v u
Copyright © myCBSEguide.com. Mass distribution in any mode is strictly prohibited.
5/5
You might also like
- Definite Integral (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandDefinite Integral (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Grade 10 Second 2Document3 pagesGrade 10 Second 2Eden Rey ParoanNo ratings yet
- 2 Ii We 7 TKB Es 6 CSN G3 S EoDocument6 pages2 Ii We 7 TKB Es 6 CSN G3 S Eony9197171No ratings yet
- Physics I Honors: Chapter 13 Practice Test: Multiple ChoiceDocument7 pagesPhysics I Honors: Chapter 13 Practice Test: Multiple ChoicefgdhNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Physics Chapter 3 Revision Problems - Answer Key: Multiple Choice Questions. Q1Document6 pagesGrade 10 Physics Chapter 3 Revision Problems - Answer Key: Multiple Choice Questions. Q1NONO0% (1)
- Physics I Honors: Chapter 13 Practice Test: Multiple ChoiceDocument7 pagesPhysics I Honors: Chapter 13 Practice Test: Multiple ChoicefgdhNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Quarter 2, Week 6: Title CardDocument30 pagesGrade 10 Quarter 2, Week 6: Title CardJeboy LaquianNo ratings yet
- 10 - Light Reflection and RefractionDocument6 pages10 - Light Reflection and RefractionsamNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Rayopticsandoptical tp01Document6 pages12 Physics Rayopticsandoptical tp01NovoBossNo ratings yet
- S10 Q2 Week-7Document10 pagesS10 Q2 Week-7Aiphrell Anne D. MoradaNo ratings yet
- FAQ PhysicsDocument30 pagesFAQ Physicsamit21oct2005No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 29-Jun-2023Document6 pagesAdobe Scan 29-Jun-2023kpssgaming923No ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper-01 Chapter 10 Light Reflection and RefractionDocument11 pagesCBSE Test Paper-01 Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refractionshubham sehgalNo ratings yet
- Science - Grade 10: Mirror and Lens EquationDocument16 pagesScience - Grade 10: Mirror and Lens EquationJames Alforte100% (3)
- 10 Science TP 10 1Document8 pages10 Science TP 10 1Ajjuu ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Physics Optics: Plane Mirrors: Science and Mathematics Education Research GroupDocument38 pagesPhysics Optics: Plane Mirrors: Science and Mathematics Education Research GroupMarilyn Castro LaquindanumNo ratings yet
- Physics Test Prep: Reflection and MirrorsDocument3 pagesPhysics Test Prep: Reflection and MirrorsvaraprasadNo ratings yet
- Ch.3.10 Magnification and Lens Formula (Ans)Document8 pagesCh.3.10 Magnification and Lens Formula (Ans)sls23142No ratings yet
- Activity 4 7 Mirrors Lenses Motors and GeneratorsDocument10 pagesActivity 4 7 Mirrors Lenses Motors and GeneratorsMarley Chelsea LevantinoNo ratings yet
- Light WorksheetDocument11 pagesLight Worksheetkobayashirei602No ratings yet
- Jones Rural School - 300555: (Please Use The Provision For Your Answers On The Back Page of This Test.)Document2 pagesJones Rural School - 300555: (Please Use The Provision For Your Answers On The Back Page of This Test.)Apple SamoyNo ratings yet
- Class 10 - Light Reflection & Refraction-Revision WorksheetDocument4 pagesClass 10 - Light Reflection & Refraction-Revision WorksheetFrederic Francois ChopinNo ratings yet
- OPTICS Revised + Extra QsDocument75 pagesOPTICS Revised + Extra Qsdoaa naieemNo ratings yet
- 08 Science Light 01Document5 pages08 Science Light 01Ranjan RoyNo ratings yet
- CP Physics Chapter 14 Light and Reflection PDFDocument4 pagesCP Physics Chapter 14 Light and Reflection PDFRashed AlawaishehNo ratings yet
- Q.2. Srlu W3 G10Document6 pagesQ.2. Srlu W3 G10Pamela IndosoNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Notes Ch09 Rayoptics and Optical InstrumentsDocument5 pages12 Physics Notes Ch09 Rayoptics and Optical InstrumentsMayank SainiNo ratings yet
- Sec Phys Optics PlanemirrorsDocument38 pagesSec Phys Optics Planemirrorsbhaskar51178No ratings yet
- Ray Optics: Reflection: Single Correct Answer TypeDocument2 pagesRay Optics: Reflection: Single Correct Answer TypeDev KhattriNo ratings yet
- CH 10 Light (Reflection 1)Document22 pagesCH 10 Light (Reflection 1)Mohammad MujtabaNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document9 pagesModule 6chef curryNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class-12 Physics Quick Revision Notes Chapter-09: Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument5 pagesCBSE Class-12 Physics Quick Revision Notes Chapter-09: Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsMayank MishraNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-02 10 Light Reflection and RefractionDocument6 pagesCbse Test Paper-02 10 Light Reflection and RefractionAchyut SinghNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document3 pagesScience 10JENY VEV GAYOMANo ratings yet
- Science 10-Quarter 2Document4 pagesScience 10-Quarter 2Dumlao DinahNo ratings yet
- Rau Optics WsDocument3 pagesRau Optics Wssagarikaarun06No ratings yet
- LP Test 2Document6 pagesLP Test 2Jade Thong EchaviaNo ratings yet
- 15 - Science - LightDocument5 pages15 - Science - LightRENJITH PAINo ratings yet
- Learning Guide SLM 56Document13 pagesLearning Guide SLM 56Kate Megan ApuliNo ratings yet
- Lab 10 Spherical Mirrors and LensesDocument16 pagesLab 10 Spherical Mirrors and LensesOtto ManNo ratings yet
- Title Card: Lesson 12: Mirror Images Are Laterally InvertedDocument16 pagesTitle Card: Lesson 12: Mirror Images Are Laterally InvertedNathan Francis Enzo NicolasNo ratings yet
- Physics 2Document11 pagesPhysics 2bort kortNo ratings yet
- Class 10 - Physics: Light-Reflection & RefractionDocument16 pagesClass 10 - Physics: Light-Reflection & RefractionSanjeev SainiNo ratings yet
- Group Bohr's Optics Section A: One MarkDocument5 pagesGroup Bohr's Optics Section A: One MarkMadhvi ShardaNo ratings yet
- GR 7 - LIGHT - ANSWER KEYDocument3 pagesGR 7 - LIGHT - ANSWER KEYJoseph JayakanthanNo ratings yet
- GR 10 - CH 10-Light QB With Solution-SubjectiveDocument25 pagesGR 10 - CH 10-Light QB With Solution-SubjectiveKishan MishraNo ratings yet
- 15.07.2020-10th Physics - LIGHT-notesDocument5 pages15.07.2020-10th Physics - LIGHT-notesSri Vishnu RamNo ratings yet
- 1Document7 pages1विनय खरेNo ratings yet
- 5 6154457525488977613Document5 pages5 6154457525488977613ankith sNo ratings yet
- OPTICSDocument16 pagesOPTICSSoumyajeet PradhanNo ratings yet
- CP Physics - Test CH 15 RefractionDocument4 pagesCP Physics - Test CH 15 RefractionRashed AlawaishehNo ratings yet
- Q3Document5 pagesQ3Kingking alcosebaNo ratings yet
- Convex Mirror Dec. 11, 2022Document8 pagesConvex Mirror Dec. 11, 2022angelbert pontemayorNo ratings yet
- Pisanio SlidesCarnivalDocument90 pagesPisanio SlidesCarnivalkenneth lopez0% (1)
- BTL TNVLDocument8 pagesBTL TNVLNguyên Nguyễn XuânNo ratings yet
- Midterm Science 10Document9 pagesMidterm Science 10ashwinnayar12No ratings yet
- NCERT ExemplarDocument10 pagesNCERT Exemplarrohitpatra708024No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Physics MCQs All Chapters PDFDocument25 pagesCBSE Class 10 Physics MCQs All Chapters PDFkrishnareddy_chintalaNo ratings yet
- Session5&6 - HK NEWTONDocument48 pagesSession5&6 - HK NEWTONDenny Febian SetiawanNo ratings yet
- G10 - Chapter Test 5 Ans - Ch.10 - 06 NOV 23Document10 pagesG10 - Chapter Test 5 Ans - Ch.10 - 06 NOV 23Urmila GNo ratings yet
- Alchemy As Donum DeiDocument15 pagesAlchemy As Donum DeiAlchemist3573No ratings yet
- 7-Development of High Precision Gear MeasuringDocument9 pages7-Development of High Precision Gear MeasuringFahrul Chayank AisyahNo ratings yet
- Dolphin (PG) College of Science & Agriculture: Fee Per SemesterDocument1 pageDolphin (PG) College of Science & Agriculture: Fee Per Semesterlincon sNo ratings yet
- MAINCOTE™ AEH-20 Acrylic-EpoxyDocument5 pagesMAINCOTE™ AEH-20 Acrylic-EpoxyAPEX SONNo ratings yet
- Kekuatan Hukum SKGRDocument15 pagesKekuatan Hukum SKGRsyahmanNo ratings yet
- Urban, City, and Town Planning Integrates Land Use Planning and Transportation Planning To Improve TheDocument37 pagesUrban, City, and Town Planning Integrates Land Use Planning and Transportation Planning To Improve TheMary Chriss ArnaizNo ratings yet
- Rulebook Newton PDFDocument16 pagesRulebook Newton PDFvaggos1988No ratings yet
- Contrastive Linguistics - D2019 (Ms. Yen)Document134 pagesContrastive Linguistics - D2019 (Ms. Yen)Lan Anh ChuNo ratings yet
- Prisms and Dispersion of Light O LevelDocument15 pagesPrisms and Dispersion of Light O LevelPascoNo ratings yet
- Ead533 The Shared Leadership InitiativeDocument3 pagesEad533 The Shared Leadership Initiativeapi-497831583No ratings yet
- SEAD - Solution Manual - 2019-2020 EditionDocument37 pagesSEAD - Solution Manual - 2019-2020 EditionYokaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 Summative Test in Earth and LifeDocument5 pagesQuarter 1 Summative Test in Earth and LifeHanna100% (1)
- Naruto - Harem of The Strong CYOA v1.0 (By Arandommark)Document56 pagesNaruto - Harem of The Strong CYOA v1.0 (By Arandommark)Diogo GalvaoNo ratings yet
- Reflection Activty 3 (Done)Document1 pageReflection Activty 3 (Done)theressa reidNo ratings yet
- Youngs ModulusDocument10 pagesYoungs Modulusconnectrix.gohetrixNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing Skills PRETESTDocument4 pagesReading and Writing Skills PRETESTREZITTE MABLES100% (1)
- The Kushite World: Beiträge Zur Sudanforschung. Beiheft 9Document16 pagesThe Kushite World: Beiträge Zur Sudanforschung. Beiheft 9Tarek Mohamed Tarek FouadNo ratings yet
- Research Introduction 1Document7 pagesResearch Introduction 1Kenneth George V. FernandezNo ratings yet
- Required: If Green Machine Company Used The FIFO and The Weighted Average Methods ofDocument6 pagesRequired: If Green Machine Company Used The FIFO and The Weighted Average Methods ofrook semayNo ratings yet
- Assignment - AER03630 3 2023Document2 pagesAssignment - AER03630 3 2023BrandonNo ratings yet
- 2 Case StudyDocument8 pages2 Case Studysehrish khawerNo ratings yet
- Colegio de Santo Cristo de Burgos Corp.: Educatio Directa DominoDocument7 pagesColegio de Santo Cristo de Burgos Corp.: Educatio Directa DominoJohn Kirby MirandaNo ratings yet
- 11 - Iso 2553 2019Document62 pages11 - Iso 2553 2019Md. Main UddinNo ratings yet
- Operator DescriptionDocument6 pagesOperator DescriptionSmart CrazyNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Reservoir Simulation in Hot Sedimentary Aquifer System Using FeflowDocument1 pageGeothermal Reservoir Simulation in Hot Sedimentary Aquifer System Using FeflowImmanuel Lumban GaolNo ratings yet
- Are Animals Getting Smarter?Document1 pageAre Animals Getting Smarter?Bismi IqbalNo ratings yet
- XiGo Note 112 Pharma and The Acorn AreaDocument3 pagesXiGo Note 112 Pharma and The Acorn Areaprakush01975225403No ratings yet
- SHE List DocumentDocument1 pageSHE List DocumentMunajamNo ratings yet
- Advanced Control Theory 2nd Nagoor KaniDocument3 pagesAdvanced Control Theory 2nd Nagoor Kaniunnvishnu20% (25)
- Group 2 - Article Review (Ads 607)Document12 pagesGroup 2 - Article Review (Ads 607)NUR AHLAM FAIQAH MOHD ROSDINo ratings yet