Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Practical P6 Tips - Dr. Nouran Rostom
Chemistry Practical P6 Tips - Dr. Nouran Rostom
Uploaded by
MaddieOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Practical P6 Tips - Dr. Nouran Rostom
Chemistry Practical P6 Tips - Dr. Nouran Rostom
Uploaded by
MaddieCopyright:
Available Formats
IGCSE Chemistry Tips for paper 6 chemistry
Tips for Chemistry P6 Practical exam👌
- Labelling tools:
(notice the difference between)
‣ Tests tube vs boiling tube. (Boiling tube is used for heating)
‣ Burette vs tap funnel. (Burette has graduations)
‣ Measuring cylinder vs gas jar. (Measuring cylinder has graduation)
m
‣ Conical flask vs round bottom flask. (Conical flask has a flat bottom)
o
‣ Beaker Vs Trough (Trough is bigger, it has no scale & usually used with inverted
t
measuring cylinders)
os
- Mistakes in given diagrams in Q.1 you are asked to mention :
R
‣ Heat under the wrong container
a n
‣ Collection of gas using the wrong method as (upward for dense gases/ downward
r
for light gases / over water for soluble gases)
ou
‣ Escape of gas (no bung is fitted when there should be one).
.r N
‣ Stirring with a metal spatula instead of glass rod.
D
‣ Drying of gas: (the delivery tubes carrying the gas into the drying agent should be
immersed in the drying agent & the one carrying the dry gas out shouldn’t be
immersed).
- Safety Precautions:
‣ Use fume cupboard for experiments releasing toxic/ harmful gases: as Halogens ,
Sulfur dioxide or Nitrogen dioxide.
‣ Use electric heater instead of bunsen burner for heating alcohols as alcohols are
flammable and may catch fire.
‣ Wear Gloves & goggles when dealing with acids as the splashes are corrosive.
Dr. Nouran Rostom Page 1 of 5
IGCSE Chemistry Tips for paper 6 chemistry
- Drawings you should be able to draw:
‣ Experimental techniques:
‣ Filtration (Flask- funnel - filter paper - filtrate - residue)
‣ Condenser (with water inlet and outlet)
m
‣ Chromatography labelled diagram
to
‣ Electrolysis:
os
‣ electroplating experiment
R
‣ inverted measuring cylinder over an electrode to collect gas
n
& measure its volume
a
‣ Rate of reaction:
r
‣ Collection of gas experiment using gas syringe + stop watch
ou
N
‣ Mass change experiment (flask over a balance with a cotton
.r
wool + stop watch)
D
- Improvements:
‣ Using burette instead of measuring cylinder: because burette is more accurate
‣ Using polystyrene cup /lagging material instead of glass beaker: to minimize
heat loss
‣ If a polystyrene cup is already used, we can add a lid to minimize heat loss.
‣ Repeat the experiment 3 times instead of once & take average for more reliable
results.
Dr. Nouran Rostom Page 2 of 5
IGCSE Chemistry Tips for paper 6 chemistry
- Taking measurements:
‣ Pay attention to the scale, is it increasing downwards (as burette or inverted
measuring cylinder) or upwards as an ordinary measuring cylinder.
‣ Pay attention to the graduations of the lab tool provided.
‣ All burette readings should be written to 1 decimal place. And if the reading is a
m
whole digit, write it down as .0 (examples: 0.0 , 15.0, 20.0 etc.)
to
‣ When reading a stop watch, make sure to convert time to the unit required in the
s
table heading (minutes or seconds not both!)
Ro
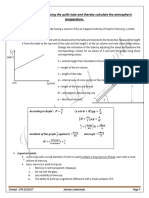
- Graphs:
‣ Draw Graphs with a pencil and label your graphs if more than one graph required.
a n
‣ Graph should exceed more than half the grid.
u r
‣ A line of best fit should always be drawn (excluding anomalies).
o
๏ Use a ruler if it’s a best fit straight line.
N
๏ Draw free hand without a ruler if its’ a best fit curve or smooth line.
.
‣ Revise reaction rate gas ( time on x axis - mass/ volume on Y- axis)
Dr
Blue line:
Adding catalyst.
Using Higher temperature or pressure,
or surface area, or mass/
concentration of the excess reagent.
Red line:
Removing catalyst.
Using lower temperature or pressure,
or surface area, or mass/
concentration of the excess reagent.
Exception Blue line:
Using higher concentration/ mass of
the limiting reagent.
Red line:
Using lower concentration/ mass of
the limiting reagent.
Dr. Nouran Rostom Page 3 of 5
IGCSE Chemistry Tips for paper 6 chemistry
- Special points for some experiments:
‣ Experiment of measuring time taken for the cross to disappear from view:
A smaller conical flask, means the time taken for the cross to disappear from view
will be shorter because depth of liquid in the flask is greater.
‣ Energy change experiments:
m
The more volume of water added to the solution, the smaller the temperature change
o
& vice versa.
st
o
‣ Titration experiments repeated with 2 different solutions for ex. (C & D)
๏ If C & D are the titrants (the liquids in the burette): the one with smaller
R
volume used is the more concentrated.
n
๏ If C & D are the liquids in the conical flask: the one that needs larger
ra
volume of the titrant to be neutralized is the more concentrated.
ou
. N
- Revise:
r
‣ Tests for cations & anions
D
‣ Tests for gases
‣ How to carry out a flame test + observations
‣ Color of copper (reddish brown/pink), copper carbonate (green) & copper salts
(blue)
‣ Color of cobalt compounds (pink)
‣ Color of carbon & manganese oxide & copper oxide (black)
‣ Smell of ammonia, ethanol, ethanoic acid, Hydrocarbons
‣ Reactivity series of metals
‣ Cracking & fermentation experiments
Dr. Nouran Rostom Page 4 of 5
IGCSE Chemistry Tips for paper 6 chemistry
- Experiments to revise for Scientific investigation Q.4:
‣ How to measure solubility of substance in water at a certain temperature.
m
‣ Separation techniques experiments.
to
‣ Electroplating experiment
os
‣ How to determine if a reaction is exo or endo by measuring temp. change.
R
‣ Which fuels releases the most energy experiment.
n
‣ Rate of reaction experiments (collecting gas by gas syringe/time or measuring
ra
decrease in mass / time)
ou
‣ Preparation of salt by excess method.
N
‣ Titration experiment to determine concentration or to compare which solution is
r .
more concentrated.
D
‣ Rusting experiment
‣ Which metal is the most reactive (faster bubbles or faster decrease in mass)
‣ Thermal decomposition of metal carbonate experiment using crucible & a lid then
extracting the metal by displacement reaction.
In any investigation write :
1. Steps including:
• Measurements: Add certain/ known volume, Weight certain mass, etc.
• Tools used: measuring cylinder, burette, balance, gas syringe, mortar & pestle etc.
• control variables for fair test: same amount, same concentration, same temp. Etc.
2. Conclusion: how the results will help you make your conclusion.
(the faster rate is the one that produced….., the more concentrated solution is the one
that makes most bubbles……, the higher the temp. Change, the better the fuel……, etc.)
Dr. Nouran Rostom Page 5 of 5
You might also like
- Core Prac 4Document5 pagesCore Prac 4Claudia ManchadoNo ratings yet
- Hydrotest - 333 AG FW 0001 - Rev03 PDFDocument26 pagesHydrotest - 333 AG FW 0001 - Rev03 PDFIhsan IchwansyahNo ratings yet
- 8.4 - Nozzle Theory PDFDocument170 pages8.4 - Nozzle Theory PDFJuan Navarro FernándezNo ratings yet
- 900MR869 Ui - 2020Document2 pages900MR869 Ui - 2020HRHDS EngenhariaNo ratings yet
- Combur 10 Test UX 11544373Document2 pagesCombur 10 Test UX 11544373anon_65360249No ratings yet
- Heat Practicals (EM) - 230613 - 001844Document17 pagesHeat Practicals (EM) - 230613 - 001844Dharsitth AshvinNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Chem 070 2Document7 pagesExperiment 2 - Chem 070 2Jenn CaoNo ratings yet
- Momentum Transfer: Fluid StaticsDocument8 pagesMomentum Transfer: Fluid StaticsMadhumita KumarNo ratings yet
- C2 - Biological MoleculesDocument12 pagesC2 - Biological MoleculesShumi TeeNo ratings yet
- GC Learning Practice Sheet 2Document3 pagesGC Learning Practice Sheet 2Aryell SalesNo ratings yet
- Taryn Claassens Science Fair Trifold - 2Document1 pageTaryn Claassens Science Fair Trifold - 2api-527913909No ratings yet
- 425.010 Vapor&Cgo & Tank Clean Hoses Test Log.Document1 page425.010 Vapor&Cgo & Tank Clean Hoses Test Log.Celal BozdoganNo ratings yet
- Urbano - Infraestructura - Servivios - Instituciones Juridicas03 - CompressedDocument14 pagesUrbano - Infraestructura - Servivios - Instituciones Juridicas03 - CompressedFederico Tomás Garcia FADU - UBANo ratings yet
- Result Sheet 69Document13 pagesResult Sheet 69SM ConsultantsNo ratings yet
- Sweetening ProcessDocument3 pagesSweetening Processمرتضى حامد كاظم رحيمNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY - Core Practical 2Document4 pagesCHEMISTRY - Core Practical 2Claudia ManchadoNo ratings yet
- Site Analysis CompressedDocument1 pageSite Analysis CompressedSupriya SamantaNo ratings yet
- Audit Iadp Bundle ChecklistDocument5 pagesAudit Iadp Bundle ChecklistAyu Ngurah SuarminiNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Temperature On Enzyme ActivityDocument6 pagesThe Effect of Temperature On Enzyme ActivityJassim AlsabtNo ratings yet
- Student Handout - Advanced Gas Tanker Training PDFDocument136 pagesStudent Handout - Advanced Gas Tanker Training PDFPrassanna Venkatesh100% (2)
- Tombo - Gasket - Genetal CatalogDocument117 pagesTombo - Gasket - Genetal CatalogAnh CaoNo ratings yet
- Rehau Awadukt Thermo 342100 UkDocument24 pagesRehau Awadukt Thermo 342100 UkpaolodownloadNo ratings yet
- Upscaling Slides May 2012Document41 pagesUpscaling Slides May 2012chrisofoma100% (1)
- Phonons PCGDocument143 pagesPhonons PCGTest PersonNo ratings yet
- A01461101 Ice & Water - Automatic Defrost Side by Side - R134ADocument2 pagesA01461101 Ice & Water - Automatic Defrost Side by Side - R134AJOSE JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Ksif Series TroubleshootingDocument25 pagesKsif Series Troubleshootingbrian kaled calderonNo ratings yet
- Nozzles: Animation of Mass Density in A Heated Supersonic Jet at Mach 1.4Document13 pagesNozzles: Animation of Mass Density in A Heated Supersonic Jet at Mach 1.4Mark Dominic KipkorirNo ratings yet
- P vs. NP NP-complete co-NP NP-hard: NtractabilityDocument66 pagesP vs. NP NP-complete co-NP NP-hard: NtractabilityMehsara IrfanNo ratings yet
- PN 91134 Rev. B Package Insert A1CNow EN - DE - FR - IT - Pro IFCCDocument2 pagesPN 91134 Rev. B Package Insert A1CNow EN - DE - FR - IT - Pro IFCCKepala HitamNo ratings yet
- SOPHIA Split Air Conditioner, TroubleshootingDocument39 pagesSOPHIA Split Air Conditioner, TroubleshootingEsteban Torres JNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument3 pagesLab Reporturmom comNo ratings yet
- Gas Reservoir 2Document30 pagesGas Reservoir 2Omer IkhlasNo ratings yet
- Equipment Used in Evaporation, The Process of Boiling A Liquid in Order To Reduce Its Volume NeedDocument30 pagesEquipment Used in Evaporation, The Process of Boiling A Liquid in Order To Reduce Its Volume NeedgauravrkadamNo ratings yet
- Flash Steam Important ArticleDocument14 pagesFlash Steam Important ArticleAhmad Riaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Risk Assessment Waste Solvent DisposalDocument4 pagesChemistry Risk Assessment Waste Solvent DisposalWay to WorldNo ratings yet
- Monitoring JenazahDocument313 pagesMonitoring JenazahAnonymous wuU2Z9vOqNo ratings yet
- GRHTJ of Separation Science - 2015 - Wei - Universal Method For The Determination of Nonionic Surfactant Content in TheDocument9 pagesGRHTJ of Separation Science - 2015 - Wei - Universal Method For The Determination of Nonionic Surfactant Content in TheSantoshi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Risk Assessment UV RadiationDocument3 pagesChemistry Risk Assessment UV RadiationWay to WorldNo ratings yet
- Final NTSE I & II Test Paper Bookelt - X - (SAT)Document135 pagesFinal NTSE I & II Test Paper Bookelt - X - (SAT)SADASHIV NAGARNo ratings yet
- TENTATIVE Formula SheetDocument2 pagesTENTATIVE Formula Sheetbroly018No ratings yet
- Instructions: Experiment 1 - Pen ChromatographyDocument6 pagesInstructions: Experiment 1 - Pen Chromatographyapi-471875811No ratings yet
- Hadjret HRSG Operation Training ManualDocument87 pagesHadjret HRSG Operation Training ManualYanis KemounNo ratings yet
- ClimaticDocument1 pageClimaticAhmed DebchiNo ratings yet
- 220 IntDocument16 pages220 IntOuld CheikhNo ratings yet
- WH-MDC07J3E5 Instrukcja Montażu PCDocument34 pagesWH-MDC07J3E5 Instrukcja Montażu PCmichal.papis.99No ratings yet
- Centre of Pressure ExperimentDocument7 pagesCentre of Pressure ExperimentNazrul IslamNo ratings yet
- Models Available Psp1 Plug-In Special Purpose Supervisory SwitchDocument2 pagesModels Available Psp1 Plug-In Special Purpose Supervisory SwitchArgile-assholeNo ratings yet
- 303-08B Engine Emission Control - 1.4L Duratorq-Tdci (DV) Diesel 2004 - 2012 Fusion Diagnosis and TestingDocument3 pages303-08B Engine Emission Control - 1.4L Duratorq-Tdci (DV) Diesel 2004 - 2012 Fusion Diagnosis and TestingHenrique AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- IndexDocument1 pageIndexGauravSaxenaNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet For Variable Speed Drives of Medium and Large PowerDocument6 pagesData Sheet For Variable Speed Drives of Medium and Large Powerbrome2014No ratings yet
- T WREX Maintenance Sched 1Document2 pagesT WREX Maintenance Sched 1rezkyfebri.sunandaNo ratings yet
- FORA IR19 Manual EN PDFDocument1 pageFORA IR19 Manual EN PDFeloisaperillaNo ratings yet
- Accurate Determination of Catalyst Loading On Glassy Carbon Disk and Its Impact On Thin Film Rotating Disk Electrode For Oxygen Reduction Reaction.Document1 pageAccurate Determination of Catalyst Loading On Glassy Carbon Disk and Its Impact On Thin Film Rotating Disk Electrode For Oxygen Reduction Reaction.Muralidhar ChourashiyaNo ratings yet
- CT Calibración de Pesas y Osnn 2020-01Document1 pageCT Calibración de Pesas y Osnn 2020-01BryanNo ratings yet
- NRG Coal Dust Monitoring - 20190731Document123 pagesNRG Coal Dust Monitoring - 20190731Dave GreinkeNo ratings yet
- FGHS2655PF Ref FrigidaireDocument2 pagesFGHS2655PF Ref FrigidaireVasti Diaz AguilarNo ratings yet
- FE Review: Thermodynamics: Are You Ready For FE?Document74 pagesFE Review: Thermodynamics: Are You Ready For FE?Christian Rally Ramos GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Talent SBWB 3Document288 pagesTalent SBWB 3Alp Özküçük100% (1)
- MT 21006 TP Unit 3 Lec 3 and 4 06 and 09 Oct 2023 CombinedDocument19 pagesMT 21006 TP Unit 3 Lec 3 and 4 06 and 09 Oct 2023 CombinedRasika MalodeNo ratings yet
- Soil Science ReviewerDocument2 pagesSoil Science ReviewerDeejee Ann de LeonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium PDFDocument24 pagesChemical Equilibrium PDFdarshan bgNo ratings yet
- Safety Bulletin 22/20: Safety Inspection Check List of Air Separation Units and Cryogenic Liquid Storages at Plant SiteDocument40 pagesSafety Bulletin 22/20: Safety Inspection Check List of Air Separation Units and Cryogenic Liquid Storages at Plant SitecarolNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Sulfur Content in Propane and Butane After Gas Purification On A Treatment UnitDocument11 pagesPrediction of Sulfur Content in Propane and Butane After Gas Purification On A Treatment UnitBaghdadi AbdelillahNo ratings yet
- Green Chemistry: Study of Acid-Base Indicator Property of Golden Beet RootDocument6 pagesGreen Chemistry: Study of Acid-Base Indicator Property of Golden Beet RootjumarniNo ratings yet
- 04 Feuillet Memento Degremont en N 4 Aquadaf BDDocument4 pages04 Feuillet Memento Degremont en N 4 Aquadaf BDSong Nguyen NguyenNo ratings yet
- 2015 U.S. NATIONAL Chemistry Olympiad: Local Section Exam Olympiad Examinations Task ForceDocument8 pages2015 U.S. NATIONAL Chemistry Olympiad: Local Section Exam Olympiad Examinations Task ForceNajmusawwa Aulia RahmahNo ratings yet
- On The Residual Strength of Aging Cast Iron TrunkDocument10 pagesOn The Residual Strength of Aging Cast Iron TrunkAlessandro SerafiniNo ratings yet
- CCA Eligible Processes 2014Document9 pagesCCA Eligible Processes 2014Carlos LouçãoNo ratings yet
- HSB-H2 Manual 2010Document78 pagesHSB-H2 Manual 2010Hasan SarfrazNo ratings yet
- Back To Basics: An Introduction To Metal Recycling: Aluminum CansDocument4 pagesBack To Basics: An Introduction To Metal Recycling: Aluminum CansRakesh Ranjan MishraNo ratings yet
- PRB 82 094517 (2010) Superconductor YSn3 AkimitsuDocument5 pagesPRB 82 094517 (2010) Superconductor YSn3 AkimitsuOctoliaTogibasaTambunanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument26 pagesAldehydes and KetonesVoteone Enhypen100% (1)
- Support Material Class 9thDocument49 pagesSupport Material Class 9thJashn RakhechaNo ratings yet
- Thesis Chiller Hongxi Yin Appendix ADocument20 pagesThesis Chiller Hongxi Yin Appendix Acefa84No ratings yet
- SN1 Vs SN2Document1 pageSN1 Vs SN2nurhanieyNo ratings yet
- Biologic Electrochemical WorkstationDocument3 pagesBiologic Electrochemical WorkstationRANJITHNo ratings yet
- Transkrip Akademik Oke 2022 Genap (Angkatan 2019) Valid-4Document194 pagesTranskrip Akademik Oke 2022 Genap (Angkatan 2019) Valid-4fahrirezasetiawanNo ratings yet
- Cell - Structure AND FunctionsDocument63 pagesCell - Structure AND FunctionsAdvayNo ratings yet
- 2nd Long QuizDocument8 pages2nd Long QuizJohnnard BelenNo ratings yet
- Ailures in Ammonia Plant Vertical Waste Heat BoilersDocument14 pagesAilures in Ammonia Plant Vertical Waste Heat BoilersMir AsifNo ratings yet
- Mist EliminatorDocument16 pagesMist Eliminatorjpsingh75No ratings yet
- Seacure Gen W DT Dynagas PDocument46 pagesSeacure Gen W DT Dynagas PAlex KuvoricNo ratings yet
- Case Studies in Construction Materials: Guneet Saini, Uthej VattipalliDocument10 pagesCase Studies in Construction Materials: Guneet Saini, Uthej VattipalliGaurav PanwarNo ratings yet
- Kf875 and Kf-Lab Mkii: Karl Fischer Moisture in Oil Test SetsDocument3 pagesKf875 and Kf-Lab Mkii: Karl Fischer Moisture in Oil Test SetsManish MishraNo ratings yet
- Exergy Analysis of A Pressurized-Water Reactor Nuclear-Power PlantDocument19 pagesExergy Analysis of A Pressurized-Water Reactor Nuclear-Power PlantJUAN ESTEBAN DURAN QUINTERONo ratings yet
- Matter and Its PropertiesDocument10 pagesMatter and Its PropertiesYT PremiumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PDFDocument31 pagesChapter 2 PDFKEVAL PATELNo ratings yet
- Fentanil Fatal CaseDocument7 pagesFentanil Fatal CaseKarla CoyagoNo ratings yet
- API MPMS ListDocument5 pagesAPI MPMS Listhtutswe0% (1)