Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Density of Sintering
Uploaded by
Amp Nurarak0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views8 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views8 pagesThe Density of Sintering
Uploaded by
Amp NurarakCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
The Density of Sintering
Purpose
- Understanding the importance of the Density of Sintering.
- As a guide to determine the density of Sintering.
What is “Sintering”
Sintering is a process of solid particles bond together with the forces between atoms (Atomic Force)
are generally used metal powder extrusion. Then baked at high temperature but below the melting point of
the metal. The most common metals used to produce solid metal with a high melting point. And in the heat
of this match. Cobalt powder that acts as a coordinating to the greasy metal powder to cling together tightly.
For instance, the Young's Modulus 𝐸𝑛 of sintered iron powders remains insensitive to sintering time,
alloying, or particle size in the original powder, but depends upon the density of the final product:
𝐸𝑛 Τ𝐸 = (𝐷 Τ𝑑)3.4
Where 𝐷 is the density, 𝐸 is Young's modulus and 𝑑 is the maximum density of iron.
Metal Powder Compaction Sintering
*The Sintering some work may be done up to two times for the efficient operation better. The hardness,
strength, stress, and higher density.
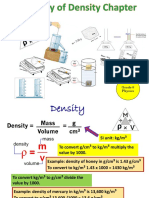
Density
Density is the unique properties of a substance. that means The little substance, whether it is small
or large. The density of a substance that is always constant.
𝐷 = Density ( 𝑔/𝑐𝑚3)
The formula 𝐷 = 𝑚/𝑣 𝑚 = Mass (𝑔)
𝑣 = Volume (𝑐𝑚3 )
The density of a material varies with temperature and pressure. This variation is typically small for
solids and liquids but much greater for gases. Increasing the pressure on an object decreases the
volume of the object and thus increases its density. Increasing the temperature of a substance.
Archimedes' principle
“Any object, wholly or partially immersed in a fluid, is buoyed up by
a force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object.”
𝐵 = ⍴𝑉𝑔
𝐵𝑎𝑙𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒 ∶ 𝐵 = 𝐹
⍴𝑉𝑔 = 𝑚𝑔 ⦁⦁⦁ ⍴ = 𝑚/𝑉
⍴𝑉 = 𝑚
Buoyancy = weight of displaced fluid.
Table sample density of different substances.
Solid Density Fluid Density Table shows a sample density of different
(Kg/m³) (Kg/m³) substances to see that all three states will have a
Styrofoam 0.005 Hydrogen 0.00009 greater density than most solid, liquid and gas. And in
gaseous compounds are less dense than solids and
Cork 0.24 Helium 0.0002
gases. We may have a density of any substance is the
Ice 0.92 Air 0.0013 relative density by the relative density of any substance
Salt 2.16 Oxygen 0.0014 defined as the ratio between the density of the
Aluminum 2.70 Carbon 0.002 substance to the density of reference materials which
dioxide use water with a density of 1.000 x 10³ kg / m³
Iron 7.87 Ethyl 0.79
alcohol
Nickel 8.90 Machine oil 0.90 𝐷𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑜𝑏𝑗𝑒𝑐𝑡
𝑆𝑝𝑒𝑐𝑖𝑓𝑖𝑐 𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑣𝑖𝑡𝑦 =
𝐷𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝑜𝑓 𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟
Copper 8.92 Water 1.00
Lead 11.34 Sea water 1.03 •
• • 𝑆𝑝𝑒𝑐𝑖𝑓𝑖𝑐 𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑣𝑖𝑡𝑦 = 𝐷𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑜𝑏𝑗𝑒𝑐𝑡
Gold 19.32 Mercury 13.55
To measure the density of sintering
Calculation
𝑊𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟 = 𝑣ρ𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟 𝑔
𝑊𝑎𝑖𝑟 = 𝑚𝑔 𝑊𝑎𝑖𝑟 = 𝑚𝑔
𝑚
Density of material (ρ) equation; ρ = 𝑣 ρ𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟 = 1 𝑔/𝑐𝑚³
𝑊𝑎𝑖𝑟 − 𝑊𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟
𝑣= ρ𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟 𝑔
𝑚 𝑊𝑎𝑖𝑟 ρ𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟 𝑔 𝑊𝑎𝑖𝑟 ρ𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟
ρ= = =
𝑣 𝑔 𝑊𝑎𝑖𝑟 −𝑊𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟 𝑊𝑎𝑖𝑟 −𝑊𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟
𝑊𝑎𝑖𝑟
••• ρ=
𝑊𝑎𝑖𝑟 − 𝑊𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟
Equipment
Laboratory Balance Weight Scale Beaker glass Thin wire
Tongs Wipers Hot air blower
Procedure
- Blow dry specimens to displace water or oil in the part.
- Weigh the part and record data (m).
- Weighing beaker filled with water and set 0.
- Weighing part in water using a thin wire. (wait for the water to the part until the stops)
- Moving the part out to mop water.
- Weighing beaker filled with water and set 0 again.
- Weighing part in water using a thin wire and record data (v).
- Calculation ⍴ = 𝑚/𝑣
caution
Be careful weight not over limit balance weight scales.
Be careful not to weigh the bubbles because that affect the test.
You might also like
- Sencore LC103 Operation and Application ManualDocument65 pagesSencore LC103 Operation and Application ManualXenawise0% (1)
- Diagrama Electrico 533DDocument2 pagesDiagrama Electrico 533DJordan RaveloNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 - Soil Composition and Index Properties F22Document23 pagesLec 4 - Soil Composition and Index Properties F22tyler bradfordNo ratings yet
- Ch5 Static FluidDocument30 pagesCh5 Static FluidALIF SYAKIR SATARNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Quarter 2: Module 5Document11 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Quarter 2: Module 5Maria Kriselle ApuhinNo ratings yet
- Fluids PDFDocument2 pagesFluids PDFRenzo AlvizNo ratings yet
- Chem 2990 Specific Gravity Readings Rev2Document6 pagesChem 2990 Specific Gravity Readings Rev2Christopher RausaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Specif GravityDocument6 pagesEffect of Specif GravityRaj BalasubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer & Heat Exchangers GuideDocument73 pagesHeat Transfer & Heat Exchangers GuideNgọc ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Group 2 T Meet314la Exp 7Document14 pagesGroup 2 T Meet314la Exp 7kimbenedictaguilar19No ratings yet
- Density A SummaryDocument11 pagesDensity A SummaryshamsNo ratings yet
- CE 108 - Lecture 1 - Introducton To FluidsDocument18 pagesCE 108 - Lecture 1 - Introducton To FluidsJeric GeronaNo ratings yet
- Pressure-in-liquids-viscocity-Bernoullis-equation-density-flow-propertiesDocument25 pagesPressure-in-liquids-viscocity-Bernoullis-equation-density-flow-propertiesmarionmbambu9No ratings yet
- Chem11 Lab1 DensityDocument6 pagesChem11 Lab1 DensitynamieNo ratings yet
- Lecture2 Fluid PropertiesDocument40 pagesLecture2 Fluid PropertiesFFF ENNo ratings yet
- Phys 1011-Chapter 3Document49 pagesPhys 1011-Chapter 3melaku zegeyeNo ratings yet
- Matter Kinetic Theory Diffusion Capillarity and Surface Tension O LevelDocument29 pagesMatter Kinetic Theory Diffusion Capillarity and Surface Tension O LevelAZORYNo ratings yet
- Michael Adeleye, PH.D, P.G. Dip - EdDocument27 pagesMichael Adeleye, PH.D, P.G. Dip - Edlar dinchiNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab 6Document8 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab 6Saad AliKhanNo ratings yet
- Pressure and Density: Key Concepts ExplainedDocument16 pagesPressure and Density: Key Concepts ExplainedKyaw MyatthuNo ratings yet
- Density and Specific Gravity: Understanding Mass and Volume RelationshipsDocument5 pagesDensity and Specific Gravity: Understanding Mass and Volume RelationshipsLorielle OlivaNo ratings yet
- G10 - Solids and FluidsDocument46 pagesG10 - Solids and FluidsOliver VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 2A Properties of Matter STANDARD PowerPointDocument19 pages2A Properties of Matter STANDARD PowerPointArielle OrendainNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Density Lab Experiment Determines Effects of Temperature on Solids and LiquidsDocument51 pagesMeasurement of Density Lab Experiment Determines Effects of Temperature on Solids and LiquidsJeremy Kyle Edson AustriaNo ratings yet
- Grade-12 General-Physics-1 Q2 Wk6 GLAKbookletDocument16 pagesGrade-12 General-Physics-1 Q2 Wk6 GLAKbookletItsme LuisNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ThermodynamicsDocument66 pagesIntroduction To ThermodynamicsMikaela Dela Cruz0% (1)
- UNit1FFO - PDF (Compatibility Mode)Document122 pagesUNit1FFO - PDF (Compatibility Mode)Pranil KarangaleNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Activity 3Document8 pagesFluid Mechanics Activity 3Cyrus RivasNo ratings yet
- Cycle 2 Experiment 1Document12 pagesCycle 2 Experiment 1Noreen Valerie SaldoNo ratings yet
- DENSITY My Teacher Once Asked Me, "Is Wool Heavier orDocument4 pagesDENSITY My Teacher Once Asked Me, "Is Wool Heavier orChristison AlorciousNo ratings yet
- Physics 06-Temperature, Heat, and Thermodynamics (2018)Document123 pagesPhysics 06-Temperature, Heat, and Thermodynamics (2018)This is ScribeNo ratings yet
- Physics 06-Temperature, Heat, and Thermodynamics (2018)Document113 pagesPhysics 06-Temperature, Heat, and Thermodynamics (2018)Kiyu ImanNo ratings yet
- Ce Ec 2 - Hydraulics 1 Part 2 PDFDocument3 pagesCe Ec 2 - Hydraulics 1 Part 2 PDFHopie LopezNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - IntroductionDocument29 pagesFluid Mechanics - IntroductionJulius Ruz BalondoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 10: Relative DensityDocument5 pagesExperiment 10: Relative Densitynatlas100% (2)
- 1 2 PDFDocument5 pages1 2 PDFJohn GaviolaNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 3 To Determine The Dry Density, Porosity and Specific Gravity of Rock MaterialDocument3 pagesExperiment # 3 To Determine The Dry Density, Porosity and Specific Gravity of Rock MaterialMuhammad Saad GorayaNo ratings yet
- Specific GravityDocument12 pagesSpecific GravityVictor OwolekeNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument85 pagesFluid MechanicsClaire De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- 1180 Exp 04, Density and Specific GravityDocument13 pages1180 Exp 04, Density and Specific GravityShaniCoolestNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Physical Quantities and MeasurementDocument23 pagesChapter 2 Physical Quantities and MeasurementHarshita MunotNo ratings yet
- Lab Quiz 1 Study GuideDocument9 pagesLab Quiz 1 Study GuideClaire DuffyNo ratings yet
- Gr9 Phy DensityDocument36 pagesGr9 Phy DensityKushagra SomaniNo ratings yet
- Other Properties of FluidsDocument19 pagesOther Properties of Fluidsmicklier baduriaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document28 pagesLecture 1Mousa MzNNo ratings yet
- Solid and Fluids: (Physics For Engineer)Document42 pagesSolid and Fluids: (Physics For Engineer)Lee TalierNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Measurements FinalDocument8 pagesHydrostatic Measurements FinalalexNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Theory PPTDocument29 pagesKinetic Molecular Theory PPTNanami MumuzunoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Summary 2Document52 pagesChemistry Summary 2SaeedNo ratings yet
- 12 WaterDocument18 pages12 WaterROGELIO TORRESNo ratings yet
- V M Mass: Chemistry I and Laboratory (HS 105) Lab Experiment: Density DeterminationDocument5 pagesV M Mass: Chemistry I and Laboratory (HS 105) Lab Experiment: Density DeterminationiiohnsoiiNo ratings yet
- BAU Fluid Man PDFDocument35 pagesBAU Fluid Man PDFMolazem Gaming -مُلازم جيمنجNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMSDocument13 pagesComprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMSVikash Rao khatodiyaNo ratings yet
- Energy Engineering: Fluid Mechanic (Lab)Document8 pagesEnergy Engineering: Fluid Mechanic (Lab)MUHAMMAD AKRAMNo ratings yet
- Experiment1-HydraDocument7 pagesExperiment1-HydraLine PestañoNo ratings yet
- Base Units and their SymbolsDocument68 pagesBase Units and their SymbolsAhmed SherifNo ratings yet
- Subject: Chemistry Laboratory: Period August - December 2021Document11 pagesSubject: Chemistry Laboratory: Period August - December 2021Alberto MartinezNo ratings yet
- Definition of Density: Density Is A Measure of The Amount of Mass in A Certain Volume. This Physical Property IsDocument9 pagesDefinition of Density: Density Is A Measure of The Amount of Mass in A Certain Volume. This Physical Property IsOsas E EghoNo ratings yet
- Archimedes' Principle ExperimentDocument10 pagesArchimedes' Principle ExperimentJedd AralesNo ratings yet
- DensityDocument38 pagesDensityvectors academyNo ratings yet
- Phsyics IA Term 1 - DENSITYDocument5 pagesPhsyics IA Term 1 - DENSITYD12No ratings yet
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Corrosion TestDocument9 pagesCorrosion TestAmp NurarakNo ratings yet
- Stamping ProcessDocument9 pagesStamping ProcessAmp NurarakNo ratings yet
- Fracture AnalysisDocument7 pagesFracture AnalysisAmp NurarakNo ratings yet
- Corrosion On Metal PartDocument8 pagesCorrosion On Metal PartAmp NurarakNo ratings yet
- Volume 2 Highways Structures: Design (Substructures and Special Structures), Materials Section 2 Special StructuresDocument86 pagesVolume 2 Highways Structures: Design (Substructures and Special Structures), Materials Section 2 Special Structuresgeorge santiagoNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic EquationsDocument34 pagesSolving Quadratic EquationsJaninne Villa Del Rey100% (1)
- Cellosize QP 100mh Tds - PDF (Paints)Document1 pageCellosize QP 100mh Tds - PDF (Paints)ca_rl_4No ratings yet
- لقطة شاشة 2023-02-02 في 11.30.55 ص PDFDocument50 pagesلقطة شاشة 2023-02-02 في 11.30.55 ص PDFFaisal AlhiallNo ratings yet
- Experiment: Woxalic AcidDocument3 pagesExperiment: Woxalic AcidShalini sahuNo ratings yet
- Soil, Module 9, FinalDocument8 pagesSoil, Module 9, FinalJulia PomaresNo ratings yet
- Probability and Stochastic Processes (5~8장)Document151 pagesProbability and Stochastic Processes (5~8장)엄준현No ratings yet
- Coagulation and Flocculation-5 A6eff65eDocument83 pagesCoagulation and Flocculation-5 A6eff65eredy puthNo ratings yet
- Making the Right Choice: Metal Detection vs. X-RayDocument27 pagesMaking the Right Choice: Metal Detection vs. X-RayCindy ChandraNo ratings yet
- Item Codes & Specification For Instrumentation CableDocument16 pagesItem Codes & Specification For Instrumentation CableZulfequar R. Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Tunnel SupportDocument19 pagesTunnel Supportabhaysinghpratap2000No ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry: 10. Perturbation TheoryDocument46 pagesPhysical Chemistry: 10. Perturbation TheoryToujours BlackroseNo ratings yet
- Green Heterogeneous Catalyst from Plantain Peels for Biodiesel ProductionDocument21 pagesGreen Heterogeneous Catalyst from Plantain Peels for Biodiesel ProductionIdemudia VictorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Motion in A Straight LineDocument36 pagesLecture 3 - Motion in A Straight LineMaitha AlhosaniNo ratings yet
- 2020 Melaka Physics K2 JawapanDocument16 pages2020 Melaka Physics K2 JawapanLincoln LawNo ratings yet
- 2016 Critical Review of State of Health Estimation Methods of Li-Ion Batteries For Real ApplicationsDocument16 pages2016 Critical Review of State of Health Estimation Methods of Li-Ion Batteries For Real ApplicationsAlaa AhmedNo ratings yet
- SunscreenDocument44 pagesSunscreenArtyom FreemanNo ratings yet
- Kennametal - Tungsten Carbide Composite Brazing Rods DatasheetDocument1 pageKennametal - Tungsten Carbide Composite Brazing Rods DatasheetsakthiNo ratings yet
- Wiring Harness (Short Circuit) - TestDocument2 pagesWiring Harness (Short Circuit) - TestIrfan Dhee DoodzNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics IDocument3 pagesEngineering Mathematics INikash SubediNo ratings yet
- Combined Effect of Damage and Plastic Anisotropy On The Ductility Limit of Thin Metal SheetsDocument8 pagesCombined Effect of Damage and Plastic Anisotropy On The Ductility Limit of Thin Metal SheetsKrunal MoreyNo ratings yet
- Catalogue: Facing BricksDocument82 pagesCatalogue: Facing BricksBipu1978No ratings yet
- Conic Sections: Circles and Their EquationsDocument26 pagesConic Sections: Circles and Their EquationsJanet ComandanteNo ratings yet
- Preformulation and Product Development: Bishnu Prasad KoiralaDocument59 pagesPreformulation and Product Development: Bishnu Prasad Koiralasaloni patelNo ratings yet
- Test Planner - Lakshya NEET 3.0 2024Document2 pagesTest Planner - Lakshya NEET 3.0 2024pj9482No ratings yet
- Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Atomic Diffusion During The Al-Cu Ultrasonic Welding ProcessDocument11 pagesMolecular Dynamics Simulations of Atomic Diffusion During The Al-Cu Ultrasonic Welding ProcessftiraNo ratings yet
- Coupled LineDocument43 pagesCoupled LineArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Charpit's Method for Solving Nonlinear PDEsDocument23 pagesCharpit's Method for Solving Nonlinear PDEsManpreet Singh68% (31)