Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Human Tissues Structure, Function and Lococation
Uploaded by
xuxi dulOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Human Tissues Structure, Function and Lococation
Uploaded by
xuxi dulCopyright:
Available Formats
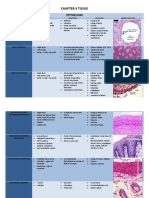
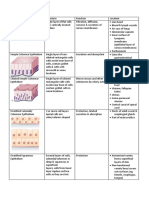
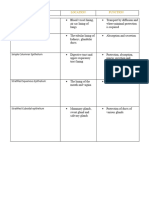
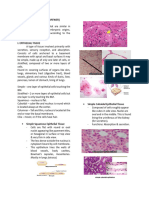
EPITHELIAL TISSUE
Photos STRUCTURE FUNCTION LOCATION
Single-layer of flat, Diffusion, filtration, Lining of blood vessels
often hexagonal cells. some secretion and and the heart, lymphatic
some protection against vessels, alveoli of the
lungs, portions of the
SIMPLE SQUAMOUS friction.
kidney tubules, lining of
EPITHELIUM serous membranes of
body cavities.
Single layer of cube- Secretion and Kidney tubules, glands
shaped cells. absorption. and their ducts, choroid
plexuses of the brain,
lining of terminal
SIMPLE CUBOIDAL bronchioles of the lungs
EPITHELIUM and surfaces of the
ovaries.
Single layer of tall, Movement of oocytes, Glands and some ducts,
narrow cells (large, secretion and bronchioles of lungs,
thin); some have cilia absorption. auditory tubes, uterus,
uterine tubes, stomach,
SIMPLE or microvilli.
intestines, gallbladder,
COLUMNAR bile ducts and ventricles
EPITHELIUM of the brain.
Single layer of cells; tall Synthesize (ciliated Lining of nasal cavity,
PSEUDOSTRATIFIE and thin and reach the tissue) and secrete nasal sinuses, auditory
D COLUMNAR free surface and others do mucus and move tubes, pharynx, trachea,
not. and bronchi of lungs.
EPITHELIUM mucus.
Several layers of cells Protects against Keratinized – outer layer
STRATIFIED that are cuboidal in the abrasion, forms a of the skin
basal layer and barrier against Non-Keratinized –
SQUAMOUS
progressively flattened mouth, throat, larynx,
EPITHELIUM infection and reduces
toward the surface. esophagus, anus, vagina,
loss of water from the inferior urethra and
body. cornea.
Multiple layers of Secretion, absorption Linings of the ducts of
STRATIFIED cube-like cells. and protection. sweat glands, esophageal
CUBOIDAL glands, mammary glands
and parts of male urethra.
EPITHELIUM
Consists of more than Secretion, protection Mammary gland ducts,
one layer of epithelial and some absorption. the larynx, and a portion
cells but only the surface of the male urethra.
STRATIFIED cells are columnar.
COLUMNAR Deeper layers are
EPITHELIUM irregular/cuboidal in
shape.
Stratified cells that Accommodates Lining of urinary bladder,
TRANSITIONAL appear cuboidal when fluctuations in the ureters, and superior
the organ or tube is not volume of fluid in an urethra.
EPITHELIUM
stretched and squamous organ or a tube;
when the organ or the
tube is stretched by
protects against the
fluid; the number of cell caustic effects of urine.
layers decreases.
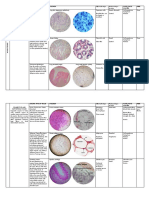
CONNECTIVE TISSUE PROPER
CONNECTIVE TISSUE PROPER: LOOSE CONNECTIVE TISSUES
PHOTOS STRUCTURE FUNCTION LOCATION
A fine network of Loose packing. Widely distributed
fibers (mostly collagen support. and throughout the body;
fibers with a few nourishment for the substance
elastic fibers) with structures with which on which basement
spaces between the it is associated membranes rest;
fibers; fibroblasts. packing between
AREOLAR
macrophages. and glands. muscles and
CONNECTIVE
lymphocytes are nerves; attaches the
TISSUE
located in the spaces skin to underlying
tissues
Little extracellular Packing material. Predominantly in
matrix surrounding thermal insulator, subcutaneous areas,
cells; the adipocytes, energy storage. and mesenteries. renal
or fat cells, are so full protection of organs pelves, around
of lipid that the against injury from kidneys, attached to
cytoplasm is pushed to being bumped or jarred the surface of the
the periphery of the colon, mammary
ADIPOSE TISSUE cell. glands, and in loose
connective tissue that
penetrates into spaces
and crevices.
Fine network of Provides a Within the lymph
reticular fibers superstructure for nodes, spleen and
irregularly arranged lymphatic and bone marrow.
RETICULAR TISSUE hemopoietic tissues.
- for storage
CONNECTIVE TISSUE PROPER: DENSE CONNECTIVE TISSUES
Matrix composed of Withstand great Tendons (attach
collagen fibers pulling forces exerted muscle to bone) and
running in somewhat in the direction of fiber ligaments (attach
the same direction in orientation due to great bones to each other);
tendons and tensile strength and also found in the
ligaments; collagen stretch resistance dermis of the skin.
DENSE REGULAR
fibers run in several organ capsules and the
COLLAGENOUS
directions in the outer layer of many
CONNECTIVE
dermis of the skin vessels
TISSUE
and in organ capsules
Matrix composed of Capable of stretching Elastic ligaments
collagen fibers and and recoiling like a between the vertebrae
elastin fibers running rubber band with and along the dorsal
in somewhat the same strength in the aspect of the neck
direction in elastic direction of fiber (nucha) and in the
ligaments elastic fibers orientation vocal cords; also
DENSE REGULAR
run in connective found in elastic
ELASTIC TISSUE
tissue of blood vessel connective tissue of
walls vessel walls
SUPPORTING CONNECTIVE TISSUE
SUPPORTING CONNECTIVE TISSUE: CARTILAGE
PHOTOS STRUCTURE FUNCTION LOCATION
Collagen fibers are Allows growth of long Growing long bones,
small and evenly bones, provides rigidity cartilage rings of the
dispersed in the with some flexibility in respiratory system,
matrix, in the making the trachea, bronchi, costal cartilage of ribs,
the matrix appear ribs, and nose; forms nasal cartilages. surface
transparent; the strong, smooth yet of bones.
HYALINE
chondrocytes are found somewhat flexible and the embryonic
CARTILAGE
in spaces, or lacunae, articulating skeleton
within the firm but surfaces; forms the
flexible matrix ernbryonic skeleton
Collagen fibers similar Somewhat flexible and Intervertebral disks,
to those in hyoline capable of symphysis, and articular
cartilage; the fibers withstanding disks (e.g., knees and
are more numerous considerable temporomandibular (jaw
FIBROCARTILAG than pressure; connects joints)
E in other cartilages structures subjected to
and are arranged in great pressure
thick bundles
Similar to hyaline Provides rigidity with External ears, epiglottis
cartilage, but matrix even more flexibility and auditory tubes.
also contains elastin than hyaline cartilage
ELASTIC fibers because elastic fibers
CARTILAGE return
to their original shape
after being stretched
SUPPORTING CONNECTIVE TISSUE: BONE
Hard, bony matrix Provides great strength All bones of the body.
predominates; many and support and
osteocytes (not seen in protects internal
BONE this bone preparation) organs, such as the
are located within brain; bone also
lacunae; the matrix is provides attachment
organized into layers sites for muscles
called lamellae and ligaments; the
joints of bones allow
rnovements
FLUID CONNECTIVE TISSUE
FLUID CONNECTIVE TISSUE: BLOOD
PHOTOS STRUCTURE FUNCTION LOCATION
Blood cells and a Transports oxygen. Within the blood
fluid matrix. carbon dioxide. vessels white blood
Hormones, nutrients cells frequently leave
waste products, and the blood vessels and
BLOOD other substances; enter the interstitial
protects the body from spaces
infections and is
involved in temperature
regulation
MUSCLE TISSUES
PHOTOS STRUCTURE FUNCTION LOCATION
Skeletal muscles cells Movement of the body; Attached to the bone or
or fibers appear under voluntary other connective
striated (banded); control. tissue.
SKELETAL cells are large, long,
MUSCLE and cylindrical, with
many nuclei.
Cardiac muscles cells Pumps the blood; under In the heart.
are cylindrical and involuntary
striated and have a (unconscious) control.
single nucleus; they
are branched and
connected to one
CARDIAC MUSCLE
another by intercalated
disks, which contain
gap junctions.
Smooth muscles cells Regulates the size of In hollow organs, such
are tapered at each organs, forces fluid as the stomach and
end, are not striated, through tubes, controls intestine; skin and
and have a single the amount of light eyes.
nucleus. entering the eye, and
produces
SMOOTH MUSCLE
“goosebumps” in the
skin; under involuntary
(unconscious) control.
NERVOUS TISSUES
STRUCTURE FUNCTION LOCATION
A neuron consists of Neurons transmit In the brain, spinal
dendrites, a cell body, information in the form cord and ganglia.
and a long axon; of action potentials,
neuroglia, or support store information, and
NEURON cells, surround the integrate and evaluate
neurons. data; neuroglia
support, protect and
form specialized sheaths
around axons.
You might also like
- Chapter 4 TissueDocument7 pagesChapter 4 TissueVince De PanoNo ratings yet
- Tissues UnfinishedDocument5 pagesTissues UnfinishedPessimus KidNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Histology Q&ADocument5 pagesEpithelial Histology Q&ANo NameNo ratings yet
- Fit Closely Has 1 Free Surface Epithelium Rests On A Basement Membrane Have No Blood Supply of Their Own From CapillariesDocument3 pagesFit Closely Has 1 Free Surface Epithelium Rests On A Basement Membrane Have No Blood Supply of Their Own From CapillariesCaithlyn KirthleyNo ratings yet
- Type of Epithelium CellDocument3 pagesType of Epithelium CellHo Shi XianNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 TissuesDocument6 pagesLesson 2 TissuesRodefe AmitNo ratings yet
- 4 - TissuesDocument13 pages4 - TissuesPrince TeodocioNo ratings yet
- WEEK 4 TRANS AnaphyDocument8 pagesWEEK 4 TRANS AnaphygazzyngsalvadorNo ratings yet
- Tissue Types and Functions GuideDocument4 pagesTissue Types and Functions GuideMicth Laica BetoyaNo ratings yet
- JI UNIT 2 Complete Notes - 9-10Document2 pagesJI UNIT 2 Complete Notes - 9-10Shubham PawadeNo ratings yet
- Tissues Pre LabDocument43 pagesTissues Pre LabCindy-chan DelfinNo ratings yet
- Title: Tissues: Simple Squamous EpitheliumDocument12 pagesTitle: Tissues: Simple Squamous EpitheliumManelli Faten Buenaventura100% (1)
- Types of Epithelial Tissues and Cell JunctionsDocument21 pagesTypes of Epithelial Tissues and Cell JunctionsbrihaspathiacademyNo ratings yet
- Four Types of Epithelial TissueDocument9 pagesFour Types of Epithelial TissueElyka AbellaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ANAPHY NOTESDocument13 pagesChapter 4 ANAPHY NOTESShannelle SinciocoNo ratings yet
- Simple Squamous Epithelium: VRMM2023Document5 pagesSimple Squamous Epithelium: VRMM2023VERONICA ROSE MAGPOCNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue Types & FunctionsDocument2 pagesEpithelial Tissue Types & FunctionsAdz Na HarNo ratings yet
- 07 Structural Organism in Animal Ncert MasterDocument12 pages07 Structural Organism in Animal Ncert MasterexercisestartNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument7 pagesConnective TissueSaif AliNo ratings yet
- A-P Chapter 4 TissueDocument21 pagesA-P Chapter 4 TissueMONIQUE VELASCONo ratings yet
- 1 EpithelialTissueWEBDocument27 pages1 EpithelialTissueWEBJR Rolf NeuqeletNo ratings yet
- Histology Table ReviewerDocument4 pagesHistology Table ReviewerDaNicaRaylaNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument40 pagesEpithelial TissueTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument6 pagesEpithelial TissueHM ChuaNo ratings yet
- Jaringan EpitelDocument20 pagesJaringan EpitelKitsune TakaNo ratings yet
- Type of Epithelium Illustration Characteristics Location FunctionDocument7 pagesType of Epithelium Illustration Characteristics Location FunctionRjosheNo ratings yet
- Epithelial and Glandular Tissues LectureDocument53 pagesEpithelial and Glandular Tissues LectureRubySzetoNo ratings yet
- The Epithelium: By: Maj Rizwan KianiDocument74 pagesThe Epithelium: By: Maj Rizwan Kianiviya7No ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue: Location of EpitheliumDocument3 pagesEpithelial Tissue: Location of EpitheliumVanyVillegasNo ratings yet
- The Tissues of The Body - The Epithelium: DR Iram IqbalDocument144 pagesThe Tissues of The Body - The Epithelium: DR Iram Iqbalimmmi100% (1)
- BIO2OO - Introduction Tissues, Classification of Living Things & Ecology 1.1.0 Animal TissueDocument19 pagesBIO2OO - Introduction Tissues, Classification of Living Things & Ecology 1.1.0 Animal TissueMark SullivanNo ratings yet
- Epithelia N Connective FunctionsDocument2 pagesEpithelia N Connective Functionsmaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- Epithelial-Cells 2Document5 pagesEpithelial-Cells 2Edeilaine JadraqueNo ratings yet
- ZOOLEC (Tissues Table)Document6 pagesZOOLEC (Tissues Table)JOHN ANDREW EVIANo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues Group 2Document39 pagesAnimal Tissues Group 2Danielle Kate MadridNo ratings yet
- Lec Activity4 Tissues PDFDocument6 pagesLec Activity4 Tissues PDFYda Maxine PalmaNo ratings yet
- Single Squamous EpitheliumDocument28 pagesSingle Squamous EpitheliumLyndonn Santos100% (1)
- Epithelial TissueDocument7 pagesEpithelial TissueJoan PaulineNo ratings yet
- Epithelial: Type of Tissue CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesEpithelial: Type of Tissue CharacteristicsGlanela ManalotoNo ratings yet
- Connective and Epithelial MSHBDocument6 pagesConnective and Epithelial MSHBPNo ratings yet
- Tissues: DR - Tooba Rehan Pharm-DDocument42 pagesTissues: DR - Tooba Rehan Pharm-DShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Epithelial TissueDocument65 pagesGroup 1 Epithelial TissuesoraruNo ratings yet
- ANIMAL TISSUE & ORGAN SYSTEMSDocument30 pagesANIMAL TISSUE & ORGAN SYSTEMShafiz amriNo ratings yet
- GUMAPAC. Lab Act 4 Epithelial TissuesDocument5 pagesGUMAPAC. Lab Act 4 Epithelial TissuesClifford CastaritasNo ratings yet
- L2 EpitheliumDocument4 pagesL2 EpitheliumGlysa MaeNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument2 pagesEpithelial TissueRona Mae LabistoNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument2 pagesAnimal TissuesMami AmihanNo ratings yet
- Histology - Epithelial TissuesDocument4 pagesHistology - Epithelial TissuesKrissa OmandamNo ratings yet
- Baguio City National Science High School Cell TypesDocument8 pagesBaguio City National Science High School Cell TypesMEDRANO, Hana Jhiemyka O.No ratings yet
- Activity No. 5 TISSUES GANDocument7 pagesActivity No. 5 TISSUES GANTORRES, EFRAIM MATTHEW S.No ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue (Epithelium) : General Characteristics of EpitheliumDocument22 pagesEpithelial Tissue (Epithelium) : General Characteristics of EpitheliumMahmoud IdlbiNo ratings yet
- Body TissuesDocument10 pagesBody TissuesAlther LorenNo ratings yet
- 4 TissuesDocument5 pages4 TissuesEly FructuosoNo ratings yet
- Histology ReviewerDocument11 pagesHistology ReviewerMaryell Denize LandichoNo ratings yet
- Jaringan Dasar 1 BDocument20 pagesJaringan Dasar 1 BJIHAN ISMAILNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 2 The Epithelial TissueDocument3 pagesLaboratory 2 The Epithelial TissueJoshtwotown EarnshawNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Mia Rev3Document5 pagesAnaphy Mia Rev3antonettevegamia3No ratings yet
- HistologyDocument16 pagesHistologyJeong song parkNo ratings yet
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)From EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)No ratings yet
- TFN WK 13 15Document57 pagesTFN WK 13 15xuxi dulNo ratings yet
- PDF ResizeDocument38 pagesPDF Resizexuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Speech of Her Excellency Corazon C. Aquino President of The Philippines During The Joint Session of The United States CongressDocument4 pagesSpeech of Her Excellency Corazon C. Aquino President of The Philippines During The Joint Session of The United States Congressjonard tanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Excerpt From Alfred McCoy and Alfredo Roces' Political Caricatures of The American EraDocument1 pageLesson 2 Excerpt From Alfred McCoy and Alfredo Roces' Political Caricatures of The American Eraxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- 2 Run Ons Fragments Comma Slices Redundancy and WordinessDocument3 pages2 Run Ons Fragments Comma Slices Redundancy and Wordinessxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- 1 BiodiversityDocument10 pages1 Biodiversityxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- TFN FinalsDocument23 pagesTFN Finalsxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Passive and active voice verbs explainedDocument14 pagesPassive and active voice verbs explainedxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Purc111 MidtermsDocument8 pagesPurc111 Midtermsxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Arta Finals Reviewer PDFDocument30 pagesArta Finals Reviewer PDFxuxi dul100% (1)
- The elements and underlying meanings in artDocument5 pagesThe elements and underlying meanings in artxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Stas Finals LecsDocument45 pagesStas Finals Lecsxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- 3 Gmo and NanotechnologyDocument10 pages3 Gmo and Nanotechnologyxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Finals ReviewerDocument193 pagesAnaphy Finals Reviewerxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- 2 Information AgeDocument3 pages2 Information Agexuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Purcomm RevDocument6 pagesPurcomm Revxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Human-tech relationship exploredDocument3 pagesHuman-tech relationship exploredxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Matm FinalsDocument7 pagesMatm Finalsxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Pupr Final LectureDocument6 pagesPupr Final Lecturexuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Stas Lecture ReviewerDocument22 pagesStas Lecture Reviewerxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- 9 Why Future Does Not Need UsDocument4 pages9 Why Future Does Not Need Usxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Midterm ReviewerDocument6 pagesMidterm Reviewerxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- 5 Human Flourishing in S and T Oct 29 2021Document3 pages5 Human Flourishing in S and T Oct 29 2021xuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Coleng Midterm Merge NotesDocument15 pagesColeng Midterm Merge Notesxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Circulatory System - The HeartDocument14 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Circulatory System - The Heartxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- 6 Human Flourishing October 26 2021Document3 pages6 Human Flourishing October 26 2021xuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions and InterjectionsDocument3 pagesConjunctions and Interjectionsxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- HAPP Week VII XDocument32 pagesHAPP Week VII Xxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Respiratory Systemxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument11 pagesThe Cellxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Hillbrandt Axel CV AH-PC E 1216Document4 pagesHillbrandt Axel CV AH-PC E 1216HillbrandtNo ratings yet
- De Longhi Heating Radiators Provide Quality, Practicality and Environmental BenefitsDocument16 pagesDe Longhi Heating Radiators Provide Quality, Practicality and Environmental BenefitsVladimirNo ratings yet
- Asco Froment 6000 Series Combined Manual PDFDocument114 pagesAsco Froment 6000 Series Combined Manual PDFEdward OsoreNo ratings yet
- Door Frame Cutout and Wire Transfer Installation GuideDocument1 pageDoor Frame Cutout and Wire Transfer Installation Guiderodney_massieNo ratings yet
- Filtration and Chromatography TechniquesDocument30 pagesFiltration and Chromatography TechniquesJayabrata DasNo ratings yet
- TSA-5 Electrical Wiring Installation Permit ApplicationDocument1 pageTSA-5 Electrical Wiring Installation Permit ApplicationMyrene Ambas-BoslengNo ratings yet
- gg1 Engineer S Controls Classic TrainsDocument1 pagegg1 Engineer S Controls Classic Trainsbaron mNo ratings yet
- .Umerical $istance 0rotection 2elay 3) 02/4%# 3!:) Nstruction - AnualDocument326 pages.Umerical $istance 0rotection 2elay 3) 02/4%# 3!:) Nstruction - AnualngocanhvyNo ratings yet
- TC 10 19 PDFDocument159 pagesTC 10 19 PDFamare addisNo ratings yet
- Transformer protection with RET670Document9 pagesTransformer protection with RET670Saransh KumarNo ratings yet
- Kovaz S.r.o.: Rod SealDocument5 pagesKovaz S.r.o.: Rod SealAyman AlhalfawyNo ratings yet
- Riser Diagram PDFDocument1 pageRiser Diagram PDFChristian FloresNo ratings yet
- Wolfson Eup3 Ch34 Test BankDocument17 pagesWolfson Eup3 Ch34 Test BankifghelpdeskNo ratings yet
- PPMP 2023 - MO - Repair & MaintenanceDocument9 pagesPPMP 2023 - MO - Repair & MaintenanceRosalie Baldivino GarsulaNo ratings yet
- 1015p Io BoardDocument13 pages1015p Io BoardContreras CarlosNo ratings yet
- Installation, Operation, and Maintenance: Packaged Fresh Air UnitDocument84 pagesInstallation, Operation, and Maintenance: Packaged Fresh Air UnitAdrian ReyesNo ratings yet
- E C S PDFDocument412 pagesE C S PDFRájDèép TrìpâţhíNo ratings yet
- 928 Diagnostics Manual v2.7Document67 pages928 Diagnostics Manual v2.7Roger Sego100% (2)
- Magnetrol TD1Document16 pagesMagnetrol TD1mrizalygani99No ratings yet
- 220kv GSSDocument46 pages220kv GSSAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- EMD-FL-V 2866048 - DsDocument8 pagesEMD-FL-V 2866048 - DsAhmad DanishNo ratings yet
- Bronzeystrainer - Kvs 200 TDocument1 pageBronzeystrainer - Kvs 200 TTiến Lý NhậtNo ratings yet
- EssayDocument12 pagesEssayapi-602966374No ratings yet
- Nissan SwotDocument40 pagesNissan SwotAbhijit Kardekar0% (1)
- Droop CalculationDocument3 pagesDroop CalculationAnonymous CO7aaHrNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and OrganisationDocument15 pagesCell Structure and Organisationzulkarnain100% (4)
- Paper PDFDocument7 pagesPaper PDFadeel rafiqNo ratings yet
- Increasing The Price of Petrol The Best WayDocument3 pagesIncreasing The Price of Petrol The Best Way樊吉No ratings yet
- GCP-HARP-1004 - College of Magics PDFDocument127 pagesGCP-HARP-1004 - College of Magics PDFMartin Gualdarrama50% (2)
- Easy Altivar 310 - ATV310HU55N4EDocument6 pagesEasy Altivar 310 - ATV310HU55N4EPhaniNo ratings yet