Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nervous System
Uploaded by
Aly HannahCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nervous System
Uploaded by
Aly HannahCopyright:
Available Formats
Nervous System
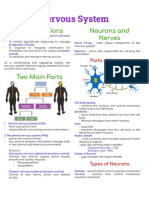
FUNCTIONS WHAT IS IT?
1. Sensory input: Fatty, protective wrapping around axons
- Sensory receptors respond to stimuli Excellent insulator
2. Integration:
- Brain & spinal cord process stimuli NODES OF RANVIER
3. Control of muscles and glands Gaps in myelin sheath where action
4. Mental activity: brain potentials develop
5. Homeostasis
SALTATORY CONDUCTION
Jumping action potentials
MAIN DIVISIONS OF NS MYELINATED AXONS
Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and spinal Conduct action potentials faster (3-15 m/s)
cord than unmyelinated due to Nodes of Ranvier
**Multiple Sclerosis
Peripheral Nervous System All neurons Disease of myeline sheath that causes loss
(PNS) outside CNS of muscle function
NEURON CHARACTERISTICS
Nerve cells
Require oxygen and glucose
Receive input, process input, produce a
response
NEURON STRUCTURES
Dendrite Receives stimulus from
other neurons or
sensory receptors
Cell body Processes stimulus
Contains nucleus
Axon Transmits stimulus to a
gland, muscle, organ, or
other neuron
TYPES OF NEURONS
MYELIN SHEATH
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY – NERVOUS SYSTEM
Nervous System
Multipolar - Many dendrites Oligodendrocytes Schwann Cells
Ex. CNS and most motor - Single axon Produce myelin sheath
neurons
Nerve tracts Nerves
Bipolar - One dendrite Collection of axons
Ex. sense organs like eye - One axon Nuclei Ganglion
and nasal cavity - One process that Collection of cell bodies
serves as the
dendrite and axon
- Have sensory ELECTRICAL SIGNALS & NEURAL
functions PATHWAYS
Resting Membrane Potential
Pseudo-unipolar - One axon Outside of cell is more + (Na+)
Ex. sensory neurons - No dendrites Inside of cell is more – (K+)
- Group together to
form ganglia Leak ion channels: Gated ion channels:
- Have sensory - Always open - Closed until opened
functions - K+ channels by specific signal
- Na+ channels
NEUROGLIA CHARACTERISTICS
- Supporting cells for neurons
- More numerous than neurons
- Can divide to produce more cells
[1] Astrocytes
Star-shaped
Most-abundant
Form blood-brain barrier
[2] Ependymal Cells
Produce and circulate cerebrospinal fluid
(CSF)
[3] Microglia
Help remove bacteria and cell debris from
CNS
Phagocytotic
[4] Oligodendrocytes
Produce myelin sheath in CNS
[5] Schwann cells
Produce myelin sheath in PNS
ORGANIZATION OF NERVOUS TISSUE
Gray matter Collection of dendrites
and cell bodies
White matter Collection of axons and
their myelin sheath
CNS PNS
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY – NERVOUS SYSTEM
Nervous System
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY – NERVOUS SYSTEM
You might also like
- (Oct 1) Nervous-SystemDocument78 pages(Oct 1) Nervous-SystemBea GualbertoNo ratings yet
- Nervous TissueDocument49 pagesNervous TissueDAVE CANALETANo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 The Nervous System (ANAPHY)Document7 pagesChapter 7 The Nervous System (ANAPHY)Krisha AvorqueNo ratings yet
- The nervous system in 40 charactersDocument12 pagesThe nervous system in 40 charactersLol lol100% (2)
- Konsep Dasar Ilmu Biokimia Dan Biologi Molekuler Untuk Sistem SarafDocument31 pagesKonsep Dasar Ilmu Biokimia Dan Biologi Molekuler Untuk Sistem SarafdiandraNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System First PartDocument15 pagesThe Nervous System First PartNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Nissl Bodies-Sites of Protein Synthesis in NeuronsDocument16 pagesNervous System: Nissl Bodies-Sites of Protein Synthesis in NeuronsZella ViaNo ratings yet
- Physio Lec 6 Apr 2021Document3 pagesPhysio Lec 6 Apr 2021Luis IbarrolaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Lecture Outline: Nerves Are VascularizedDocument6 pagesChapter 12 Lecture Outline: Nerves Are VascularizedBEATRIZ MITZI BEHAGAN BALINGITNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesThe Nervous SystemnixicoleNo ratings yet
- Nervous System PDFDocument9 pagesNervous System PDFJomeena MaeNo ratings yet
- (w14) Nervous Tissue and Nervous SystemDocument7 pages(w14) Nervous Tissue and Nervous Systemden mNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissues HandoutsDocument6 pagesNervous Tissues HandoutsKelly TrainorNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy Unit 5 Notes ReviewerDocument16 pagesAnaPhy Unit 5 Notes Reviewer쥬얼이No ratings yet
- Transes Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesTranses Nervous SystemAlther LorenNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Reviewer (Semi Finals)Document5 pagesAnaphy Reviewer (Semi Finals)Sophia Mae ClavecillaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Reviewer (Semi Finals)Document28 pagesAnaphy Reviewer (Semi Finals)Sophia Mae ClavecillaNo ratings yet
- Neurology Week 1 Trans 01 31 23Document3 pagesNeurology Week 1 Trans 01 31 23anime listNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue Development and ComponentsDocument5 pagesNervous Tissue Development and ComponentsAlyssa AlferezNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Support Cells and Peripheral Nervous System FunctionsDocument5 pagesNervous System Support Cells and Peripheral Nervous System FunctionsBrent ValdespinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesChapter 8 - Nervous SystemlalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 AnaphyDocument11 pagesChapter 7 AnaphySymonette OcturaNo ratings yet
- BioPsychology Chapter 34Document10 pagesBioPsychology Chapter 34Johnreih BanggaNo ratings yet
- CNS PNS: Absent in AxonsDocument6 pagesCNS PNS: Absent in AxonsDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Nervous SystemDocument39 pagesUnit 2 - Nervous SystemzulieyanaNo ratings yet
- Functions of the nervous systemDocument20 pagesFunctions of the nervous systemLapitan Jared Anne S.No ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves Carry Impulses To and From The: The Central Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesCranial Nerves Carry Impulses To and From The: The Central Nervous SystemLuiciaNo ratings yet
- 1 Nervous System OutlinesDocument45 pages1 Nervous System OutlinesTestingAccNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy: Muh - Iqbal Basri Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversityDocument19 pagesNeuroanatomy: Muh - Iqbal Basri Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversitySuardimanAchoNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy - Nervous TissueDocument73 pagesAnaPhy - Nervous TissuesoraruNo ratings yet
- Excitable TissueDocument117 pagesExcitable Tissueur.yared21No ratings yet
- Histology 7 Nerve TissueDocument82 pagesHistology 7 Nerve TissueAbdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Histology of Nervous Tissue: Neurons, Glia, SynapsesDocument39 pagesHistology of Nervous Tissue: Neurons, Glia, SynapsesRamesh KumarNo ratings yet
- NEUROANATOMY IntroductionDocument10 pagesNEUROANATOMY IntroductionIshant SinghNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ANAPHY NotesDocument10 pagesNervous System ANAPHY NotesAlloiza CaguiclaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesNervous SystemSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- Histology of Nervous TissueDocument35 pagesHistology of Nervous TissueGlenn Rey D. AninoNo ratings yet
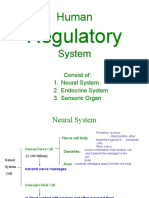
- Human Regulatory SystemDocument37 pagesHuman Regulatory SystemRudolfNo ratings yet
- #4 Nervous-SystemDocument19 pages#4 Nervous-SystemLapitan Jared Anne S.No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesNervous SystemYUAN FRANCIS SINGCULANNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: © 2009 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument110 pagesThe Nervous System: © 2009 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights ReservedMica BernardoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesAnaphy Nervous SystemAndrea SaldivarNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Nervous TissueDocument43 pagesPhysiology of Nervous TissueD Tek100% (1)
- Mindmap Bio621 Chapter1Document3 pagesMindmap Bio621 Chapter1MizahNo ratings yet
- Nervous System 2Document7 pagesNervous System 2Darlin Karyle EncisoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy MIDTERMS ReviewerDocument45 pagesAnaphy MIDTERMS Reviewerangelita aquinoNo ratings yet
- Unit III Nervous System and ElectromyographyDocument100 pagesUnit III Nervous System and ElectromyographymanasiNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy Lab Nervous NotesDocument7 pagesAnaPhy Lab Nervous NotesDING ANG BATONo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Nervous ReviewerDocument18 pagesChapter 8 - Nervous Reviewerchristian anchetaNo ratings yet
- 49 Neural Regulation in Animals-2018 PDFDocument61 pages49 Neural Regulation in Animals-2018 PDFlaw0516No ratings yet
- CNS PNS: Lipofuscin: Wear and TearDocument10 pagesCNS PNS: Lipofuscin: Wear and TearDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Introduction Into The Nervous System 2017-18Document58 pagesIntroduction Into The Nervous System 2017-18maodNo ratings yet
- CSE485 Lec3 Neurons SensationPerception M2021Document30 pagesCSE485 Lec3 Neurons SensationPerception M2021Monica PonnamNo ratings yet
- lecture 1Document30 pageslecture 1Osama adel Mohamed SmadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 (Anaphy)Document2 pagesChapter 8 (Anaphy)SKYdrum H20No ratings yet
- Pearson Nervous System ReviewerDocument8 pagesPearson Nervous System ReviewerViaBNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Session 1Document104 pagesNervous System Session 1Jojo LouNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing 64 PagsDocument64 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing 64 Pagstanya nNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesNervous Systemsophialara.vitug.nurNo ratings yet
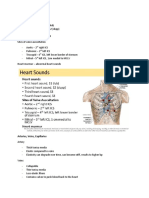
- Heart Sounds and Cardiac Cycle GuideDocument9 pagesHeart Sounds and Cardiac Cycle GuideAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Organic Compounds: Functional GroupsDocument34 pagesOrganic Compounds: Functional GroupsAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Quantum Numbers S3Document16 pagesQuantum Numbers S3Aly HannahNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument10 pagesUrinary SystemAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Quantum NumbersDocument4 pagesQuantum NumbersAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Health AssessmentDocument10 pagesPrenatal Health AssessmentAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Properties of AtomsDocument3 pagesMagnetic Properties of AtomsAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Pt. 2 SummaryDocument16 pagesGas Laws Pt. 2 SummaryAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Mole ConceptDocument5 pagesMole ConceptAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Combined & Ideal Gas LawDocument12 pagesCombined & Ideal Gas LawAly HannahNo ratings yet
- AtomsDocument8 pagesAtomsAly HannahNo ratings yet
- IMF Liquids and SolidsDocument29 pagesIMF Liquids and SolidsAly HannahNo ratings yet
- IsomersDocument15 pagesIsomersAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Electron Configuration & Orbital DiagramDocument3 pagesElectron Configuration & Orbital DiagramAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System Defense GuideDocument10 pagesLymphatic System Defense GuideAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Functions and AnatomyDocument13 pagesRespiratory System Functions and AnatomyAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument17 pagesChemical BondingAly HannahNo ratings yet
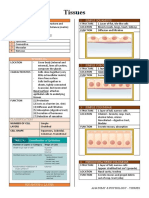
- Tissues: Types and FunctionsDocument4 pagesTissues: Types and FunctionsAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument5 pagesBlood VesselsAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Organization of the Human BodyDocument8 pagesOrganization of the Human BodyAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Amco Veba Marine - Brochure - LRDocument24 pagesAmco Veba Marine - Brochure - LRHươngTpuNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Pruning Equipment American Arborist Supplies, Tree Care, Climbing EquipmentDocument1 pagePneumatic Pruning Equipment American Arborist Supplies, Tree Care, Climbing EquipmentSalman JoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Chemical EquilibriumDocument29 pagesChapter 14 Chemical EquilibriumlynloeNo ratings yet
- Columbus Files Motion To Dismiss Bankruptcy Claim by Latitude Five25 OwnersDocument38 pagesColumbus Files Motion To Dismiss Bankruptcy Claim by Latitude Five25 OwnersWSYX/WTTENo ratings yet
- Design & Operation of Clean Room-1Document39 pagesDesign & Operation of Clean Room-1Hafizur Rahman0% (1)
- Design of A Tuned Intake Manifold - H. W. Engelman (ASME Paper 73-WA/DGP-2)Document9 pagesDesign of A Tuned Intake Manifold - H. W. Engelman (ASME Paper 73-WA/DGP-2)david_luzNo ratings yet
- Pantheon-Katalog Eng WebDocument16 pagesPantheon-Katalog Eng WebJoe DoeNo ratings yet
- Category D Fluid ServiceDocument2 pagesCategory D Fluid Serviceaslam.ambNo ratings yet
- Wood Plastic and CompositesDocument5 pagesWood Plastic and CompositesBenjie LatrizNo ratings yet
- Bread and Pastry Production NCII June 10, 2019 - July 03, 2019 ReviewerDocument14 pagesBread and Pastry Production NCII June 10, 2019 - July 03, 2019 ReviewerJames BaculaNo ratings yet
- Rules For The CertificationDocument84 pagesRules For The CertificationhdelriovNo ratings yet
- Queer Ecology Critique - Georgetown 2014Document104 pagesQueer Ecology Critique - Georgetown 2014Evan JackNo ratings yet
- Essotherm 500 PDFDocument8 pagesEssotherm 500 PDFdonyaNo ratings yet
- F0a7c Compal LA-A994p r1.0 2014Document38 pagesF0a7c Compal LA-A994p r1.0 2014DeyProNo ratings yet
- Well Rounded.: 360 CassetteDocument12 pagesWell Rounded.: 360 CassetteMonty Va Al MarNo ratings yet
- Conduction Calorimetric Investigation of The Effect of Retarders On The Hydration of Portland CementDocument15 pagesConduction Calorimetric Investigation of The Effect of Retarders On The Hydration of Portland CementAlfredo Landaverde GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Circuits Review P2Document44 pagesCircuits Review P2José CastilloNo ratings yet
- Resource Guide: Three Phase PowerDocument8 pagesResource Guide: Three Phase PowerddNo ratings yet
- Legend of Nueva VizcayaDocument10 pagesLegend of Nueva VizcayaAndreanna Maria100% (1)
- Time Rates ExplainedDocument6 pagesTime Rates ExplainedAljohn Escalona100% (1)
- Thermal Performance of Air-Cooled Condensing Units by CFD SimulationDocument2 pagesThermal Performance of Air-Cooled Condensing Units by CFD SimulationFauziah JeraiNo ratings yet
- Random Variate Generation-1Document21 pagesRandom Variate Generation-1Christian Delas AlasNo ratings yet
- 3 Pipe Mod For Vectra BDocument2 pages3 Pipe Mod For Vectra BEmirhan DöngelNo ratings yet
- 3M CatalogueDocument32 pages3M Cataloguefandi.azs37No ratings yet
- Terpin Hydrate Oral SolutionDocument1 pageTerpin Hydrate Oral SolutionAbelard Maria EscrivaNo ratings yet
- Common Mistakes in Dimensional Calibration MethodsDocument16 pagesCommon Mistakes in Dimensional Calibration MethodssujudNo ratings yet
- A Grammar of Anong Language Death Under Intense ContactDocument409 pagesA Grammar of Anong Language Death Under Intense ContacthaoyichuanNo ratings yet
- Effect of Pregnancy Induced Hypertension on Mothers and Babies Hematological ProfilesDocument3 pagesEffect of Pregnancy Induced Hypertension on Mothers and Babies Hematological ProfilesAbdifatah AhmedNo ratings yet
- Understanding of AVO and Its Use in InterpretationDocument35 pagesUnderstanding of AVO and Its Use in Interpretationbrian_schulte_esp803100% (1)
- Confined Space Entry: OSHA Standard 1910.146Document38 pagesConfined Space Entry: OSHA Standard 1910.146SKH CultureNo ratings yet