Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Preengineeredbuildingpptrit 150822180736 Lva1 App6891
Uploaded by
Garvit Chandrayan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views27 pagesThis document discusses a study of pre-engineered buildings conducted by four students under the guidance of a professor. The objectives were to model, analyze, and design a pre-engineered building structure using Staad Pro. Load calculations were performed and load combinations analyzed. The results showed that the pre-engineered building design reduced steel quantity, support reactions, deflection, shear force, and maximum moment compared to a conventional steel building. Advantages of pre-engineered buildings included reduced cost, quality control, and ease of future expansions.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses a study of pre-engineered buildings conducted by four students under the guidance of a professor. The objectives were to model, analyze, and design a pre-engineered building structure using Staad Pro. Load calculations were performed and load combinations analyzed. The results showed that the pre-engineered building design reduced steel quantity, support reactions, deflection, shear force, and maximum moment compared to a conventional steel building. Advantages of pre-engineered buildings included reduced cost, quality control, and ease of future expansions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views27 pagesPreengineeredbuildingpptrit 150822180736 Lva1 App6891
Uploaded by
Garvit ChandrayanThis document discusses a study of pre-engineered buildings conducted by four students under the guidance of a professor. The objectives were to model, analyze, and design a pre-engineered building structure using Staad Pro. Load calculations were performed and load combinations analyzed. The results showed that the pre-engineered building design reduced steel quantity, support reactions, deflection, shear force, and maximum moment compared to a conventional steel building. Advantages of pre-engineered buildings included reduced cost, quality control, and ease of future expansions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 27
Submitted By:
Shubham V. Parab 1202016
Akshay A. Nikam 1202019
Sujit H. Sonwalkar 1202015
Aniket K. Mane 1202032
Under the guidance of :Prof.P.M.Mohite
Objectives
To study pre engineered building.
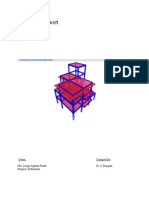
To prepare a model of P.E.B.
To analyze structure using Staad Pro.
To design sections, connections etc.
To study the effect of P.E.B. for following issues:
To reduce complexity on site.
To achieve accuracy.
Speed of work.
Pre Engineered Building
Steel buildings in which excess steel is avoided by
Tapering the sections.
Tapering is done as per Bending Moment
requirements.
Components are manufactured in factory and
assembled on site.
Larger plate dimensions are used in areas of higher
load effects.
Plan
Elevation
Problem statement
Internal dimensions of building: l=60 m, b=15 m
Height of building up to eaves level= 6 m
Location of building= Islampur (pune region)
Type of roofing = G.I.sheets
Area of opening (permeability of building 5% to 20%)
Angle of rafter = < 100
Spacing between two columns = 6 m
Number of frames = 10
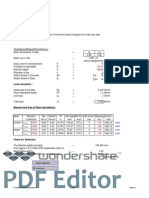
Load calculation
Dead load:
1. Wight of purlin :5 kg/m2
2. Weight of sheeting :5 kg/m2
Total weight :10 kg/m2=0.1kN/m2
3. Self weight of tapered section
Live load
Live load =0.75 kN/m2 (Angle lesthan 10 0)
= 0.75*6
Live load =4.5 kN/m2
Collateral load:
Collateral load = 0.2* 6 =1.2 KN/M
(Assumed)
Wind load
Load comination
Load combination of strength:
(D.L.+L.L.)*1.5+1.05 *C.L.
(D.L.+W.L.S.)*1.5
(D.L.+W.R.P.)*1.5
(D.L.+W.R.S.)*1.5
(D.L.+W.P.P.)*1.5
(D.L.+W.P.S.)*1.5
(D.L.+L.L.)*1.2+1.05*C.L.+0.6* W.L.P.
(D.L.+L.L.)*1.2+1.05*C.L.+0.6* W.L.S.
(D.L.+L.L.)*1.2+1.05*C.L.+0.6* W.R.P.
(D.L.+L.L.)*1.2+1.05*C.L.+0.6* W.R.S.
(D.L.+L.L.)*1.2+1.05*C.L.+0.6* W.P.P.
(D.L.+L.L.)*1.2+1.05*C.L.+0.6* W.P.S.
Load combination of serviceability:
(D.L.+L.L.+C.L.)*1
D.L.* 1+(L.L.+C.L+W.L.P.)*0.8
D.L.* 1+(L.L.+C.L+W.L.S.)*0.8
D.L.* 1+(L.L.+C.L+W.R.P.)*0.8
D.L.* 1+(L.L.+C.L+W.R.S.)*0.8
D.L.* 1+(L.L.+C.L+W.P.P.)*0.8
D.L.* 1+(L.L.+C.L+W.P.S.)*0.8
(D.L.+W.L.P.)*1
(D.L.+W.L.S.)*1
(D.L.+W.R.P.)*1
(D.L.+W.R.S.)*1
(D.L.+W.P.P.)*1
(D.L.+W.P.S.)*1
B.M.D.
CONVENTIONAL PRE ENGINEERED
BUILDING BUILDING
Results
Sl. No. Description PEB CSB
1 Steel Take Off (kN) 12.194 84.595
2 Support Reaction (kN) 10.62 375.582
3 Maximum deflection (mm) 39.48 8.611
4 Maximum Shear Force (kN) 66.894 453.981
5 Maximum Moment (kNm) 175.52 908.577
Advantages
PEB System is zero maintenance & superior in strength
than conventional.
Lower Cost.
Quality Control.
Large Clear Spans.
strict quality control environment, thereby ensuring
superior quality & finish.
Easier to incorporate future expansions
Disadvantages
Not used for multi-storey building.
Technical person is required on site.
Special Machinery is required.
Design of member takes more time.
Conclusion
Using of PEB instead of CSB may be reducing the steel
quantity.
Reduction in the steel quantity definitely reducing the
dead load.
Reduction in the dead load reducing the size of
Foundation.
Using of PEB increase the Aesthetic view of structure.
Applications
WARE HOUSES
INDUSTRIAL SHEDS
FACTORIES
WORKSHOPS
OFFICES
GAS STATIONS
VEHICLE PARKING SHEDS
SHOW ROOMS
AIRCRAFT HANGERS
SCHOOLS
SPORTS AND RECREATIONAL FACILITIES
Erecting P.E.B.
Reference
Limit State Design in Structural Steel- M. Y . Shiyekar.
Pre-Engineered metal Buildings the latest trend in building
construction‖ by K.K.Mitra – Gen. Manager (marketing)
Lloyd Insulations (India) Limited
IS : 800 - 2007 :- General Construction In Steel - Code of
Practice.
IS : 875 (Part 1) - 1987 :- Code of Practice for Design Loads
(Other Than Earthquake) for Buildings
IS : 875 (Part 2) - 1987 :- Code of Practice for Design
Loads (Other Than Earthquake) for Buildings and
Structures- Live Loads.
IS : 875 (Part 3) - 1987 :- Code of Practice for Design
You might also like
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Structural Analysis and Design Report of Car Wash Center: September, 2017Document30 pagesStructural Analysis and Design Report of Car Wash Center: September, 2017Samikshya ShahNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Steel Buildings: A Practical Guide for Structures and EnvelopesFrom EverandSustainable Steel Buildings: A Practical Guide for Structures and EnvelopesBernhard HaukeNo ratings yet
- Warehouse DBR 29-07-2020Document6 pagesWarehouse DBR 29-07-2020KaushikNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Pre-Engineered Building With Subjected To Seismic Loads Using E-TabsDocument4 pagesDesign and Analysis of Pre-Engineered Building With Subjected To Seismic Loads Using E-TabsFaisal AminNo ratings yet
- Modernisation, Mechanisation and Industrialisation of Concrete StructuresFrom EverandModernisation, Mechanisation and Industrialisation of Concrete StructuresNo ratings yet
- Sgepl-Dcbl - S01-Ce-Doc-05 - Mms Design Calc & Staad Report - r03Document321 pagesSgepl-Dcbl - S01-Ce-Doc-05 - Mms Design Calc & Staad Report - r03Sumit TyagiNo ratings yet
- Infrastructure Systems for Nuclear EnergyFrom EverandInfrastructure Systems for Nuclear EnergyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Element 45 - 1538-NOTE 2Document35 pagesElement 45 - 1538-NOTE 2hadeer youns100% (1)
- Introduction to Design of Building StructuresFrom EverandIntroduction to Design of Building StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (22)
- Design Calculations: For Steel StructureDocument46 pagesDesign Calculations: For Steel Structurethiện50% (2)
- PEB StructuresDocument36 pagesPEB StructuresVikas Singh Chandel100% (7)
- Full SynopsisDocument12 pagesFull SynopsisAg NeerajNo ratings yet
- Truss Design For 60m Span PDFDocument7 pagesTruss Design For 60m Span PDFPn Ekanayaka100% (1)
- College Building DBRDocument171 pagesCollege Building DBRchetanchintaNo ratings yet
- Design Basis Report: Case Study: Commercial BuildingDocument6 pagesDesign Basis Report: Case Study: Commercial BuildingMargaux MacalinoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 SeniorDocument55 pagesAssignment 2 SeniorRohit SarodeNo ratings yet
- Pran RFL (Factory Building-4) Olipur, SayestagonjDocument13 pagesPran RFL (Factory Building-4) Olipur, Sayestagonjshafiq_05No ratings yet
- Design and Analysis OF Multi-Storied BuildingsDocument41 pagesDesign and Analysis OF Multi-Storied BuildingsDeepak Bharati100% (1)
- STRUCTURAL DESIGN ReportDocument25 pagesSTRUCTURAL DESIGN ReportRajendra AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Design of Peb StructureDocument36 pagesDesign of Peb StructureAnonymous UibQYvc675% (4)
- Full MPDocument25 pagesFull MPAzhar AndikanNo ratings yet
- Slab Design CombinedDocument28 pagesSlab Design CombinedEr. Rajendra Acharaya0% (1)
- Designofsteelstructures BS5950 PDFDocument100 pagesDesignofsteelstructures BS5950 PDFavisheklochunNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Industrial TrainingDocument38 pagesSeminar On Industrial TrainingGirish KgNo ratings yet
- Gate Cyllabus For SivilDocument36 pagesGate Cyllabus For SivilShubhabrata BarmaNo ratings yet
- Characteristic Performance of PEB Vs CSBDocument19 pagesCharacteristic Performance of PEB Vs CSBAyon SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Irjet V7i9576Document4 pagesIrjet V7i9576umashankaryaligarNo ratings yet
- Project 2 ReportDocument26 pagesProject 2 Reportarjun kumarNo ratings yet
- PEB StructuresDocument36 pagesPEB StructuresDass DassNo ratings yet
- Optimum Design of An Industrial Warehouse Using Staad-ProDocument4 pagesOptimum Design of An Industrial Warehouse Using Staad-PromahalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel Elements As Per Is 800Document28 pagesDesign of Steel Elements As Per Is 800Darshit Vejani100% (1)
- Affordable Housing DesignDocument17 pagesAffordable Housing DesignClethHirenNo ratings yet
- Irjet V5i6276Document5 pagesIrjet V5i6276Vinit KondapureNo ratings yet
- Design of Tension MemberDocument37 pagesDesign of Tension MemberTariq HasanNo ratings yet
- Design Base Report - A5Document11 pagesDesign Base Report - A5pravincs_007No ratings yet
- IT Park DesignDocument53 pagesIT Park DesignYashu YashuNo ratings yet
- Analysis Report: Residential Building, Dhapasi, KathmanduDocument7 pagesAnalysis Report: Residential Building, Dhapasi, KathmanduKalpanaNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Peb-StructuresDocument36 pagesDokumen - Tips Peb-Structuresrahulshah3994No ratings yet
- DesignDocument of G+22 Roof Canopy R5-02 OCT2016 PDFDocument188 pagesDesignDocument of G+22 Roof Canopy R5-02 OCT2016 PDFmsiddiq1No ratings yet
- Final Report On WordDocument15 pagesFinal Report On WordBheemm Bomjan Professional TrainerNo ratings yet
- Irjet V5i6276 PDFDocument5 pagesIrjet V5i6276 PDFAkula VeerrajuNo ratings yet
- Load Calculations PDFDocument19 pagesLoad Calculations PDFJeffrey Buquing ValdezNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument28 pages1 IntroductionStar998No ratings yet
- Review of Typified Designs of Trusses in The Context of Revised IS CodeDocument7 pagesReview of Typified Designs of Trusses in The Context of Revised IS CodeBasava SowmyaNo ratings yet
- Analysis & Design of (G+5) Building (RCC+Steel) Using Staad-ProDocument3 pagesAnalysis & Design of (G+5) Building (RCC+Steel) Using Staad-ProShravil SingroleNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Steel StructureDocument5 pagesIntroduction of Steel StructureAbhi ANo ratings yet
- The FinalDocument45 pagesThe FinalEndalk azeneNo ratings yet
- Design Report ALH 250Document18 pagesDesign Report ALH 250Sanjeev VermaNo ratings yet
- Design Report ALH 250 PDFDocument18 pagesDesign Report ALH 250 PDFSanjeev VermaNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument12 pagesAbstractErwin MaguideNo ratings yet
- Design Base Report - A5Document11 pagesDesign Base Report - A5pravincs_007No ratings yet
- Structural Design Calculations of Canopy Structure at Al Khanoor SchoolDocument5 pagesStructural Design Calculations of Canopy Structure at Al Khanoor Schoolraj vaddiNo ratings yet
- DBR How To MakeDocument15 pagesDBR How To Maketanmay271100% (1)
- Cost, Analysis and Design of Steel-Concrete Composite Structure RCC StructureDocument6 pagesCost, Analysis and Design of Steel-Concrete Composite Structure RCC Structureasingh400No ratings yet
- BEC 304 Steel and Timber DesignDocument18 pagesBEC 304 Steel and Timber DesignSeng Suen100% (1)
- Review PaperDocument6 pagesReview PaperdhanarajNo ratings yet
- (Unit) Title of The Chapter Name of FacilitatorDocument35 pages(Unit) Title of The Chapter Name of FacilitatorDipesh BasnetNo ratings yet
- Calculation SheetDocument12 pagesCalculation SheetMuraleedharan100% (1)
- Acousticsofbuildings 180820065330Document45 pagesAcousticsofbuildings 180820065330Garvit ChandrayanNo ratings yet
- Communication SystemsDocument18 pagesCommunication SystemsGarvit ChandrayanNo ratings yet
- Gas SupplyDocument13 pagesGas SupplyGarvit ChandrayanNo ratings yet
- URBANDESIGN PRESENTATION 12.05.22 CompressedDocument1 pageURBANDESIGN PRESENTATION 12.05.22 CompressedGarvit ChandrayanNo ratings yet
- Garvit (Ele)Document1 pageGarvit (Ele)Garvit ChandrayanNo ratings yet
- Gurukul ProgramDocument3 pagesGurukul ProgramGarvit ChandrayanNo ratings yet
- PIAR U.G. Thesis Orientation 2021 - Google FormsDocument15 pagesPIAR U.G. Thesis Orientation 2021 - Google FormsGarvit ChandrayanNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology Synopsis: AbstractDocument2 pagesResearch Methodology Synopsis: AbstractGarvit ChandrayanNo ratings yet
- List of Pharma Companies in GujaratDocument22 pagesList of Pharma Companies in Gujaratraj jogia83% (6)
- HowtoselectofpilingrigDocument9 pagesHowtoselectofpilingrigflashtronNo ratings yet
- S/N Company Name Field of Specialisation Date of Issue Expiry DateDocument3 pagesS/N Company Name Field of Specialisation Date of Issue Expiry DateVirah Sammy ChandraNo ratings yet
- MS For Dismantling of Existing Bridges From Shahbazpur To Zero Point PDFDocument18 pagesMS For Dismantling of Existing Bridges From Shahbazpur To Zero Point PDFMd. AlamgirNo ratings yet
- The Art of Steel Engineering... : AlfanarsteelDocument6 pagesThe Art of Steel Engineering... : AlfanarsteelDen BillNo ratings yet
- CET303 SyllabusDocument11 pagesCET303 SyllabusdipinnediyaparambathNo ratings yet
- Classification of Roads and Thier DetailsDocument6 pagesClassification of Roads and Thier DetailsNino Celso AstilleroNo ratings yet
- Jobs and Occupations VocabularyDocument2 pagesJobs and Occupations VocabularyAngel Capichi LunaNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument12 pagesCase StudyedenNo ratings yet
- Beyond The Mud Hut - The Return of Raw-Earth Architecture - Financial Times PDFDocument7 pagesBeyond The Mud Hut - The Return of Raw-Earth Architecture - Financial Times PDFJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 Introduction To The FieldDocument30 pagesChap 1 Introduction To The FieldKhalid AhmedNo ratings yet
- CE100 Final ExamDocument5 pagesCE100 Final ExamKlariz BorneaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Maintained Load Test (MLT) and Pile Driving Analyzer (PDA) in Measuring Bearing Capacity of Driven Reinforced Concrete PilesDocument7 pagesEvaluation of Maintained Load Test (MLT) and Pile Driving Analyzer (PDA) in Measuring Bearing Capacity of Driven Reinforced Concrete PilesAnonymous eAfIJ5Wu3INo ratings yet
- Hdpe Pipe Wall Thickness CalculationsDocument1 pageHdpe Pipe Wall Thickness CalculationsTsouki TsoukiNo ratings yet
- Stone Veneer Installaton GuideDocument12 pagesStone Veneer Installaton GuideJelaiNo ratings yet
- Esthec TerraceDocument22 pagesEsthec TerracemadhivananspNo ratings yet
- Climate & Architecture: Submitted by Chinmay Tirthakar Semester Ii Section - A Piads, NagpurDocument10 pagesClimate & Architecture: Submitted by Chinmay Tirthakar Semester Ii Section - A Piads, NagpurChinmay TirthakarNo ratings yet
- Failures of Gabion Walls: Ganesh C. Chikute, Ishwar P. SonarDocument7 pagesFailures of Gabion Walls: Ganesh C. Chikute, Ishwar P. SonarnavigareeNo ratings yet
- Proposal For Verification of In-Situ Concrete StrengthDocument36 pagesProposal For Verification of In-Situ Concrete StrengthYF NNo ratings yet
- Building RegulationDocument12 pagesBuilding RegulationOscarKonzultNo ratings yet
- Test Certificate: Portland Pozzolana Cement (Fly Ash Based)Document1 pageTest Certificate: Portland Pozzolana Cement (Fly Ash Based)Manash Protim GogoiNo ratings yet
- 29 - Monorail 800 2007Document7 pages29 - Monorail 800 2007Powerhouse ShaftNo ratings yet
- 10 Eaton Rd. 1 PDFDocument1 page10 Eaton Rd. 1 PDFJoel SalialamNo ratings yet
- Two Way Slab DesignDocument16 pagesTwo Way Slab DesignMandar NadgaundiNo ratings yet
- Structural Report Ajay FinalDocument62 pagesStructural Report Ajay FinalSravani Prabhala100% (2)
- CONCEPT DESIGN ALUM C.W SCHUCO ANDALUSIA Rev01.10.03.222Document118 pagesCONCEPT DESIGN ALUM C.W SCHUCO ANDALUSIA Rev01.10.03.222MoustafaNo ratings yet
- Sprinkler DesignDocument63 pagesSprinkler DesignChandaKundaNo ratings yet
- Mapefill MC 06Document4 pagesMapefill MC 06Yudi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- 5188 600th ABG BarracksDocument2 pages5188 600th ABG BarracksTivoj PorrasNo ratings yet
- Vol42No10 FullDocument84 pagesVol42No10 FullMarco PalmaNo ratings yet