Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earth Science Reviewer
Uploaded by
Wensil Faith0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views6 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views6 pagesEarth Science Reviewer
Uploaded by
Wensil FaithCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
EARTH SCIENCE REVIEWER 2.
Stratosphere – Ozone layer (planes
(omg sht is getting real) can be seen here)
3. Mesosphere – coldest layer (“Meso”
WEEK 1: EARTH means middle)
- Earth is the only planet in the solar 4. Thermosphere – hottest layer (where
system known to harbor life. Earth is in the the Aurora Borealis can be seen)
GOLDILOCKS ZONE. 5. Exosphere – outermost layer
- Earth is the only place in the known (spacecrafts can be seen here)
universe confirmed to nest life and is the only Something to remember!!!
one known for sure to have LIQUID WATER The 4 Subsystems are interconnected,
on the SURFACE. ex: volcanic eruption, it affects all of the
Reasons why earth is a living planet subsystems.
1. It has the right distance from the sun.
2. It is protected from harmful solar PROPERTIES OF MINERALS
radiation by its magnetic field. Minerals are:
3. The atmosphere keeps us warm. 1. Naturally Occurring
4. It has the right amount of ingredients 2. Inorganic
for life. Including water and carbon. 3. Homogenous Solid
4. Definite chemical Composition
Question to remember!!! 5. Orderly crystalline structure
Why Is Earth Called the living planet?
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF MINERALS
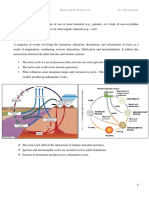
ORIGIN & STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH A. Color
(THE 4 SUBSYSTEMS) - It is the most observable
1. Biosphere – is made up of the parts of characteristics of a mineral.
Earth where life exists-all ecosystems. - Minerals color may change
2. Hydrosphere – is the total amount of depending on the surface.
water on a planet. It includes water on B. Streak
the surface of the planet, underground - Color of a mineral in powdered
and in the air. form.
Reasons why water is ESSENTIAL C. Hardness
o It can be in any form (solid, liquid, - It is a measure of the resistance of
gas) a mineral (not specifically surface)
o Water has a neutral PH scale to abrasion.
o Water is a good conductor of heat &
energy)
o It is a UNIVERSAL SOLVENT
o Water is a high specific key
3. Geosphere – includes rocks and
minerals on Earth.
Layers of the Earth
• Crust
• Mantle
• Core (inner and outer)
✓ The outer core is liquid because it
does not have enough pressure to
sustain itself.
4. Atmosphere – the atmosphere is a
gaseous barrier that protects the
earth. D. Cleavage and Fracture
• The atmosphere is made up of: 78% - Cleavage refers to the tendency of
nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% of minerals to break along very
other gases. smooth, flat and shiny surfaces.
Layers of the Atmosphere A mineral fracture may break along
1. Troposphere – lowest layer (clouds are random, irregular surfaces.
present here)
E. Crystal Habit other bodies of water at the Earth’s
- The external/natural shape of a surface.
crystal or groups of crystals is
displayed/observed as these
crystals grow in open spaces.
F. Diaphaneity/Amount of Transparency
- Ability to allow light to pass
through it. This is affected by
chemical makeup of the mineral
shape.
G. Luster
- It is how light is reflected off a
surface.
- A mineral with high luster is very
reflective. Lithification – it is the process of compaction
H. Tenacity and cementation of sediments.
- Describes the minerals reaction to Compaction- occurs when layers of sediment
stress. compress the rock below it.
Cementation – is when sediments are glued
WEEK 2: ROCKS together by minerals deposited between
- A rock is a solid collection of them.
mineral grains that grow or Remember: Different types of fossils can be
become cemented together. seen/embedded in sedimentary rocks.
- There are 3 kinds of rocks:
TYPES OF SEDIMENTARY ROCK:
Igneous, Sedimentary and
• Clastic Sedimentary Rock – it is
Metamorphic rocks.
formed by mechanical weathering.
IGNEOUS ROCK
• Chemical Sedimentary Rock – it is
• They are formed through the cooling
formed when dissolved materials
and solidification of magma or lava.
precipitate from solution.
• Volcanic/Plutonic rocks
• Organic Sedimentary Rock – it is
Classification of Igneous Rocks
formed from the build up of plants and
o Intrusive Igneous Rock (Course
or animals.
grained/Phaneritic texure) – this
METAMORPHIC ROCKS
type of rock is formed from
- Came from pre-existing rocks
solidification of magma below the
called parent rocks.
surface. They have large crystals of
- Subjected to heat, pressure, and
minerals that forms overtime through
chemically-active fluids.
a slow process of crystallization in a
- Its parent rock can be an igneous,
magma.
sedimentary or metamorphic rock.
o Extrusive Igneous Rock (Fine
Factors that Influence metamorphism:
grained/Aphanitic texture – This
1. Heat
type of rock is formed through a
2. Pressure
faster rate of solidification of lava
3. Chemically-active fluids
on the surface of the Earth.
Example of metamorphic rocks:
Mineral Composition of Igneous Rocks
Granite – Gneiss
Felsic – Is composed mostly of light-colored
Sandstone – Quartzite
silicates. Ex: Granite
Shale – Slate
Mafic – it contains a substantial amount of
We classify metamorphic rocks as
dark colored silicates. Ex: Basalt, Gabbro
FOLIATED and NON-FOLIATED.
Intermediate – rocks with composition from
1. Foliated – formed through pressure
dark and light silicates. Ex: Diorite
due to compression. It has differential
SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
pressure.
- Is formed by the deposition and
2. Non-Foliated – it has no foliation or
cementation of mineral or organic
bands. It has equal or not enough
particles on the floor of oceans and
pressure to compress it.
3 FACORS THAT CREATES THE ROCK CYCLE: - Shallow, horizontally located
1. The movement of Plate Tectonics deposits or ores.
2. Weathering 3. DREDGING
3. Erosion - Process of mining
materials/minerals from the
bottom of a body of water,
including rivers, lakes and oceans.
B. Underground mining
- Is used to extract the rocks,
minerals and other precious stones
that can be found beneath the
earth’s surface.
- Most expensive in terms of
production cost.
- Mponeng gold mine, located in
Johannesburg, South Africa is the
deepest mine in the world.
MINERAL PROCESSING
• Sampling – is the removal of a portion
WEEK 3: ORE MINERALS/MINING which represents a whole, needed for
Mining – is the process of mineral extraction the analysis of the materials.
from a rock seam or ore – a natural rock or • Analysis – is important to evaluate the
sediment containing one or more valuable valuable component in an ore. This
minerals. includes chemical, mineral and
Ore Extracting – raw materials, mining, particle size analysis.
deposited beneath the earth. • Comminution – is the process where
A. Surface Mining the valuable components of the ore is
- It is used to extract ore minerals separated through crushing and
near the surface of the earth. grinding.
- In surface mining, the ground is • Concentration – involves the
blasted so that ores near the separation of the valuable minerals
Earth’s surface can be removed to from the raw materials.
the surrounding and is carried to • Dewatering – uses the concentration
refineries to extract the minerals. to convert it to usable materials.
- Surface mining can be destructive
to the mining surrounding FOSSIL FUELS
landscape. - Fossil fuels are basically remains
1. OPEN PIT MINING of plants and animals that died
- This is the most common type of millions of years ago. (non-
surface mining. Open pit means a renewable kay dugay man na
big hole in the ground. form)
- It is Less expensive, safer, easy - They are all composed of
and fast. hydrocarbons.
2. STRIP MINING 3 MAJOR TYPES OF FOSSIL FUELS
- This mining type involves the 1. Coal - it is important and primary
removal of a thin strip of fossil fuel present on Earth.
overburden above a desired o ANTHRACITE – it is brittle and has
deposit, dumping the removed a black lustrous coal, often called
overburden behind the deposit, as HARD COAL, containing 86% to
extracting the desired deposit, 97% carbon.
creating a second parallel strip in o BITUMINOUS – it usually has a
the same manner, and depending high heating value and it is the
depositing the waste materials most common type of coal used in
from that second strip unto the electricity generation. It appears
first strip. (libog noh?) smooth at first glance, but it has
layer of you look closely. It has - The best energy source on Earth
45% to 86% carbon. because it is already stead and
o SUBBITOMINOUS – black in color dependable.
and dull and has a higher heating D. Geothermal Energy
value than lignite. It has 35% to - It uses steam obtained from these
45% carbon. geothermal reservoirs to generate
o LIGNITE – brown coal (baby coal), electricity.
it is the lowest grade coal with a - Wells are drilled at the appropriate
crumbly and high moisture content. locations to bring this geothermal
It has 25% to 35% carbon. energy up to the surface.
Types of Geothermal Powerplant
1. Dry Steam Powerplant – This is the
simplest and oldest type of
geothermal plant. It directly uses
steam from the reservoir to operate
the turbine.
2. Flash Steam Powerplant – The most
employed in geothermal plants today.
(taas ang process ani )
3. Binary Cycle Powerplant - Binary
powerplants are a recent
development. They have made it
2. Oil – is an organic material mostly
possible to produce electricity from
algae, which was buried in mud at the
geothermal reservoirs with
bottom of the sea and lakes.
temperatures lower than 150-degree
- Petroleum in Latin means Rock Oil.
Celsius.
- Liquified Fossil Fuel
3. Natural Gas – it is mostly composed
ADVANTAGES OF USING RES:
- It is renewable
of methane.
- No harmful gases are emitted
- Naturally occurring hydrocarbon
- No greenhouse effects
gas with the mixture of methane.
- Cost of fuel is negligible
- It can be extracted through
- Capital cost is 40-60% less than
drilling.
thermal & nuclear plants.
WEEK 4: RENEWABLE ENERGY DISADVANTAGES OF USING RES:
- Availability at certain regions only
- Is energy derived from natural
- Low efficiency
resources that are replenished at a
- It is hard to replace fossil fuels
higher rate than they are
because of its energy capacity.
consumed.
A. Solar Energy WATER AS A RESOURCE
- An impressive renewable resource Water Sources
that can substitute fossil fuels. - Surface Water
- It can be utilized to generating - Glaciers
electricity from solar cells, - Underwater flow
permitting people to access - Groundwaters
electricity without letting go of Where’s Water (kadtong vid)
destructive gassed into the - Drinkable water is mostly hidden
atmosphere. underground.
B. Wind Energy - There is Blue and Green water: Blue
- Another source of energy that is water are rivers, lakes,
very functional is wind power and groundwaters while Green water is
presently, it is the quickest- water inside soil/agriculture.
developing energy that can be Water Cycle
accessed. - Condensation – Precipitation –
C. Hydroelectric Energy/Power Collection – Evaporation
- The most reliable source of energy -
Water Pollutants - Organisms/Biological factors
- Water stress (water is insufficient - Landscape/Topography
for its need) - Parent Material (it determines
- Population growth what type of soil will form)
- Expansion of Business activity Residual soil – are formed through
- Climate change weathering of its underlying rock.
- Depletion of Aquifers Soil Texture – defined as the relative
High Temperature = Low Oxygen proportion of the particle sizes in the soil –
WEEK 5: SOIL sand, silt and clay.
- Unconsolidated mineral and Sand – 2.00-0.05mm
organic material on the immediate Silt – 0.05 – 0.002mm
surface of the Earth that serves as Clay - <0.002mm
the natural medium for the growth
of land plants/plant growth.
Soil forms the PEDOSPHERE
- Soil is the living skin of the Earth
- The soil is teeming with life. It is
teeming with a variety of various
types of life microbes. It is the
unconsolidated mineral or organic
material.
7 Roles of Soil
• Soil serves as the media for the
growth of all kinds of plants.
• Soils modify the atmosphere by
emitting and absorbing gases like
CO2, methane, water vapor, and dust.
• Soils provide habitats for animals that
live in the soil to organisms that
account for most of the living things
on Earth.
How to calculate soil texture?
• Soils absorb, hold, release, alter and
Divide the depth of each layer of soil by the
purify most of the water in terrestrial
total depth in the jar, and multiply by 100.
systems.
• Soils process recycled nutrients,
including carbon, so that living things
can use them over and over again.
• Soils serve as an engineering media
for the construction of foundations,
roadbeds, dams, and buildings, and
can both preserve or destroy artifacts
of human endeavors.
• Soil act as a living filter to clean water
before it moves into an aquifer.
Soil Composition
- 25% water
- 25% air
- 45% minerals
- 5% organic matter
It takes 200-400 years to make soil, thus
LAYERS A,B,C are the basic layers of soil.
making soil a nonrenewable source and it is
Soil Orders
finite.
1. Gelisols – Frozen soils found in the
FACTORS THAT AFFECT SOIL FORMATION
coldest regions on Earth
- Time
2. Histosols – High organic content and
- Weather/climate
wet
3. Spodosols – Sandy and acidic soils o Liquid Waste
found in moist climates that often o Gaseous waste
support dense forests. o Bio, Nonbio, Hazardous, NonHazard
4. Andisols – composed of volcanic ash Wastes according to Generation (Origin)
5. Oxisols – Very weathered and • Municipal Solid Waste
common in tropical climates • Industrial Waste
6. Vertisols – Claylike soils that shrink • Agricultural Waste
and swell • Fishery Waste
7. Aridisols – Very dry soils in arid • Radioactive Waste
regions • E-Waste
8. Ultisols – Weathered soils • Biomedical Waste
9. Mollisols – Deep and fertile soils WASTE MANAGEMENT
10. Alfisols – Moderately weathered • Landfills – easiest buhaton
productive soils found in temperate • Incineration – sunugon ang waste
and humid regions unya I limpyo pana ang gaseous
11. Inceptisols – Slightly developed, waste para ma gamit.
young soils found on steep slopes and • Compost and Mulch
mountain ranges • 3 R’s
12. Entisols – Newly-formed soils found in
steep rocky lands
Human Activities affecting Quality of Soil
- Farming
- Construction & Development
- Mining
- Waste Disposal
Protection & Conservation of Soil
- Soil conservation techniques are
intended to preserve soil in place
and maintain its fertility.
• Conservation Tillage – To limit the Source Reduction
number of times a field is tilled,
plowed each year, to reduce the soil
being washed away.
• Terraces Planting – Crops are planted
on the flat tops of the terraces to hold
rainwater and prevent it from running
downhill.
• Forest Protection
• Buffer strips
• Fewer Concrete Surfaces
• Plant Windbreak Areas
• Crop rotation
• Water the soil
• Maintain the pH level
• Indigenous Crop
• Afforestation
• Monitor Grazing
• Dams
• Fertilizers (Organic dili Synthetic)
• No soil compacting
WEEK 6: WASTE
Waste – are unwanted or unusable materials.
Kinds of Waste:
o Solid waste
You might also like
- Metamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandMetamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Midterms ReviewerDocument4 pagesEarth Science Midterms ReviewerMerck ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Science PointersDocument3 pagesEarth and Science PointersDominico Jr Pojas TanNo ratings yet
- Rock Types: Igneous, Sedimentary, and MetamorphicDocument6 pagesRock Types: Igneous, Sedimentary, and MetamorphicDenjay CatalanNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Earth Necessary for Life and Rock ClassificationDocument11 pagesCharacteristics of Earth Necessary for Life and Rock ClassificationStephanie GraceNo ratings yet
- Earth-Science-lesson-1-8 (Kean Endencio)Document4 pagesEarth-Science-lesson-1-8 (Kean Endencio)timothybadiola99No ratings yet
- Eal Module 2Document7 pagesEal Module 2Angelina Jolai CentenoNo ratings yet
- The Rock Cycle: Formation of Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic RocksDocument7 pagesThe Rock Cycle: Formation of Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic RocksGLENMAR VINEGASNo ratings yet
- Minerals AND Rocks: Earth and Life ScienceDocument20 pagesMinerals AND Rocks: Earth and Life ScienceAbella, Jhenkent P.No ratings yet
- Petrology y YyyDocument1 pagePetrology y YyyJaymi MananganNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science - Week 4 Module 4Document2 pagesEarth and Life Science - Week 4 Module 4Aya CatanghalNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science - ReviewerDocument6 pagesEarth & Life Science - ReviewerellyznicolecNo ratings yet
- Module 4 (Classification of Rocks)Document2 pagesModule 4 (Classification of Rocks)AkiNo ratings yet
- Petrology Wps OfficeDocument4 pagesPetrology Wps OfficeDante PazNo ratings yet
- Earthsci Lesson (Rocks&minerals)Document3 pagesEarthsci Lesson (Rocks&minerals)Ara MaglangitNo ratings yet
- Final Update Earths Rocks and Their ClassificationsDocument19 pagesFinal Update Earths Rocks and Their Classificationsfinnlevine207No ratings yet
- Rocks and their Classification ExplainedDocument4 pagesRocks and their Classification ExplainedShahid AbbasNo ratings yet
- Classification of Rocks and Rock Cycle notesDocument4 pagesClassification of Rocks and Rock Cycle noteshkenger100% (1)
- Earth Materials and ResourcesDocument5 pagesEarth Materials and Resourceshezekiah minNo ratings yet
- Petrology GeoDocument2 pagesPetrology GeoLorenz Gabriel RoxasNo ratings yet
- The Rock Cycle: How Rocks Form and Change Over TimeDocument26 pagesThe Rock Cycle: How Rocks Form and Change Over TimeEsfher Andal EscarezNo ratings yet
- Geology M2 ReviewerDocument7 pagesGeology M2 ReviewerDenjay CatalanNo ratings yet
- Rocks and the Rock Cycle: A GuideDocument20 pagesRocks and the Rock Cycle: A GuideKristine BaguinatNo ratings yet
- Classification of RocksDocument11 pagesClassification of RocksAkshay EverNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Earth ScienceDocument5 pagesReviewer Earth ScienceinamowtoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science 1st QuarterDocument7 pagesEarth and Life Science 1st QuarterIrish AlmidaNo ratings yet
- Earth Life Science Week 2 Final 1Document17 pagesEarth Life Science Week 2 Final 1Ronald ArtilleroNo ratings yet
- 9.classification of RocksDocument30 pages9.classification of RocksKim Clauwie AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Science 11 ReviewerDocument10 pagesScience 11 ReviewerArgie MabagNo ratings yet
- Rocks and the Rock Cycle LectureDocument7 pagesRocks and the Rock Cycle LectureMarco PlaysNo ratings yet
- Earth Science 1st Quarterly Assessment ReviewersDocument3 pagesEarth Science 1st Quarterly Assessment ReviewersMark JedrickNo ratings yet
- Classification of Rocks: Quarter 1, Week 2Document18 pagesClassification of Rocks: Quarter 1, Week 2Ronald ArtilleroNo ratings yet
- ELSDocument14 pagesELSAshley Faith AgunosNo ratings yet
- Group5 WrittenReport-1Document13 pagesGroup5 WrittenReport-1arani ahmad ridhaNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter NotesDocument6 pages1st Quarter NotesCherry Pink VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science M1-6Document9 pagesEarth Science M1-6Marxinne PajarinNo ratings yet
- ELS Quarter 1 REVIEWER ModifiedDocument3 pagesELS Quarter 1 REVIEWER ModifiedASh tabaogNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Earth ScieDocument10 pagesLesson 2 Earth Sciecrizanne barsatanNo ratings yet
- The 3 Types of Rocks and Their Properties ExplainedDocument77 pagesThe 3 Types of Rocks and Their Properties ExplainedDon't mind meNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Reviewer (G-12)Document9 pagesEarth Science Reviewer (G-12)D-Jay LigotNo ratings yet
- Classify Rocks with Ease: A Guide to Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic ClassificationDocument11 pagesClassify Rocks with Ease: A Guide to Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic ClassificationTeacher Charlyn VlogNo ratings yet
- EARTH SCIENCE RocksDocument26 pagesEARTH SCIENCE RocksDAKSINo ratings yet
- Earth Science S1Q1 Periodical Reviewer - AllDocument6 pagesEarth Science S1Q1 Periodical Reviewer - AllSunNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in EARTH and LIFE SCIENCE 11Document4 pagesReviewer in EARTH and LIFE SCIENCE 11ashryn blaizeNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Lesson 4 RocksDocument66 pagesEarth and Life Lesson 4 RocksMagdalena TagubaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 RocksDocument22 pagesModule 4 RocksAQUINO JAYSON KIERNo ratings yet
- Earth and Earth SystemsDocument11 pagesEarth and Earth SystemsKimberly LopezNo ratings yet
- Rocks Geography Study Material NotesDocument3 pagesRocks Geography Study Material NotesSTEPHEN AOCKIAM MNo ratings yet
- Mary Joy Dequito 2 (PPT Presentation) FINALDocument48 pagesMary Joy Dequito 2 (PPT Presentation) FINALROSE ANN JAWADNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Minerals and Rocks Part 2Document6 pagesUnit 2 Minerals and Rocks Part 2Bryle James BialaNo ratings yet
- Rocks: Three Types of RocksDocument3 pagesRocks: Three Types of RocksSevilla RonabelleNo ratings yet
- Batuan BekuDocument49 pagesBatuan BekuAdistiNo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument3 pagesSolar SystemReychel LunaNo ratings yet
- MineralsDocument3 pagesMineralsAngelika IngosanNo ratings yet
- Rock and Extrusive Igneous RockDocument1 pageRock and Extrusive Igneous Rocklovely venia m jovenNo ratings yet
- Week 3-4Document53 pagesWeek 3-4michael delinNo ratings yet
- (Notes) Minerals and RocksDocument4 pages(Notes) Minerals and RocksDenver Cho-oyNo ratings yet
- Answer To Module 2 (Earth and Life Science)Document9 pagesAnswer To Module 2 (Earth and Life Science)Angel MarieNo ratings yet
- Earth Process Fact SheetsDocument5 pagesEarth Process Fact SheetsLoui Mark Loui MarkNo ratings yet
- Personal Development ReviewerDocument4 pagesPersonal Development ReviewerWensil FaithNo ratings yet
- Blue and Yellow Scrapbook Algrebra PresentationDocument38 pagesBlue and Yellow Scrapbook Algrebra PresentationWensil FaithNo ratings yet
- Elec OutputDocument21 pagesElec OutputWensil FaithNo ratings yet
- Taylor SweepDocument4 pagesTaylor SweepWensil FaithNo ratings yet
- Cerro Lindo Site Visit Presentation VF PDFDocument41 pagesCerro Lindo Site Visit Presentation VF PDFEdinssonRamosNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Subsurface Investigation - 1992 - : Section/Article DescriptionDocument10 pagesGeotechnical Subsurface Investigation - 1992 - : Section/Article DescriptionMarwan MokhadderNo ratings yet
- Cervato - Frodeman (2012) The Significance of Geologic Time - Cultural, Educational, and Economic FrameworksDocument10 pagesCervato - Frodeman (2012) The Significance of Geologic Time - Cultural, Educational, and Economic FrameworksNaGiNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Earth's SubsystemDocument13 pagesMODULE 2 Earth's SubsystemMark Daniel LopezNo ratings yet
- 17CE3508 Oct 2020Document2 pages17CE3508 Oct 2020Dr.GV Rama Subba Rao CE, VRSECNo ratings yet
- Some Upper Jurassic Ammonites of The Genus Rasenia From ScotlandDocument6 pagesSome Upper Jurassic Ammonites of The Genus Rasenia From ScotlandardeegeeNo ratings yet
- Tsunami 190907112349Document21 pagesTsunami 190907112349Nikhil RNo ratings yet
- Aysha VES Interpretation FiDocument23 pagesAysha VES Interpretation FiDereje MergaNo ratings yet
- Soliman DFIT ArticleDocument8 pagesSoliman DFIT Articlecj100% (1)
- Rock and Soil DescriptionsDocument11 pagesRock and Soil DescriptionsDevendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Tayo ch1Document6 pagesTayo ch1Oladipo EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument26 pagesBiogeochemical Cyclesaisyah Wardah201No ratings yet
- Topography NotesDocument3 pagesTopography Noteszainab billalNo ratings yet
- Routine Instrumental and Visual Monitoring of Dams Based On Potential Failure Modes Analysis (2013) PDFDocument34 pagesRoutine Instrumental and Visual Monitoring of Dams Based On Potential Failure Modes Analysis (2013) PDFMarceloToribioFloresNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Different Calculation Methods of The Geological Strength Index (GSI) Based On Qualitative and Quantitative ApproachesDocument18 pagesComparative Analysis of Different Calculation Methods of The Geological Strength Index (GSI) Based On Qualitative and Quantitative ApproachesHongha NguyenNo ratings yet
- Passed 299-11-19 Kalinga The Wrath of Volcano - Activity Sheets in Science 9Document29 pagesPassed 299-11-19 Kalinga The Wrath of Volcano - Activity Sheets in Science 9HELMA ARIOLANo ratings yet
- South Africa's Standard Specifications for Road and Bridge WorksDocument106 pagesSouth Africa's Standard Specifications for Road and Bridge WorksTSHEPO DIKOTLANo ratings yet
- PRO - ECO1 - S8-G1 - 14-18 JuinDocument349 pagesPRO - ECO1 - S8-G1 - 14-18 JuinCHALABI FARES100% (1)
- Deep Compaction Methods and ApplicationsDocument20 pagesDeep Compaction Methods and ApplicationsJerry IshayaNo ratings yet
- Earthwork in Cold Regions: DitchingDocument24 pagesEarthwork in Cold Regions: DitchingMohd Nizamuddin Mohamad NoorNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics: Christine Mae Balid Rjay Jimenez Jireh ElliotDocument21 pagesPlate Tectonics: Christine Mae Balid Rjay Jimenez Jireh ElliotJuly Roland CabrisosNo ratings yet
- Speech Landforms in TopographyDocument3 pagesSpeech Landforms in TopographyElvis MadridNo ratings yet
- Types of Cement in RocksDocument12 pagesTypes of Cement in Rockssher afganNo ratings yet
- Floor SlabDocument36 pagesFloor SlabAlvaritopito90No ratings yet
- PNPA Admission Test CoverageDocument7 pagesPNPA Admission Test Coveragecarol indangan100% (3)
- Barbieri, M. Et Al. Experiencing Visible and Invisible Metal Casting Techniques in The Bronze Age ItalyDocument9 pagesBarbieri, M. Et Al. Experiencing Visible and Invisible Metal Casting Techniques in The Bronze Age ItalyRenan Falcheti PeixotoNo ratings yet
- SPE-121928 Field Development and Productivity Improvement in ... Synergistic Approach To Carbonate Fracture AcidizingDocument10 pagesSPE-121928 Field Development and Productivity Improvement in ... Synergistic Approach To Carbonate Fracture AcidizingBruceNo ratings yet
- Sedimentology and StratigraphyDocument432 pagesSedimentology and Stratigraphyjoão50% (2)
- Exploring Earth's SurfaceDocument16 pagesExploring Earth's SurfaceMartha Inés RocaNo ratings yet
- Module 1-Introduction To Soil ScienceDocument5 pagesModule 1-Introduction To Soil ScienceJr BagaporoNo ratings yet