Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Workshop 2021
Uploaded by
Sandeep K0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views10 pagesThis document discusses pedigree analysis and the different types of inheritance patterns that can be analyzed through pedigrees. It describes autosomal dominant and recessive inheritance, as well as sex-linked (X-linked) recessive and dominant inheritance and Y-linked inheritance. For each type of inheritance, it provides examples of disorders and explains the genotypes involved and how the condition is passed down. Pedigrees are useful for determining inheritance patterns and predicting traits in future generations.
Original Description:
Original Title
1628101478217_workshop 2021
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses pedigree analysis and the different types of inheritance patterns that can be analyzed through pedigrees. It describes autosomal dominant and recessive inheritance, as well as sex-linked (X-linked) recessive and dominant inheritance and Y-linked inheritance. For each type of inheritance, it provides examples of disorders and explains the genotypes involved and how the condition is passed down. Pedigrees are useful for determining inheritance patterns and predicting traits in future generations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views10 pagesWorkshop 2021
Uploaded by
Sandeep KThis document discusses pedigree analysis and the different types of inheritance patterns that can be analyzed through pedigrees. It describes autosomal dominant and recessive inheritance, as well as sex-linked (X-linked) recessive and dominant inheritance and Y-linked inheritance. For each type of inheritance, it provides examples of disorders and explains the genotypes involved and how the condition is passed down. Pedigrees are useful for determining inheritance patterns and predicting traits in future generations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
PEDIGREE ANALYSIS
• The study of an inherited trait in a group of related individuals to
determine the pattern and characteristics of the trait.
• A pedigree is a diagram of family relationships that uses symbols to
represent the inheritance of a particular trait .
Symbols used in pedigree
TYPES OF PEDIGREE
Pedigree
Autosomal Sex linked
Recessive Dominant Recessive
Dominant E.g. Albinism, E.g. Retinitis E.g.
E.g. Myotonic dystropy, Cystic Fibrosis Pigmentosa, Colourblindness,
Huntington’s Disease Chondrodysplasia Haemophilia
punctata
Genotype
Autosomal recessive genotype
• AA-normal; Aa-carrier; aa-affected
Autosomal dominant genotype
• AA-affected; Aa-affected; aa-normal
X linked recessive genotype
• XX-normal female, XY-normal male
• XX’-carrier; X’X’-affected
• X’Y-affected
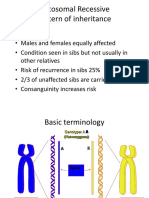
Autosomal recessive
• In autosomal recessive inheritance , both copies of the
gene in each cell have mutations. The parents of an
individual with an autosomal recessive condition each
carry one copy of the mutated gene, but they typically do
not show signs and symptoms of the condition.
Autosomal dominant
• One mutated copy of the gene in each cell is sufficient
for a person to be affected by an autosomal dominant
disorder. In some cases, an affected person inherits the
condition from an affected parent. In others, the
condition may result from a new mutation in the gene
and occur in people with no history of the disorder in
their family.
X-linked recessive
• X-linked recessive disorders are also caused by mutations in genes on
the X chromosome. In males (who have only one X chromosome), one
altered copy of the gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the condition.
In females (who have two X chromosomes), a mutation would have to
occur in both copies of the gene to cause the disorder. Because it is
unlikely that females will have two altered copies of this gene, males
are affected by X-linked recessive disorders much more frequently than
females. A characteristic of X-linked inheritance is that fathers cannot
pass X-linked traits to their sons (no male-to-male transmission). This
type of cross is also called criss cross inheritance.
X-linked dominant
• X-linked dominant disorders are caused by mutations in genes on
the X chromosome, one of the two sex chromosomes in each cell. In
females (who have two X chromosomes), a mutation in one of the two
copies of the gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the disorder. In
males (who have only one X chromosome), a mutation in the only
copy of the gene in each cell causes the disorder. In most cases, males
experience more severe symptoms of the disorder than females. A
characteristic of X-linked inheritance is that fathers cannot pass X-
linked traits to their sons (no male-to-male transmission).
Y-linked
• A condition is considered Y-linked if the mutated gene that causes
the disorder is located on the Y chromosome, one of the two sex
chromosomes in each of a male's cells. Because only males have a Y
chromosome, in Y-linked inheritance, a mutation can only be passed
from father to son.
• Eg:Y chromosome infertility, some cases of Swyer syndrome
Advantage of pedigree
• It reveals whether the DNA is transmitted from one generation to the
other without alteration. It can also help in predicting the
characteristics of the future generations of a particular species. It also
helps in finding the presence or absence of a trait in the heterozygous
or homozygous state.
• Pedigrees are used to analyze the pattern of inheritance of a particular
trait throughout a family. Pedigrees show the presence or absence of a
trait as it relates to the relationship among parents, offspring, and
siblings.
You might also like
- RAMS For Testing & Commissioning of HVACDocument42 pagesRAMS For Testing & Commissioning of HVACAnandu AshokanNo ratings yet
- Personal Statement On (MSC Social Work)Document2 pagesPersonal Statement On (MSC Social Work)StephenNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Care PlanDocument2 pagesAcute Pain Care PlanKim Biro Turner86% (37)
- Oil and Gas: Safety Passport (Ogsp)Document10 pagesOil and Gas: Safety Passport (Ogsp)kerolcarroll100% (1)
- Baum (2015) The New Public HealthDocument23 pagesBaum (2015) The New Public HealthjamieNo ratings yet
- Howlett and Ramesh Educational Policy ModelDocument11 pagesHowlett and Ramesh Educational Policy ModelJaquelyn Montales100% (1)
- Modes of InheritanceDocument47 pagesModes of Inheritancesudhir_narang_3No ratings yet
- 2-1 Patterens of InheritanceDocument48 pages2-1 Patterens of InheritanceOrtiz ErmelizaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 Second SemesterDocument49 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Second SemesterRuthie TabanguilNo ratings yet
- SEX-LINKED Inheritance - 6 PDFDocument36 pagesSEX-LINKED Inheritance - 6 PDFMikko Cagnayo0% (1)
- 91 Human Genetics 3 With AnnopdfDocument35 pages91 Human Genetics 3 With Annopdfnikhil naniNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument27 pagesGeneticsRose HaliliNo ratings yet
- 10th Grade Sex-Linked TraitsDocument5 pages10th Grade Sex-Linked TraitsAnika HinkovaNo ratings yet
- Session 1-1 InheritanceDocument20 pagesSession 1-1 InheritancejoNo ratings yet
- Genetics: Mode of InheritanceDocument46 pagesGenetics: Mode of InheritanceHandrex MadrigalNo ratings yet
- Sexlinkedgenes DemoDocument57 pagesSexlinkedgenes DemopearlNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6A - Genetic PedigreesDocument43 pagesLecture 6A - Genetic Pedigreesnizobell50% (2)
- Human Genetics and PedigreeDocument100 pagesHuman Genetics and PedigreeMuna MaranNo ratings yet
- Sex Linkage 2Document29 pagesSex Linkage 2Kathlyn QuibsNo ratings yet
- Sex Linked Genes: The Xs and Ys of GeneticsDocument21 pagesSex Linked Genes: The Xs and Ys of GeneticsYetzirah LeeNo ratings yet
- 7.0 Cytology - Pedigree Analysis 2Document29 pages7.0 Cytology - Pedigree Analysis 2Patrick DingcoNo ratings yet
- PedigreeDocument28 pagesPedigreePixelVoidNo ratings yet
- Modes of InheritanceDocument18 pagesModes of InheritancedrmanojkulNo ratings yet
- Medical Genetics: Mode of InheritanceDocument35 pagesMedical Genetics: Mode of InheritanceSadiNo ratings yet
- Genetic Pedigree InterpretationDocument46 pagesGenetic Pedigree Interpretationkaren milloNo ratings yet
- SEX LINKED GENES Margie de LeonDocument37 pagesSEX LINKED GENES Margie de LeonCarmsNo ratings yet
- Heredity and EvolutionDocument65 pagesHeredity and EvolutionAbdul KarimNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 - Pedigree and Genetic Counseling (1) .PPTX 2Document53 pagesLesson 9 - Pedigree and Genetic Counseling (1) .PPTX 2lanceferdinand.tan.pharmaNo ratings yet
- Gene Disorders mbbs2Document31 pagesGene Disorders mbbs2Subham YadavNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and Medelian Genetics Lecture CondenDocument12 pagesMeiosis and Medelian Genetics Lecture Condenapi-295110496No ratings yet
- GenPop 2 - Pola Pewarisan SifatDocument29 pagesGenPop 2 - Pola Pewarisan SifatMonicha Yhuyhen SafitriNo ratings yet
- SexLinkage TraitsDocument56 pagesSexLinkage TraitsAnna Grace Lobigas RanocoNo ratings yet
- Genetics and EvolutionDocument6 pagesGenetics and EvolutionCherry Grace Articulo DabuconNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Genetics in Humans: Mutaz AminDocument32 pagesMendelian Genetics in Humans: Mutaz AminMustafa Khalid MustafaNo ratings yet
- Sex Linkage 2Document25 pagesSex Linkage 2Al DeligeroNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics Lecture 07Document7 pagesCytogenetics Lecture 07Dianne NolascoNo ratings yet
- Human Genetics and PedigreeDocument37 pagesHuman Genetics and Pedigreekholoud220100% (1)
- 3 Sex-Linked TraitsDocument42 pages3 Sex-Linked TraitsMario RectoNo ratings yet
- Autosomal Recessive Pattern of InheritanceDocument39 pagesAutosomal Recessive Pattern of InheritanceYUFFANo ratings yet
- The Chromosomes On Which Genes Are Located Can Affect The Expression of TraitsDocument24 pagesThe Chromosomes On Which Genes Are Located Can Affect The Expression of TraitsQueen1982 KNo ratings yet
- Care of Mother, Child, at Risk With Problems NotesDocument8 pagesCare of Mother, Child, at Risk With Problems NotescelinaNo ratings yet
- Patterns of InheritanceDocument22 pagesPatterns of InheritanceKetch Tim InfanteNo ratings yet
- Non Mendelian InheritanceDocument28 pagesNon Mendelian Inheritancearcelie tiranteNo ratings yet
- Sex Linked Genes &Document9 pagesSex Linked Genes &Ristner Tacay BalucanagNo ratings yet
- PedigreeDocument34 pagesPedigreeJason Fry100% (1)
- Modes of Inheritance, XD, XR, Y-Linked, MitochondrialDocument44 pagesModes of Inheritance, XD, XR, Y-Linked, MitochondrialErin HillNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Chromosome Basis of HeredityDocument90 pagesLecture 3 - Chromosome Basis of Hereditymubita T.S. AkalalukaNo ratings yet
- Genetics & InheritanceDocument5 pagesGenetics & InheritanceClaraNo ratings yet
- Autosomal DisordersDocument6 pagesAutosomal Disordersapi-19976646No ratings yet
- What Is A Pedigree.Document7 pagesWhat Is A Pedigree.Sheryl Lou AngelesNo ratings yet
- Homework # 1Document5 pagesHomework # 1Gladys VigiliaNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Disorder FinalsDocument15 pagesMendelian Disorder FinalskanagadurgaNo ratings yet
- 04 Pedigree AnalysisDocument13 pages04 Pedigree AnalysisKenneth MercadoNo ratings yet
- Pedigree 2023 BSMSDocument30 pagesPedigree 2023 BSMSPramitabha BaralNo ratings yet
- Human Genetics in Nursing Practice NUR 473: by Dr. Khaloud Alzahrani Assistant Professor in Molecular GeneticsDocument45 pagesHuman Genetics in Nursing Practice NUR 473: by Dr. Khaloud Alzahrani Assistant Professor in Molecular GeneticsBarrak AldosaryNo ratings yet
- Genetics and Evolution SUMMARY NOTESDocument6 pagesGenetics and Evolution SUMMARY NOTESPrabhNo ratings yet
- SSN MM Block 3 - GeneticsDocument238 pagesSSN MM Block 3 - GeneticsyogurtNo ratings yet
- Inborn Error of MetabolismDocument59 pagesInborn Error of MetabolismMadhu Sudhan PandeyaNo ratings yet
- 2 Sex Linked InheritanceDocument49 pages2 Sex Linked Inheritancekethanacc2No ratings yet
- G9 Biology U4-1Document33 pagesG9 Biology U4-1朱國修No ratings yet
- Genes, Chromosomes, and Human GeneticsDocument61 pagesGenes, Chromosomes, and Human GeneticsDimo PratannaNo ratings yet
- What Are The Different Ways in Which A Genetic Condition Can Be Inherited?Document4 pagesWhat Are The Different Ways in Which A Genetic Condition Can Be Inherited?Chad ParasNo ratings yet
- Dasar Genetika+molekulerDocument45 pagesDasar Genetika+molekulerAGASTI MERCU SUANo ratings yet
- Genetics 2Document42 pagesGenetics 2Sujit KoiralaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document6 pagesGeneral Biology 2Christianne Joseph MonzonNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Inheritance in Man: Catalogs of Autosomal Dominant, Autosomal Recessive, and X-Linked PhenotypesFrom EverandMendelian Inheritance in Man: Catalogs of Autosomal Dominant, Autosomal Recessive, and X-Linked PhenotypesNo ratings yet
- Independence Day - 75 CompressedDocument6 pagesIndependence Day - 75 CompressedSandeep KNo ratings yet
- KMS Biology Xii 2Document8 pagesKMS Biology Xii 2Sandeep KNo ratings yet
- 12 Preboard-2021Document14 pages12 Preboard-2021Sandeep KNo ratings yet
- WhatsApp Image 2022-07-30 at 8.40.11 PMDocument3 pagesWhatsApp Image 2022-07-30 at 8.40.11 PMSandeep KNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance HW3Document5 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance HW3Sandeep KNo ratings yet
- Chapter6 hw2Document4 pagesChapter6 hw2Sandeep KNo ratings yet
- Physics by Discover TemplateDocument15 pagesPhysics by Discover TemplateSandeep KNo ratings yet
- Manual, Blood CultureDocument41 pagesManual, Blood CultureFilipus HendiantoNo ratings yet
- Permit To Work DCPLDocument8 pagesPermit To Work DCPLRajat SonkarNo ratings yet
- PDF Q1 Mod 3 SMAW Grade 9 EnhancedDocument20 pagesPDF Q1 Mod 3 SMAW Grade 9 Enhancedelizer encarnacionNo ratings yet
- 5th European Patients' Rights Day - Giovanna Giacomuzzi, Pharmaceutical Group of The European UnionDocument13 pages5th European Patients' Rights Day - Giovanna Giacomuzzi, Pharmaceutical Group of The European UnionCittadinanzattiva onlusNo ratings yet
- David Moises Memorial High SchoolDocument8 pagesDavid Moises Memorial High SchoolRonald ArtilleroNo ratings yet
- Quiz-Number-0ne - Acosta JR., Fernando N., Bs Psychology 2BDocument3 pagesQuiz-Number-0ne - Acosta JR., Fernando N., Bs Psychology 2BFernando Acosta Jr.No ratings yet
- Senior Thesis 2022Document19 pagesSenior Thesis 2022api-608954316No ratings yet
- Bmi Baseline Auto 2019-2020Document1 pageBmi Baseline Auto 2019-2020Angelo SinfuegoNo ratings yet
- 10 Symptoms of PneumoniaDocument3 pages10 Symptoms of PneumoniaYidnekachew Girma AssefaNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics and Input DevicesDocument7 pagesErgonomics and Input DevicesY.InayatNo ratings yet
- CPR 2Document3 pagesCPR 2Baebee Lou100% (1)
- Colourism in Asia PacificDocument5 pagesColourism in Asia PacificFozan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Science 7 ActivityDocument2 pagesScience 7 ActivityTrixie MercadoNo ratings yet
- Rekapitulasi Desember 2021 SipDocument555 pagesRekapitulasi Desember 2021 SipadminIHC cakramedikaNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Kualitas Udara Ruang Yang Berhubungan Dengan Angka Kuman Di Ruang Operasi Rumah Sakit Sumber Hidup Di Kota Ambon 2020Document9 pagesPemeriksaan Kualitas Udara Ruang Yang Berhubungan Dengan Angka Kuman Di Ruang Operasi Rumah Sakit Sumber Hidup Di Kota Ambon 2020tedilevinrarianNo ratings yet
- Clear Aligners, A Milestone in Invisible Orthodontics - A Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesClear Aligners, A Milestone in Invisible Orthodontics - A Literature ReviewInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Doi Tuyen Online 21 25Document7 pagesDoi Tuyen Online 21 25Johnny JohnnieeNo ratings yet
- Graduate School, Chulalongkorn University Application Form For Combined Scholarship For International Graduate Students For Academic Year, SemesterDocument4 pagesGraduate School, Chulalongkorn University Application Form For Combined Scholarship For International Graduate Students For Academic Year, SemesterHiếu Nguyễn MinhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Pathogenesis of Infectious DiseasesDocument18 pagesChapter 14 Pathogenesis of Infectious DiseasesedemcantosumjiNo ratings yet
- Case Study-Eukaryotic Diversity GROUP 7Document2 pagesCase Study-Eukaryotic Diversity GROUP 7Amal JosephNo ratings yet
- SMAW PrinciplesDocument89 pagesSMAW Principlesdonnyars1979No ratings yet
- Vacutug Operation & Basic Maintenance: For MK-II Through MK-VIIDocument73 pagesVacutug Operation & Basic Maintenance: For MK-II Through MK-VIIrupakhasanNo ratings yet
- Medical Clinic Standards v.1Document13 pagesMedical Clinic Standards v.1ummuawisyNo ratings yet
- A Short Article About Stress (Eng-Rus)Document2 pagesA Short Article About Stress (Eng-Rus)Егор ШульгинNo ratings yet