Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ICU One Pager Chest Tubes
Uploaded by
Mohamed MahmoudCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ICU One Pager Chest Tubes
Uploaded by
Mohamed MahmoudCopyright:
Available Formats
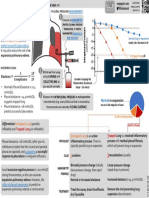
ASSESSMENT OF CHEST DRAINS by Nick Mark MD ONE
onepagericu.com Link to the
most current
@nickmmark version →
Stepwise assessment of Chest Tube Function
(For details for chest
TUBE POSITIONING tube insertion see
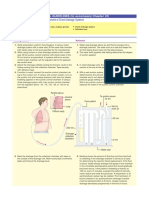
Underwater chest drain system combines DRAINAGE, a one-
Look at the CXR: is the chest tube correctly Procedure way valve (WATER SEAL), and allows a precise amount of
positioned to drain air/fluid? Are all six of the side Checklists)
negative pressure to be applied (PRESSURE REGULATOR).
holes within the chest cavity? Has it moved since a Modern systems provide the same functions.
prior CXR?
• If a chest tube is mal-positioned it may need to
The old three bottle system illustrates the functionality: w all
be removed/replaced. To ction
su
CHEST TUBE OUTPUT
How much fluid output has there been in the last 24
hours? Check the DRAINAGE area of the chest drain.
• Generally, it is reasonable to remove a chest tube
if the output is <200 ml/day. Note that there are usually
• If a tube stops draining, fibrinolytics can be used 6 side holes on chest tubes.
to clear obstructions. CHEST TUBE SIZING & POSITIONING
Tubes sized by internal diameter (1 Fr =
10-20 cm
TIDALING (RESPIRATORY VARIATION) 0.3 mm). Recommended size varies by
Tidaling indicates that the chest drain is within the indication:
2cm
pleura and transducing the pleural pressures. Look • 14-22 Fr stable pneumothorax
for movement of the indicator ball in the chest • 24-28 Fr tension pneumothorax PRESSURE
DRAINAGE WATER SEAL
drain. Also look for cyclic movement of fluid in • 28-32 Fr hemothorax/empyema Allows air to escape from REGULATOR
Collects and
dependent loops of tubing. • Smaller pigtail drains placed by
quantifies fluid the thorax if the pressure Determines how
• You can temporarily disconnect suction (bend Seldinger technique may have
draining from the rises above +2cmH2o. much suction is
the suction tubing to occlude it) to make it equivalent outcomes. Bubbles indicate the
thorax. applied.
easier to evaluate tidaling. Ideal direction where tube is placed: presence of air leak.
• For air ! anterior superiorly
• For fluid ! posterior inferior A modern chest drain looks different but has the same functions:
AIR LEAK
Air leak is the presence of bubbles in the WATER
SEAL chamber indicating that air is present within the WEANING A CHEST TUBE
chest (or a leak is present in the drainage system). • Generally, chest tubes are initially
Intermittent air leak occurring with the respiratory placed on suction. This facilitates Accordion indicates
cycle (typically at end inspiration) indicates an injury air/fluid removal from the thorax. if suction is applied.
to the lung or airways. Have the patient cough to see • Upon resolution of the pneumothorax When deflated (not
if air leak occurs with higher pressures. or drainage of an effusion, suction can visible) no suction is
Continuous air leak – throughout the respiratory be discontinued (this is called “being connected.
cycle suggests either a large injury to lung or airways on water seal”)
or a leak in the tubing. • Clamping a chest tube simulates
removal. Though usually unnecessary, Indicator Ball moves up
this is done prior to removal to and down transducing the
SUCTION intra-thoracic pressure.
ensure a pneumothorax does not
v1.0 (2020-07-04)
Is the drain connected to suction? How much recur. This can be useful if considering
suction is applied? Be cautious about applying -20 removing a chest tube while on Column markings
suction to large effusions as rapid drainage can positive pressure ventilation. quantify the degree of
precipitate re-expansion pulmonary edema.
air leak: scored 1-7.
You might also like
- Chest TubesDocument1 pageChest TubesQueenNo ratings yet
- Flow Initiationswabbing Reverse Circulation Coil TubingDocument17 pagesFlow Initiationswabbing Reverse Circulation Coil TubingMahtab SajnaniNo ratings yet
- Use of Drains in Surgery:: A ReviewDocument8 pagesUse of Drains in Surgery:: A ReviewPark ChanyeolNo ratings yet
- Liquid Ring Vacuum Pumps: KinneyDocument12 pagesLiquid Ring Vacuum Pumps: KinneyTrang DangNo ratings yet
- 022 MDT Sampling Training PDFDocument6 pages022 MDT Sampling Training PDFミス・ ナディアNo ratings yet
- DrainsDocument19 pagesDrainspaulineNo ratings yet
- CIP Cleaning in Place: The Circulation of Non Foaming Cleaners Without Dismantling The EquipmentDocument23 pagesCIP Cleaning in Place: The Circulation of Non Foaming Cleaners Without Dismantling The EquipmenttomkingNo ratings yet
- Wellsharp Definitions Reference DocumentDocument15 pagesWellsharp Definitions Reference DocumentBarbare RenNo ratings yet
- CHOKE Valve - Acv12Document2 pagesCHOKE Valve - Acv12limaeronNo ratings yet
- Nursing Managment of Chest Tubes: by Alice Leung RN, BSN, PCCNDocument55 pagesNursing Managment of Chest Tubes: by Alice Leung RN, BSN, PCCNFrancis Xavier S. Mendez0% (1)
- PCRRT Workshop Handbook 1 PDFDocument13 pagesPCRRT Workshop Handbook 1 PDFYusufa Fil ArdyNo ratings yet
- Caring For Patients With Chest Tubes PDFDocument10 pagesCaring For Patients With Chest Tubes PDFSavanna ChambersNo ratings yet
- Control ValvesDocument50 pagesControl ValvesReaderRRGHT93% (15)
- C6 Fluid Friction Measurement (Issue 2) PDFDocument4 pagesC6 Fluid Friction Measurement (Issue 2) PDFdjafarNo ratings yet
- VessleDocument50 pagesVessleNguyễn HưngNo ratings yet
- 03 Drilling Recent Development - UI 17 Sep 2006Document34 pages03 Drilling Recent Development - UI 17 Sep 2006Dian L.No ratings yet
- Pressure Balanced Drilling Bumper Sub: Instruction Manual 4410Document17 pagesPressure Balanced Drilling Bumper Sub: Instruction Manual 4410Foros IscNo ratings yet
- Water Hammer ArresterDocument4 pagesWater Hammer ArresterdescslamNo ratings yet
- Viernes Jamaeca B. Aben 3412 Lec Module 3 PDFDocument11 pagesViernes Jamaeca B. Aben 3412 Lec Module 3 PDFBanana QNo ratings yet
- 37.principle of HDDocument24 pages37.principle of HDanandafauziaNo ratings yet
- Indications of JP DrainsDocument9 pagesIndications of JP DrainsDelbrynth MitchaoNo ratings yet
- Perforation Techniques For Production MaximizationDocument5 pagesPerforation Techniques For Production MaximizationanoopscribdNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note 13 - Column SizingDocument32 pagesLecture Note 13 - Column SizingHanguk Germerio ShinNo ratings yet
- Decanter DesignDocument3 pagesDecanter DesignFiza Nnazlan100% (5)
- Aerated Grit Chamber Design ParametersDocument26 pagesAerated Grit Chamber Design ParametersMarc NguyenNo ratings yet
- Scale and Dirt Control - Munters - PWDocument3 pagesScale and Dirt Control - Munters - PWDon GivsyitNo ratings yet
- A Large Spinning-Band Fractionating ColumnDocument4 pagesA Large Spinning-Band Fractionating ColumnNestor Armando Marin SolanoNo ratings yet
- Chest Tube InsertionDocument36 pagesChest Tube InsertionskripsianiNo ratings yet
- Osborne-Reynolds Apparatus to Exhibit Laminar, Transitional and Turbulent flowDocument9 pagesOsborne-Reynolds Apparatus to Exhibit Laminar, Transitional and Turbulent flowMuhammad Abdullah Zafar GhauriNo ratings yet
- L02 - 1 - Hemodialysis-Part 1Document20 pagesL02 - 1 - Hemodialysis-Part 1Tec Mohamed A. MengedNo ratings yet
- Hemodialysis Machine Guide: Anatomy, Clearance & Dialysis ProcessesDocument20 pagesHemodialysis Machine Guide: Anatomy, Clearance & Dialysis ProcessesTec Mohamed A. MengedNo ratings yet
- 2) Module - 1 Boiler Mountings and AccessoriesDocument33 pages2) Module - 1 Boiler Mountings and AccessoriesA48Rayan PereiraNo ratings yet
- Design of Sedimentation Basins: Prof. Dr. Jabbar H. Al-BaidhaniDocument49 pagesDesign of Sedimentation Basins: Prof. Dr. Jabbar H. Al-BaidhaniFaisal Ahsan SadmanNo ratings yet
- Pipelines and Pipe NetworksDocument6 pagesPipelines and Pipe NetworksMohammad Mustafa MirzadNo ratings yet
- Setup and Management of Chest Drainage SystemsDocument2 pagesSetup and Management of Chest Drainage SystemsSITTIE JOBAISAH TOMINAMAN ALINo ratings yet
- Check Valve PrimerDocument1 pageCheck Valve PrimerAsep HermanNo ratings yet
- 6 Well Control System CDocument64 pages6 Well Control System CHamid Reza BabaeiNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Reservoir & Well AspectsDocument46 pagesIntroduction to Reservoir & Well AspectsNamraqlayth ALNOFALNo ratings yet
- 5 Mud System-Lecture-5 PDFDocument26 pages5 Mud System-Lecture-5 PDFأبراهيم كريم كاظم100% (1)
- Design and Flow Coefficient Analysis of Globe Valve As Control Valve Using MATLABDocument5 pagesDesign and Flow Coefficient Analysis of Globe Valve As Control Valve Using MATLABInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Why Check Valves SlamDocument2 pagesWhy Check Valves SlamBramJanssen76No ratings yet
- CM&CD works on Canals and Design of Lift Irrigation SchemesDocument126 pagesCM&CD works on Canals and Design of Lift Irrigation Schemessri sri sai traders kadapaNo ratings yet
- Cushioning System Cushion Features: Typical Straight Cushion Vickers Solid Profiled Cushion Theoretical Ideal CushionDocument6 pagesCushioning System Cushion Features: Typical Straight Cushion Vickers Solid Profiled Cushion Theoretical Ideal Cushionsuresh muthuramanNo ratings yet
- Abrassive Perforating Via Coiled Tubing RevisitedDocument4 pagesAbrassive Perforating Via Coiled Tubing RevisitedRachel PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- Pump-Pipe Systems Design OptimizedDocument64 pagesPump-Pipe Systems Design OptimizedNeetor TendekayiNo ratings yet
- Cyclones/Circuit Operations in A Metallurgical PlantDocument24 pagesCyclones/Circuit Operations in A Metallurgical PlantChelseaNo ratings yet
- Static Gravimetric Method With Flying Start-and-Finish ForDocument6 pagesStatic Gravimetric Method With Flying Start-and-Finish ForMarco LatosaNo ratings yet
- Residual Strength of Liquefied Sand: Laboratory vs Field TestsDocument9 pagesResidual Strength of Liquefied Sand: Laboratory vs Field TestsJulio BetancurNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Wetting Agents Using Student ExperimentsDocument2 pagesEvaluating Wetting Agents Using Student ExperimentsKrupali Umeshkumar KapadiyaNo ratings yet
- Purcell 1949Document10 pagesPurcell 1949pavka789No ratings yet
- Annulus Reclosable Circulating Valve Ps PDFDocument2 pagesAnnulus Reclosable Circulating Valve Ps PDFluisNo ratings yet
- Force Exerted On Pressure ConduitsDocument30 pagesForce Exerted On Pressure ConduitsCeline LaraNo ratings yet
- DTW TrainingPresentation DesignOfTeruvianIntakeDocument21 pagesDTW TrainingPresentation DesignOfTeruvianIntakePrincess AnnNo ratings yet
- Orifice Tubes WeirsDocument13 pagesOrifice Tubes Weirsalfarero.tristangiovannNo ratings yet
- Tsda Sedimentadores de Tubos PDFDocument4 pagesTsda Sedimentadores de Tubos PDFAndres OsorioNo ratings yet
- Brentwood - CL - Tube Settler DesApp - 2011 - en PDFDocument4 pagesBrentwood - CL - Tube Settler DesApp - 2011 - en PDFagomilNo ratings yet
- Reverse Osmosis Treatment of Drinking WaterFrom EverandReverse Osmosis Treatment of Drinking WaterRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Turbulent Buoyant Jets and Plumes: HMT: The Science & Applications of Heat and Mass Transfer. Reports, Reviews & Computer ProgramsFrom EverandTurbulent Buoyant Jets and Plumes: HMT: The Science & Applications of Heat and Mass Transfer. Reports, Reviews & Computer ProgramsNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical 2021-2022 MohamedDocument2 pagesMedical Surgical 2021-2022 MohamedMohamed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- المراجعة النهائية Ems كامل يناير 2022Document189 pagesالمراجعة النهائية Ems كامل يناير 2022prasad gowdaNo ratings yet
- NO Answer: Frequently Asked Questions (Faq) ON Unifi TV Content Update 2022Document10 pagesNO Answer: Frequently Asked Questions (Faq) ON Unifi TV Content Update 2022Mohamed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Chest Physiotherapy Techniques and Nursing CareDocument30 pagesChest Physiotherapy Techniques and Nursing CareMohamed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Mark True or FalseDocument1 pageMark True or FalseMohamed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Assignment 2: Mark True or FalseDocument1 pageMicrobiology Assignment 2: Mark True or FalseMohamed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- 3 Step NCLEX Study PlanDocument1 page3 Step NCLEX Study PlanMohamed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Record SummaryDocument2 pagesNursing Care Record SummaryMohamed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Quiz On Nutrition Ist ChapterDocument1 pageQuiz On Nutrition Ist ChapterMohamed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- ICU One Pager Vasopressors.1.2Document1 pageICU One Pager Vasopressors.1.2Mohamed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Patient EducationDocument6 pagesPatient EducationMohamed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- ICU One Pager Pleural ManometryDocument1 pageICU One Pager Pleural ManometryMohamed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- ICU One Pager EVD V11Document1 pageICU One Pager EVD V11Mohamed Mahmoud100% (1)
- Pathophysiology HemothoraxDocument1 pagePathophysiology HemothoraxFlauros Ryu Jabien50% (4)
- TOPIC 1 - History of RT (Prof. Ethics - MNGT & Health Care Ethics)Document12 pagesTOPIC 1 - History of RT (Prof. Ethics - MNGT & Health Care Ethics)Ben JilhanoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPNiño LuceroNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet for Hydraulic OilDocument6 pagesSafety Data Sheet for Hydraulic OilaminNo ratings yet
- Product Identification and Manufacture Information.: Msds-1Document4 pagesProduct Identification and Manufacture Information.: Msds-1hse indacoNo ratings yet
- PneumothoraxDocument52 pagesPneumothoraxtrisna satrianaNo ratings yet
- Asthmatic Attack: Miriti M.D Masters of Clinical Medicine Accidents and Emergency Facilitator: DR Simba DR MburuguDocument26 pagesAsthmatic Attack: Miriti M.D Masters of Clinical Medicine Accidents and Emergency Facilitator: DR Simba DR MburuguDennis MiritiNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet SummaryDocument6 pagesSafety Data Sheet SummaryMASH TLMOSNo ratings yet
- A Global TextBook of Radiology IIDocument705 pagesA Global TextBook of Radiology IIannatabashidzeNo ratings yet
- Fentanyl Fact Sheet Ver 7-26-18Document11 pagesFentanyl Fact Sheet Ver 7-26-18BrianNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Disorder Note BSC 3rd YearDocument41 pagesRespiratory Disorder Note BSC 3rd YearNancyNo ratings yet
- Servo-N Hands On Guide-En-non UsDocument16 pagesServo-N Hands On Guide-En-non UsGabriela Mex MoraNo ratings yet
- ICU equipment essentialsDocument15 pagesICU equipment essentialsZobaeir AhamedNo ratings yet
- Procedural Sedation GuideDocument9 pagesProcedural Sedation GuideZayar SweNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Critical Care NursingDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Critical Care NursingAngielyn Ramos Oloraza100% (2)
- ASHRAE 62.1-2013 - OUTDOOR AIR TableDocument4 pagesASHRAE 62.1-2013 - OUTDOOR AIR TableJerry Han100% (6)
- Breathing at Depth Physiologic and Clinical Aspects of Diving While Breathing Compressed Gas.Document26 pagesBreathing at Depth Physiologic and Clinical Aspects of Diving While Breathing Compressed Gas.FebyNo ratings yet
- Hlimkhawpui - 28.02.2021Document2 pagesHlimkhawpui - 28.02.2021JC LalthanfalaNo ratings yet
- Saf06 Check List For Entry & Work in Enclosed Spaces PTWDocument5 pagesSaf06 Check List For Entry & Work in Enclosed Spaces PTWDmytroNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination: Prof. Ezekiel M. WafulaDocument19 pagesPhysical Examination: Prof. Ezekiel M. Wafulaokwadha simionNo ratings yet
- C.a.t-Hse-Cses & SBM-01Document50 pagesC.a.t-Hse-Cses & SBM-01M AbidNo ratings yet
- FUNDAMENTALS OF NURSING Part 1Document11 pagesFUNDAMENTALS OF NURSING Part 1Ganesh BoreyNo ratings yet
- MATERI HAND HIGYNE DR - AhmadDocument40 pagesMATERI HAND HIGYNE DR - AhmadAhmad Dailah SudrajatNo ratings yet
- Lab Report - Circulation and RespirationDocument4 pagesLab Report - Circulation and RespirationSimranNo ratings yet
- Abs Af360Document5 pagesAbs Af360DAVID LIMNo ratings yet
- ChartingDocument2 pagesChartingKristine OlitinNo ratings yet
- Health Status and Travel Declaration FormDocument1 pageHealth Status and Travel Declaration FormArmand HapinatNo ratings yet
- Merit Is A Must! - A Clinical Clerk's Guide To Oral Revalida EmergenciesDocument177 pagesMerit Is A Must! - A Clinical Clerk's Guide To Oral Revalida Emergencies유미Yoo100% (1)
- Vitamin D3 5GDocument7 pagesVitamin D3 5GLuis SuescumNo ratings yet
- A (ACLS) - 2015: Dvanced Cardiac Life SupportDocument52 pagesA (ACLS) - 2015: Dvanced Cardiac Life SupportNajmussaqibNo ratings yet