Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Homeostasis - Reviewer
Uploaded by
Eva Marie Gaa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageThis document summarizes homeostasis, which refers to the body's ability to maintain stable internal conditions even when external factors change. Homeostasis involves negative feedback mechanisms that sense disturbances and counteract them to restore balance. It affects key areas like body temperature, water levels, oxygen/carbon dioxide levels, and blood glucose. The body uses receptors to detect changes, control centers to set reference points and determine responses, and effectors to enact those responses. Most homeostatic systems use negative feedback, where a response counters the original stimulus, like a thermostat. Positive feedback amplifies stimuli in limited cases like blood clotting or childbirth. Together these feedback mechanisms help regulate chemicals and keep the body functioning properly.
Original Description:
Original Title
HOMEOSTASIS- REVIEWER
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes homeostasis, which refers to the body's ability to maintain stable internal conditions even when external factors change. Homeostasis involves negative feedback mechanisms that sense disturbances and counteract them to restore balance. It affects key areas like body temperature, water levels, oxygen/carbon dioxide levels, and blood glucose. The body uses receptors to detect changes, control centers to set reference points and determine responses, and effectors to enact those responses. Most homeostatic systems use negative feedback, where a response counters the original stimulus, like a thermostat. Positive feedback amplifies stimuli in limited cases like blood clotting or childbirth. Together these feedback mechanisms help regulate chemicals and keep the body functioning properly.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageHomeostasis - Reviewer
Uploaded by
Eva Marie GaaThis document summarizes homeostasis, which refers to the body's ability to maintain stable internal conditions even when external factors change. Homeostasis involves negative feedback mechanisms that sense disturbances and counteract them to restore balance. It affects key areas like body temperature, water levels, oxygen/carbon dioxide levels, and blood glucose. The body uses receptors to detect changes, control centers to set reference points and determine responses, and effectors to enact those responses. Most homeostatic systems use negative feedback, where a response counters the original stimulus, like a thermostat. Positive feedback amplifies stimuli in limited cases like blood clotting or childbirth. Together these feedback mechanisms help regulate chemicals and keep the body functioning properly.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
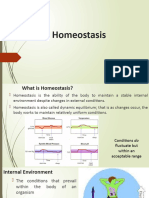
A&P: HOMEOSTASIS
Chapter 3 o in order to maintain internal balance,
HOMEOSTASIS the body needs to have its counter
response, and this is how negative
Homeostasis feedback works. The variables are
- maintenance of a stable internal the situations which throws off the
environment balance and the counter response is
- A dynamic state of equilibrium no your negative feedback mechanism
matter what changes are occurring o counter response to the variable or
outside the body the situation
- Necessary for normal body
functioning and to sustain life 2. Positive feedback
- Describes the body’s ability to o Increases the original stimulus to
maintain relatively stable internal push the variable farther
conditions even though the outside o In the body this only occurs in blood
world is continuously changing clotting and during the birth of a
- The literal translation of homeostasis baby
is “unchanging” o enhancing more the variable
- (homeo=the same, stasis=standing
still which is not true).
- In general, the body is in Maintaining Homeostasis
homeostasis when its needs are
adequately met and it is functioning All homeostatic mechanisms have three
smoothly. components in common.
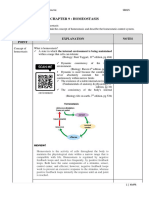
Receptor – senses change in
Homeostatic Imbalance
environment
- A disturbance in homeostasis
Control Center – Regulates set-point
resulting in disease
of variables
Major areas that need homeostasis: Effector – organ that acts in
Body temperature (shiver, blood response to changes
flow)
Water level (thirsty, urinate) The body communicates through neural and
Co2/O2 (breathe heavy) hormonal control systems
Blood glucose (hunger) Receptor
- Responds to changes in the
environment (stimuli)
FEEDBACK MECHANISMS - Sends information to control center
• Help control amounts of chemicals Control center
to maintain homeostatic - Determines set point
mechanisms. E.g. HORMONES - Analyzes information
• Most homeostatic mechanisms are - Determines appropriate response
regulated by negative feedback.
Effector
1. Negative feedback - Provides a means for response to
o Includes most homeostatic control the stimulus
mechanisms
o Shuts off the original stimulus, or
reduces its intensity
o Works like a household thermostat
Eva Marie Gaa, R.N.
1
You might also like
- Johanna Jane H. Macasero - Anaphy Homeostasis TransesDocument4 pagesJohanna Jane H. Macasero - Anaphy Homeostasis TransesJohanna MacaseroNo ratings yet
- Maintain Fairly Stable Conditions Necessary For SurvivalDocument4 pagesMaintain Fairly Stable Conditions Necessary For SurvivalHANNAH ANGELINA ALFONSONo ratings yet
- Boundless Biology: Homeostatic ProcessDocument14 pagesBoundless Biology: Homeostatic ProcessJohnRommelMoradoNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis: Presented By: Ayesha Ehsan Roll No: HESC19115033 Class: Presented To: Sir Umair QadirDocument23 pagesHomeostasis: Presented By: Ayesha Ehsan Roll No: HESC19115033 Class: Presented To: Sir Umair QadirMúdâsîr Ùsmâñ BâlochNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument16 pagesHomeostasisDr M K GuptaNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument16 pagesHomeostasisMerly MorgianaNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument15 pagesHomeostasisAchira DeemanthaNo ratings yet
- Define Homeostasis and Describe The Importance of HomeostasisDocument3 pagesDefine Homeostasis and Describe The Importance of HomeostasisRandomNo ratings yet
- g8. HomeostasisDocument39 pagesg8. HomeostasisKaycee Louchel OccenaNo ratings yet
- How The: Nervous SystemDocument51 pagesHow The: Nervous SystemKurt John DecenaNo ratings yet
- Maintaining A Balance Part 5Document43 pagesMaintaining A Balance Part 5educator56No ratings yet
- LN in HomeostasisDocument2 pagesLN in HomeostasisAra GordonNo ratings yet
- ANFISDocument463 pagesANFISns.sara.alfarsaNo ratings yet
- Feedback MechanismDocument2 pagesFeedback MechanismMayne Ramzelle TamanoNo ratings yet
- Regulation and ControlDocument3 pagesRegulation and ControlDanzel PhilbertNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument46 pagesHomeostasisHeswer RajNo ratings yet
- GenBio 2 FinalsDocument7 pagesGenBio 2 FinalsPanot na BilogNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis and Feedback MechanismsDocument23 pagesHomeostasis and Feedback MechanismsDimple MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Biology2 L1 Homeostasis and Feedback Mechanisms 1 PDFDocument14 pagesBiology2 L1 Homeostasis and Feedback Mechanisms 1 PDFCaryll Andre VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Maintaining A Balance PDFDocument33 pagesMaintaining A Balance PDFtimeflies23No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 HomeostasisDocument4 pagesChapter 4 Homeostasislidsay.fgNo ratings yet
- 2 - HomeostasisDocument33 pages2 - Homeostasisnikitachaudhary1220No ratings yet
- Environmental Homeostasis Homeostasis: Acting On An OrganismDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Homeostasis Homeostasis: Acting On An OrganismAtifMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Biophysical and Psychosocial Cocepts in Nursing PracticeDocument36 pagesBiophysical and Psychosocial Cocepts in Nursing PracticeJoel AlmoguerraNo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICS Notes 1Document2 pagesBIOENERGETICS Notes 1Hya LaniogNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument69 pagesUntitledNaveen HabeebNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Physiology:: December 7, 2021 Berrak YEGENDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Physiology:: December 7, 2021 Berrak YEGENErdem AltunNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Patton Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesAnatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Patton Solutions Manualinnodate.haemapodbtgdt100% (24)
- Oral Physioloy Lecture 1 PDFDocument33 pagesOral Physioloy Lecture 1 PDFHabeeb AL-AbsiNo ratings yet
- Module 1B-Homeostasis (Revised)Document15 pagesModule 1B-Homeostasis (Revised)Rafael SumayaNo ratings yet
- Feedbach of Nervous MechanismDocument17 pagesFeedbach of Nervous MechanismsdjturaNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument18 pagesHomeostasisEmelia DeeNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis: Unit 2, Topic 1Document24 pagesHomeostasis: Unit 2, Topic 1qwertNo ratings yet
- Anaphy TransDocument5 pagesAnaphy TransMARYA AJI ADANNo ratings yet
- Feedback Mechanisms: By: Lenny Ann Kate ReyesDocument15 pagesFeedback Mechanisms: By: Lenny Ann Kate ReyesLenny Ann Kate ReyesNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument21 pagesHomeostasisCassandra MaaloufNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis: Talkie Time and RecapDocument72 pagesHomeostasis: Talkie Time and RecapKathleen Anne LandarNo ratings yet
- Feedback MechanismsDocument7 pagesFeedback MechanismsClem Aisha Mae FajardoNo ratings yet
- HOMEOSTASISDocument21 pagesHOMEOSTASISalyaainsyirah04No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Patton Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesAnatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Patton Solutions ManualPaulaJamesjcrb100% (51)
- Intro To PhysiologyDocument1 pageIntro To PhysiologyKNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Organismal BiologyDocument2 pagesLesson 2 Organismal BiologyJoey II Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Week 3Document4 pagesAnaphy Week 3Lea FajardoNo ratings yet
- IV.D. HomeostasisDocument19 pagesIV.D. HomeostasisDarwin NoolNo ratings yet
- 4-Foundation Block Lecture 4 (Homeostasis I)Document24 pages4-Foundation Block Lecture 4 (Homeostasis I)listodartNo ratings yet
- Regulation and Control4ppDocument9 pagesRegulation and Control4ppshan mackNo ratings yet
- PHYSIO ReviewerDocument3 pagesPHYSIO ReviewerPHILYP EPHRAIM PARANGALANNo ratings yet
- First Semester 2020/2021Document37 pagesFirst Semester 2020/2021low luffecussNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis Control SystemDocument1 pageHomeostasis Control SystemRica NorcioNo ratings yet
- SCIE 10-Q3-Negative and Positive Fedback MechanismDocument25 pagesSCIE 10-Q3-Negative and Positive Fedback MechanismJoana CastilloNo ratings yet
- Role of Homeostasis in Human Physiology A ReviewDocument5 pagesRole of Homeostasis in Human Physiology A ReviewNathaly ZiékteNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis in The EcosystemDocument13 pagesHomeostasis in The EcosystemascxxigamingNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis Feedback MechanismsDocument46 pagesHomeostasis Feedback MechanismsElaiza BeloiraNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Lesson 1 - Feedback MechanismDocument46 pagesModule 2 - Lesson 1 - Feedback Mechanismdavido davidoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ObjectDocument42 pagesIntroduction To ObjectHanan KemalNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis FakyuDocument217 pagesHomeostasis FakyuHafizszul FeyzulNo ratings yet
- Departemen Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera UtaraDocument47 pagesDepartemen Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera UtaraRhena Fitria KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Hormonal and Alkaline Diet For Women: Reverse Ailments and Heal the Body Naturally Inspired By Barbara Oneill Self Heal By DesignFrom EverandHormonal and Alkaline Diet For Women: Reverse Ailments and Heal the Body Naturally Inspired By Barbara Oneill Self Heal By DesignNo ratings yet
- Intro To Anaphy - ReviewerDocument5 pagesIntro To Anaphy - ReviewerEva Marie GaaNo ratings yet
- Terms & Planes - ReviewerDocument3 pagesTerms & Planes - ReviewerEva Marie GaaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - ReviewerDocument8 pagesRespiratory System - ReviewerEva Marie GaaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System - ReviewerDocument11 pagesCardiovascular System - ReviewerEva Marie GaaNo ratings yet
- Pioneers of BiochemistryDocument2 pagesPioneers of BiochemistryEva Marie GaaNo ratings yet
- Biochem of Carbohydrates - ReviewerDocument6 pagesBiochem of Carbohydrates - ReviewerEva Marie GaaNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument3 pagesCARBOHYDRATESEva Marie GaaNo ratings yet
- ABGDocument7 pagesABGEva Marie GaaNo ratings yet
- Cell ReviewerDocument6 pagesCell ReviewerEva Marie GaaNo ratings yet
- Biology Alevel AQA Checklist Ready For UseDocument4 pagesBiology Alevel AQA Checklist Ready For UseM BNo ratings yet
- LP3 AnswersDocument12 pagesLP3 AnswersRazell Jean ArazaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument12 pagesRespiratory SystemTricia CabiliNo ratings yet
- We Achieve Therapuetic Success: Price List For Medical ProfessionalsDocument24 pagesWe Achieve Therapuetic Success: Price List For Medical ProfessionalsMicula ArabellaNo ratings yet
- Allergic DisordersDocument20 pagesAllergic DisorderskiyoorexenNo ratings yet
- wbi14-01-rms-20240118Document34 pageswbi14-01-rms-20240118Hamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Holzel Et AlDocument38 pagesHolzel Et Alayza.aftab24No ratings yet
- Anatomy N PhysiologyDocument10 pagesAnatomy N Physiologynaem nadzriNo ratings yet
- 57-Article Text-95-1-10-20190529Document17 pages57-Article Text-95-1-10-20190529Ridwan SodiqNo ratings yet
- CIE Alevel Biology Mock Papers Paper 2 As Structured Questions Sample PagesDocument96 pagesCIE Alevel Biology Mock Papers Paper 2 As Structured Questions Sample PagesSalman Farsi TaharatNo ratings yet
- بنك الأسئلةDocument775 pagesبنك الأسئلةسماح صلاح100% (1)
- Chapter 13 Cardiovascular ResponsesDocument32 pagesChapter 13 Cardiovascular ResponsesMARIA FERNANDA RONDONNo ratings yet
- Pelvic FractureDocument18 pagesPelvic FractureTantyaNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development: Bruno MarciniakDocument20 pagesGrowth and Development: Bruno MarciniakOmar Sanchez PazNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Image Quality When Evaluating Blood Flow atDocument25 pagesOptimizing Image Quality When Evaluating Blood Flow atRazan AlayedNo ratings yet
- Norvell ARG and Role in Renal InnervationDocument11 pagesNorvell ARG and Role in Renal InnervationGNo ratings yet
- ChrismDocument2 pagesChrismCorey SiebenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Test BankDocument20 pagesChapter 14 Test BankquynhphamftNo ratings yet
- Studi Kasus: Profil Sel Darah Merah Anjing Yang TerinfeksiDocument5 pagesStudi Kasus: Profil Sel Darah Merah Anjing Yang TerinfeksiI Kadek Adi Krisna WidiantaraNo ratings yet
- Vertebrates: Amphibians, Reptiles, Aves and Mammals: Dr. Nnamdi H. AMAEZEDocument32 pagesVertebrates: Amphibians, Reptiles, Aves and Mammals: Dr. Nnamdi H. AMAEZEAkingboye MaxwellNo ratings yet
- Adel Wanas. General ComplicationsDocument40 pagesAdel Wanas. General ComplicationsFathy AlhallagNo ratings yet
- Module: Lie Detection Techniques (3/1) : at The End of This Chapter The Student's Should Be Able To UnderstandDocument84 pagesModule: Lie Detection Techniques (3/1) : at The End of This Chapter The Student's Should Be Able To Understandjonas ventolinaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology of The Male Female Reproductive SystemDocument17 pagesAnatomy Physiology of The Male Female Reproductive SystemLilian JerotichNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesCardiovascular SystemNashreen QtqtNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Stress Management For Life A Research Based Experiential Approach 5th Edition Michael Olpin Margie HessonDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Stress Management For Life A Research Based Experiential Approach 5th Edition Michael Olpin Margie HessonJamesNewmanazpy100% (32)
- Extramedullary Hematopoiesis - A New Look at The Underlying Stem Cell Niche, Theories of Development, and Occurrence in AnimalsDocument16 pagesExtramedullary Hematopoiesis - A New Look at The Underlying Stem Cell Niche, Theories of Development, and Occurrence in AnimalsGabriel CoutoNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Depression Current Identification BiomarkersDocument16 pagesPostpartum Depression Current Identification Biomarkersolyvia lenseNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic Drainage of Head & NeckDocument96 pagesLymphatic Drainage of Head & NeckRoopa PatilNo ratings yet
- Gaurav Kumar Hemnani - UNIT TEST 2 - MOVEMENT IN AND OUT OF CELLS - BIOLOGICAL MOLECULESDocument7 pagesGaurav Kumar Hemnani - UNIT TEST 2 - MOVEMENT IN AND OUT OF CELLS - BIOLOGICAL MOLECULESSlavic GauravNo ratings yet
- Gupta Divye Module3 Appendix Block5 Subgrp1Document50 pagesGupta Divye Module3 Appendix Block5 Subgrp1Shashi Royal TNNo ratings yet