Professional Documents
Culture Documents
12 Formula
Uploaded by
Naveed KhanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
12 Formula
Uploaded by
Naveed KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
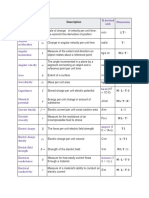
Derived quantity Symbol Description SI derived unit Dimension
Absement Measure of sustained displacement: the first
A
integral with respect to time of displacement
m⋅ s L T
Absorbed dose rate Absorbed dose received per unit of time Gy/s L2 T−3
Acceleration Rate of change of velocity per unit time: the
a→
second time derivative of position
m/s2 L T−2
Angular acceleration ωa Change in angular velocity per unit time rad/s2 T−2
Angular momentum Measure of the extent and direction an object
L
rotates about a reference point
kg⋅m2/s M L2 T−1
The angle incremented in a plane by a
Angular velocity ω segment connecting an object and a rad/s T−1
reference point per unit time
Area A Extent of a surface m2 L2
Area density ρA Mass per unit area kg⋅m −2
M L−2
Capacitance C Stored charge per unit electric potential farad (F = C/V) M−1 L−2 T4 I2
Catalytic activity concentration Change in reaction rate due to presence of
a catalyst per unit volume of the system
kat⋅m−3 L−3 T−1 N
Chemical potential Energy per unit change in amount of
μ
substance
J/mol M L2 T−2 N−1
Change of jounce per unit time: the fifth time
Crackle c→ m/s5 L T−5
derivative of position
Current density J → Electric current per unit cross-section area A/m2 L−2 I
Received radiation adjusted for the effect on
Dose equivalent H sievert (Sv = m2/s2) L2 T−2
biological tissue
Dynamic viscosity Measure for the resistance of an
v
incompressible fluid to stress
Pa⋅s M L−1 T−1
Electric charge Q The force per unit electric field strength coulomb (C = A⋅s) T I
Electric charge density ρQ Electric charge per unit volume C/m3 L−3 T I
Electric displacement field D→ Strength of the electric displacement C/m2 L−2 T I
Electric field strength E→ Strength of the electric field V/m M L T−3 I−1
Measure for how easily current flows through
Electrical conductance G siemens (S = Ω−1) M−1 L−2 T3 I2
a material
Electrical conductivity σ Measure of a material's ability to conduct an
electric current
S/m M−1 L−3 T3 I2
Energy required to move a unit charge
Electric potential φ through an electric field from a reference volt (V = J/C) M L2 T−3 I−1
point
Electrical resistance R Electric potential per unit electric current ohm (Ω = V/A) M L2 T−3 I−2
Electrical resistivity Bulk property equivalent of electrical
ρe
resistance
ohm-metre (Ω⋅m) M L3 T−3 I−2
Energy E Energy J M L2 T−2
Energy density ρE Energy per unit volume J⋅m−3 M L−1 T−2
Entropy Logarithmic measure of the number of
S
available states of a system
J/K M L2 T−2 Θ−1
Force F→ Transfer of momentum per unit time newton (N = kg⋅m⋅s−2) M L T−2
Number of (periodic) occurrences per unit
Frequency f hertz (Hz = s−1) T−1
time
Half-life Time for a quantity to decay to half its initial
t1/2
value
s T
Heat Q Thermal energy joule (J) M L2 T−2
Heat capacity Cp Energy per unit temperature change J/K M L2 T−2 Θ−1
Heat flux density ϕQ Heat flow per unit time per unit surface area W/m2 M T−3
Illuminance Ev Luminous flux per unit surface area lux (lx = cd⋅sr/m2) L−2 J
Impedance Resistance to an alternating current of a ohm (Ω)
Z
given frequency, including effect on phase M L2 T−3 I−2
Impulse J Transferred momentum newton-second (N⋅s = kg⋅m/s) M L T−1
Inductance Magnetic flux generated per unit current henry (H)
L
through a circuit
M L2 T−2 I−2
Irradiance Electromagnetic radiation power per unit
E
surface area
W/m2 M T−3
Intensity I Power per unit cross sectional area W/m2 M T−3
Jerk Change of acceleration per unit time: the
j→
third time derivative of position
m/s3 L T−3
Jounce (or snap) Change of jerk per unit time: the fourth time
s→
derivative of position
m/s4 L T−4
Linear density ρl Mass per unit length kg⋅m−1 M L−1
Luminous flux (or luminous power) F Perceived power of a light source lumen (lm = cd⋅sr) J
Mach number (or mach) Ratio of flow velocity to the local speed of unitless
M
sound
1
Magnetic field strength H Strength of a magnetic field A/m L−1 I
Measure of magnetism, taking account of the
Magnetic flux Φ weber (Wb) M L2 T−2 I−1
strength and the extent of a magnetic field
Measure for the strength of the magnetic
Magnetic flux density B tesla (T = Wb/m2) M T−2 I−1
field
Magnetization M Amount of magnetic moment per unit volume A/m L−1 I
Mass of a substance as a fraction of the total
Mass fraction x kg/kg 1
mass
(Mass) Density (or volume density) ρ Mass per unit volume kg/m3 M L−3
Mean lifetime τ Average time for a particle of a substance to
decay
s T
Molar concentration C Amount of substance per unit volume mol⋅m−3 L−3 N
Molar energy Amount of energy present in a system per
unit amount of substance
J/mol M L2 T−2 N−1
Molar entropy Entropy per unit amount of substance J/(K⋅mol) M L2 T−2 Θ−1 N−1
Molar heat capacity Heat capacity of a material per unit amount
c
of substance
J/(K⋅mol) M L2 T−2 Θ−1 N−1
Moment of inertia Inertia of an object with respect to angular
I
acceleration
kg⋅m2 M L2
Momentum p→ Product of an object's mass and velocity kg⋅m/s M L T−1
Measure for how the magnetization of
Permeability μs material is affected by the application of an H/m M L T−2 I−2
external magnetic field
Measure for how the polarization of a
Permittivity εs material is affected by the application of an F/m M−1 L−3 T4 I2
external electric field
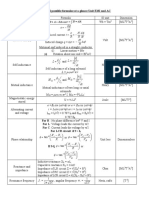
Plane angle θ Ratio of circular arc length to radius radian (rad) 1
Power P Rate of transfer of energy per unit time watt (W) M L2 T−3
Pressure p Force per unit area pascal (Pa = N/m2) M L−1 T−2
Pop Rate of change of crackle per unit time: the
p→
sixth time derivative of position
m/s6 L T−6
(Radioactive) Activity A Number of particles decaying per unit time becquerel (Bq = Hz) T−1
Ionizing radiation energy absorbed by
(Radioactive) Dose D gray (Gy = m2/s2) L2 T−2
biological tissue per unit mass
Power of emitted electromagnetic radiation
Radiance L W/(m2⋅sr) M T−3
per unit solid angle per emitting source area
Radiant intensity Power of emitted electromagnetic radiation
I
per unit solid angle
W/sr M L2 T−3
Reaction rate r Rate of a chemical reaction for unit time mol/(m3⋅s) N L−3 T−1
Refractive index n Factor by which the phase velocity of light is reduced in a medium
unitless 1
{\
displaystyle
Reluctance resistance to the flow of magnetic flux H−1 M−1 L−2 T2 I2
{\mathcal
{R}}}
Solid angle Ratio of area on a sphere to its radius steradian (sr)
Ω
squared
1
Specific energy Energy density per unit mass J⋅kg−1 L2 T−2
Specific heat capacity c Heat capacity per unit mass J/(K⋅kg) L T−2 Θ−1
2
Specific volume v Volume per unit mass (reciprocal of density) m3⋅kg−1 M−1 L3
Spin S Quantum-mechanically defined angular momentum of a particle
kg⋅m2⋅s−1 M L2 T−1
Strain ε Extension per unit length unitless 1
Stress σ Force per unit oriented surface area Pa M L−1 T−2
Surface tension Energy change per unit change in surface
γ
area
N/m or J/m2 M T−2
{\
steepest rate of temperature change at a
Temperature gradient displaystyle K/m Θ L−1
particular location
\nabla T}
Measure for the ease with which an object
Thermal conductance conducts heat
W/K M L2 T−3 Θ−1
Thermal conductivity Measure for the ease with which a material
λ
conducts heat
W/(m⋅K) M L T−3 Θ−1
Measure for the ease with which an object
Thermal resistance R
resists conduction of heat
K/W M−1 L−2 T3 Θ
Measure for the ease with which a material
Thermal resistivity Rλ
resists conduction of heat
K⋅m/W M−1 L−1 T3 Θ
Product of a force and the perpendicular
Torque τ distance of the force from the point about newton-metre (N⋅m) M L2 T−2
which it is exerted
Velocity Moved distance per unit time: the first time
v→
derivative of position
m/s L T−1
Volume V Three dimensional extent of an object m3 L3
Volumetric flow rate Rate of change of volume with respect to
Q
time
m3⋅s−1 L3 T−1
Wavelength Perpendicular distance between repeating
λ
units of a wave
m L
Repetency or spatial frequency: the number
Wavenumber k m−1 L−1
of cycles per unit distance
Wavevector Repetency or spatial frequency vector: the
k→
number of cycles per unit distance
m−1 L−1
Weight w Gravitational force on an object newton (N = kg⋅m/s2) M L T−2
Work W Transferred energy joule (J) M L2 T−2
Young's modulus E Ratio of stress to strain pascal (Pa = N/m2) M L−1 T−2
You might also like
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Derived Quantity SI Derived Unit Dimension: Symb Ol DescriptionDocument6 pagesDerived Quantity SI Derived Unit Dimension: Symb Ol Descriptionlokesh choudharyNo ratings yet
- Base SI units and derived units explainedDocument10 pagesBase SI units and derived units explainedRaef AhmedNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities - (Standards and Units) - 2Document5 pagesPhysical Quantities - (Standards and Units) - 2gayathri gayuNo ratings yet
- List of Physical Quantities: Base Quantity Symbol Description CommentsDocument12 pagesList of Physical Quantities: Base Quantity Symbol Description CommentsAnas ImdadNo ratings yet
- Oil Field Trainee TestDocument102 pagesOil Field Trainee TesteditinggroNo ratings yet
- Physics: List of Formulae for Circular Motion, Gravitation & MoreDocument19 pagesPhysics: List of Formulae for Circular Motion, Gravitation & MoreSucharita KumarNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 02 - MeasurementsDocument1 pageACTIVITY 02 - MeasurementsLat Jiro YadanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Phyiscs - Electromagnetic Induction FormulaeDocument13 pagesCBSE Class 12 Phyiscs - Electromagnetic Induction FormulaeGaganNo ratings yet
- Electricians Licence 'A' (Domestic) - Maltese SyllabusDocument307 pagesElectricians Licence 'A' (Domestic) - Maltese Syllabusdavidegrima100% (17)
- M T L T N I I: Physical Quantity Unit SymbolDocument3 pagesM T L T N I I: Physical Quantity Unit SymbolMark ArceNo ratings yet
- File 3 EMI and AC Group 4Document13 pagesFile 3 EMI and AC Group 4JOHNNo ratings yet
- ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND A.C. FORMULAEDocument13 pagesELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND A.C. FORMULAESsNo ratings yet
- Reading 1Document11 pagesReading 1shafyvonommyNo ratings yet
- CircuitsDocument22 pagesCircuitsapi-3732151100% (1)
- DC CircuitsDocument14 pagesDC CircuitsRaeniel SoritaNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Analysis and SimilitudeDocument25 pagesDimensional Analysis and Similitudejllama20004321No ratings yet
- Module I-1 Electricity & MagnetismDocument15 pagesModule I-1 Electricity & MagnetismCarmie BasilloteNo ratings yet
- Electronics Engineering Review BasicsDocument15 pagesElectronics Engineering Review BasicsCarmie Basillote BulalaNo ratings yet
- SI System IntroductionDocument19 pagesSI System IntroductionmyscribdzoneNo ratings yet
- SI Units and Symbols Used in The Guide: Subject Physical Quantity Symbol Name UnitDocument5 pagesSI Units and Symbols Used in The Guide: Subject Physical Quantity Symbol Name UnitbalaramankrishnanNo ratings yet
- Mechnotes: Unit Iv Dimensional and Model AnalysisDocument23 pagesMechnotes: Unit Iv Dimensional and Model AnalysisSHYAM SUNDARNo ratings yet
- Vector Scalar and Units ReviewDocument43 pagesVector Scalar and Units ReviewGumball DumballNo ratings yet
- 1st Term BookletDocument288 pages1st Term BookletAhmed ElabasyNo ratings yet
- Key Quantities, Symbols and UnitsDocument3 pagesKey Quantities, Symbols and UnitsXian Cong KoayNo ratings yet
- Mole ObjectiveDocument26 pagesMole ObjectiveDevil WalkerNo ratings yet
- Dimensional FormulaDocument6 pagesDimensional FormulaHemanth Gowda0% (1)
- All Dimensional Formula List PDF Free Download PDF HunterDocument5 pagesAll Dimensional Formula List PDF Free Download PDF HunterSarthak Kamli100% (1)
- All Dimensional Formula List PDF Free Download PDF HunterDocument5 pagesAll Dimensional Formula List PDF Free Download PDF HunterIrangaMadhuhansi SellahewaNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument6 pagesCurrent ElectricitySumiya AzizNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantity: ExamplesDocument19 pagesPhysical Quantity: ExamplesAbhishek TiwariNo ratings yet
- Notebook 1: Lindsey ShrinerDocument3 pagesNotebook 1: Lindsey Shrinerapi-338662480No ratings yet
- Elohim Physics Units and DimensionsDocument1 pageElohim Physics Units and DimensionsMoh BroNo ratings yet
- 3 Current ElectricityDocument31 pages3 Current ElectricityPallavi PalluNo ratings yet
- Resistance Vs Temperature Experiment Lab ReportDocument7 pagesResistance Vs Temperature Experiment Lab ReportEmily Gatlin67% (3)
- Physics EoS1 1819 V2Document12 pagesPhysics EoS1 1819 V2farid oluwasegun SHITTUNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems II Formula SheetDocument2 pagesCommunication Systems II Formula SheetGreenThumb100% (5)
- Class 11 Term 1 Short NotesDocument12 pagesClass 11 Term 1 Short NotesDhawanpreet kaurNo ratings yet
- Lect-5-Solar Flat Plate CollectorDocument25 pagesLect-5-Solar Flat Plate CollectorVISHAL VNo ratings yet
- Stucor Ce3391 deDocument141 pagesStucor Ce3391 deAnish KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Dimensions, Units, and Physical Quantities: Fluid Mechanics Demystifi EdDocument4 pages1.1 Dimensions, Units, and Physical Quantities: Fluid Mechanics Demystifi EdWanda Aulia SukmaNo ratings yet
- Phyics HandbookDocument8 pagesPhyics HandbookStephen HillNo ratings yet
- 1EQ - Science - Important Concept & Questions - EngDocument22 pages1EQ - Science - Important Concept & Questions - Engsachindv276No ratings yet
- Review of Electromagnetics: Chapter 0-2Document22 pagesReview of Electromagnetics: Chapter 0-2Hari HaranNo ratings yet
- Physics SymbolsDocument2 pagesPhysics SymbolsAbdul SamiNo ratings yet
- SI Units and Dimensions: by Prof M BasannaDocument4 pagesSI Units and Dimensions: by Prof M Basannaembi76No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: Physical Origins and Rate Equations: Chapter One Sections 1.1 and 1.2Document11 pagesHeat Transfer: Physical Origins and Rate Equations: Chapter One Sections 1.1 and 1.2Kerlly HolaNo ratings yet
- Ch1 Sec 1&2 InsDocument27 pagesCh1 Sec 1&2 Insmaha aleneziNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - 00 0 SymbolsDocument3 pagesMathcad - 00 0 SymbolsBASICNo ratings yet
- Leo Betis Morales Thermodyanmics Reviewer NotesDocument12 pagesLeo Betis Morales Thermodyanmics Reviewer NotesVynz JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 IntroductionDocument30 pagesChapter1 Introductionpamanh97No ratings yet
- 3 Current ElectricityDocument21 pages3 Current ElectricitySakshi KantNo ratings yet
- Upward and Downward Continuation: January 2007Document4 pagesUpward and Downward Continuation: January 2007HarshNo ratings yet
- Notes BookDocument81 pagesNotes BookJason JiaNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities, Units and DimensionsDocument12 pagesPhysical Quantities, Units and Dimensionsdavid ama100% (1)
- Solved Problems in Electrical & Safety Engineering 2014Document28 pagesSolved Problems in Electrical & Safety Engineering 2014hshshdhdNo ratings yet
- Paper 4Document14 pagesPaper 4Saheera HazarikaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 and 4 - Dimensional Analysis and Centrifugal PumpsDocument5 pagesUnit 3 and 4 - Dimensional Analysis and Centrifugal PumpsPavithran JNo ratings yet
- Linear Network Theory: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionFrom EverandLinear Network Theory: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionNo ratings yet
- 42RE Shifting SolutionsDocument2 pages42RE Shifting SolutionsMatt Hurd0% (1)
- Rope Wrapped Around A Fixed PoleDocument4 pagesRope Wrapped Around A Fixed PoleRajeev DayalaniNo ratings yet
- 1102v-4g EuropaDocument75 pages1102v-4g EuropaΜερκουρηςκαπαNo ratings yet
- H 825 DatasheetDocument7 pagesH 825 Datasheetcosmin_butanescuNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Shear Rheometer - Pavement InteractiveDocument10 pagesDynamic Shear Rheometer - Pavement InteractiveMuhammad FaheemNo ratings yet
- Hoek-Brown A Mohr-CoulombDocument7 pagesHoek-Brown A Mohr-CoulombUriel Vélez OrejuelaNo ratings yet
- Free Live Online Master Classes from Expert TeachersDocument11 pagesFree Live Online Master Classes from Expert TeachersReetika MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 ThermochemistryDocument77 pagesLecture 4 ThermochemistryHiep NguyenNo ratings yet
- Gravitational WellDocument8 pagesGravitational WellIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- RC Building Seismic DesignDocument33 pagesRC Building Seismic DesignAnta Cristina IonescuNo ratings yet
- Structural Engg. Refresher (Sept. 22,2021)Document4 pagesStructural Engg. Refresher (Sept. 22,2021)ELMERNo ratings yet
- ELEC3100 B17 Potentials 20181Document36 pagesELEC3100 B17 Potentials 20181mike huntNo ratings yet
- Vortex Mathematics & The Fibonacci Spiral: Unlocking The Fibonacci SequenceDocument8 pagesVortex Mathematics & The Fibonacci Spiral: Unlocking The Fibonacci Sequenceextemporaneous80% (5)
- FlotationDocument3 pagesFlotationtrabajosicNo ratings yet
- Magnetotransport in NanostructuresDocument33 pagesMagnetotransport in NanostructuresMaterials Research InstituteNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Through a Spherical ContainerDocument41 pagesHeat Transfer Through a Spherical ContainerAhmad Alifian LirajabiNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument18 pagesProjectile MotionJan Michael SuarezNo ratings yet
- Strenght of Materials (ES-64)Document353 pagesStrenght of Materials (ES-64)api-3836341100% (14)
- KutunDocument12 pagesKutunJhon Edgar Pinilla VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Forces and FieldsDocument8 pagesElectrostatic Forces and FieldsAryan DeepNo ratings yet
- Notes Prust yDocument47 pagesNotes Prust yHarsha Vardhan Reddy AppidiNo ratings yet
- RF SlabDocument8 pagesRF Slabcheligp1981No ratings yet
- Advanced Design of Steel and Concrete Composite StructuresDocument25 pagesAdvanced Design of Steel and Concrete Composite StructuresCristian BlanaruNo ratings yet
- Section A: Without DimplesDocument16 pagesSection A: Without DimplesLim WcNo ratings yet
- File PDFDocument23 pagesFile PDFNil Kamal80% (5)
- Conduction and Convection Heat Transfer Assignment-Week 3Document12 pagesConduction and Convection Heat Transfer Assignment-Week 3SAWAN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Vedic PhysicsDocument34 pagesVedic PhysicsKamalakarAthalyeNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design Rules For Flat Bottom Cylindrical Liquid Storage Tanks PDFDocument35 pagesSeismic Design Rules For Flat Bottom Cylindrical Liquid Storage Tanks PDFJose Felix AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Dynamics MDB 2043 Rectilinear Kinematics: Erratic MotionDocument7 pagesDynamics MDB 2043 Rectilinear Kinematics: Erratic MotionNaqib NordinNo ratings yet
- Body of The Book - FinalDocument95 pagesBody of The Book - FinalCoup De GráceNo ratings yet