Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Radio Wave: History of Radio Waves
Uploaded by
Lmfao YasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Radio Wave: History of Radio Waves
Uploaded by
Lmfao YasCopyright:
Available Formats
HISTORY of RADIO WAVES
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
In 1887, Heinrich Hertz
demonstrated the reality of
Maxwell's electromagnetic
waves by experimentally
generating radio waves in his laboratory, showing
that they exhibited the same wave properties as
light: standing waves, refraction, diffraction, and
polarization. Radio waves, originally called
"Hertzian waves", were first used for
communication in the mid 1890s by Guglielmo
Marconi, who developed the first practical radio
RADIO WAVE transmitters and receivers. The modern term "radio
-an electromagnetic wave of a frequency between wave" replaced the original name "Hertzian wave"
about 104 and 1011 or 1012 Hz, as used for long- around 1912.
distance communication. HISTORY of RADIO WAVES
• Have the longest wavelengths in the Guglielmo Marconi was awarded the Nobel Prize
electromagnetic spectrum. in physics in 1909 to
• Have wavelengths that range from less than a commemorate his
centimeter to tens or even hundreds of meters. development of wireless
• Radio waves are used to transmit radio and telegraphy after he was able to
television signals. send a long-wave radio signal
across the Atlantic Ocean.
Band Frequencies Band Frequencies USES of RADIO WAVES
VLF (Very VHF (Very Global Positioning Systems (GPS) measure the time
Low) 10 - 30 kHz High) 30 - 300 MHz it takes a radio wave to travel from several satellites
UHF (Ultra 300 MHz - to the receiver, determining the distance to each
LF (Low) 30 - 300 kHz High) 2.9 GHz satellite.
SHF
MF 300 kHz - 3 (Super 2.9 GHz - 30
(Medium) MHz High) GHz
A radio telescope is a form of
EHF
(Extremely 30 GHz and
radio receiver used in
HF (High) 3 - 30 MHz High) above astronomy. In contrast to an
"ordinary" telescope, which receives
Radio waves are one of many forms of visible light, a radio telescope "sees" radio waves
electromagnetic (EM) radiation, emitted by radio sources, typically by means of a
Radio waves of the standard AM broadcast band large parabolic ("dish") antenna, or arrays of them.
have longer wavelength (ranging from 180-550
meters) compared to the short radio waves for FM A radio picks up radio waves
band (ranging from 2.8-3.4 meters). through an antenna and converts
Radio Frequency (RF) it to sound waves. Each radio
Is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3kHz station in an area broadcasts at
to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of a different frequency.
radio waves, and the alternating currents that carry
radio signals. Radio Navigation Systems are the basis for landing
is the frequency range used in radio, extending of the aircraft, regardless of whether are concerned
from around twenty thousand times per second en-route or terminal means.
(20 kHz) to around three hundred billion times per Other USES of RADIO WAVES
second (300 GHz).
HISTORY of RADIO WAVES ➢ Cellular telephones, Wireless
LANs
Radio waves were first ➢ Keyless entry
predicted by mathematical ➢ AM & FM radio
work done in 1867 by Scottish ➢ Garage-door openers
mathematical physicist James ➢ Satellite radio
Clerk Maxwell. Maxwell ➢ Police radar, Radar detectors, Doppler radar
noticed wavelike properties of ➢ Satellite tracking & communications
light and similarities in electrical and magnetic
observations.
RW 2019- PCSHS
You might also like
- Our Protective Atmosphere: What Is Electromagnetic Energy? DiscoveryDocument1 pageOur Protective Atmosphere: What Is Electromagnetic Energy? DiscoveryShiarica Mae NeriNo ratings yet
- Radio WavesDocument14 pagesRadio WavesSian Dasstin TanNo ratings yet
- Gelombang RadioDocument28 pagesGelombang RadioRyoshipukuNo ratings yet
- ModulationDocument170 pagesModulationKen0% (1)
- Green and Pink Doodle Hand Drawn Science Project PresentationDocument7 pagesGreen and Pink Doodle Hand Drawn Science Project PresentationMIKKA ZALAMEANo ratings yet
- Where It All Got StartedDocument9 pagesWhere It All Got StartedJaguarNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves and The em SpectrumDocument9 pagesElectromagnetic Waves and The em SpectrumJoepeteNo ratings yet
- Radio WavesDocument17 pagesRadio WavesVic Ashley Almoete100% (2)
- E g1 Pertacorta-Cuadra Radio-WavesDocument24 pagesE g1 Pertacorta-Cuadra Radio-WavesGeio Nicolai CatreNo ratings yet
- Amplitude and Frequency ModulationDocument116 pagesAmplitude and Frequency ModulationPatrick Joshua GlimadaNo ratings yet
- RAN Radio Theory: By: Zuliana Ismail, 2010Document45 pagesRAN Radio Theory: By: Zuliana Ismail, 2010zulianaNo ratings yet
- Radio Broadcast Technology: Harsh VardhanDocument11 pagesRadio Broadcast Technology: Harsh VardhanLaraAssiNo ratings yet
- Green and Pink Doodle Hand Drawn Science Project PresentationDocument6 pagesGreen and Pink Doodle Hand Drawn Science Project PresentationMIKKA ZALAMEANo ratings yet
- 1a. Review Radio TheoryDocument46 pages1a. Review Radio TheoryRhonny AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document7 pagesScience 10Jeryca Joy PascualNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Avio MidtermsDocument9 pagesReviewer in Avio MidtermsSantos MaineNo ratings yet
- Communication Antenna PDFDocument9 pagesCommunication Antenna PDFJaison PhilipNo ratings yet
- Radio Communication (RADIO)Document15 pagesRadio Communication (RADIO)Jerome TeañoNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 1: Faculty Dr. Mustafa Habib ChowdhuryDocument11 pagesLecture - 1: Faculty Dr. Mustafa Habib ChowdhuryNASIM eeeNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Microwave Antenna and ApplicationsDocument34 pagesIntroduction of Microwave Antenna and ApplicationsdineshNo ratings yet
- Physics Papers Radio Wave Group: SMK - SMAK Bogor School of Year 2015 / 2016Document14 pagesPhysics Papers Radio Wave Group: SMK - SMAK Bogor School of Year 2015 / 2016Septina R NurhalimahNo ratings yet
- WAVESDocument6 pagesWAVESadam_lane_18No ratings yet
- Boundless Physics: Radio WavesDocument29 pagesBoundless Physics: Radio WavesYollyNo ratings yet
- ECE 3001 Analog Communication SystemsDocument23 pagesECE 3001 Analog Communication SystemsYaganti pavan saiNo ratings yet
- Radio Wave PropagationDocument18 pagesRadio Wave PropagationElisha The drummerNo ratings yet
- Radio Waves PresentationDocument16 pagesRadio Waves PresentationAlaina AmaliaNo ratings yet
- ZZZCZCZDocument18 pagesZZZCZCZMarvin SinuesNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Introduction To MicrowavesDocument22 pagesTopic 1 Introduction To MicrowavesmaizatulNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument7 pagesScience ReviewerAsh Abanilla100% (1)
- Science Reviewer q2Document6 pagesScience Reviewer q2Samuel IdoNo ratings yet
- Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT)Document12 pagesSelf-Learning Home Task (SLHT)Ryzza RetubadoNo ratings yet
- MicrowavesDocument11 pagesMicrowavesHrithikNo ratings yet
- 03-Radiation-Propagation of WavesDocument18 pages03-Radiation-Propagation of Waves0322-3713No ratings yet
- Kathan Irish 2018603017: Av7212 Technical Seminar and Report WritingDocument52 pagesKathan Irish 2018603017: Av7212 Technical Seminar and Report Writingkathan Irish RNo ratings yet
- Used As A Symbol in Measuring Wavelength.: Heinrich Hertz - Radio WaveDocument7 pagesUsed As A Symbol in Measuring Wavelength.: Heinrich Hertz - Radio WavePSYCHO / FLOWNo ratings yet
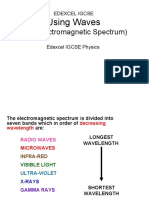
- (The Electromagnetic Spectrum) : Using WavesDocument44 pages(The Electromagnetic Spectrum) : Using WavesSam JordanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Wave Propagation: by Dr. Malik AbdurazzaqDocument30 pagesElectromagnetic Wave Propagation: by Dr. Malik AbdurazzaqMOHAMMADNo ratings yet
- 2 IGCSE 32 UsingWavesDocument53 pages2 IGCSE 32 UsingWavesMahan ZwixNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Transmission Media 17IT083, 17IT084Document55 pagesUnit 4: Transmission Media 17IT083, 17IT084Nayan PatilNo ratings yet
- Fun Intro To EMS WorksheetDocument6 pagesFun Intro To EMS WorksheetgraceNo ratings yet
- Radio Navigation SlidesDocument42 pagesRadio Navigation Slidessegunajayi71No ratings yet
- Cs 480: Mobile Networks: Lecture PowerpointsDocument54 pagesCs 480: Mobile Networks: Lecture PowerpointsTigerNo ratings yet
- RadioDocument15 pagesRadioyashlaNo ratings yet
- RF CommunicationDocument9 pagesRF CommunicationNaren KumarNo ratings yet
- TE 7005 RF & Microwave Engineering: Semester Spring 2013 Engr. Ghulam ShabbirDocument89 pagesTE 7005 RF & Microwave Engineering: Semester Spring 2013 Engr. Ghulam ShabbirBasir UsmanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Radio Waves Part 1Document24 pagesLesson 4 Radio Waves Part 1Azziely-Arah Santiago PabroNo ratings yet
- L.N - Ra&i - Unit - 2Document17 pagesL.N - Ra&i - Unit - 2FIGHTER WINGS AVIATION COLLEGENo ratings yet
- Introduction To Optical Communication SystemsDocument52 pagesIntroduction To Optical Communication SystemsJosé LópezNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Electromagnetic WavesDocument7 pagesThe Nature of Electromagnetic WavesAmarah IbraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document13 pagesLecture 1MONEER THAMEERNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves & Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument3 pagesElectromagnetic Waves & Electromagnetic SpectrumRuperto Alarilla Palomaria Jr.No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 RFDocument5 pagesChapter 1 RFAnil ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Radio Waves (Week 7)Document18 pagesRadio Waves (Week 7)Shane VinceNo ratings yet
- Microwave Communication Chapter 1Document29 pagesMicrowave Communication Chapter 1LeowNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument50 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumMisty Vito100% (1)
- Wireless Communication Main ReportDocument41 pagesWireless Communication Main ReportPraveen BanThiaNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document38 pagesScience 10Angelo LiwanagNo ratings yet
- Radio Waves and MicrowavesDocument25 pagesRadio Waves and Microwavesporshathegreat156No ratings yet
- Presentation BasicDocument42 pagesPresentation BasicSharifah Syed HamzahNo ratings yet
- InfraredDocument1 pageInfraredLmfao YasNo ratings yet
- Microwave: Electromagnetic WavesDocument1 pageMicrowave: Electromagnetic WavesLmfao YasNo ratings yet
- Ultraviolet Rays: HazardsDocument1 pageUltraviolet Rays: HazardsLmfao YasNo ratings yet
- Photo CollageDocument7 pagesPhoto CollageLmfao YasNo ratings yet
- ArchaebacteriaDocument5 pagesArchaebacteriaLmfao YasNo ratings yet
- Argumentative Essay English 10Document2 pagesArgumentative Essay English 10Lmfao YasNo ratings yet
- EXTRA QUESTIONS MotionDocument3 pagesEXTRA QUESTIONS MotionhelloNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Physics - Equations & Formulae: Higher Tier Only Separate Physics OnlyDocument2 pagesAQA GCSE Physics - Equations & Formulae: Higher Tier Only Separate Physics OnlyLuisNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Atomic Structure - AnswersDocument7 pagesUnit 5 Atomic Structure - Answerscom 2501No ratings yet
- Multi Variable Calculus Question BankDocument12 pagesMulti Variable Calculus Question BankSwetha BavandlaNo ratings yet
- High Gain Miniaturised Photonic Band Gap Terahertz Antenna For Size Limited ApplicationsDocument8 pagesHigh Gain Miniaturised Photonic Band Gap Terahertz Antenna For Size Limited ApplicationsRodrigo PaivaNo ratings yet
- Bohr ModelDocument18 pagesBohr Modelkarim adelNo ratings yet
- Science8 Pretest 1st QuarterDocument2 pagesScience8 Pretest 1st QuarterRAYMUND RODILLONo ratings yet
- Topic Wise Analysis: Unit & Topic Name No of Questions Total Marks % WeightageDocument6 pagesTopic Wise Analysis: Unit & Topic Name No of Questions Total Marks % WeightageSagar TiwariNo ratings yet
- 141B PS3 SP10Document1 page141B PS3 SP10Yenhao Philip ChenNo ratings yet
- Formative Assessment 8Document1 pageFormative Assessment 8bashadelacruz7No ratings yet
- Concept Strengthening Sheet (CSS-01) Based On FTS-01&02 (A& B) - PhysicsDocument9 pagesConcept Strengthening Sheet (CSS-01) Based On FTS-01&02 (A& B) - PhysicsGarvit ModiNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Fundamentals Particles QsDocument10 pagesAtomic Structure Fundamentals Particles QsJesulayomi BolajiNo ratings yet
- Ii Pu Physics Answerkeys SRS Pu College PDFDocument11 pagesIi Pu Physics Answerkeys SRS Pu College PDFSachin YadavNo ratings yet
- Addmaths Pyq - Vectors (Summer) MsDocument31 pagesAddmaths Pyq - Vectors (Summer) MsjosephchengNo ratings yet
- Imperfection in Solids: Problems Microscopic TechniquesDocument57 pagesImperfection in Solids: Problems Microscopic TechniquesFahad afzalNo ratings yet
- Board Reviewer in PhyChePri - pdf-1Document1 pageBoard Reviewer in PhyChePri - pdf-1Garcia RaphNo ratings yet
- Kinetics of A Particle-ExDocument20 pagesKinetics of A Particle-ExDerrick Maatla MoadiNo ratings yet
- Alt STD ModelDocument3 pagesAlt STD ModelChris AntoniadesNo ratings yet
- D and F PW New ModuDocument32 pagesD and F PW New ModuIshant SankhalaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-2 Module 7Document17 pagesTutorial-2 Module 7salkr30720No ratings yet
- Generalised Conic SectionsDocument47 pagesGeneralised Conic Sections1stGuyGamezNo ratings yet
- George Haller - Transport Barriers and Coherent Structures in Flow Data - Advective, Diffusive, Stochastic and Active Methods-Cambridge University Press (2023)Document427 pagesGeorge Haller - Transport Barriers and Coherent Structures in Flow Data - Advective, Diffusive, Stochastic and Active Methods-Cambridge University Press (2023)Cesar RosalesNo ratings yet
- O Level Worksheets PHYSICS.Document337 pagesO Level Worksheets PHYSICS.ChaudhryAbdullah85% (61)
- DRB Rectilinear Translation Free Fall and Variable Accelerated MotionDocument5 pagesDRB Rectilinear Translation Free Fall and Variable Accelerated MotionZina CabreraNo ratings yet
- Question ReportDocument56 pagesQuestion ReportAkash AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Lab Report #3: Standard Proctor Test For SoilsDocument11 pagesLab Report #3: Standard Proctor Test For SoilsNguywn DuongNo ratings yet
- Naveen Kumar PPT On Projectile MotionDocument17 pagesNaveen Kumar PPT On Projectile MotionBARUN SINGHNo ratings yet
- IB Physics Data BookletDocument16 pagesIB Physics Data Bookletzoe campbellNo ratings yet
- Dirac of Particles: 1, On The Theory Spin and Non-Relativistic LimitDocument8 pagesDirac of Particles: 1, On The Theory Spin and Non-Relativistic LimitdanielufmaNo ratings yet
- Solid State Physics Chapter 0Document11 pagesSolid State Physics Chapter 0Sergio NuñezNo ratings yet
- Alcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsFrom EverandAlcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsFrom EverandEvaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Concise Guide to OTN optical transport networksFrom EverandConcise Guide to OTN optical transport networksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Set Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNFrom EverandSet Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Hacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.From EverandHacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- PHP BLUEPRINT: An Essential Beginners Guide to Learn the Realms of PHP From A-ZFrom EverandPHP BLUEPRINT: An Essential Beginners Guide to Learn the Realms of PHP From A-ZNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsFrom EverandMicrosoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Designing and Building Security Operations CenterFrom EverandDesigning and Building Security Operations CenterRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamFrom EverandAWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mastering Linux Security and Hardening - Second Edition: Protect your Linux systems from intruders, malware attacks, and other cyber threats, 2nd EditionFrom EverandMastering Linux Security and Hardening - Second Edition: Protect your Linux systems from intruders, malware attacks, and other cyber threats, 2nd EditionNo ratings yet
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionFrom EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Computer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityFrom EverandComputer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Software-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachFrom EverandSoftware-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Computer Networking: The Complete Guide to Understanding Wireless Technology, Network Security, Computer Architecture and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCNA and CCENT)From EverandComputer Networking: The Complete Guide to Understanding Wireless Technology, Network Security, Computer Architecture and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCNA and CCENT)No ratings yet
- FTTx Networks: Technology Implementation and OperationFrom EverandFTTx Networks: Technology Implementation and OperationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamFrom EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamNo ratings yet
- Practical TCP/IP and Ethernet Networking for IndustryFrom EverandPractical TCP/IP and Ethernet Networking for IndustryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- ITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideFrom EverandITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)