Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plant Structure and Growth
Uploaded by
Cielo PulmaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Plant Structure and Growth
Uploaded by
Cielo PulmaCopyright:
Available Formats
PLANT STRUCTURE AND GROWTH
Origin of wheat cultivation: region of the Middle East dubbed the "Fertile Crescent".
A major leap forward occurred in the latter half of the 20th century. "Green Revolution"
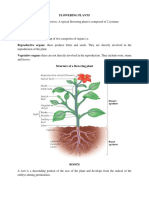
ANGIOSPERMS
Two major groups of angiosperms; monocots & eudicots
MONOCOTS
- are grass and grass-like flowering plants, the seeds of which typically contain only one
embryonic leaf or cotyledon.
EUDICOTS
- Are a clade of flowering plants mainly characterized by having two seed leaves upon
germination.
Basic Organs of a Plant Body: Roots, Stems, Leaves
PLANT ORGAN: ROOTS
FUNCTION: Anchors plant firmly in the soil, Absorbing water and nutrients Production of Hormones.
The plant Body has two connecting systems; The root system and the shoot system
1. Root system consists of components below ground that supports the plant and absorbs water
and minerals.
2. Shoot system consists of all plant components above the ground and has two portions, the
vegetative/ non-reproductive (leaves and stems), and reproductive parts (flowers and fruits).
Roots can also be aerial
or aerating, that is
growing above ground or
especially up above
water.
ROOT HAIR - a filamentous extension of an epidermal cell near the tip of a rootlet that functions in
absorption of water and minerals.
Tap root system - main roots
grow down vertically, and
from which smaller lateral
roots arise. (e.g. carrots)
Fibrous root system - forms
a dense network of roots
that also helps with soil
erosion ( e.g. lawn grasses,
wheat, rice, and corn)
PLANT ORGAN: STEM
FUNCTION: Transport water and solutes between roots and leaves. Produces and supports appendages
of plant (leaves, flowers, fruits.
EXTERNAL STRUCTURE OF A STEM
Nodes - the points at which the leaves are attached
Internodes- the portions of the stem between nodes.
Buds - are undeveloped or embryonic shoots
Terminal Bud or Apical Bud is the area that is the primary growth point at the tip of the stem
that forms the dominant bud.
Axillary Bud is an embryonic or organogenic shoot located in the axil of a leaf.
Apical dominance- In many plants, the terminal bud produces hormones that inhibit the growth
of the axillary buds
The stalk that extends from the stem to the base of the leaf is the petiole
PLANT ORGAN: LEAVES
Function: leaves Are responsible for photosynthesis (making food), respiration (using oxygen to burn
food), and transpiration (releasing excess water vapor).
BASIC LEAF FEATURES: LEAF BLADE, PETIOLE, & STIPULES
BLADE - the broad portion of a leaf
Apex- leaf tip
Margin- leaf edge boundary area (can be smooth, jagged/ toothed, lobed, or parted)
Veins- vascular tissue bundles that support the leaf and transport nutrients
Midrib- travels the length of the leaf and branches to each side to produce veins of vascular tissue
Base- area of the leaf that connects the blade to the petiole
PERIOLE - the thin stalk that attaches leaf to a stem
Leaves that do not have a petiole and are directly connected to the stem are called sessile leaves.
STIPULES - the leaf-like structures at the leaf base
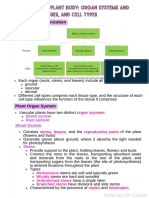
Types of Plant Tissues
Plant tissues fall into one of two general types
Meristematic tissue Permanent tissue
-Are either undifferentiated or - Tissues that has completed its growth and
incompletely differentiated and are differentiation, and is incapable of cell
capable of cell division. Have not attained division. Have attained definite form and
definite form and size and has dense and size and have a thin layer of cytoplasm
abundant cytoplasm. around vacuole.
- Consists of three types: Apical, Lateral, and - Simple – Parenchyma, Collenchyma, and
Intercalar. Sclerenchyma Complex – Xylem & Phloem
Three Tissue systems that make up the Plant Body
DERMAL TISSUE SYSTEM
- is the plant’s outer protective covering it forms the first line of defense against physical
damage and infectious organisms consists of a single layer of tightly packed cells called the
epidermis-which has a waxy coating called the cuticle.
VASCULAR TISSUE SYSTEM
- It is made up of xylem and phloem tissues and provides support and long-distance transport
between the root and shoot systems.
DERMAL TISSUE SYSTEM
- Tissues that are neither dermal nor vascular It accounts for most of the bulk of a young
plant, filling the spaces between the epidermis and vascular tissue system. Ground tissue
internal to the vascular tissue is called pith, and ground tissue external to the vascular tissue
is called cortex.
You might also like
- Raymond Pallet 8210 Parts Manual Service Maintenance ManualDocument23 pagesRaymond Pallet 8210 Parts Manual Service Maintenance Manualscotthicks170301ped99% (131)
- Aboriginal Plant Use List W PicturesDocument9 pagesAboriginal Plant Use List W PicturesAli AbaliNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science: How Plants SurviveDocument9 pagesEarth & Life Science: How Plants Survivejames bonfNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY II NotesDocument8 pagesBIOLOGY II NotesDarwin SawalNo ratings yet
- Andamun Tle106 ReportDocument34 pagesAndamun Tle106 ReportNaharia RangirisNo ratings yet
- BASIC BIOLOGY NOTES Sem 1 Part 2Document7 pagesBASIC BIOLOGY NOTES Sem 1 Part 2Polee SheaNo ratings yet
- Structure: Plant Form and FunctionDocument12 pagesStructure: Plant Form and FunctionPhilippines QatarNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Process of PlantsDocument2 pagesMetabolic Process of PlantsShana GamingNo ratings yet
- Morphology of PlantsDocument58 pagesMorphology of PlantsRishikesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- The Plant BodyDocument2 pagesThe Plant BodyIJ SeducoNo ratings yet
- Leaves: Arnie Hajas Cherrie Mengorio Precious Jewel OrticioDocument15 pagesLeaves: Arnie Hajas Cherrie Mengorio Precious Jewel OrticioJnll JstnNo ratings yet
- Biology Lecture Notes: (Stemer'S Guide)Document22 pagesBiology Lecture Notes: (Stemer'S Guide)AbdoNo ratings yet
- PLANTS: KEY ANATOMY AND REPRODUCTIONDocument20 pagesPLANTS: KEY ANATOMY AND REPRODUCTIONMarie Angelie AcapNo ratings yet
- Roots & StemsDocument12 pagesRoots & StemserincoleNo ratings yet
- Roots, Stems and Leaves: Structure and FunctionsDocument64 pagesRoots, Stems and Leaves: Structure and FunctionsJeli Mae Ysabel PerezNo ratings yet
- GS BIO 206. Functional Organization in PlantsDocument9 pagesGS BIO 206. Functional Organization in PlantsChary Johanne MenesesNo ratings yet
- Tissues System of The Plant BodyDocument47 pagesTissues System of The Plant BodyJana Natassia SilvaNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues and OrgansDocument10 pagesPlant Tissues and OrganskristineNo ratings yet
- Plant Parts and Its Function: Module 1 For CollegeDocument9 pagesPlant Parts and Its Function: Module 1 For CollegeYan DechosNo ratings yet
- Main Function of LeavesDocument3 pagesMain Function of LeavesAndrea AnoverNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functiond of PlantsDocument5 pagesParts and Functiond of PlantsCjoy MañiboNo ratings yet
- Tissues and Typical Plant BodyDocument4 pagesTissues and Typical Plant BodyKhyla Grace DijenoNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Plant OrgansDocument76 pagesChapter Four Plant OrgansASHFAQ AHMADNo ratings yet
- Biological ScienceDocument6 pagesBiological ScienceprincexavierfrancismNo ratings yet
- Plant Biology VocabularyDocument8 pagesPlant Biology Vocabularydevadas panickerNo ratings yet
- Genbio Long Quiz 2 ReviewerDocument42 pagesGenbio Long Quiz 2 ReviewerEthan Erika BionaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom PlantaeDocument19 pagesKingdom PlantaeDanny DonNo ratings yet
- First Look Background InformationDocument6 pagesFirst Look Background Informationahuddle1No ratings yet
- 03-Flowering PlantsDocument45 pages03-Flowering PlantsMaku MichaelNo ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument62 pagesPlant ReproductionAdonis BesaNo ratings yet
- Plant TissuesDocument32 pagesPlant TissuesVikneswaran Gunahlan Nesh100% (2)
- Reinforcement Plant Growth: Beaconhouse School System Unit: Class: VIIDocument8 pagesReinforcement Plant Growth: Beaconhouse School System Unit: Class: VIIAleena Zahra Naqvi/TCHR/BMBNo ratings yet
- Botany RootsDocument6 pagesBotany RootsKrianne Chris DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Morphology of PlantsDocument7 pagesMorphology of PlantsCRYSTAL A. ARIETANo ratings yet
- Botany-Plant Morphology-Anatomy-PhysiologyDocument89 pagesBotany-Plant Morphology-Anatomy-PhysiologyNehaNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Primaryplantbodyrootstemleaves 171115154203Document76 pagesChapter4 Primaryplantbodyrootstemleaves 171115154203chelseapujeda4No ratings yet
- The Plant Tissues.Document41 pagesThe Plant Tissues.JenniferNo ratings yet
- Muntinlupa National High School Tunasan AnnexDocument6 pagesMuntinlupa National High School Tunasan AnnexShaine DelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Plant and Their Systems, Gr-7, AdyalaDocument15 pagesPlant and Their Systems, Gr-7, AdyalaSidra UsmanNo ratings yet
- Plant science vocabulary termsDocument7 pagesPlant science vocabulary termsGABRIELLA ANISNo ratings yet
- Botany RootsDocument49 pagesBotany RootsCudal, Estephanie RoseNo ratings yet
- How The Plant SurviveDocument16 pagesHow The Plant SurvivedhonaNo ratings yet
- Plant Biology Guide on Organ Systems, Tissues, and StructuresDocument27 pagesPlant Biology Guide on Organ Systems, Tissues, and Structuresashok parmarNo ratings yet
- 2 General Biology 2 - Parts of The Plants HDocument57 pages2 General Biology 2 - Parts of The Plants HBLESSIE MARIE ACADEMIANo ratings yet
- Diwey Perez Ikitan Jomer Jireh Pinalapal Jane Prudenciano Ruffa Prudenciano Marvin Carl Chico Tintin Pastor TagapuenDocument29 pagesDiwey Perez Ikitan Jomer Jireh Pinalapal Jane Prudenciano Ruffa Prudenciano Marvin Carl Chico Tintin Pastor TagapuenKristina PonceNo ratings yet
- Acs Lab No. 3Document6 pagesAcs Lab No. 3Karyl GregorioNo ratings yet
- PLANTDocument23 pagesPLANTAngelito HalmainNo ratings yet
- PLANT BIOLOGY Plant Form and FunctionDocument12 pagesPLANT BIOLOGY Plant Form and FunctionNis DancelNo ratings yet
- 1osc03 PlantkingdomDocument4 pages1osc03 PlantkingdomIrene AragonesesNo ratings yet
- 528211336-2-General-Biology-2-Part PlantsDocument58 pages528211336-2-General-Biology-2-Part PlantsPeter MascarenhasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21 The Stem (Primary Structure of Flowering Plant Body)Document9 pagesLecture 21 The Stem (Primary Structure of Flowering Plant Body)maheen akramNo ratings yet
- Bot 121Document12 pagesBot 121eirrehs ellaNo ratings yet
- Primary Plant Body Brainiac ?Document6 pagesPrimary Plant Body Brainiac ?davidoluwadimu28No ratings yet
- II1 IB RevisionDocument3 pagesII1 IB RevisionMedinaNo ratings yet
- Botany Basics EssentialsDocument92 pagesBotany Basics EssentialsMichael OduorNo ratings yet
- Structure N Function of PlantDocument36 pagesStructure N Function of Plantndzani_latifaturNo ratings yet
- BoooplDocument2 pagesBoooplChristian Josh DinoyNo ratings yet
- An Aggregation of Similarly Specialized Cells Which Together Perform Specialized Functions Are CalledDocument44 pagesAn Aggregation of Similarly Specialized Cells Which Together Perform Specialized Functions Are CalledAlanie RakimNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument30 pagesPlantsRanin, Manilac Melissa SNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions of Plant OrgansDocument32 pagesStructures and Functions of Plant OrgansDanielle AnonuevoNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions of Plant OrgansDocument32 pagesStructures and Functions of Plant OrgansPaula SanicoNo ratings yet
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet
- Social Stratification in the Philippines: Classes and EffectsDocument1 pageSocial Stratification in the Philippines: Classes and EffectsCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Electroscope Laboratory ActivityDocument3 pagesElectroscope Laboratory ActivityCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Survey ReportDocument3 pagesSurvey ReportCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Health Declaration Form SteftiDocument1 pageHealth Declaration Form SteftiJen-Jen L. ElonaNo ratings yet
- Cielo S. Pulma Grade 12 - Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDocument1 pageCielo S. Pulma Grade 12 - Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition & TransportDocument2 pagesPlant Nutrition & TransportCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Research Possible QuestionsDocument1 pageResearch Possible QuestionsCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- VARIOUS TECHNIQUES FOR SUMMARIZING ACADEMIC TEXTSDocument2 pagesVARIOUS TECHNIQUES FOR SUMMARIZING ACADEMIC TEXTSCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry QuizDocument3 pagesChemistry QuizCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Transactional Communication: Communication StrategiesDocument12 pagesUnit 3 Transactional Communication: Communication StrategiesCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- English QuizDocument3 pagesEnglish QuizCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Recitation Notes For PR2Document7 pagesRecitation Notes For PR2Cielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Repair and Maintenance JPRDocument1 pageRepair and Maintenance JPRCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Logistic Officer JRDocument1 pageLogistic Officer JRCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Study VAK Model and Discover Your Dominant Learning StyleDocument1 pageStudy VAK Model and Discover Your Dominant Learning StyleCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Confras Unit 2 PartiiDocument1 pageConfras Unit 2 PartiiCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Listening is Key to Effective CommunicationDocument4 pagesListening is Key to Effective CommunicationCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- COACCON Exercise2Document12 pagesCOACCON Exercise2Cielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Cost Accounting Cycle: 4.1 Difference Between Merchandising and Manufacturing OperationDocument13 pagesUnit 4: Cost Accounting Cycle: 4.1 Difference Between Merchandising and Manufacturing OperationCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Joint and By-Product Costing SystemDocument8 pagesUnit 7: Joint and By-Product Costing SystemCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 8: Activity Based Costing and Back-FlushDocument5 pagesUnit 8: Activity Based Costing and Back-FlushCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- NonverbalDocument1 pageNonverbalCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Nature and Classification of Human ActsDocument5 pagesUnderstanding the Nature and Classification of Human ActsCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Human Acts and Their ModifiersDocument20 pagesHuman Acts and Their ModifiersCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Ends of Human Acts and The Norms ofDocument37 pagesUnit 4 Ends of Human Acts and The Norms ofCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- For Scribd 1Document2 pagesFor Scribd 1Louise Bagus SutrisnoNo ratings yet
- Intimate Wedding Packages Savanna DecorationDocument6 pagesIntimate Wedding Packages Savanna DecorationHi suhadi RayuNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles ExplainedDocument46 pagesMeiosis and Sexual Life Cycles ExplainedKavindu MunasingheNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae Phylum Anthophyta: Systematics LaboratoryDocument6 pagesKingdom Plantae Phylum Anthophyta: Systematics LaboratorySIlverNo ratings yet
- Poisonous weeds threaten livestockDocument6 pagesPoisonous weeds threaten livestockCla SaguilNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology 17 Reproduction in PlantsDocument45 pagesO Level Biology 17 Reproduction in PlantsHamzu GamingNo ratings yet
- Zidni Amalia A24170146 BIO CONTROL AGENDocument4 pagesZidni Amalia A24170146 BIO CONTROL AGENzidni amaliaNo ratings yet
- Plant HormoneDocument20 pagesPlant HormoneNeetenin NeeteninNo ratings yet
- Devansh Jain Investigatory Project BiologyDocument25 pagesDevansh Jain Investigatory Project BiologyAKSHAY JAIN100% (1)
- Coffee EstablishmentDocument23 pagesCoffee EstablishmentAMERUDIN DIMALANASNo ratings yet
- Pyricularia monitoring methodologyDocument2 pagesPyricularia monitoring methodologyDaniel Salazar ParraNo ratings yet
- Fragrant False Garlic Occurrence in IndiaDocument5 pagesFragrant False Garlic Occurrence in IndiaJose Franco NaviaNo ratings yet
- No-Foam Wreaths: Get Ready For A Blooming Beautiful ChristmasDocument76 pagesNo-Foam Wreaths: Get Ready For A Blooming Beautiful ChristmasTaniNo ratings yet
- The Origin of Epiphytic CactiDocument126 pagesThe Origin of Epiphytic Cactikengelking8No ratings yet
- Physical and mechanical properties of laminated lumber using berenuk fruit as a natural preservative additiveDocument5 pagesPhysical and mechanical properties of laminated lumber using berenuk fruit as a natural preservative additivePandhu Satriya WasistaNo ratings yet
- Climbing Angiosperms of Manas National Park, Assam: Diversity and EthnobotanyDocument8 pagesClimbing Angiosperms of Manas National Park, Assam: Diversity and EthnobotanyAngel Eduardo Moreno AlboresNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Plants of The World - Volume 1 Chemical Constituents, Traditional and Modern Medicinal Uses PDFDocument496 pagesMedicinal Plants of The World - Volume 1 Chemical Constituents, Traditional and Modern Medicinal Uses PDFJose Rene Salinas CantonNo ratings yet
- 1 Sugar CaneDocument61 pages1 Sugar CanechagirdsocietyNo ratings yet
- Bio101 Important Short NotesDocument23 pagesBio101 Important Short Notesasma zahidNo ratings yet
- African Violet E-Newsletter November 2015Document6 pagesAfrican Violet E-Newsletter November 2015Ana Irina CrînganuNo ratings yet
- Industrial Arts IIDocument14 pagesIndustrial Arts IIjoyce serraNo ratings yet
- Seed Science and Technology1Document25 pagesSeed Science and Technology1DYCENo ratings yet
- Kingdom MycotaDocument33 pagesKingdom MycotaSariska MehraNo ratings yet
- Toxic and Non-Toxic Plant List - Cats - ASPCADocument81 pagesToxic and Non-Toxic Plant List - Cats - ASPCAÁlvaro GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Plant DescriptionDocument3 pagesPlant DescriptionJanine CamachoNo ratings yet
- Morphology of AngiospermDocument7 pagesMorphology of AngiospermSagarNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy BookDocument100 pagesPharmacognosy BookYoussef ElhamamyNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument6 pagesBiologySuraj KumarNo ratings yet