Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HP Repro
Uploaded by
Rhzyl Moira CadapOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HP Repro
Uploaded by
Rhzyl Moira CadapCopyright:
Available Formats
Sexual reproduction
The process by which organisms produce offspring by making germ cells called gametes (GAM-e ̄ts _
spouses).
After the male gamete(sperm cell) unites with the female gamete (secondary oocyte)—an event called
fertilization—
the resulting cell contains one set of chromosomes from each parent.
The gonads—testes in males and ovaries in females—produce gametes and secrete sex hormones.
Various ducts then store and transport the gametes
Accessory sex glands produce substances that protect the gametes and facilitate their movement.
Supporting structures, such as the penis in males and the uterus in females, assist the delivery of
gametes, and
the uterus is also the site for the growth of the embryo and fetus during pregnancy.
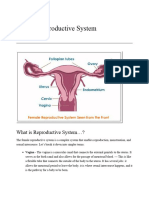
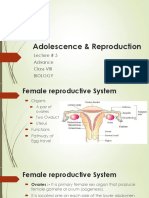
Female Reproductive System
Functions
1. Formation of female gametes (ova)
2. Reception of male gametes (Spermatozoa)
3. Provision of suitable environment for fertilization of the ovum by spermatozoa and development of
the
resultant fetus
4. Parturition – childbirth
5. Lactation – nourishment of the baby
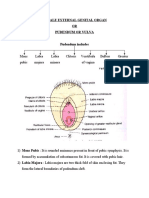
INTERNAL REPRODUCTIVE ORGANS
1. Ovaries
paired, almond shaped solid structures (3 cm x 1.5 – 2 cm x 1 cm) lying on either side of the womb
near the
outer walls of the pelvis.
Femal Gonads.
Suspended in the broad ligaments of the uterus by MESOVARIUM.
TUNICA ALBUGINEA – whitish collagenous connective tissue capsule, beneath the epithelium
OVARIAN CORTEX – deep down the tunica albuginea consists of ovarian follicles
Produce 1 gametes, secondary oocytes that develop into mature eggs after fertilization and 2
hormones
2. Fallopian Tubes (oviducts)
Paired muscular tubes approximately 12 cm long and extends laterally from the uterus
Free ends open into the peritoneal cavity close to the ovaries
Road for sperm to reach the ovum and transport secondary oocytes
INFUNDIBULUM is funnel-shaped portion of each tube and is close to the ovary
AMPULLA ussually where sperm and ovum meet for fertilization.
3. Uterus or womb
Organ where baby grows
Located in pelvis between the urinary bladder and rectum
Same shape and size than that of an inverted pear
Functions to receive, retain, and nourish a fertilized egg
Site of implantation of a fertilized ovum, development of the fetus during pregnancy, and labor
No fertilization – source of menstrual flow
BODY – major portion
FUNDUS – superior rounded portion above the entrance of the uterine tubes
CERVIX – Inferior narrow portion which protrudes into the vagina
UTERINE CAVITY – interior of the body
CERVICAL CANAL – Interior of the cervix
Cervical canal opens to uterine cavity at the INTERNAL OS and into the vagina at the EXTERNAL OS
3 layers
i. Endometrium - 2 Layers
Stratum Functionalis – lines the inner cavity sloughs off during menstruation
Stratum Basalis – permanent deeper layer, give rise to new S. Functionalis
ii. Myometrium
Contracts during labor and childbirth
iii. Perimetrium
Covers the urinary bladder and forms a shallow pouch
4. Vagina
Lies between the bladder and the rectum and extends from the cervix to the exterior body
Receptacle for the penis during intercourse, outlet for menstrual flow and passageway for childbirth
HYMEN – thin fold of mucosa at the distal end, would rupture and bleed during first intercourse
FORNIX – recess sorounding the vaginal attachment to the cervix
You might also like
- Structure and Function of the Male and Female Reproductive SystemsDocument83 pagesStructure and Function of the Male and Female Reproductive SystemsMagy Tabisaura GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesFemale Reproductive Systemreignda774No ratings yet
- Human Reproductive System Yr 11 Biology 114629Document7 pagesHuman Reproductive System Yr 11 Biology 114629Zach ZaneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document4 pagesChapter 3melanielampera17No ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIVEDocument89 pagesREPRODUCTIVEJohn MichaelMackayNo ratings yet
- Animal Reproduction - Class PresentationDocument120 pagesAnimal Reproduction - Class PresentationRenz Dela Cruz ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Animal ReproductionDocument93 pagesAnimal ReproductionunattractiveyouNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document3 pagesScience 10Andrea JimenezNo ratings yet
- Adv - Adolescence and Reproduction - Lec Notes 6Document5 pagesAdv - Adolescence and Reproduction - Lec Notes 605 Nalin PrabhatNo ratings yet
- CLS224 Lecture 13 1 PDFDocument30 pagesCLS224 Lecture 13 1 PDFmike RNo ratings yet
- Male and Female Reproductive Systems ExplainedDocument5 pagesMale and Female Reproductive Systems ExplainedRovina Narayan DiasNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument17 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemYsthanamhire TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Physiology - Ii Year BemsDocument10 pagesPhysiology - Ii Year BemsKumar M V ScNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument25 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemJay PornelaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy ReportDocument17 pagesAnatomy ReportMabeth PagatpatNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive Anatomy GuideDocument8 pagesFemale Reproductive Anatomy GuideNanen CaminceNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument11 pagesThe Reproductive Systemdevgod729No ratings yet
- Reproductive SytemDocument2 pagesReproductive SytemHanna Rezqah P. YusophNo ratings yet
- Reproductive - Systems - in - Vertebrates ss2Document12 pagesReproductive - Systems - in - Vertebrates ss2Ezeh PrincessNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Human Beings (Part 1)Document40 pagesSexual Reproduction in Human Beings (Part 1)puspita8967628No ratings yet
- Human Reproduction: Important NotesDocument6 pagesHuman Reproduction: Important NotesHema KamatNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi REPRO BETINADocument31 pagesFisiologi REPRO BETINADesy NataliaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System HandoutDocument21 pagesReproductive System HandoutJei SanNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument10 pagesReproductionttvignesuwarNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Reproductive SystemDocument48 pagesStructure and Function of The Reproductive SystemJohnryl FranciscoNo ratings yet
- HumanreproductionpptDocument59 pagesHumanreproductionpptsugi sivamNo ratings yet
- Biology (Human Reproductive Anatomy) Lecture Notes or Book NotesDocument6 pagesBiology (Human Reproductive Anatomy) Lecture Notes or Book NotesCharline Lucille BanoNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction CH-03, Bio, Class-XiiDocument69 pagesHuman Reproduction CH-03, Bio, Class-Xiisumitdhakad543No ratings yet
- Reproduction in Human BeingsDocument6 pagesReproduction in Human BeingsanjupalNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesThe Reproductive SystemPak LypNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument29 pagesReproductive SystemGrace Marfa OreñoNo ratings yet
- 8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesDocument13 pages8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesAndre KachigambaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesReproductive SystemMary Grace NovidaNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive System: Alyssa Ashley R. DiegoDocument46 pagesThe Reproductive System: Alyssa Ashley R. DiegoteacherashleyNo ratings yet
- The Human Reproductive System FinalDocument16 pagesThe Human Reproductive System FinalIlac Tristan BernardoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument36 pagesReproductive SystemLeah Beth CañedoNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Human Reproduction New Vocabulary: English WordDocument9 pagesGrade 6 Human Reproduction New Vocabulary: English WordSalome TamaraNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Human Reproduction New Vocabulary: English WordDocument9 pagesGrade 6 Human Reproduction New Vocabulary: English WordCRISTIAN RAFAEL MENDOZA MALDONADONo ratings yet
- Reproduction in HumansDocument4 pagesReproduction in HumansIsra OmerNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction - II Puc - Regular NotesDocument23 pagesHuman Reproduction - II Puc - Regular NotesVasudevNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System: A Female's Internal Reproductive Organs Are The Vagina, Uterus, Fallopian Tubes, and OvariesDocument4 pagesFemale Reproductive System: A Female's Internal Reproductive Organs Are The Vagina, Uterus, Fallopian Tubes, and OvariesMikka Ella BolanosNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument13 pagesReproductive SystemAlicia ValverdeNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in AnimalsDocument12 pagesReproduction in AnimalsYuh moddaNo ratings yet
- Xii Zool Ch3 Human Reproduction HssliveDocument8 pagesXii Zool Ch3 Human Reproduction HsslivePrituNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On The Parts and Functions of The Female Reproductive System by Madel May EgeraDocument5 pagesLecture Notes On The Parts and Functions of The Female Reproductive System by Madel May EgeraMadel May D EgeraNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-03-28 at 10.17.47 PMDocument127 pagesScreenshot 2022-03-28 at 10.17.47 PMqdvvqvxn7gNo ratings yet
- Human reproduction organs functionsDocument4 pagesHuman reproduction organs functionsTasneem HamdyNo ratings yet
- Biology NoteDocument9 pagesBiology NotejuliaNo ratings yet
- OB NormalsDocument14 pagesOB NormalsLouie John AbilaNo ratings yet
- 12b. Reproduction Female ReproductionDocument16 pages12b. Reproduction Female ReproductionNishant ShahNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes RevisedDocument5 pagesBio Notes Revised青木ケイNo ratings yet
- PSGUNP279020221123075249578Unit 2 - Lesson 3 - Human Reproductive System - OrgansDocument11 pagesPSGUNP279020221123075249578Unit 2 - Lesson 3 - Human Reproductive System - OrgansAshneel ChakravortyNo ratings yet
- Female and Male Reproductive SystemsDocument5 pagesFemale and Male Reproductive SystemsPol HuelarNo ratings yet
- GEC SELF Lesson 5-Activity 5Document9 pagesGEC SELF Lesson 5-Activity 5Hannah Lee LumosbogNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Male and Female Rep. SystemDocument21 pagesLesson 3 Male and Female Rep. SystemHye JinNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesMale Reproductive SystemLatrell GelacioNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument18 pagesThe Reproductive Systemcmillica1176No ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 3 BIOMEDICAL PERSPECTIVE IN GENDER AND SEXUALiTYDocument9 pagesACTIVITY 3 BIOMEDICAL PERSPECTIVE IN GENDER AND SEXUALiTYMASTER CLINTONNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Educational 4Document4 pagesLaboratory Educational 4Rhzyl Moira CadapNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Educational 6Document7 pagesLaboratory Educational 6Rhzyl Moira CadapNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Educational 7Document5 pagesLaboratory Educational 7Rhzyl Moira CadapNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Educational 5Document3 pagesLaboratory Educational 5Rhzyl Moira CadapNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Educational 2Document4 pagesLaboratory Educational 2Rhzyl Moira CadapNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Educational 3Document4 pagesLaboratory Educational 3Rhzyl Moira CadapNo ratings yet
- HP RespiDocument4 pagesHP RespiRhzyl Moira CadapNo ratings yet
- HP Repro 2Document4 pagesHP Repro 2Rhzyl Moira CadapNo ratings yet
- Common Lab Equipment UsesDocument4 pagesCommon Lab Equipment UsesRhzyl Moira CadapNo ratings yet
- HP Repro 4Document2 pagesHP Repro 4Rhzyl Moira CadapNo ratings yet
- Understanding Common Text StructuresDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Common Text StructuresRhzyl Moira CadapNo ratings yet
- HP Repro 3Document3 pagesHP Repro 3Rhzyl Moira CadapNo ratings yet
- Understanding Common Text StructuresDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Common Text StructuresRhzyl Moira CadapNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive System 5esDocument10 pagesHuman Reproductive System 5esJoseph Joel AlmagroNo ratings yet
- Quiz ReproductiveDocument78 pagesQuiz ReproductiveMedShare86% (7)
- Penile Inversion Vaginoplasty TechniqueDocument2 pagesPenile Inversion Vaginoplasty Techniquecathylamont816No ratings yet
- AHD - 121 AssignmentDocument11 pagesAHD - 121 AssignmentNikhilNo ratings yet
- The Clitoris During IntercourseDocument9 pagesThe Clitoris During Intercourseapi-370596565% (17)
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument16 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- Female External Genital OrganDocument6 pagesFemale External Genital OrganSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System: Gonads or Primary Sex Organs Accessory Reproductive OrgansDocument59 pagesReproductive System: Gonads or Primary Sex Organs Accessory Reproductive OrgansMaiko KamodaNo ratings yet
- Normal Genitalia, Vision and Neurological AssessmentDocument3 pagesNormal Genitalia, Vision and Neurological AssessmentMaki BaldescoNo ratings yet
- Artificial Insemination GuideDocument3 pagesArtificial Insemination Guidesagi muNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Orchiectomy in Bilateral Cryptorchid DogsDocument8 pagesCase Report: Orchiectomy in Bilateral Cryptorchid Dogslastbeat productionNo ratings yet
- Female reproductive system parts and functionsDocument2 pagesFemale reproductive system parts and functionsRaquel Cartera83% (24)
- Anatomical Relationship Between Urethra and Clitoris: The Journal of Urology July 1998Document7 pagesAnatomical Relationship Between Urethra and Clitoris: The Journal of Urology July 1998FaePapoulesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of DUBDocument18 pagesPathophysiology of DUBAnna San100% (2)
- The Reproductive System: Hormones, Development & PubertyDocument38 pagesThe Reproductive System: Hormones, Development & PubertyVANSHIKA AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Human Sexuality: Concepts, Definitions, Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument133 pagesHuman Sexuality: Concepts, Definitions, Anatomy & PhysiologyRick100% (1)
- The Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesThe Reproductive SystemZahraa SamirNo ratings yet
- Histology of Male Reproductive SystemDocument56 pagesHistology of Male Reproductive SystemMuhammad Irfan100% (2)
- Module 5 Lesson 2 - DiscoveriesDocument2 pagesModule 5 Lesson 2 - Discoveriesdeez nutsNo ratings yet
- OB OSCE Reviewer 2014Document3 pagesOB OSCE Reviewer 2014Princess Jeanne Roque GairanodNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Vaginal BleedingDocument41 pagesAbnormal Vaginal BleedingAnnisa Westania DanialNo ratings yet
- Ma'am Cantos Module 4Document5 pagesMa'am Cantos Module 4emmanuelNo ratings yet
- 3 - Puberty Male Notes - TeacherDocument3 pages3 - Puberty Male Notes - Teacherapi-241585431100% (1)
- Anatomy & Physiology: Male Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesAnatomy & Physiology: Male Reproductive Systemkristel ludangcoNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 Transes Prelim 1Document7 pagesNCM 107 Transes Prelim 1Tatel JocelleNo ratings yet
- 1st Summative Test Science 5 3rd QuarterDocument38 pages1st Summative Test Science 5 3rd QuarterEdna ZaraspeNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnostics of Female Sexual FluidsDocument9 pagesDifferential Diagnostics of Female Sexual Fluidsjohannbach85No ratings yet
- 2011 Introduction To Maternity Pediatric Nursing Solution Manual 6th EditionDocument24 pages2011 Introduction To Maternity Pediatric Nursing Solution Manual 6th EditionAndrewFoleydegk100% (42)
- Insersi PesariumDocument21 pagesInsersi PesariumiFha AM.No ratings yet
- A Case Study About Cervical PolypsDocument8 pagesA Case Study About Cervical PolypsJisel-Apple BulanNo ratings yet