Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math 9 Q4 WK1 Las4
Uploaded by
Ariel Jay Belgira VelaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Math 9 Q4 WK1 Las4
Uploaded by
Ariel Jay Belgira VelaCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: Grade & Section: Score:
School: Teacher: Subject: Math 9
LAS Writer: JOHANNAH Y. ACHURRA Content Editor: MA. LANI PAÑA
Lesson Topic: Six Trigonometric Ratios. (Quarter 4 Wk. 1 LAS 1)
Learning Targets: Illustrates the six trigonometric ratios: sine, cosecant, cosine, secant, tangent and cotangent.
(M9GE-IVa-1.1)
Reference(s): Bryant, M., 2014. Mathematics 9 Learner’s Material. 1st ed. Pasig City: Vibal Group, Inc., pp.438-439.
CONTENT
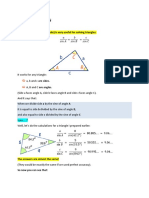
Solving a right triangle means finding the measure of the remaining parts.
𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 ℎ𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒
sin 𝜃 = 𝑐𝑠𝑐 𝜃 =
ℎ𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒 𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒
𝑎𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 ℎ𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒
𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝜃 = 𝑠𝑒𝑐 𝜃 =
ℎ𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒 𝑎𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡
𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 𝑎𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡
𝑡𝑎𝑛 𝜃 = 𝑐𝑜𝑡 𝜃 =
𝑎𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒
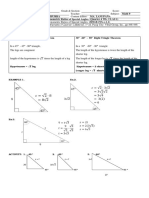
EXAMPLE 1. Solving a right triangle given the length of one leg and the measure of one Acute angle.
Triangle ACB is right-angled at C. If A = 63 ̊ and a = 11cm, find B, b and c.
𝑚∠𝐵 + 𝑚∠𝐴 = 90° to solve for c, use sine function
𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒
𝑚∠𝐵 = 90° − 63° sin 𝜃 = ℎ𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒
𝑚∠𝐵 = 27°
𝑎
to solve for b, use tangent function. sin A = 𝑐
𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 𝑎 11
tan 𝜃 = = sin 63 ̊ = ;
𝑎𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑏 𝑐
11
tan 63 ̊ = ; c = 12.25
𝑏
11 11
b = tan 63° = 1.9626 = 5.60
2. Solving a right triangle given the length of the two legs.
Triangle ACB is right –angled at C. If a= 18.5 and b=14.2, find c, A and B.
To find C, use Pythagorean Theorem
c 2 = a 2 + b2
c2 = (18.5)2 + (14.2)2
c2 = 543.89
c = √543.89
c = 23.32
To find A, use tangent function;
𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 𝑎 18.5
tan 𝜃 = = = = 1.3028;
𝑎𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑏 14.2
A = tan-1 1.3028;
A = 52° .
B = 90 °– 52° = 38 °
ACTIVITY
1.
Find b,c and B Find A,B and c
You might also like
- TheBigBookOfTeamCulture PDFDocument231 pagesTheBigBookOfTeamCulture PDFavarus100% (1)
- AromatherapyDocument15 pagesAromatherapymurrmurreNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Motor BookDocument252 pagesMotor BookKyaw KhNo ratings yet
- Tom Rockmore - Hegel's Circular EpistemologyDocument213 pagesTom Rockmore - Hegel's Circular Epistemologyluiz100% (1)
- Cesars WayDocument20 pagesCesars WayToni TursićNo ratings yet
- Contemplation (Murāqaba) and Spiritual Focus/attention (Tawajjuh) in The Pre-Mujaddidi Naqshibandi OrderDocument5 pagesContemplation (Murāqaba) and Spiritual Focus/attention (Tawajjuh) in The Pre-Mujaddidi Naqshibandi OrderShahmir ShahidNo ratings yet
- MATH 9 Q4 MELC 1 To 4Document27 pagesMATH 9 Q4 MELC 1 To 4Ella de la Cruz Gulanes100% (1)
- Ericsson Private 5G Solution BriefDocument5 pagesEricsson Private 5G Solution BriefTanesan WyotNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Las q4 Melc 1.1Document4 pagesMath 9 Las q4 Melc 1.1Maria Sophia PradoNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument13 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesAriel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan Math 9 4th Quarter Com.#43 Session 1Document10 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan Math 9 4th Quarter Com.#43 Session 1Amelita Tupaz0% (1)
- Curriculum Vitae: Career ObjectiveDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Career ObjectiveRākesh Rakhi100% (1)
- Math 9 Quarter 4Document12 pagesMath 9 Quarter 4Maria Sadaran100% (1)
- Automatic Tools For High Availability in Postgresql: Camilo Andrés EcheverriDocument9 pagesAutomatic Tools For High Availability in Postgresql: Camilo Andrés EcheverriRegistro PersonalNo ratings yet
- IGCSEFM TrigonometryII 3DTrigSineCosineDocument28 pagesIGCSEFM TrigonometryII 3DTrigSineCosinesreelakshmi100% (1)
- Mathematics Activity Sheet Quarter 4 - MELC 1Document11 pagesMathematics Activity Sheet Quarter 4 - MELC 1Rose BrazaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 Week 1Document8 pagesQuarter 4 Week 1Josiah hernandezNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Q4 WK1 Las3Document1 pageMath 9 Q4 WK1 Las3Ariel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- Review Module 1Document5 pagesReview Module 1aljohnbondad121521No ratings yet
- Activity Sheets in Mathematics 9Document4 pagesActivity Sheets in Mathematics 9Ella AltNo ratings yet
- Mathematics9 Quarter4 Week6 Module6Document6 pagesMathematics9 Quarter4 Week6 Module6Wilson OrtizNo ratings yet
- Introduction To TrigonometryDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Trigonometrymarjorie antonioNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Quarter 4 Week 7-Ms. TimaDocument7 pagesMath 9 Quarter 4 Week 7-Ms. TimaJuvy Rose TimaNo ratings yet
- Trigo Q.4 L5 - 1 1Document9 pagesTrigo Q.4 L5 - 1 1Angel AquinoNo ratings yet
- Note of IB DP Math Lesson Seven - Sine and Cosine Rules, Radian and BearingDocument16 pagesNote of IB DP Math Lesson Seven - Sine and Cosine Rules, Radian and BearingJerry DNo ratings yet
- Math 9 q4 Week 1Document6 pagesMath 9 q4 Week 1Millet Castillo100% (1)
- Trigonometric Identities Last PushDocument14 pagesTrigonometric Identities Last Pushpatiencemampane962No ratings yet
- Math 9 Q4 WK1 Las2Document1 pageMath 9 Q4 WK1 Las2Ariel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- 2312 - Section 4.1 Special Triangles and Trigonometric RatiosDocument8 pages2312 - Section 4.1 Special Triangles and Trigonometric RatiosKeiah A. QuiliopeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Worked SolutionsDocument126 pagesChapter 8 Worked SolutionsSophia ShiNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Quarter 4 Week 7-Ms. TimaDocument8 pagesMath 9 Quarter 4 Week 7-Ms. Timajuvy rose timaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 15, 16 & 17 - Further TrigonometryDocument26 pagesLesson 15, 16 & 17 - Further TrigonometryAbdul rafay ImranNo ratings yet
- P1 Chp9 TrigonometricRatios PDFDocument41 pagesP1 Chp9 TrigonometricRatios PDFPrince YugNo ratings yet
- AIRs LM - Math 9 - Q4 Week 8 Module 6 Teresa A. VillanuevaDocument14 pagesAIRs LM - Math 9 - Q4 Week 8 Module 6 Teresa A. VillanuevaCharles VillafuerteNo ratings yet
- Math12 - L2 (Trigonometry of Right Triangles)Document13 pagesMath12 - L2 (Trigonometry of Right Triangles)Lisa GarciaNo ratings yet
- Q4 W4 Solving Right TrianglesDocument41 pagesQ4 W4 Solving Right TrianglesAkysha sheenNo ratings yet
- MATH 9 Activity Sheet 2 Q3 Week 1Document1 pageMATH 9 Activity Sheet 2 Q3 Week 1Reng Carlo CadornaNo ratings yet
- MATH - GR9 - QTR4-MODULE-5-FINAL (25 Pages)Document25 pagesMATH - GR9 - QTR4-MODULE-5-FINAL (25 Pages)lyzaNo ratings yet
- M9GE IVa 1 BDocument6 pagesM9GE IVa 1 BSaharah Pundug100% (1)
- Mathematics: Quarter 4Document9 pagesMathematics: Quarter 4tugahan marstonNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Mathematics B 1to9 Trigonometry SET SDocument5 pagesIGCSE Mathematics B 1to9 Trigonometry SET SS.A.KarzaviNo ratings yet
- Elective Math NotesDocument9 pagesElective Math NotesAgape PonceNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Trigonometry - Part 3Document3 pagesFundamentals of Trigonometry - Part 3leilay003No ratings yet
- Lesson 10 Engineering Mathematics I Production OptionDocument22 pagesLesson 10 Engineering Mathematics I Production OptionRobert K OtienoNo ratings yet
- Math9 Q4 W1-W8-52pagesDocument52 pagesMath9 Q4 W1-W8-52pagesRaien RiveraNo ratings yet
- Local Media4505255725670601155Document14 pagesLocal Media4505255725670601155Xypher NNo ratings yet
- TrigDocument14 pagesTrigSuyash PatilNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Trigonometric RatiosDocument3 pagesLesson 1 Trigonometric RatiosBenster Andrew AlcaideNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Trigonometric RatiosDocument3 pagesLesson 1 Trigonometric RatiosBenster Andrew AlcaideNo ratings yet
- ESci 110 - N046 - Lesson 8.1 AssessmentDocument4 pagesESci 110 - N046 - Lesson 8.1 AssessmentIvy PerezNo ratings yet
- 2021 M11 Wk01 WS Trigonometry 1 (Student) - 1616068594287 - Mpw3oDocument3 pages2021 M11 Wk01 WS Trigonometry 1 (Student) - 1616068594287 - Mpw3oRAVI ANANTHAKRISHNANNo ratings yet
- 2021 M11 Wk01 WS Trigonometry 1 (Student) - 1616068594287 - Mpw3oDocument3 pages2021 M11 Wk01 WS Trigonometry 1 (Student) - 1616068594287 - Mpw3oRAVI ANANTHAKRISHNANNo ratings yet
- 2021 M11 Wk01 WS Trigonometry 1 (Student) - 1616068594287 - Mpw3oDocument3 pages2021 M11 Wk01 WS Trigonometry 1 (Student) - 1616068594287 - Mpw3oRAVI ANANTHAKRISHNANNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument6 pagesReviewerBasubas Charls Freinster RoseNo ratings yet
- Igcse FM: Trigonometry IIDocument28 pagesIgcse FM: Trigonometry IITravel Unlimited100% (1)
- Las Math9 Q4 W5Document12 pagesLas Math9 Q4 W5Maxene Angelie RabanalNo ratings yet
- Tugas Perbandingan TrigonometriDocument3 pagesTugas Perbandingan TrigonometriHAVES MATHNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 4: Week 4 (W4-W5) Learning Activity SheetDocument8 pagesMathematics: Quarter 4: Week 4 (W4-W5) Learning Activity SheetMagilyn DonatoNo ratings yet
- Finals ModuleDocument22 pagesFinals ModuleTin MhudzNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 4: Week 6 (W8-W9) Learning Activity SheetDocument8 pagesMathematics: Quarter 4: Week 6 (W8-W9) Learning Activity SheetMagilyn DonatoNo ratings yet
- The Law of SinesDocument6 pagesThe Law of SinesPaula FanaNo ratings yet
- VCV TR TS001Document9 pagesVCV TR TS001Los loconesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Trigonometry and Hyperbolic Functions - TrigonometryDocument21 pagesLesson 6 Trigonometry and Hyperbolic Functions - TrigonometryRobert K OtienoNo ratings yet
- PPT-4 Solid GeometryDocument122 pagesPPT-4 Solid GeometryeunniceNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 NotesDocument15 pagesUnit 6 NotesÉva HuszárNo ratings yet
- GCSE Trigonometry2SineCosineRuleDocument33 pagesGCSE Trigonometry2SineCosineRuletprojasNo ratings yet
- EGAR - ME 66 Activity 1Document2 pagesEGAR - ME 66 Activity 1Narfred EgarNo ratings yet
- For PrintDocument8 pagesFor PrintAriel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Q4 WK1 Las2Document1 pageMath 9 Q4 WK1 Las2Ariel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Q4 WK2 Las1Document1 pageMath 9 Q4 WK2 Las1Ariel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- Week 10Document14 pagesWeek 10Ariel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document9 pagesWeek 1Ariel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Day 2Document8 pagesWeek 2 - Day 2Ariel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- DLL-WK 3-LC 3,4,5Document12 pagesDLL-WK 3-LC 3,4,5Ariel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document10 pagesWeek 2Ariel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- DLL-WK 9-LC 15, 16Document14 pagesDLL-WK 9-LC 15, 16Ariel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- DLL-WK 8-LC 14Document9 pagesDLL-WK 8-LC 14Ariel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- DLL-WK 7-LC 12,13Document11 pagesDLL-WK 7-LC 12,13Ariel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- DLL-WK 6-LC 10,11Document13 pagesDLL-WK 6-LC 10,11Ariel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- DLL-WK 4-LC 5,6Document13 pagesDLL-WK 4-LC 5,6Ariel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- DLL-WK 2-LC 2Document11 pagesDLL-WK 2-LC 2Ariel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- DLL-WK 1-LC 1Document12 pagesDLL-WK 1-LC 1Ariel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- Brigada Eskwela: School Accomplishment Report XIIDocument3 pagesBrigada Eskwela: School Accomplishment Report XIIAriel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- Activity-Design-Brigada Eskwela 2022Document5 pagesActivity-Design-Brigada Eskwela 2022Ariel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- Weekly Learning Plan Mapeh 10Document13 pagesWeekly Learning Plan Mapeh 10Ariel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- Teacher's Socio Demographic Profile As To:: Input Process OutputDocument1 pageTeacher's Socio Demographic Profile As To:: Input Process OutputAriel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesAriel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- Weekly Learning Plan MAPEH 7Document12 pagesWeekly Learning Plan MAPEH 7Ariel Jay Belgira VelaNo ratings yet
- Ultraviolet RadiationDocument3 pagesUltraviolet RadiationbirlacementNo ratings yet
- Maharishi Language of Gravity - SoS 27Document3 pagesMaharishi Language of Gravity - SoS 27Prof. MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Datasheet TBJ SBW13009-KDocument5 pagesDatasheet TBJ SBW13009-KMarquinhosCostaNo ratings yet
- High School Physics Rutherford Atom Lesson 27Document4 pagesHigh School Physics Rutherford Atom Lesson 27John JohnsonNo ratings yet
- User Manual PocketBookDocument74 pagesUser Manual PocketBookmisu2001No ratings yet
- Grade 7 Math Lesson 22: Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials Learning GuideDocument4 pagesGrade 7 Math Lesson 22: Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials Learning GuideKez MaxNo ratings yet
- Stamp 07 eDocument6 pagesStamp 07 eDumitru TuiNo ratings yet
- CN Blue Love Rigt Lyrics (Romanized)Document3 pagesCN Blue Love Rigt Lyrics (Romanized)Dhika Halet NinridarNo ratings yet
- 8 TH Linear Equations DBDocument1 page8 TH Linear Equations DBParth GoyalNo ratings yet
- Ip TunnelingDocument15 pagesIp TunnelingBon Tran HongNo ratings yet
- Spring Newsletter 2014-LockedDocument4 pagesSpring Newsletter 2014-Lockedapi-244488788No ratings yet
- CrumpleZonesSE (Edit)Document12 pagesCrumpleZonesSE (Edit)Dah Unknown MarksmenNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Unstable or Astatic Gravimeters and Marine Gravity SurveyDocument9 pagesAssignment On Unstable or Astatic Gravimeters and Marine Gravity Surveyraian islam100% (1)
- High School Department PAASCU Accredited Academic Year 2017 - 2018Document6 pagesHigh School Department PAASCU Accredited Academic Year 2017 - 2018Kevin T. OnaroNo ratings yet
- Soal PTS Vii BigDocument6 pagesSoal PTS Vii Bigdimas awe100% (1)
- A Technical Report ON Centre of Pressure ONA Plane Surface ExperimentDocument13 pagesA Technical Report ON Centre of Pressure ONA Plane Surface ExperimentVictor OwolekeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34 Esip For FinalDocument35 pagesChapter 34 Esip For FinalJeaniel BorlingNo ratings yet
- Pavlishchuck Addison - 2000 - Electrochemical PotentialsDocument6 pagesPavlishchuck Addison - 2000 - Electrochemical PotentialscomsianNo ratings yet
- Math Cad 15Document3 pagesMath Cad 15Kim ChanthanNo ratings yet
- Dr. N. Kumarappan IE (I) Council Candidate - Electrical DivisionDocument1 pageDr. N. Kumarappan IE (I) Council Candidate - Electrical Divisionshanmugasundaram32No ratings yet
- Philips fwt9200Document37 pagesPhilips fwt9200Alex BrazNo ratings yet