Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Index 3
Uploaded by
HONEY LYN GUTIERREZOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Index 3
Uploaded by
HONEY LYN GUTIERREZCopyright:
Available Formats
STRENGTH OF MATERIALS
INDIVIDUAL EXERCISE #3
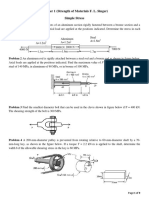
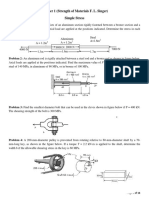
W = 33.46kN 1. Determine the largest weight that can be supported by the two
wires AB and AC. The working stresses are 100 MPa for AB and
150 MPa for AC. The cross sectional areas of AB and AC are
400mm2 and 200mm2, respectively.
2.
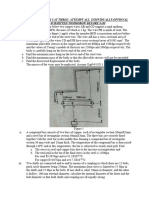
8. A compound shaft is consisting of steel segment and aluminum
10.
T=678.05N-m segment is acted upon by two torques as shown. Determine the
maximum permissible value of T subject to the following
conditions. The angle of rotation at the free end is 6 degrees and
W = 19.08kN 3.2. Determine the weight of the heaviest cylinder that can be
supported by the structure shown if the cross sectional area of the
cable is 120mm2 and its allowable stress is 80MPa.
a) t = 0.78 in 4.3. A hole is to be punched out of a plate having a shearing strength
of 40 ksi. The compressive stress in the punch is limited to 50 ksi.
b) d= 0.8 in (a) Compute the maximum thickness of the plate from which a
hole 2.5 in. in diameter can be punched. (b) If the plate is 0.25 in.
5. thick, determine the diameter of the smallest hole that can be 9. A composite shaft is manufactured by shrink-fitting a steel sleeve
11.
punched T=603.19N-m over a brass core so that the two parts act as a single solid bar in
torsion. The outer diameters of the two parts are ds = 40 mm for
the brass core and db = 50 mm for the steel sleeve. The shear
moduli of elasticity are Gb = 35 GPa for the brass and Gs = 80
GPa for the steel. Allowable shear stresses in the brass and steel
are 48 MPa and 80 MPa, respectively. Determine the maximum
permissible torque in N-m that may be applied to the shaft.
10. Two solid shafts of different materials are rigidly fastened together
12.
f = 3452.85 psi and attached to rigid supports as shown. The torque, T = 10 kip in
is applied at the junction of the two segments. Compute the
P = 77.79kN6.4. A rectangular piece of wood, 50 mm by 100 mm in section, is used maximum shearing stress developed in the assembly..
as a compression block as shown. Determine the maximum axial
force P that can be safely applied to the block if the compressive
stress in the wood is limited to 20 MPa and the shearing stress
parallel to the grain is limited to 5 MPa. The grain makes an angle
of 20o with the horizontal.
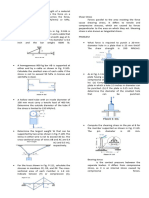
b = 17.46mm7. 5. A 200 mm diameter pulley is prevented from rotating relative to a
60-mm-diameter shaft by a 70-mm-long key. If a torque 2.2 kN·m
is applied to the shaft, determine the width b if the allowable
shearing stress in the key is 60 MPa.
11. The bronze bar 3m long with a cross sectional area of 350 mm2
13.
Tf=40.83 C is placed between two rigid supports. At a temperature of 20
degrees, the bronze bar is stress free Find the temperature at
which the compressive stress in the bar will be 30 MPa. Use α =
18µm/m o C and E = 80 GPa.
12. A steel rod with a cross-sectional area of 150mm2 is stretched
14.
f=126.93 MPa between two fixed points. The tensile load at 20oC is 5000N. What
a) d=13.49 mm 8.6. The joint is fastened together using two bolts. Determine the will be the stress at -20o C? At what temperature will the stress
required diameter of the bolts if the failure shear stress for the be zero? αsteel = 11.7x10-6/oC and E=200GPa.
b) fb= 2965.88/t MPa bolts is 350 MPa. Use a factor of safety for shear of 2.5. Calculate
the maximum bearing stress on the members connected. 13. A cylindrical tank 8m in diameter is 12m high. If the tank is
15.
t=11.77mm completely filled with water, determine the required thickness of
tank plating if the allowable stress is 40MPa.
16.
14. The tank shown in the figure is fabricated from steel plate.
t=18.75mm Determine the minimum thickness of the tank plating if the internal
pressure is 1.5MPa and the allowable stress is 40MPa.
P = 12.08kN 9.7. A bronze bar is fastened between a steel bar and an aluminum
bar as shown in the following figure. Axial loads are applied as
indicated. Find the largest value of P that will not exceed an overall
deformation of 3.0 mm, or the following stresses: 140 MPa in the
steel, 120 MPa in the bronze, and 80 MPa in the aluminum.
Assume that the assembly is suitably braced against buckling.
Use Est = 200 GPa, Eal = 70 GPa, and Ebr = 83 GPa.
Engr. Dustin Glenn Cuevas
STRENGTH OF MATERIALS
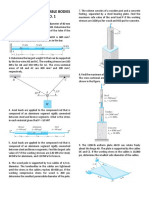
15. A rigid block of mass M is supported by three symmetrically
W=22 358.41 kg17.
spaced rods as shown. Each copper rod has an area of 900mm2
Ecopper =120GPa and the allowable stress is 70MPa. The steel
rod has an area of 1200mm2, Esteel=200GPa and allowable
stress of 140MPa. Determine the largest mass M which can be
supported.
a) d=273.11mm 16.
18. A vertical post 2.5-meters high must support a lateral load 12 kN
at its upper end as shown in the figure. Two plans are proposed—
b) d=207.55mm a solid wood post and a hollow aluminum tube. What is the
minimum required diameter of the wood post if the allowable
bending stress in the wood is 15 MPa? What is the minimum
required outer diameter of the aluminum tube if its wall thickness
is to be one-eighth of the outer diameter and the allowable
bending stress in the aluminum is 50 MPa?
a) fmax= 0.66MPa 19.
17. A T-shaped section is subjected to a vertical shear force of V =
10,000 lb. The cross-sectional dimensions are flange width, bf =
b) fmin= 4.83MPa
100 mm, flange thickness, tf = 25 mm, gross depth of h = 200 mm
fmax= 5.82MPa
and web thickness of 25 mm. Determine the maximum shear
stress in the flange and maximum and minimum shear stresses in
the web.
Engr. Dustin Glenn Cuevas
You might also like
- Tutorial 6 PDFDocument3 pagesTutorial 6 PDFSaketh BoggavarapuNo ratings yet
- Review Module - Structural Engineering: Rass TeelDocument2 pagesReview Module - Structural Engineering: Rass TeelJohn andre Mariano100% (1)
- Tutorial 3Document2 pagesTutorial 3AmrinaAkmal0% (1)
- Worked Solution To Various QuestionsDocument29 pagesWorked Solution To Various QuestionsJohn MutumaNo ratings yet
- Exercise-No 1Document2 pagesExercise-No 1SunflowerNo ratings yet
- Preboards-Assignment 7Document12 pagesPreboards-Assignment 7vandiazvanNo ratings yet
- ME-1203 Solid Mechanics-EEE (Solved Problem Slide)Document9 pagesME-1203 Solid Mechanics-EEE (Solved Problem Slide)sadfNo ratings yet
- Answer: 6872.23 LBFT: Problem 304 Problem 327Document2 pagesAnswer: 6872.23 LBFT: Problem 304 Problem 327Bianca GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Strength Matls Board ReviewDocument20 pagesStrength Matls Board ReviewErika RamosNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets Strength of Materials 1Document3 pagesProblem Sets Strength of Materials 1Ho BiNo ratings yet
- Torsion ProblemsDocument7 pagesTorsion ProblemsLouie G NavaltaNo ratings yet
- Mec03-Problems (Stress and Strain)Document11 pagesMec03-Problems (Stress and Strain)Benedict LucilaNo ratings yet
- Strema 102Document4 pagesStrema 102Hazel VidallonNo ratings yet
- Worksheet & AssignmentDocument2 pagesWorksheet & AssignmentAdnan Shafi100% (3)
- Chapter - 3 - Torsion - Class ExamplesDocument14 pagesChapter - 3 - Torsion - Class ExamplesCandice MdakaNo ratings yet
- STREMADocument1 pageSTREMAIcon Byl P. VergaraNo ratings yet
- Cat Solid MechanicsDocument1 pageCat Solid MechanicsMoses TheuriNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets-StressDocument9 pagesProblem Sets-StressZie Agustin67% (3)
- Macaraeg, Czarina Mae B. Bsabe 3-1 Quiz No.4Document13 pagesMacaraeg, Czarina Mae B. Bsabe 3-1 Quiz No.4Czarina Mae MacaraegNo ratings yet
- ME-2127 Solid Mechanics-MSEDocument14 pagesME-2127 Solid Mechanics-MSEFazle RabbyNo ratings yet
- MDB Assestment 1 PDFDocument3 pagesMDB Assestment 1 PDFClarence Jay AcaylarNo ratings yet
- Board Exam Problems-SteelDocument5 pagesBoard Exam Problems-SteelAngela Mae Francisco100% (1)
- Problems and Solutions: Simple Stress: Problem 104Document10 pagesProblems and Solutions: Simple Stress: Problem 104Bone Rai Yan Buta-OneNo ratings yet
- Sample PS 2Document2 pagesSample PS 2james arajaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials QP BANKDocument15 pagesStrength of Materials QP BANKmechfameNo ratings yet
- Quiz No 1 - Set D PDFDocument2 pagesQuiz No 1 - Set D PDFMayoune Nasinopa GalvezNo ratings yet
- Assignment Problems (LSD-method, RC-I) : MM N F M KNDocument5 pagesAssignment Problems (LSD-method, RC-I) : MM N F M KNTemesgen100% (4)
- CE8395-SOM Class Question BankDocument3 pagesCE8395-SOM Class Question BankAzharNo ratings yet
- Review Module 31 SMAT2 Part2 Nov2021Document1 pageReview Module 31 SMAT2 Part2 Nov2021John Andre MarianoNo ratings yet
- For Printing Bolted ConnectionDocument10 pagesFor Printing Bolted ConnectionLouvern Jake Dosono Reyes67% (3)
- Strength WorksheetDocument9 pagesStrength WorksheetHabtamu GetaNo ratings yet
- ExamsDocument13 pagesExamsJulie-Ann AutorNo ratings yet
- 3 1-TorsionstressandstrainDocument19 pages3 1-TorsionstressandstrainKim HarlyNo ratings yet
- Simple Stress: Fundamentals of Deformable BodiesDocument3 pagesSimple Stress: Fundamentals of Deformable Bodiesreymart cereneoNo ratings yet
- Steel Design Regular Review Apr 2023Document2 pagesSteel Design Regular Review Apr 2023Carlo Magno Olano JrNo ratings yet
- Prelim MeDocument1 pagePrelim MeLester Neil LomodNo ratings yet
- SOMDocument14 pagesSOMAditya ojhaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1Document3 pagesAssignment - 1chritNo ratings yet
- Es 13 Thy Prob Set 1 I. Stresses: Max MaxDocument5 pagesEs 13 Thy Prob Set 1 I. Stresses: Max MaxMichael Sean DeangNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 1 MD-1..Document3 pagesAssignment No 1 MD-1..Yadnyesh TaNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 2Document2 pagesAssignment No 2Abhishek BordoloiNo ratings yet
- Mid Pre BoardDocument6 pagesMid Pre BoardJonathanNo ratings yet
- SolveDocument2 pagesSolveJea Clarie Mendioro Espinas67% (3)
- Muranga Ees 201 Tut 1Document3 pagesMuranga Ees 201 Tut 1jonathan otienoNo ratings yet
- Quiz No 2 - Set ADocument2 pagesQuiz No 2 - Set AMayoune Nasinopa Galvez100% (1)
- rr220102 Strength of Materials IIDocument7 pagesrr220102 Strength of Materials IISRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Statically IndeterminateDocument7 pagesStatically IndeterminateballDISCOVERIES PHballDISCOVERIESNo ratings yet
- HandoutsDocument3 pagesHandoutssheena Marjorie Cabidog100% (1)
- Handouts PDFDocument3 pagesHandouts PDFMayoune GalvezNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 1Document37 pagesAssignment No. 1Vishal DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Strength 2 DLSU DasmaDocument1 pageStrength 2 DLSU Dasmabandureview2324No ratings yet
- MEGA Review Module - Strength of Materials 2 (Part 2)Document1 pageMEGA Review Module - Strength of Materials 2 (Part 2)Study BuddiesNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Competency Exam 2014 - 20152Document1 pageStrength of Materials Competency Exam 2014 - 20152Justine Marowe AustriaNo ratings yet
- TD RDMDocument3 pagesTD RDMIbtissam LachguerNo ratings yet
- Quiz No 1Document2 pagesQuiz No 1Tris ZackNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 2.Document4 pagesStrength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 2.Jesus RodeloNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument2 pagesStrength of MaterialsLebron JamesNo ratings yet
- Paper ID (A08011: B.Tech. (Sem. - 3'd)Document3 pagesPaper ID (A08011: B.Tech. (Sem. - 3'd)bravo16893No ratings yet
- INDEX 1 (Questions)Document1 pageINDEX 1 (Questions)HONEY LYN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- M1 - Introduction To Engineering ManagementDocument3 pagesM1 - Introduction To Engineering ManagementHONEY LYN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Review Notes February 022023Document7 pagesReview Notes February 022023HONEY LYN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Qs 004 Module 3 CompilationDocument52 pagesQs 004 Module 3 CompilationHONEY LYN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Qs 004 Module 1 2 CompilationDocument85 pagesQs 004 Module 1 2 CompilationHONEY LYN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- M2 - Social Responsibility and Decision MakingDocument6 pagesM2 - Social Responsibility and Decision MakingHONEY LYN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Qs 004 Module 4 CompilationDocument25 pagesQs 004 Module 4 CompilationHONEY LYN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- QS 003 Module 1 2 CompilationDocument64 pagesQS 003 Module 1 2 CompilationHONEY LYN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- QS 003 Module 3 CompilationDocument27 pagesQS 003 Module 3 CompilationHONEY LYN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- QS 002 Prelim CompilationDocument79 pagesQS 002 Prelim CompilationHONEY LYN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- QS 002 Midterm CompilationDocument443 pagesQS 002 Midterm CompilationHONEY LYN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 - QS-002 - GutierrezDocument11 pagesAssignment 4 - QS-002 - GutierrezHONEY LYN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- QS 002 Module 3 CompilationDocument200 pagesQS 002 Module 3 CompilationHONEY LYN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - QS-002 - GutierrezDocument7 pagesAssignment 2 - QS-002 - GutierrezHONEY LYN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 - QS-002 - GutierrezDocument3 pagesAssignment 3 - QS-002 - GutierrezHONEY LYN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - QS-002 - GutierrezDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 - QS-002 - GutierrezHONEY LYN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Module 1-3Document6 pagesModule 1-3HONEY LYN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document2 pagesModule 1HONEY LYN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering - BesavillaDocument178 pagesGeotechnical Engineering - BesavillaHONEY LYN GUTIERREZ0% (1)
- Jejejeje Lo HiceDocument37 pagesJejejeje Lo HiceGank Sfk100% (2)
- Euro IV BH117L ABS6 Diagnostic Sys For DwBus 080226 PDFDocument64 pagesEuro IV BH117L ABS6 Diagnostic Sys For DwBus 080226 PDFdenis_butuci100% (1)
- Massey Ferguson 6497 TRACTOR (TIER 3) ( - T176049) Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 3906158)Document19 pagesMassey Ferguson 6497 TRACTOR (TIER 3) ( - T176049) Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 3906158)bvk2980022No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Balancing of ROTATING MASSES PDFDocument46 pagesUnit 4 Balancing of ROTATING MASSES PDFRichard Mortimer100% (2)
- Deluxe Installation Manual FinalDocument21 pagesDeluxe Installation Manual FinalAPNo ratings yet
- Noise and Vibration From Railway Vehicles: David Thompson and Chris JonesDocument47 pagesNoise and Vibration From Railway Vehicles: David Thompson and Chris JonesVICTOR HUGO ORTIZ MOSCOSONo ratings yet
- How Stem Finish Affects Friction and FE With Graphite-Based Control Valve Packing PDFDocument22 pagesHow Stem Finish Affects Friction and FE With Graphite-Based Control Valve Packing PDFAlexandreAguilarNo ratings yet
- AgardDocument249 pagesAgardAysun Güven0% (1)
- CME 3303 HW 6 Solution PDFDocument4 pagesCME 3303 HW 6 Solution PDFrum kaunNo ratings yet
- SM HD785-7 Sen01274-14Document1,815 pagesSM HD785-7 Sen01274-14Lucio Valderrama100% (2)
- Automatic Tyre Pressure Inflation SystemDocument3 pagesAutomatic Tyre Pressure Inflation SystemKarthick MNo ratings yet
- LR1300SXDocument24 pagesLR1300SXstephen prosserNo ratings yet
- Air Duct Dimensions and Weights Data Sheet EN PDFDocument3 pagesAir Duct Dimensions and Weights Data Sheet EN PDFkggganiNo ratings yet
- Advisory: CircularDocument11 pagesAdvisory: CircularCandace FrankNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NC and CNC Machines CNC Controls and RS274 ProgrammingDocument36 pagesIntroduction To NC and CNC Machines CNC Controls and RS274 ProgrammingAnonymous ztnAl2No ratings yet
- Buoyancy and Stability: 2005 Pearson Education South Asia Pte LTDDocument74 pagesBuoyancy and Stability: 2005 Pearson Education South Asia Pte LTDDickson LeongNo ratings yet
- "Big Red": Taylor Industrial Truck Preliminary SpecificationsDocument4 pages"Big Red": Taylor Industrial Truck Preliminary SpecificationsNeil DesaiNo ratings yet
- Ratings and Specifications: Allison TransmissionDocument2 pagesRatings and Specifications: Allison TransmissionSarra ChoucheneNo ratings yet
- 2d Bow Truster Brunvoll Thruster Type Fu 80 LTC 2250 142Document142 pages2d Bow Truster Brunvoll Thruster Type Fu 80 LTC 2250 142Volodymyr BakotaNo ratings yet
- 2010 - Allison Parts Price ListDocument71 pages2010 - Allison Parts Price ListRavinder Singh100% (4)
- Chapter Six: Heat Transfer With Phase ChangeDocument32 pagesChapter Six: Heat Transfer With Phase ChangeNOBLEMANNo ratings yet
- Toyota Avensis 2003-2007 Electrical Wiring RoutingDocument27 pagesToyota Avensis 2003-2007 Electrical Wiring Routingmvidovic201086% (7)
- 1716,1734,1751,1769 - Highrise and Earthquake Resistant ConstructionDocument34 pages1716,1734,1751,1769 - Highrise and Earthquake Resistant ConstructionFAB RAHINo ratings yet
- 80KLD Underground MBRDocument4 pages80KLD Underground MBRAshmita RajNo ratings yet
- Section: MDT Geotechnical ManualDocument52 pagesSection: MDT Geotechnical ManualjaffnaNo ratings yet
- HCR1200 BrochDocument4 pagesHCR1200 Brochmed_tataNo ratings yet
- Manual Rhino - 2012Document55 pagesManual Rhino - 2012pfylNo ratings yet
- Electrical Control Valves EX4 / EX5 / EX6 / EX7 / EX8Document9 pagesElectrical Control Valves EX4 / EX5 / EX6 / EX7 / EX8Ruben MarichalNo ratings yet
- Vent To Flare 1683883352Document31 pagesVent To Flare 1683883352saheem_783617392No ratings yet
- Building Services - HVAC - SpecificationDocument55 pagesBuilding Services - HVAC - SpecificationVũ Quang TiệpNo ratings yet